
Features
•
High Performance, Low Power AVR
®
8-bit Microcontroller
•
Advanced RISC Architecture
– 131 Powerful Instructions - Most Single Clock Cycle Execution
– 32 x 8 General Purpose Working Registers
– Fully Static Operation
– Up to 4 MIPS Throughput at 4 MHz
•
High Endurance Non-volatile Memorie segments
– 8K/16K Bytes of In-System Self-Programmable Flash Program
Memory(ATmega8HVA/16HVA)
– 256 Bytes EEPROM
– 512 Bytes Internal SRAM
– Write/Erase cycles: 10,000 Flash/100,000 EEPROM
– Data Retention: 20 years at 85°C /100 years at 25°C
(1)
– Programming Lock for Software Security
•
Battery Management Features
– One or Two Cells in Series
– Over-current Protection (Charge and Discharge)
– Short-circuit Protection (Discharge)
– High Voltage Outputs to Drive N-Channel Charge/Discharge FETs
•
Peripheral Features
– Two configurable 8- or 16-bit Timers with Separate Prescaler, Optional Input
Capture (IC), Compare Mode and CTC
– SPI - Serial Programmable Interface
– 12-bit Voltage ADC, Four External and One Internal ADC Inputs
– High Resolution Coulomb Counter ADC for Current Measurements
– Programmable Watchdog Timer
•
Special Microcontroller Features
– debugWIRE On-chip Debug System
– In-System Programmable via SPI ports
– Power-on Reset
– On-chip Voltage Regulator with Short-circuit Monitoring Interface
– External and Internal Interrupt Sources
– Sleep Modes:
Idle, ADC Noise Reduction, Power-save, and Power-off
•
Additional Secure Authentication Features available only under NDA
•
Packages
– 36-pad LGA
– 28-lead TSOP
•
Operating Voltage: 1.8 - 9V
•
Maximum Withstand Voltage (High-voltage pins): 28V
•
Temperature Range: - 20°C to 85°C
•
Speed Grade: 1-4 MHz
8-bit
Microcontroller
with 8K/16K
Bytes In-System
Programmable
Flash
ATmega8HVA
ATmega16HVA
Preliminary
Summary
8024AS–AVR–04/08
2
8024AS–AVR–04/08
ATmega8HVA/16HVA
1.
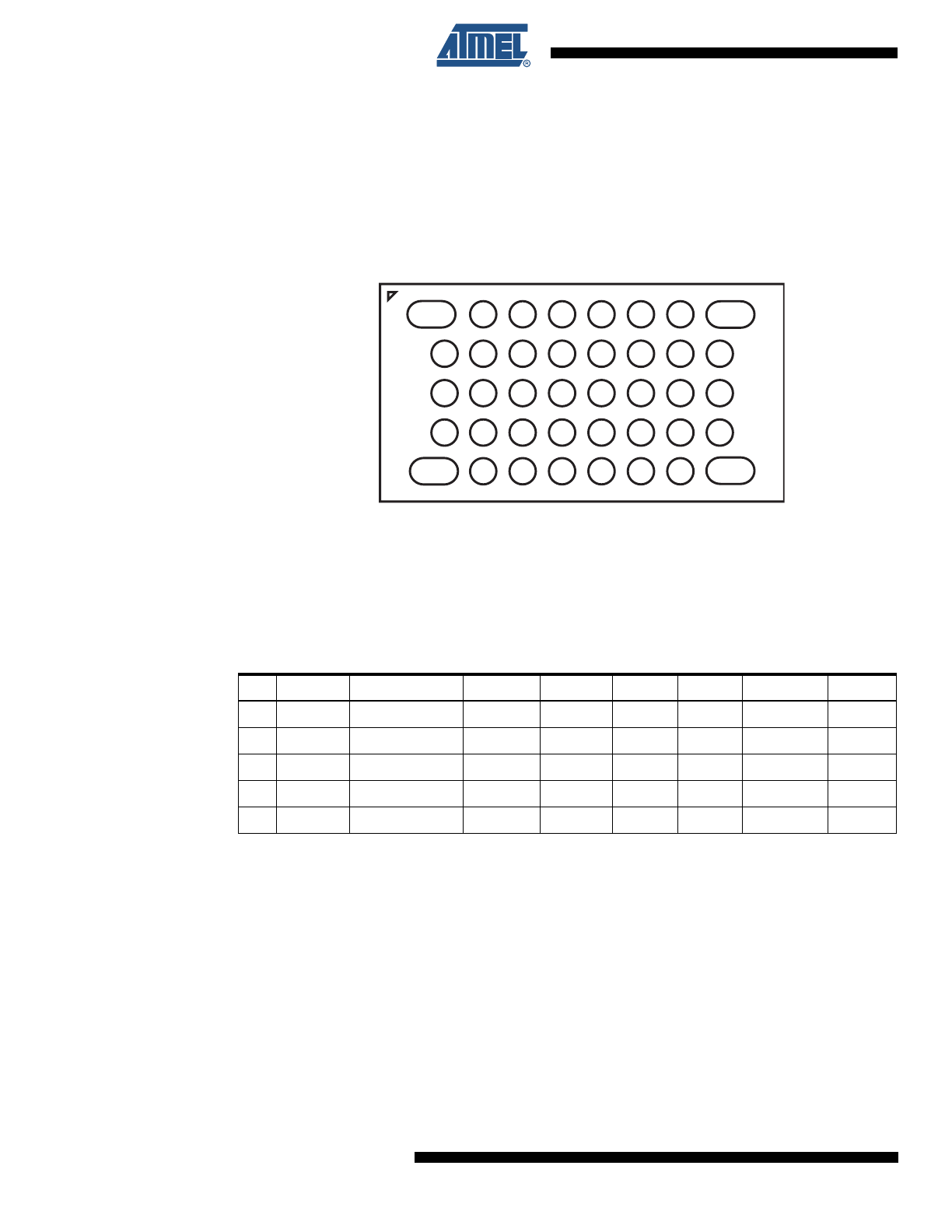
Pin Configurations
1.1
LGA
Figure 1-1.
LGA - Pinout ATmega8HVA/16HVA
Figure 1-2.
LGA - pinout ATmega8HVA/16HVA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
A
DNC
PV2
PV1
NV
GND
OC
OD
DNC
B
CF2P
CF2N
VFET
CF1P
GND
PC0
DNC
GND
