NOTE: This is a summary document.
The complete document is available on
the Atmel website at www.atmel.com.
Features
•
Incorporates the ARM7TDMI
®
ARM
®
Thumb
®
Processor Core
– High-performance 32-bit RISC Architecture
– High-density 16-bit Instruction Set
– Leader in MIPS/Watt
– EmbeddedICE
™
•
8K Bytes On-chip SRAM
– 32-bit Data Bus
– Single-clock Cycle Access
•
Fully-programmable External Bus Interface (EBI)
– Maximum External Address Space of 64M Bytes
– Up to 8 Chip Selects
– Software Programmable 8/16-bit External Databus
•
8-level Priority, Individually Maskable, Vectored Interrupt Controller
– 4 External Interrupts, Including a High-priority Low-latency Interrupt Request
•
32 Programmable I/O Lines
•
3-channel 16-bit Timer/Counter
– 3 External Clock Inputs
– 2 Multi-purpose I/O Pins per Channel
•
2 USARTs
– 2 Dedicated Peripheral Data Controller (PDC) Channels per USART
•
Programmable Watchdog Timer
•
Advanced Power-saving Features
– CPU and Peripheral Can Be Deactivated Individually
•
Fully Static Operation:
– 0 Hz to 40 MHz Internal Frequency Range at 3.0V, 85
°
C
•
1.8V to 3.6V Operating Range
•
-40
°
C to +85
°
C Temperature Range
•
Available in a 100-lead LQFP Package (Green)
1.
Description
The AT91M40800 microcontroller is a member of the Atmel AT91 16/32-bit microcon-
troller family, which is based on the ARM7TDMI processor core. This processor has a
high-performance 32-bit RISC architecture with a high-density 16-bit instruction set
and very low power consumption. In addition, a large number of internally banked reg-
isters result in very fast exception handling, making the device ideal for real-time
control applications.
The AT91M40800 microcontroller features a direct connection to off-chip memory,
including Flash, through the fully-programmable External Bus Interface (EBI). An
eight-level priority vectored interrupt controller, in conjunction with the Peripheral Data
