LMD18201 3A, 55V H-Bridge
General Description
The LMD18201 is a 3A H-Bridge designed for motion control
applications. The device is built using a multi-technology pro-
cess which combines bipolar and CMOS control circuitry
with DMOS power devices on the same monolithic structure.
The H-Bridge configuration is ideal for driving DC and step-
per motors. The LMD18201 accommodates peak output cur-
rents up to 6A. Current sensing can be achieved via a small
sense resistor connected in series with the power ground
lead. For current sensing without disturbing the path of cur-
rent to the load, the LMD18200 is recommended.
Features
n
Delivers up to 3A continuous output
n
Operates at supply voltages up to 55V
n
Low R
DS(ON)
typically 0.33
Ω
per switch
n
TTL and CMOS compatible inputs
n
No “shoot-through” current
n
Thermal warning flag output at 145˚C
n
Thermal shutdown (outputs off) at 170˚C
n
Internal clamp diodes
n
Shorted load protection
n
Internal charge pump with external bootstrap capability
Applications
n
DC and stepper motor drives
n
Position and velocity servomechanisms
n
Factory automation robots
n
Numerically controlled machinery
n
Computer printers and plotters
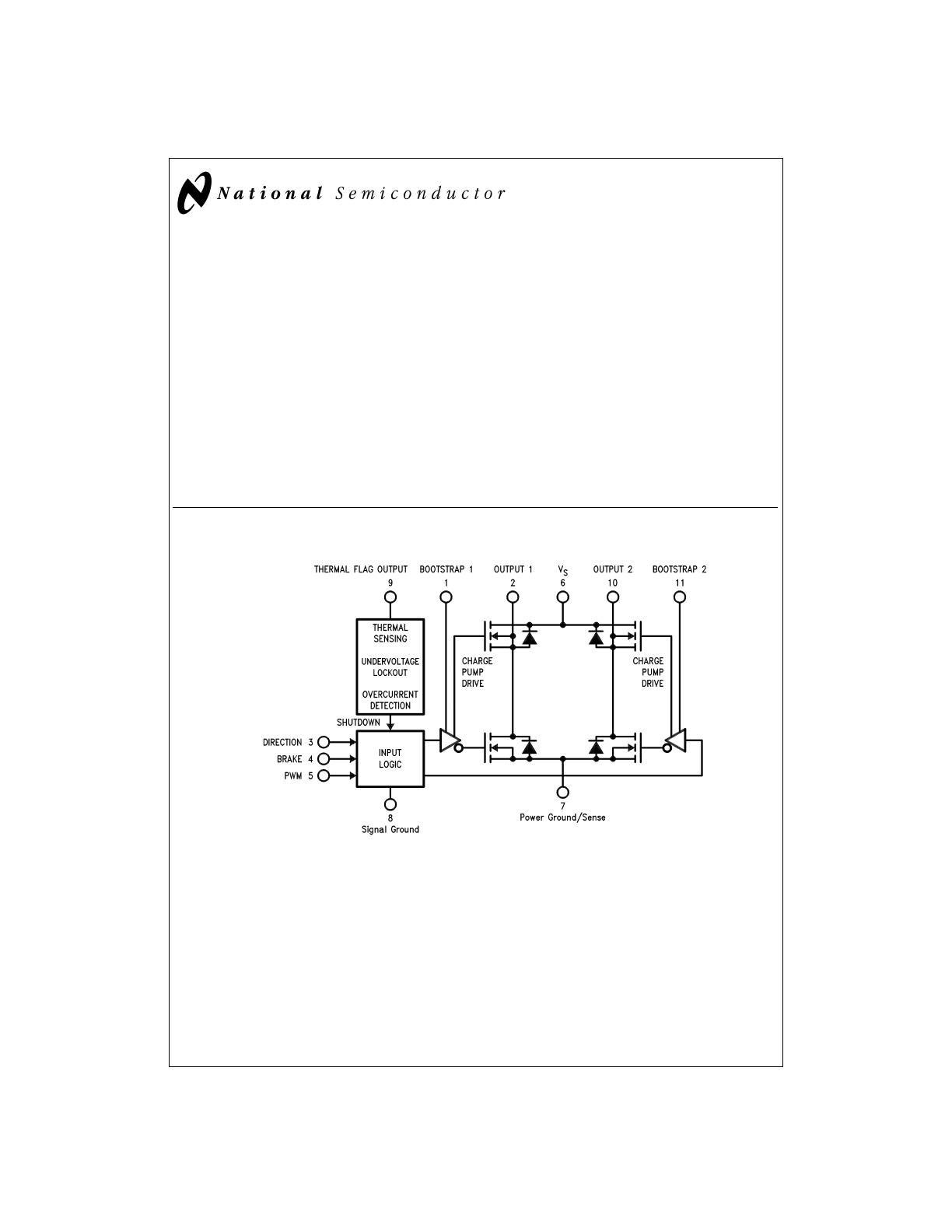
Functional Diagram
DS010793-1
FIGURE 1. Functional Block Diagram of LMD18201
April 1998
LMD18201
3A,
55V
H-Bridge
© 1998 National Semiconductor Corporation
DS010793
www.national.com
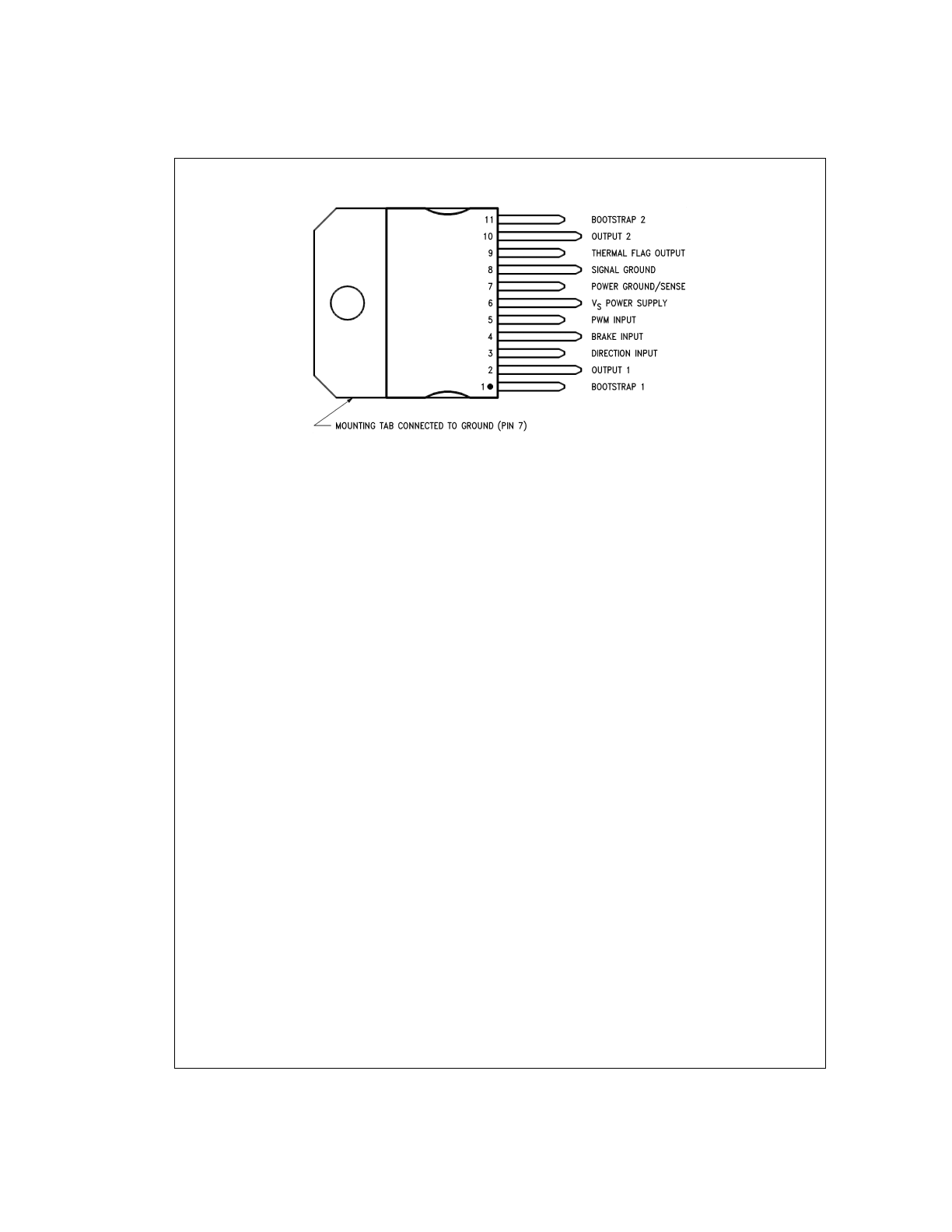