C
VREF
VREFGND
VREG
CF1N
VCC
GND
GND
BATT
D
PI
NI
GND
GND
GND
PB2
PB3
GND
E
DNC
DNC
PA1
PA0
PB1
PB0
RESET
DNC
A
B
C
D
E
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8

3
8024AS–AVR–04/08
ATmega8HVA/16HVA
1.2
TSOP
Figure 1-3.
TSOP - pinout ATmega8HVA/16HVA
1.3
Pin Descriptions
1.3.1
VFET
Input to the internal voltage regulator.
1.3.2
VCC
Digital supply voltage. Normally connected to VREG.
1.3.3
VREG
Output from the internal voltage regulator.
1.3.4
CF1P/CF1N/CF2P/CF2N
CF1P/CF1N/CF2P/CF2N are the connection pins for connecting external fly capacitors to the
step-up regulator.
1.3.5
VREF
Internal Voltage Reference for external decoupling.
1.3.6
VREFGND
Ground for decoupling of Internal Voltage Reference. Do not connect to GND or SGND on PCB.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
PV2
PV1
NV
GND
VFET
CF1P
CF1N
CF2P
CF2N
VREG
VREFGND
PI
NI
PA0 (ADC0/SGND/T0)
PA1 (ADC1/SGND/T1)
PA2 (RESET/dW)
PB0 (SS/CKOUT)
PB1 (SCK)
PB2 (MOSI/INT1)
VREF
PB3 (MISO/INT2)
GND
VCC
PC0 (RXD/TXD/INT0)
BATT
GND
OC
OD

4
8024AS–AVR–04/08
ATmega8HVA/16HVA
1.3.7
GND
Ground
1.3.8
Port A (PA1..PA0)
Port A serves as a low-voltage 2-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected
for each bit). As inputs, Port A pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port A pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port A also serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega8HVA/16HVA as
listed in
”Alternate Functions of Port A” on page 70
.
1.3.9
Port B (PB3..PB0)
Port B is a low-voltage 4-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for
each bit). As inputs, Port B pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port B pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port B also serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega8HVA/16HVA as
listed in
”Alternate Functions of Port B” on page 71
.
1.3.10
PC0
Port C serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega8HVA/16HVA as listed in
”Alternate Functions of Port C” on page 61
.
1.3.11
OC
High voltage output to drive Charge FET.
1.3.12
OD
High voltage output to drive Discharge FET.