Controller, significantly improves the real-time performance of the device.
The device is manufactured using Atmel’s high-density CMOS technology. By com-
bining the ARM7TDMI processor core with on-chip high-speed memory and a wide
range of peripheral functions on a monolithic chip, the AT91M40800 is a powerful
microcontroller that offers a flexible, cost-effective solution to many compute-intensive
embedded control applications.
AT91 ARM
Thumb
Microcontrollers
AT91M40800
Summary
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
2
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
2.
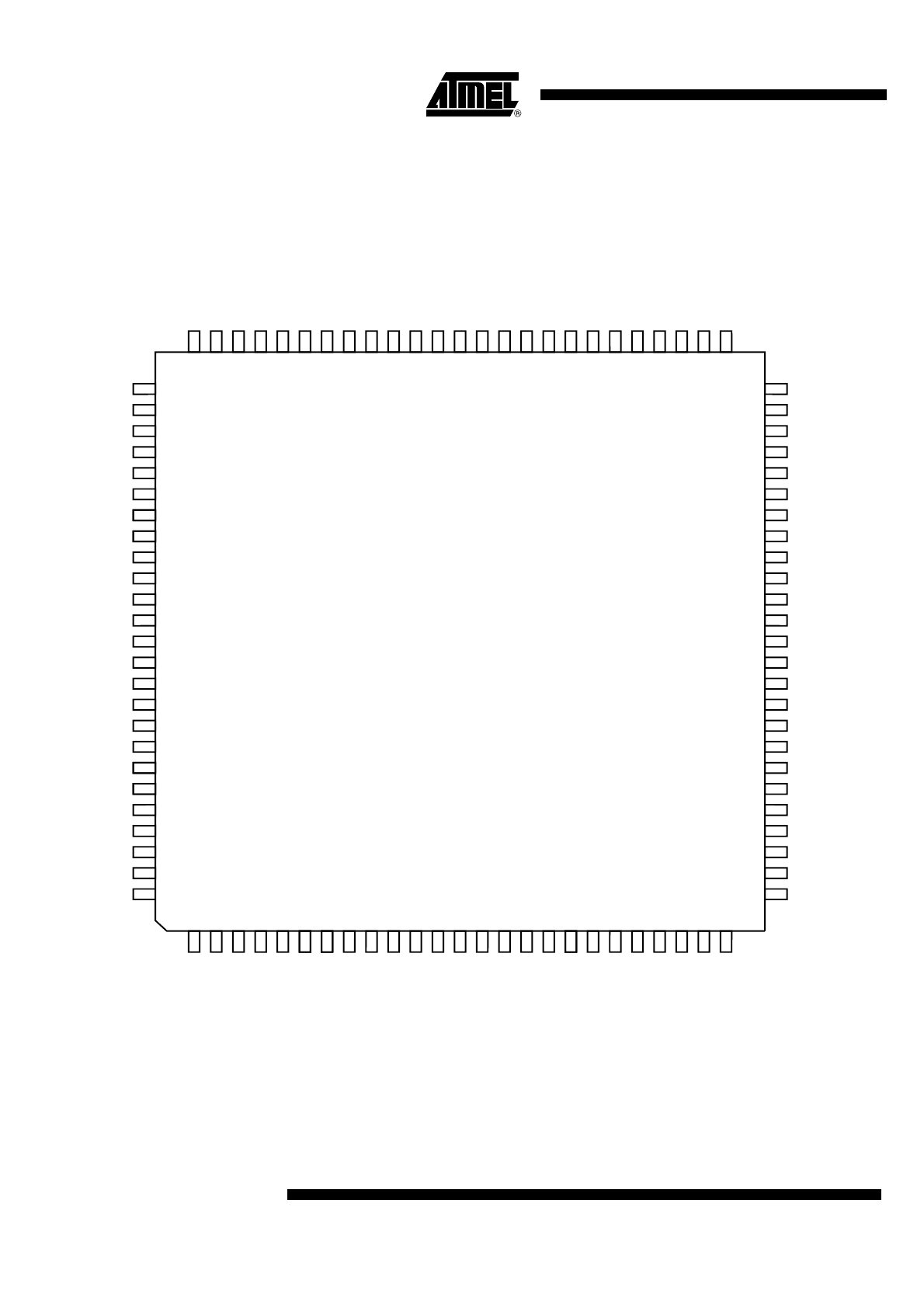
Pin Configuration
Figure 2-1.
AT91M40800 Pinout (Top View)
P21/TXD1/NTRI
P20/SCK1
P19
P18
P17
P16
P15/RXD0
P14/TXD0
P13/SCK0
P12/FIQ
GND
P11/IRQ2
P10/IRQ1
VDD
VDD
P9/IRQ0
P8/TIOB2
P7/TIOA2
P6/TCLK2
P5/TIOB1
P4/TIOA1
P3/TCLK1
GND
GND
P2/TIOB0
P1/TIOA0
P0/TCLK0
D15
D14
D13
D12
VDD
D11
D10
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
GND
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
P31/A23/CS4
P30/A22/CS5
VDD
VDD
P29/A21/CS6
P22/RXD1
NWR1/NUB
GND
NRST
NWDOVF
VDD
MCKI
P23
P24/BMS
P25/MCKO
GND
GND
TMS
TDO
TCK
NRD/NOE
NWR0/NWE
VDD
VDD
NWAIT
NCS0
NCS1
P26/NCS2
P27/NCS3
A0/NLB
A1
A2A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
VDD
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
GND
GND
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
P28/A20/CS7
GND
1
25
100-lead TQFP
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
116
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
26
50
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
75
51
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
100
76
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
TDI
3
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
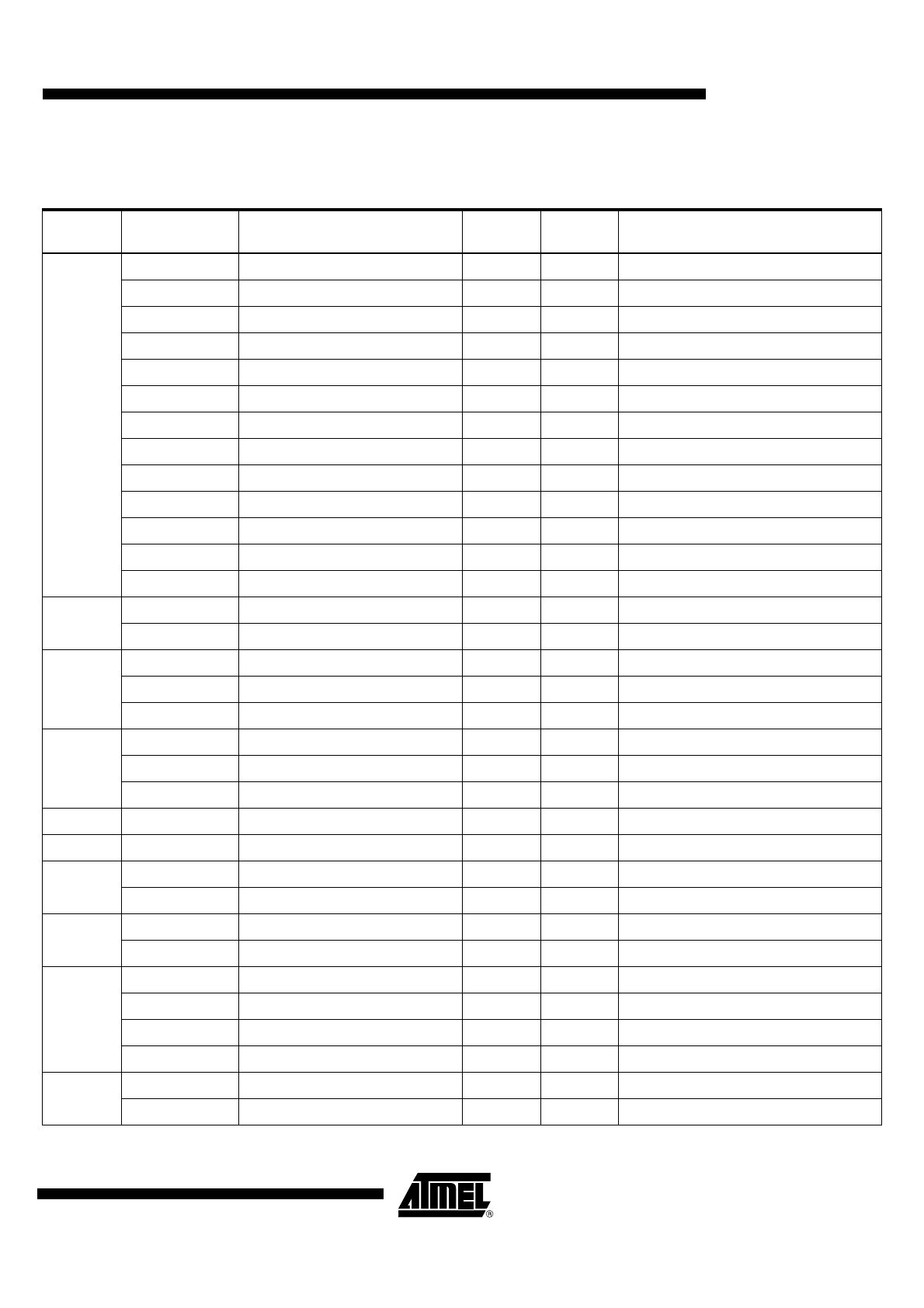
3.
Pin Description
Table 3-1.
AT91M40800 Pin Description