Connection Diagram and Ordering Information
DS010793-2
Top View
Order Number LMD18201T
See NS Package Number TA11B
www.national.com
2
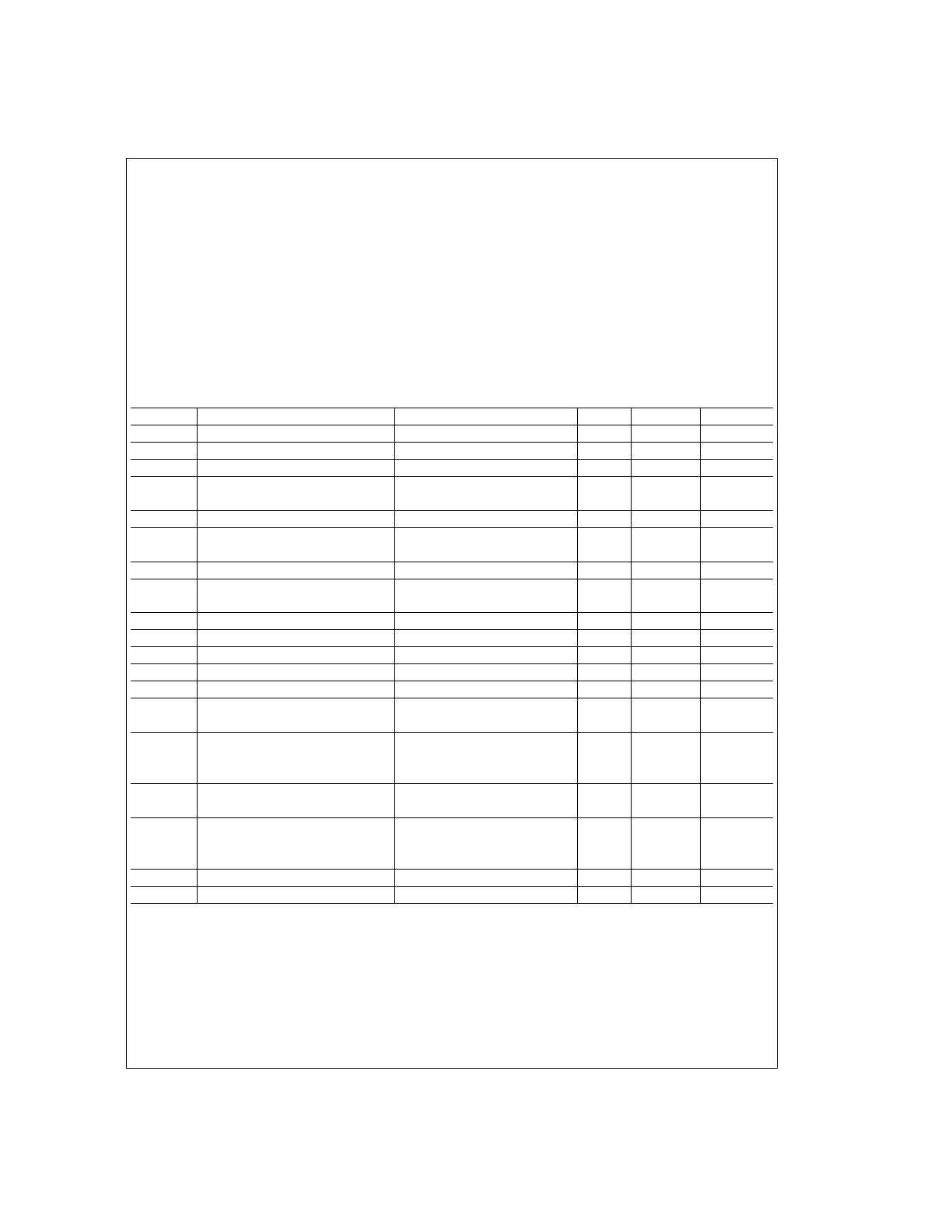
Absolute Maximum Ratings
(Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Total Supply Voltage (V
S
, Pin 6)
60V
Voltage at Pins 3, 4, 5 and 9
12V
Voltage at Bootstrap Pins (Pins 1 and 11)
V
OUT
+ 16V
Peak Output Current (200 ms)
6A
Continuous Output Current (Note 2)
3A
Power Dissipation (Note 3)
25W
Sense Voltage (Pin 7 to Pin 8)
+0.5V to −1.0V
Power Dissipation (T
A
= 25˚C, Free Air)
3W
Junction Temperature, T
J(max)
150˚C
ESD Susceptibility (Note 4)
1500V
Storage Temperature, T
STG
−40˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec.)
300˚C
Operating Ratings
(Note 1)
Junction Temperature, T
J
−40˚C to +125˚C
V
S
Supply Voltage
+12V to +55V
Electrical Characteristics
(Note 5)
The following specifications apply for V
S
= 42V, unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply over the entire operating
temperature range, −40˚C
≤
T
J
≤
+125˚C, all other limits are for T
A
= T
J
= 25˚C.
Symbol
Parameter
Conditions
Typ
Limit
Units
R
DS(ON)
Switch ON Resistance
Output Current = 3A (Note 6)
0.33
0.4/0.6
Ω
(max)
R
DS(ON)
Switch ON Resistance
Output Current = 6A (Note 6)
0.33
0.4/0.6
Ω
(max)
V
CLAMP
Clamp Diode Forward Drop
Clamp Current = 3A (Note 6)
1.2
1.5
V (max)
V
IL
Logic Low Input Voltage
Pins 3, 4, 5