1.3.13
NI
NI is the filtered negative input from the current sense resistor.
1.3.14
PI
PI is the filtered positive input from the current sense resistor.
1.3.15
NV/PV1/PV2
NV, PV1, and PV2 are the inputs for battery cells 1 and 2.
1.3.16
BATT
Input for detecting when a charger is connected.
1.3.17
RESET/dw
Reset input. A low level on this pin for longer than the minimum pulse length will generate a
reset, even if the clock is not running. The minimum pulse length is given in Table 11 on page
38. Shorter pulses are not guaranteed to generate a reset. This pin is also used as debugWIRE
communication pin.
5
8024AS–AVR–04/08
ATmega8HVA/16HVA
2.
Overview
The ATmega8HVA/16HVA is a monitoring and protection circuit for 1-cell and 2-cell Li-ion appli-
cations with focus on high security/authentication, accurate monitoring, low cost and high
utilization of the cell energy. The device contains secure authentication features as well as
autonomous battery protection during charging and discharging. The chip allows very accurate
accumulated current measurements using an 18-bit ADC with a resolution of 0.84 µV. The fea-
ture set makes the ATmega8HVA/16HVA a key component in any system focusing on high
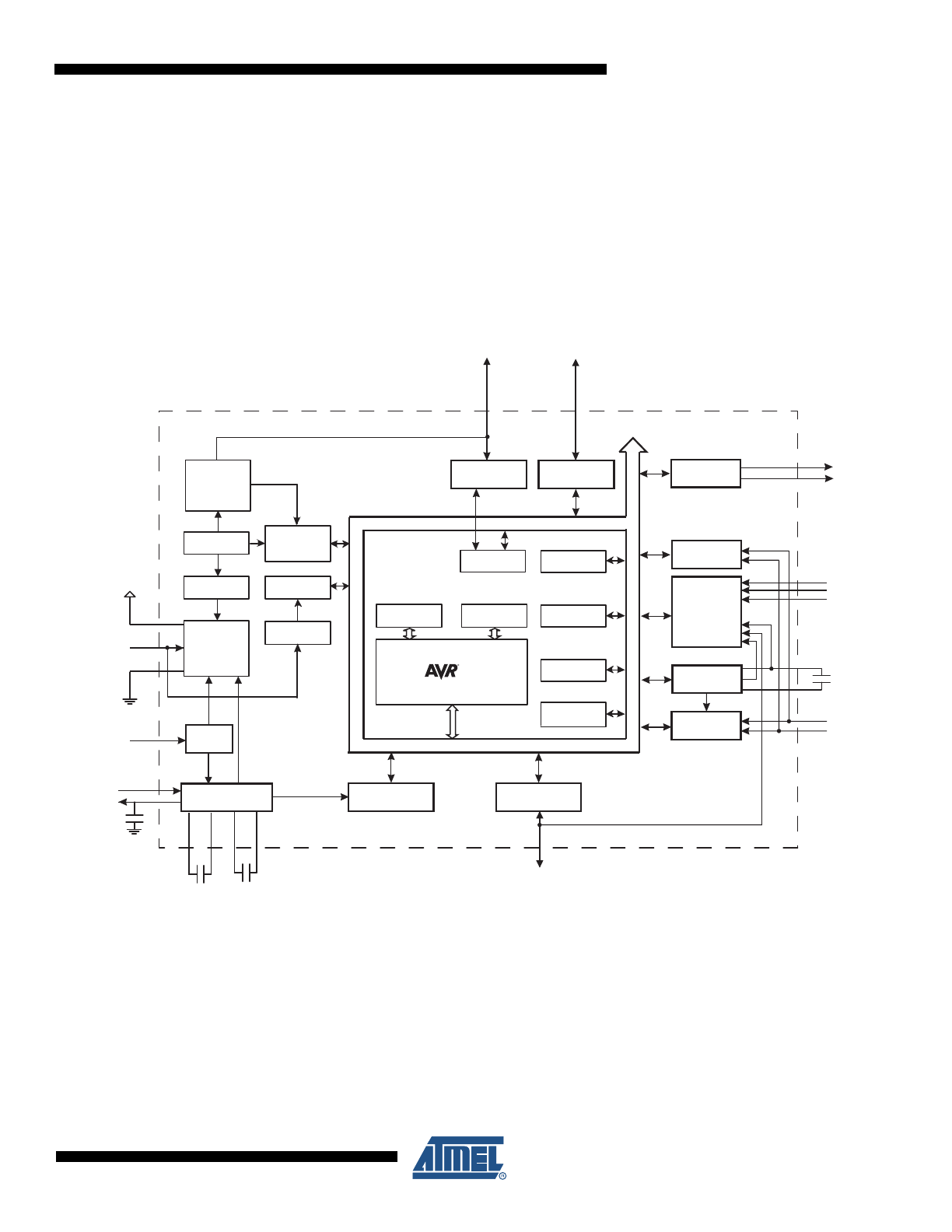
security, battery protection, accurate monitoring, high system utilization and low cost.
Figure 2-1.
Block Diagram
A combined step-up and linear voltage regulator ensures that the chip can operate with supply
voltages as low as 1.8V for 1-cell applications. The regulator automatically switches to linear
mode when the input voltage is sufficiently high, thereby ensuring a minimum power consump-
tion at all times. For 2-cell applications, only linear regulation is enabled. The regulator
capabilities, combined with an extremely low power consumption in the power saving modes,
greatly enhances the cell energy utilization compared to existing solutions.
The chip utilizes Atmel's patented Deep Under-voltage Recovery (DUVR) mode that supports
pre-charging of deeply discharged battery cells without using a separate Pre-charge FET.
PORTA (2)
SRAM
Flash
CPU
EEPROM
PV2
NV
OC
OD
FET
Control
Voltage
ADC
Voltage
Reference
Coulumb
Counter ADC
GND
VCC
RESET/dW
Power
Supervision
POR &
RESET
Watchdog
Oscillator
Watchdog
Timer
Oscillator
Circuits /
Clock
Generation
VREF
VREFGND
PI
NI
PA1..0
PA1..0
8/16-bit T/C1
8/16-bit T/C0
PORTB (4)
PB3..0
SPI
Voltage
Regulator
Charger
Detect
VFET
VREG
BATT
PV1
DATA BUS
CF1N
CF2N
CF1P CF2P
VPTAT
Battery
Protection
Security
Module
PORTC (1)
PC0
Voltage Regulator
Monitor Interface
PB0
Oscillator
Sampling
Interface
Program
Logic
debugWIRE

6
8024AS–AVR–04/08
ATmega8HVA/16HVA
The ATmega8HVA/16HVA contains a 12-bit ADC that can be used to measure the voltage of
each cell individually. The ADC can also be used to monitor temperature, either on-chip temper-
ature using the built-in temperature sensor, external temperature using thermistors connected to
dedicated ADC inputs. The ATmega8HVA/16HVA contains a high-voltage tolerant, open-drain
IO pin that supports serial communication. Programming can be done in-system using the 4
General Purpose IO ports that support SPI programming.
The AVR core combines a rich instruction set with 32 general purpose working registers. All the
32 registers are directly connected to the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), allowing two independent
registers to be accessed in one single instruction executed in one clock cycle. The resulting
architecture is more code efficient while achieving throughputs up to ten times faster than con-
ventional CISC microcontrollers.
The MCU includes 8K/16K bytes of In-System Programmable Flash with Read-While-Write
capabilities, 256 bytes EEPROM, 512 bytes SRAM, 32 general purpose working registers, 6
general purpose I/O lines, debugWIRE for On-chip debugging and SPI for In-system Program-
ming, two flexible Timer/Counters with Input Capture and compare modes, internal and external
interrupts, a 12-bit Sigma Delta ADC for voltage and temperature measurements, a high resolu-
tion Sigma Delta ADC for Coulomb Counting and instantaneous current measurements,
Additional Secure Authentication Features, an authonomous Battery Protection module, a pro-
grammable Watchdog Timer with wake-up capabilities, and software selectable power saving
modes.
The AVR core combines a rich instruction set with 32 general purpose working registers. All the
32 registers are directly connected to the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), allowing two indepdent
registers to be accessed in one single instruction executed in one clock cycle. The resulting
architecture is more code efficient while achieving throughputs up to ten times faster than con-
ventional CISC microcontrollers.
The device is manufactured using Atmel’s high voltage high density non-volatile memory tech-
nology. The On-chip ISP Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed In-System,
through an SPI serial interface, by a conventional non-volatile memory programmer or by an On-
chip Boot program running on the AVR core. By combining an 8-bit RISC CPU with In-System
Self-Programmable Flash, fuel gauging ADCs, dedicated battery protection circuitry, and a volt-
age regulator on a monolithic chip, the ATmega8HVA/16HVA is a powerful microcontroller that
provides a highly flexible and cost effective solution for Li-ion Smart Battery applications.