−0.1
V (min)
0.8
V (max)
I
IL
Logic Low Input Current
V
IN
= −0.1V, Pins = 3, 4, 5
−10
µA (max)
V
IH
Logic High Input Voltage
Pins 3, 4, 5
2
V (min)
12
V (max)
I
IL
Logic High Input Current
V
IN
= 12V, Pins = 3, 4, 5
10
µA (max)
Undervoltage Lockout
Outputs Turn OFF
9
V (min)
11
V (max)
T
JW
Warning Flag Temperature
Pin 9
≤
0.8V, I
L
= 2 mA
145
˚C
V
F(ON)
Flag Output Saturation Voltage
T
J
= T
JW
, I
L
= 2 mA
0.15
V
I
F(OFF)
Flag Output Leakage
V
F
= 12V
0.2
10
µA (max)
T
JSD
Shutdown Temperature
Outputs Turn OFF
170
˚C
I
S
Quiescent Supply Current
All Logic Inputs Low
13
25
mA (max)
t
D(ON)
Output Turn-On Delay Time
Sourcing Outputs, I
OUT
= 3A
300
ns
Sinking Outputs, I
OUT
= 3A
300
ns
t
ON
Output Turn-On Switching Time
Bootstrap Capacitor = 10 nF
Sourcing Outputs, I
OUT
= 3A
100
ns
Sinking Outputs, I
OUT
= 3A
80
ns
t
D(OFF)
Output Turn-Off Delay Times
Sourcing Outputs, I
OUT
= 3A
200
ns
Sinking Outputs, I
OUT
= 3A
200
ns
t
OFF
Output Turn-Off Switching Times
Bootstrap Capacitor = 10 nF
Sourcing Outputs, I
OUT
= 3A
75
ns
Sinking Outputs, I
OUT
= 3A
70
ns
t
PW
Minimum Input Pulse Width
Pins 3, 4 and 5
1
µs
t
CPR
Charge Pump Rise Time
No Bootstrap Capacitor
20
µs
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. DC and AC electrical specifications do not apply when operating
the device beyond its rated operating conditions.
Note 2: See Application Information for details regarding current limiting.