The ATmega8HVA/16HVA AVR is supported with a full suite of program and system develop-
ment tools including: C Compilers, Macro Assemblers, Program Debugger/Simulators, and On-
chip Debugger.
The ATmega8HVA/16HVA is a low-power CMOS 8-bit microcontroller based on the AVR archi-
tecture. It is part of the AVR Smart Battery family that provides secure authentication, highly
accurate monitoring and autonomous protection for Lithium-ion battery cells.

7
8024AS–AVR–04/08
ATmega8HVA/16HVA
2.1
Comparison Between ATmega8HVA and ATmega16HVA
The ATmega8HVA and ATmega16HVA differ only in memory size and interrupt vector size.
Table 2-1
summarizes the different configuration for the two devices.
3.
Disclaimer
All Min, Typ and Max values contained in this datasheet are preliminary estimates based on sim-
ulations and characterization of other AVR microcontrollers manufactured on the same process
technology. Final values will be available after the device is characterized.
4.
Resources
A comprehensive set of development tools, application notes and datasheets are available for
download on http://www.atmel.com/avr.
Note:
1.
5.
Data Retention
Reliability Qualification results show that the projected data retention failure rate is much less
than 1 PPM over 20 years at 85°C or 100 years at 25°C.
Table 2-1.
Configuration summary
Device
Flash
Interrupt vector size
ATmega8HVA
8K
1 Word
ATmega16HVA
16K
2 Word
8
8024AS–AVR–04/08
ATmega8HVA/16HVA
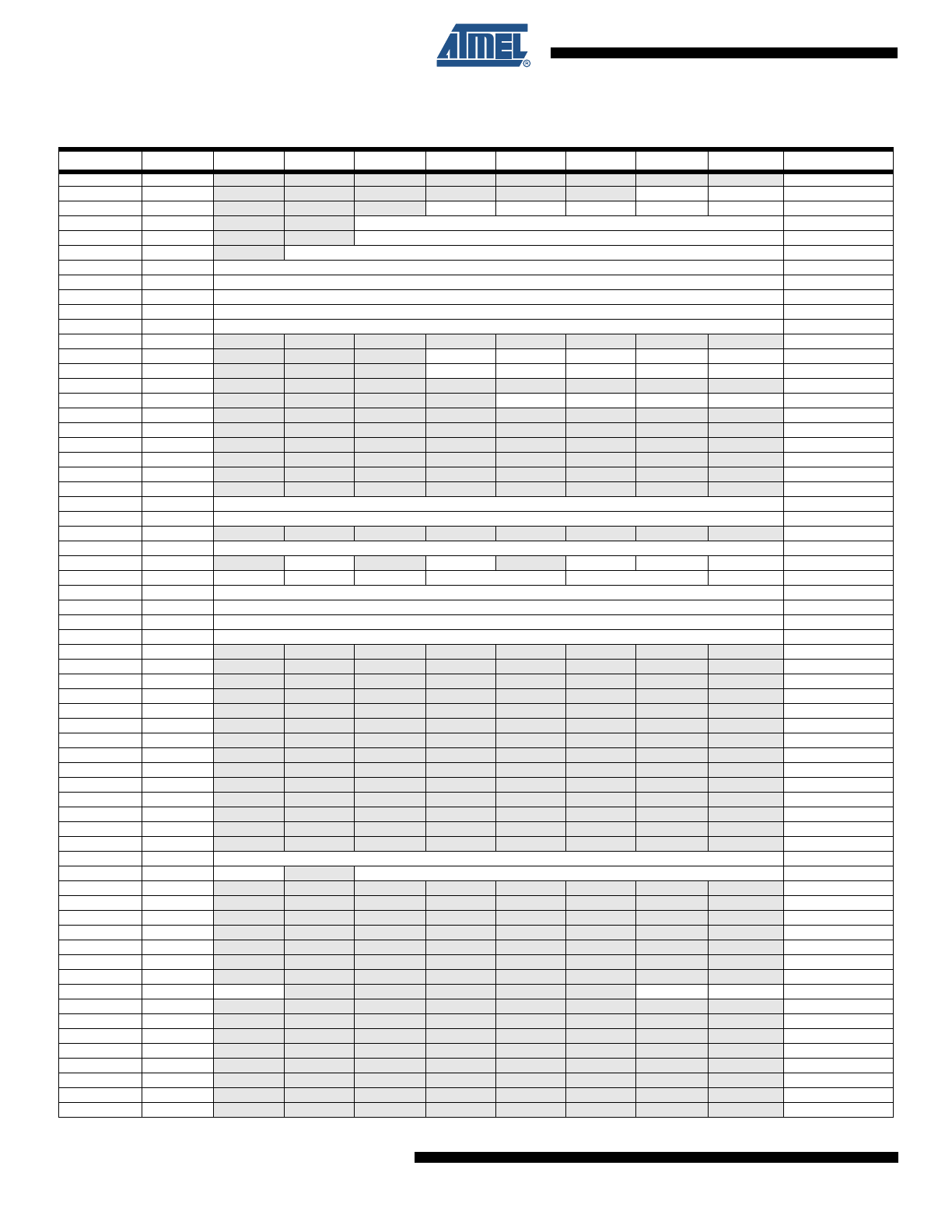
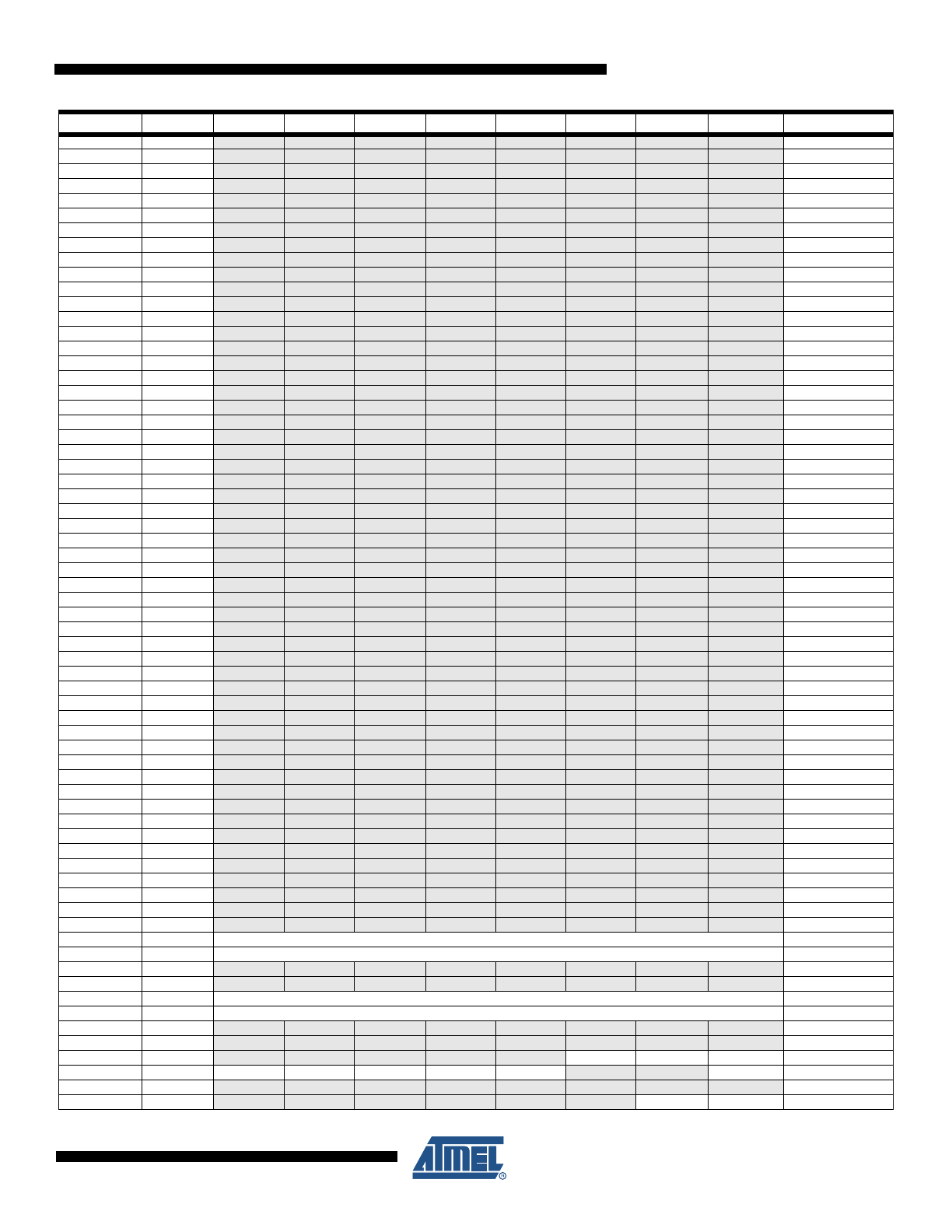
6.
Register Summary
Address
Name
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Page
(0xFF)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xFE)
BPPLR
–
–
–
–
–
–
BPPLE
BPPL
127
(0xFD)
BPCR
–
–
–
SCD
DOCD
COCD
DHCD
CHCD
127
(0xFC)
BPHCTR
–
–
HCPT[5:0]
130
(0xFB)
BPOCTR
–
–
OCPT[5:0]
129
(0xFA)
BPSCTR
–
SCPT[6:0]
128
(0xF9)
BPCHCD
CHCDL[7:0]
132
(0xF8)
BPDHCD
DHCDL[7:0]
132
(0xF7)
BPCOCD
COCDL[7:0]
131
(0xF6)
BPDOCD
DOCDL[7:0]
131
(0xF5)
BPSCD
SCDL[7:0]
131
(0xF4)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xF3)
BPIFR
–
–
–
SCIF
DOCIF
COCIF
DHCIF
CHCIF
134
(0xF2)
BPIMSK
–
–
–
SCIE
DOCIE
COCIE
DHCIE
CHCIE
133
(0xF1)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xF0)
FCSR
–
–
–
–
DUVRD
CPS
DFE
CFE
138
(0xEF)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xEE)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xED)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xEC)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xEB)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xEA)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xE9)
CADICH
CADIC[15:8]
110
(0xE8)
CADICL
CADIC[7:0]
110
(0xE7)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xE6)
CADRC
CADRC[7:0]
111
(0xE5)
CADCSRB
–
CADACIE
–
CADICIE
–
CADACIF
CADRCIF
CADICIF
109
(0xE4)
CADCSRA
CADEN
CADPOL
CADUB
CADAS[1:0]
CADSI[1:0]
CADSE
107
(0xE3)
CADAC3
CADAC[31:24]
110
(0xE2)
CADAC2
CADAC[23:16]
110
(0xE1)
CADAC1
CADAC[15:8]
110
(0xE0)
CADAC0
CADAC[7:0]
110
(0xDF)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xDE)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xDD)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xDC)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xDB)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xDA)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xD9)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xD8)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xD7)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xD6)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xD5)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xD4)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xD3)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xD2)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xD1)
BGCRR
BGCR[7:0]
119
(0xD0)
BGCCR
BGD
–
BGCC[5:0]
118
(0xCF)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xCE)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xCD)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xCC)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xCB)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xCA)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xC9)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xC8)
ROCR
ROCS
–
–
–
–
–
ROCWIF
ROCWIE
123
(0xC7)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xC6)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xC5)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xC4)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xC3)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xC2)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xC1)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xC0)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
9
8024AS–AVR–04/08
ATmega8HVA/16HVA
(0xBF)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xBE)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xBD)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xBC)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xBB)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xBA)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xB9)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xB8)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xB7)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xB6)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xB5)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xB4)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xB3)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xB2)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xB1)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xB0)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xAF)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xAE)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xAD)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xAC)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xAB)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xAA)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xA9)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xA8)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xA7)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xA6)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xA5)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xA4)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xA3)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xA2)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xA1)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0xA0)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x9F)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x9E)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x9D)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x9C)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x9B)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x9A)