Note 3: The maximum power dissipation must be derated at elevated temperatures and is a function of T
J(max)
,
θ
JA
, and T
A
. The maximum allowable power dissi-
pation at any temperature is P
D(max)
= (T
J(max)
− T
A
)/
θ
JA
, or the number given in the Absolute Ratings, whichever is lower. The typical thermal resistance from junction
to case (
θ
JC
) is 1.0˚C/W and from junction to ambient (
θ
JA
) is 30˚C/W. For guaranteed operation T
J(max)
= 125˚C.
Note 4: Human-body model, 100 pF discharged through a 1.5 k
Ω
resistor. Except Bootstrap pins (pins 1 and 11) which are protected to 1000V of ESD.
Note 5: All limits are 100% production tested at 25˚C. Temperature extreme limits are guaranteed via correlation using accepted SQC (Statistical Quality Control)
methods. All limits are used to calculate AOQL, (Average Outgoing Quality Level).
Note 6: Output currents are pulsed (t
W
<
2 ms, Duty Cycle
<
5%).
3
www.national.com
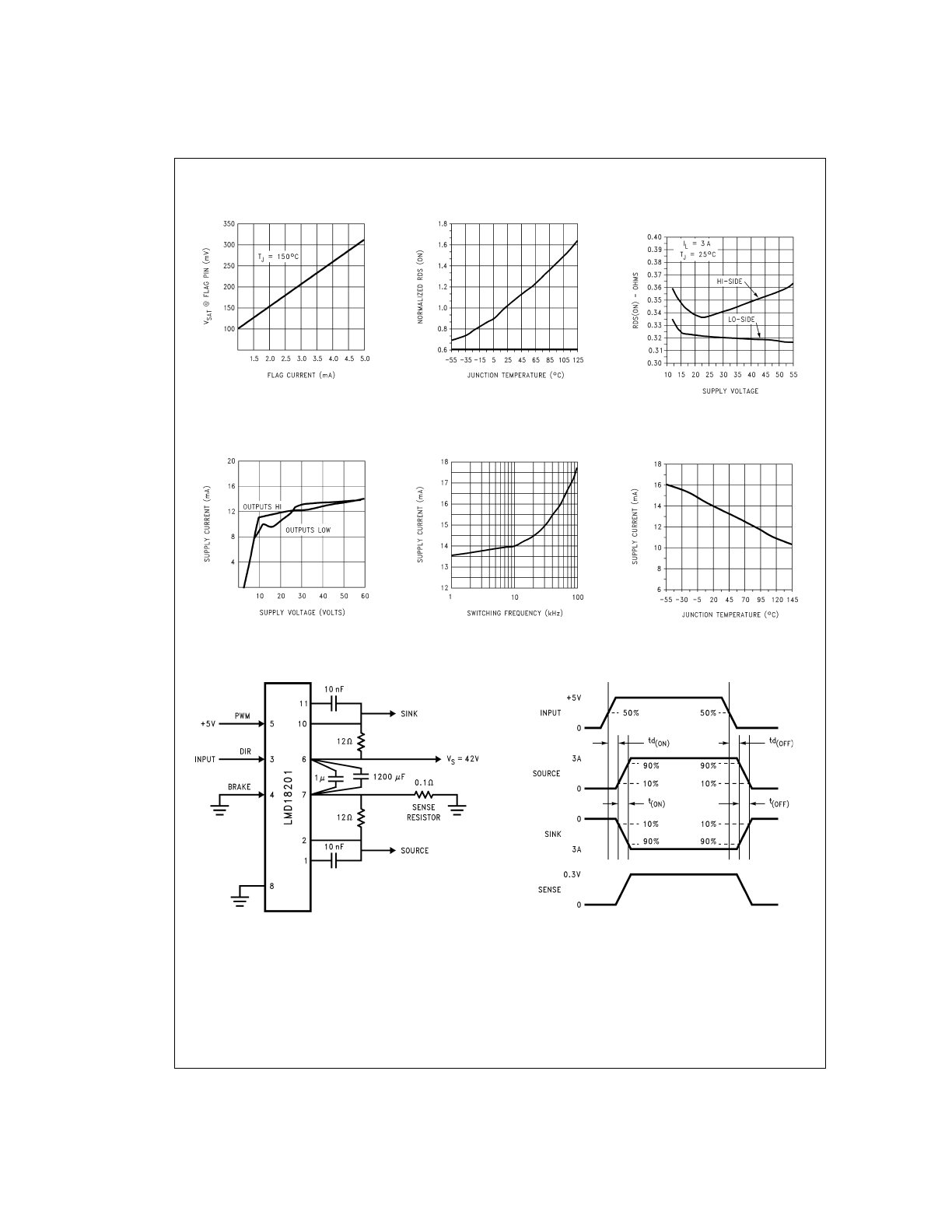
Typical Performance Characteristics
Test Circuit
Switching Time Definitions
V
SAT
vs Flag Current
DS010793-12
R
DS(ON)
vs Temperature
DS010793-13
R
DS(ON)
vs
Supply Voltage
DS010793-14
Supply Current vs
Supply Voltage
DS010793-15
Supply Current vs
Frequency (V
S
= 42V)
DS010793-16
Supply Current vs
Temperature (V
S
= 42V)
DS010793-17
DS010793-8
DS010793-9
www.national.com
4
Pinout Description
(See Connection Diagram)
Pin 1, BOOTSTRAP 1 Input: Bootstrap capacitor pin for half
H-Bridge number 1. The recommended capacitor (10 nF) is
connected between pins 1 and 2.
Pin 2, OUTPUT 1: Half H-Bridge number 1 output.
Pin 3, DIRECTION Input: See
Table 1
. This input controls
the direction of current flow between OUTPUT 1 and OUT-
PUT 2 (pins 2 and 10) and, therefore, the direction of rotation
of a motor load.
Pin 4, BRAKE Input: See
Table 1
. This input is used to
brake a motor by effectively shorting its terminals. When
braking is desired, this input is taken to a logic high level and
it is also necessary to apply logic high to PWM input, pin 5.
The drivers that short the motor are determined by the logic
level at the DIRECTION input (Pin 3): with Pin 3 logic high,
both current sourcing output transistors are ON; with Pin 3
logic low, both current sinking output transistors are ON. All
output transistors can be turned OFF by applying a logic high
to Pin 4 and a logic low to PWM input Pin 5; in this case only
a small bias current (approximately −1.5 mA) exists at each
output pin.
Pin 5, PWM Input: See
Table 1
. How this input (and DIREC-
TION input, Pin 3) is used is determined by the format of the
PWM Signal.
Pin 6, V
S
Power Supply
Pin 7, POWER GROUND/SENSE Connection: This pin is
the ground return for the power DMOS transistors of the
H-Bridge. The current through the H-Bridge can be sensed
by adding a small, 0.1
Ω
, sense resistor from this pin to the
power supply ground.
Pin 8, SIGNAL GROUND: This is the ground return for the
internal logic circuitry used to control the PWM switching of
the H-Bridge.
Pin 9, THERMAL FLAG Output: This pin provides the ther-
mal warning flag output signal. Pin 9 becomes active-low at
145˚C (junction temperature). However the chip will not shut
itself down until 170˚C is reached at the junction.
Pin 10, OUTPUT 2: Half H-Bridge number 2 output.
Pin 11, BOOTSTRAP 2 Input: Bootstrap capacitor pin for
half H-Bridge number 2. The recommended capacitor
(10 nF) is connected between pins 10 and 11.
TABLE 1. Logic Truth Table
PWM
Dir
Brake
Active Output Drivers
H
H
L
Source 1, Sink 2
H
L
L
Sink 1, Source 2
L
X
L
Source 1, Source 2
H
H
H
Source 1, Source 2
H
L
H
Sink 1, Sink 2
L
X
H
NONE
Application Information
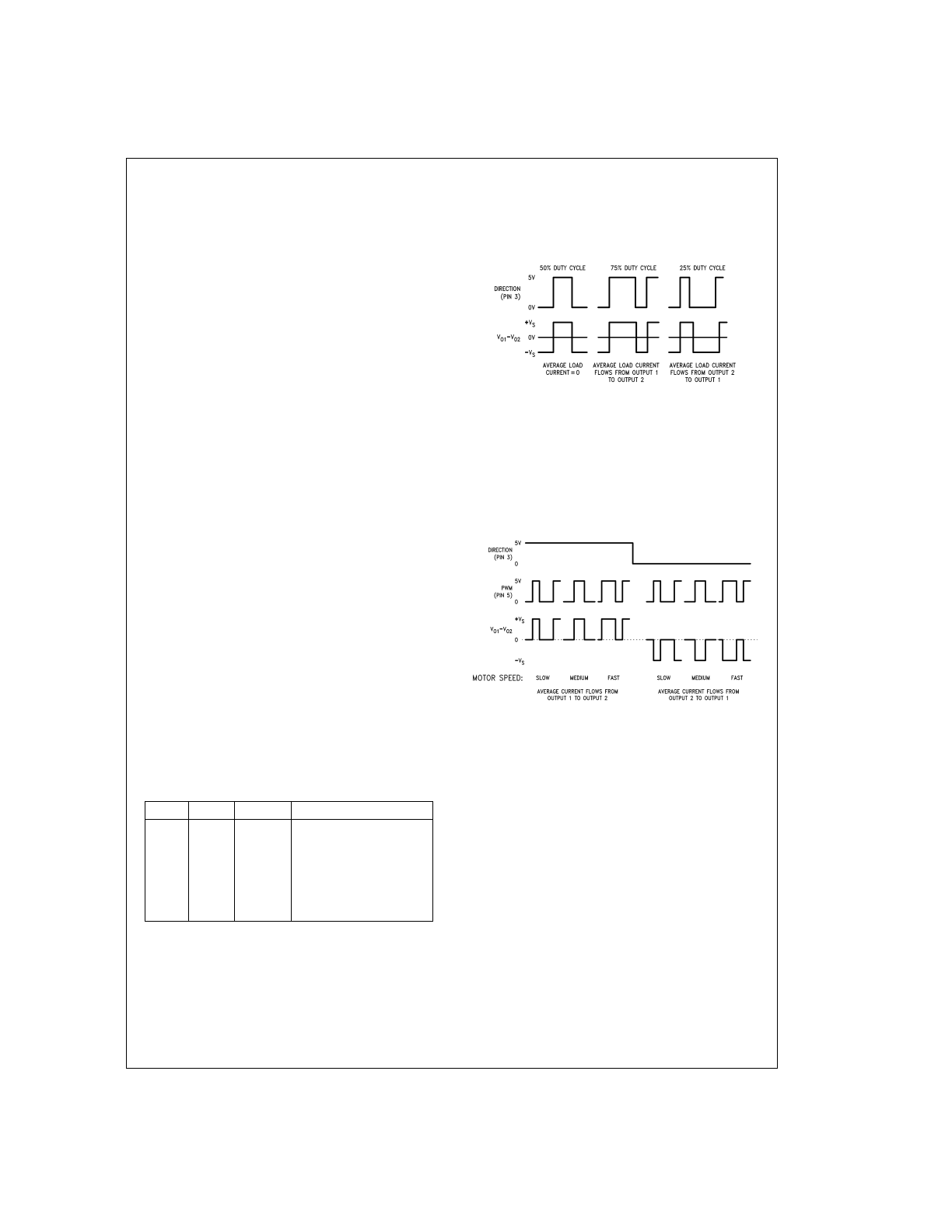
TYPES OF PWM SIGNALS
The LMD18201 readily interfaces with different forms of
PWM signals. Use of the part with two of the more popular
forms of PWM is described in the following paragraphs.