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x99)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x98)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x97)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x96)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x95)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x94)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x93)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x92)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x91)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x90)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x8F)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x8E)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x8D)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x8C)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x8B)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x8A)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x89)
OCR1B
Timer/Counter1 – Output Compare Register B
92
(0x88)
OCR1A
Timer/Counter1 – Output Compare Register A
91
(0x87)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x86)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x85)
TCNT1H
Timer/Counter1 (8 Bit) High Byte
91
(0x84)
TCNT1L
Timer/Counter1 (8 Bit) Low Byte
91
(0x83)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x82)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x81)
TCCR1B
–
–
–
–
–
CS12
CS11
CS10
76
(0x80)
TCCR1A
TCW1
ICEN1
ICNC1
ICES1
ICS1
–
–
WGM10
90
(0x7F)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x7E)
DIDR0
–
–
–
–
–
–
PA1DID
PA0DID
116
Address
Name
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Page
10
8024AS–AVR–04/08
ATmega8HVA/16HVA
(0x7D)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x7C)
VADMUX
–
–
–
–
VADMUX[3:0]
114
(0x7B)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x7A)
VADCSR
–
–
–
–
VADEN
VADSC
VADCCIF
VADCCIE
114
(0x79)
VADCH
–
–
–
–
VADC Data Register High byte
115
(0x78)
VADCL
VADC Data Register Low byte
115
(0x77)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x76)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x75)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x74)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x73)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x72)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x71)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x70)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x6F)
TIMSK1
–
–
–
–
ICIE1
OCIE1B
OCIE1A
TOIE1
92
(0x6E)
TIMSK0
–
–
–
–
ICIE0
OCIE0B
OCIE0A
TOIE0
92
(0x6D)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x6C)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x6B)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x6A)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x69)
EICRA
–
–
ISC21
ISC20
ISC11
ISC10
ISC01
ISC00
56
(0x68)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x67)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x66)
FOSCCAL
Fast Oscillator Calibration Register
30
(0x65)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x64)
PRR0
–
–
PRVRM
–
PRSPI
PRTIM1
PRTIM0
PRVADC
39
(0x63)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x62)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
(0x61)
CLKPR
CLKPCE
–
–
–
–
–
CLKPS1
CLKPS0
31
(0x60)
WDTCSR
WDIF
WDIE
WDP3
WDCE
WDE
WDP2
WDP1
WDP0
49
0x3F (0x5F)
SREG
I
T
H
S
V
N
Z
C
9
0x3E (0x5E)
SPH
SP15
SP14
SP13
SP12
SP11
SP10
SP9
SP8
12
0x3D (0x5D)
SPL
SP7
SP6
SP5
SP4
SP3
SP2
SP1
SP0
12
0x3C (0x5C)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
0x3B (0x5B)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
0x3A (0x5A)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
0x39 (0x59)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
0x38 (0x58)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
0x37 (0x57)
SPMCSR
–
–
SIGRD
CTPB
RFLB
PGWRT
PGERS
SPMEN
147
0x36 (0x56)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
0x35 (0x55)
MCUCR
–
–
CKOE
PUD
–
–
–
–
73/31
0x34 (0x54)
MCUSR
–
–
–
OCDRF
WDRF
BODRF
EXTRF
PORF
49
0x33 (0x53)
SMCR
–
–
–
–
SM[2:0]
SE
39
0x32 (0x52)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
0x31 (0x51)
DWDR
debugWIRE Data Register
140
0x30 (0x50)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
0x2F (0x4F)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
0x2E (0x4E)
SPDR
SPI Data Register
103
0x2D (0x4D)
SPSR
SPIF
WCOL
–
–
–
–
–
SPI2X
102
0x2C (0x4C)
SPCR
SPIE
SPE
DORD
MSTR
CPOL
CPHA
SPR1
SPR0
101
0x2B (0x4B)
GPIOR2
General Purpose I/O Register 2
23
0x2A (0x4A)
GPIOR1
General Purpose I/O Register 1
23
0x29 (0x49)
OCR0B
Timer/Counter0 Output Compare Register B
92
0x28 (0x48)
OCR0A
Timer/Counter0 Output Compare Register A
91
0x27 (0x47)
TCNT0H
Timer/Counter0 (8 Bit) High Byte
91
0x26 (0x46)
TCNT0L
Timer/Counter0 (8 Bit) Low Byte
91
0x25 (0x45)
TCCR0B
–
–
–
–
–
CS02
CS01
CS00
76
0x24 (0x44)
TCCR0A
TCW0
ICEN0
ICNC0
ICES0
ICS0
–
–
WGM00
90
0x23 (0x43)
GTCCR
TSM
–
–
–
–
–
–
PSRSYNC
0x22 (0x42)
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
0x21 (0x41)
EEAR
EEPROM Address Register Low Byte
19
0x20 (0x40)
EEDR
EEPROM Data Register
19
0x1F (0x3F)
EECR
–
–
EEPM1
EEPM0
EERIE
EEMPE
EEPE
EERE
19
0x1E (0x3E)
GPIOR0
General Purpose I/O Register 0
23
0x1D (0x3D)
EIMSK
–
–
–
–
–
INT2
INT1
INT0
57
0x1C (0x3C)
EIFR
–
–
–
–
–
INTF2
INTF1
INTF0
57
Address
Name
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Page