Simple, locked anti-phase PWM consists of a single, vari-
able duty-cycle signal in which is encoded both direction and
amplitude information (see
Figure 2
). A 50% duty-cycle
PWM signal represents zero drive, since the net value of
voltage (integrated over one period) delivered to the load is
zero. For the LMD18201, the PWM signal drives the direc-
tion input (pin 3) and the PWM input (pin 5) is tied to logic
high.
Sign/magnitude PWM consists of separate direction (sign)
and amplitude (magnitude) signals (see
Figure 3
). The (ab-
solute) magnitude signal is duty-cycle modulated, and the
absence of a pulse signal (a continuous logic low level) rep-
resents zero drive. Current delivered to the load is propor-
tional to pulse width. For the LMD18201, the DIRECTION in-
put (pin 3) is driven by the sign signal and the PWM input
(pin 5) is driven by the magnitude signal.
USING THE THERMAL WARNING FLAG
The THERMAL FLAG output (pin 9) is an open collector tran-
sistor. This permits a wired OR connection of thermal warn-
ing flag outputs from multiple LMD18201’s, and allows the
user to set the logic high level of the output signal swing to
match system requirements. This output typically drives the
interrupt input of a system controller. The interrupt service
routine would then be designed to take appropriate steps,
such as reducing load currents or initiating an orderly system
shutdown. The maximum voltage compliance on the flag pin
is 12V.
SUPPLY BYPASSING
During switching transitions the levels of fast current
changes experienced may cause troublesome voltage tran-
sients across system stray inductances.
It is normally necessary to bypass the supply rail with a high
quality capacitor(s) connected as close as possible to the V
S
Power Supply (Pin 6) and POWER GROUND (Pin 7). A 1 µF
high-frequency ceramic capacitor is recommended. Care
should be taken to limit the transients on the supply pin be-
low the Absolute Maximum Rating of the device. When oper-
ating the chip at supply voltages above 40V a voltage sup-
DS010793-4
FIGURE 2. Locked Anti-Phase PWM Control
DS010793-5
FIGURE 3. Sign/Magnitude PWM Control
5
www.national.com
Application Information
(Continued)
pressor (transorb) such as P6KE62A is recommended from
supply to ground. Typically the ceramic capacitor can be
eliminated in the presence of the voltage suppressor. Note
that when driving high load currents a greater amount of sup-
ply bypass capacitance (in general at least 100 µF per Amp
of load current) is required to absorb the recirculating cur-
rents of the inductive loads.
CURRENT LIMITING
Current limiting protection circuitry has been incorporated
into the design of the LMD18201. With any power device it is
important to consider the effects of the substantial surge cur-
rents through the device that may occur as a result of
shorted loads. The protection circuitry monitors the current
through the upper transistors and shuts off the power device
as quickly as possible in the event of an overload condition
(the threshold is set to approximately 10A). In a typical motor
driving application the most common overload faults are
caused by shorted motor windings and locked rotors. Under
these conditions the inductance of the motor (as well as any
series inductance in the V
CC
supply line) serves to reduce
the magnitude of a current surge to a safe level for the
LMD18201. Once the device is shut down, the control cir-
cuitry will periodically try to turn the power device back on.
This feature allows the immediate return to normal operation
once the fault condition has been removed. While the fault
remains however, the device will cycle in and out of thermal
shutdown. This can create voltage transients on the V
CC
supply line and therefore proper supply bypassing tech-
niques are required.
The most severe condition for any power device is a direct,
hard-wired (“screwdriver”) long term short from an output to
ground. This condition can generate a surge of current
through the power device on the order of 15 Amps and re-
quire the die and package to dissipate up to 500W of power
for the short time required for the protection circuitry to shut
off the power device. This energy can be destructive, particu-
larly at higher operating voltages (
>
30V) so some precau-
tions are in order. Proper heat sink design is essential and it
is normally necessary to heat sink the V
CC
supply pin (pin 6)
with 1 square inch of copper on the PC board.
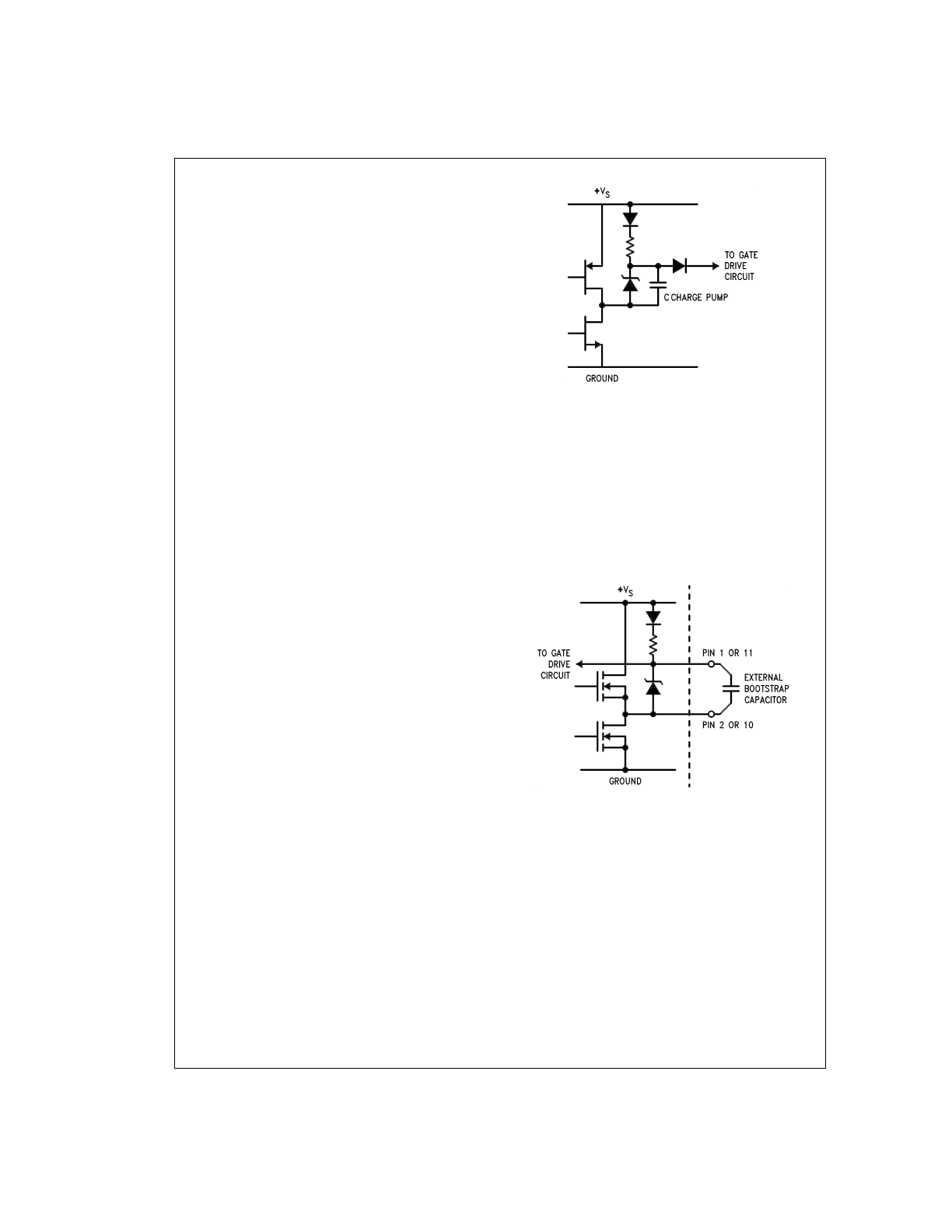
INTERNAL CHARGE PUMP AND USE OF
BOOTSTRAP CAPACITORS
To turn on the high-side (sourcing) DMOS power devices,
the gate of each device must be driven approximately 8V
more positive than the supply voltage. To achieve this an in-
ternal charge pump is used to provide the gate drive voltage.
As shown in (
Figure 4
), an internal capacitor is alternately
switched to ground and charged to about 14V, then switched
to V
S
thereby providing a gate drive voltage greater than V
S
.
This switching action is controlled by a continuously running
internal 300 kHz oscillator. The rise time of this drive voltage
is typically 20 µs which is suitable for operating frequencies
up to 1 kHz.
For higher switching frequencies, the LMD18201 provides
for the use of external bootstrap capacitors. The bootstrap
principle is in essence a second charge pump whereby a
large value capacitor is used which has enough energy to
quickly charge the parasitic gate input capacitance of the
power device resulting in much faster rise times. The switch-
ing action is accomplished by the power switches them-
selves (
Figure 5
). External 10 nF capacitors, connected from
the outputs to the bootstrap pins of each high-side switch
provide typically less than 100 ns rise times allowing switch-
ing frequencies up to 500 kHz.
INTERNAL PROTECTION DIODES
A major consideration when switching current through induc-
tive loads is protection of the switching power devices from
the large voltage transients that occur. Each of the four
switches in the LMD18201 have a built-in protection diode to
clamp transient voltages exceeding the positive supply or
ground to a safe diode voltage drop across the switch.
The reverse recovery characteristics of these diodes, once
the transient has subsided, is important. These diodes must
come out of conduction quickly and the power switches must
be able to conduct the additional reverse recovery current of
the diodes. The reverse recovery time of the diodes protect-
ing the sourcing power devices is typically only 70 ns with a
reverse recovery current of 1A when tested with a full 3A of
forward current through the diode. For the sinking devices
the recovery time is typically 100 ns with 4A of reverse cur-
rent under the same conditions.
DS010793-6
FIGURE 4. Internal Charge Pump Circuitry
DS010793-7
FIGURE 5. Bootstrap Circuitry
www.national.com
6
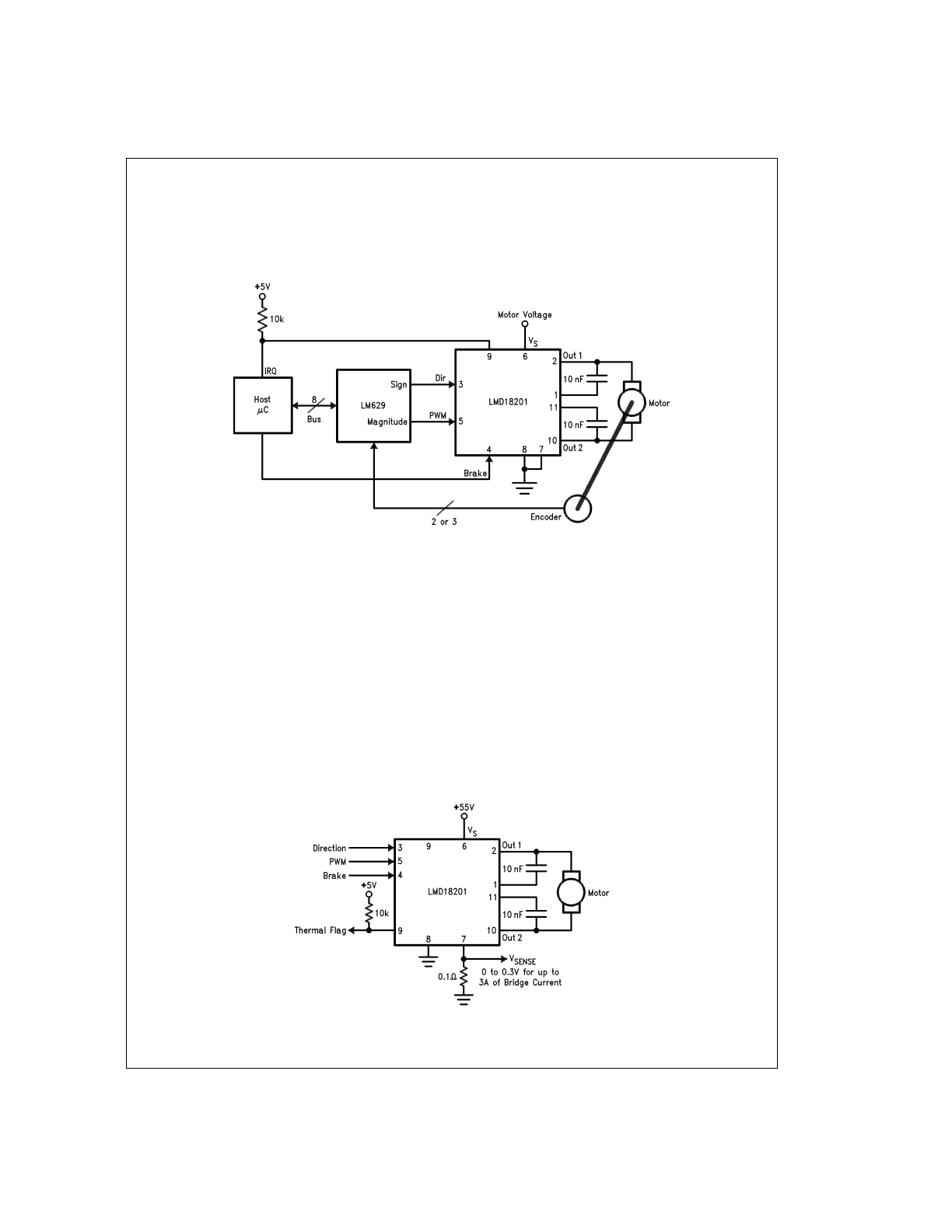
Typical Applications
BASIC MOTOR DRIVER
The LMD18201 can directly interface to any Sign/Magnitude
PWM controller. The LM629 is a motion control processor
that outputs a Sign/Magnitude PWM signal to coordinate ei-
ther positional or velocity control of DC motors. The
LMD18201 provides fully protected motor driver stage.
CURRENT SENSING
In many motor control applications it is desirable to sense
and control the current through the motor. For these types of
applications a companion product, the LMD18200, is also
available. The LMD18200 is identical to the LMD18201 but
has current sensing transistors that output a current directly
proportional to the current conducted by the two upper
DMOS power devices to a separate current sense pin. This
technique does not require a low valued, power sense resis-
tor and does not subtract from the available voltage drive to
the motor.
To sense the bridge current through the LMD18201 requires
the addition of a small sense resistor between the power
ground/sense pin (Pin 7) and the actual circuit ground (see
Figure 7
). This resistor should have a value of 0.1
Ω
or less to
stay within the allowable voltage compliance of the sense
pin, particularly at higher operating current levels. The volt-
age between power ground/sense (Pin 7) and the signal
ground (Pin 8) must stay within the range of −1V to +0.5V. In-
ternally there is approximately 25
Ω
between pins 7 and 8
and this resistance will slightly reduce the value of the exter-
nal sense resistor. Approximately 70% of the quiescent sup-
ply current (10 mA) flows out of pin 7. This will cause a slight
offset to the voltage across the sense resistor when the
bridge is not conducting. During reverse recovery of the in-
ternal protection diodes the voltage compliance between
pins 7 and 8 may be exceeded. The duration of these spikes
however are only approximately 100 ns and do not have
enough time or energy to disrupt the operation of the
LMD18201.
DS010793-10
FIGURE 6. Basic Motor Driver
DS010793-11
FIGURE 7. Current Sensing
7
www.national.com
Physical Dimensions
inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT DE-
VICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT OF NATIONAL SEMI-
CONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or sys-
tems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into
the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and whose fail-
ure to perform when properly used in accordance
with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can
be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury
to the user.
2. A critical component in any component of a life support
device or system whose failure to perform can be rea-
sonably expected to cause the failure of the life support
device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
National Semiconductor
Corporation
Americas
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
Fax: 1-800-737-7018
Email: support@nsc.com
www.national.com
National Semiconductor
Europe
Fax: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 85
English
Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 78 32
Français Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 93 58
Italiano
Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-534 16 80
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Response Group
Tel: 65-2544466
Fax: 65-2504466
Email: sea.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Ltd.
Tel: 81-3-5620-6175
Fax: 81-3-5620-6179
11-Lead TO-220 Power Package (T)
Order Number LMD18201T
NS Package Number TA11B
LMD18201
3A,
55V
H-Bridge
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