Module
Name
Function
Type
Active
Level
Comments
EBI
A0 - A23
Address Bus
Output
–
All valid after reset
D0 - D15
Data Bus
I/O
–
NCS0 - NCS3
Chip Select
Output
Low
CS4 - CS7
Chip Select
Output
High
A23 - A20 after reset
NWR0
Lower Byte 0 Write Signal
Output
Low
Used in Byte Write option
NWR1
Upper Byte 1 Write Signal
Output
Low
Used in Byte Write option
NRD
Read Signal
Output
Low
Used in Byte Write option
NWE
Write Enable
Output
Low
Used in Byte Select option
NOE
Output Enable
Output
Low
Used in Byte Select option
NUB
Upper Byte Select
Output
Low
Used in Byte Select option
NLB
Lower Byte Select
Output
Low
Used in Byte Select option
NWAIT
Wait Input
Input
Low
BMS
Boot Mode Select
Input
–
Sampled during reset
AIC
FIQ
Fast Interrupt Request
Input
–
PIO-controlled after reset
IRQ0 - IRQ2
External Interrupt Request
Input
–
PIO-controlled after reset
TC
TCLK0 - TCLK2
Timer External Clock
Input
–
PIO-controlled after reset
TIOA0 - TIOA2
Multipurpose Timer I/O pin A
I/O
–
PIO-controlled after reset
TIOB0 - TIOB2
Multipurpose Timer I/O pin B
I/O
–
PIO-controlled after reset
USART
SCK0 - SCK1
External Serial Clock
I/O
–
PIO-controlled after reset
TXD0 - TXD1
Transmit Data Output
Output
–
PIO-controlled after reset
RXD0 - RXD1
Receive Data Input
Input
–
PIO-controlled after reset
PIO
P0 - P31
Parallel IO line
I/O
–
WD
NWDOVF
Watchdog Overflow
Output
Low
Open-drain
Clock
MCKI
Master Clock Input
Input
–
Schmidt trigger
MCKO
Master Clock Output
Output
–
Reset
NRST
Hardware Reset Input
Input
Low
Schmidt trigger
NTRI
Tri-state Mode Select
Input
Low
Sampled during reset
ICE
TMS
Test Mode Select
Input
–
Schmidt trigger, internal pull-up
TDI
Test Data Input
Input
–
Schmidt trigger, internal pull-up
TDO
Test Data Output
Output
–
TCK
Test Clock
Input
–
Schmidt trigger, internal pull-up
Power
VDD
Power
Power
–
GND
Ground
Ground
–
4
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
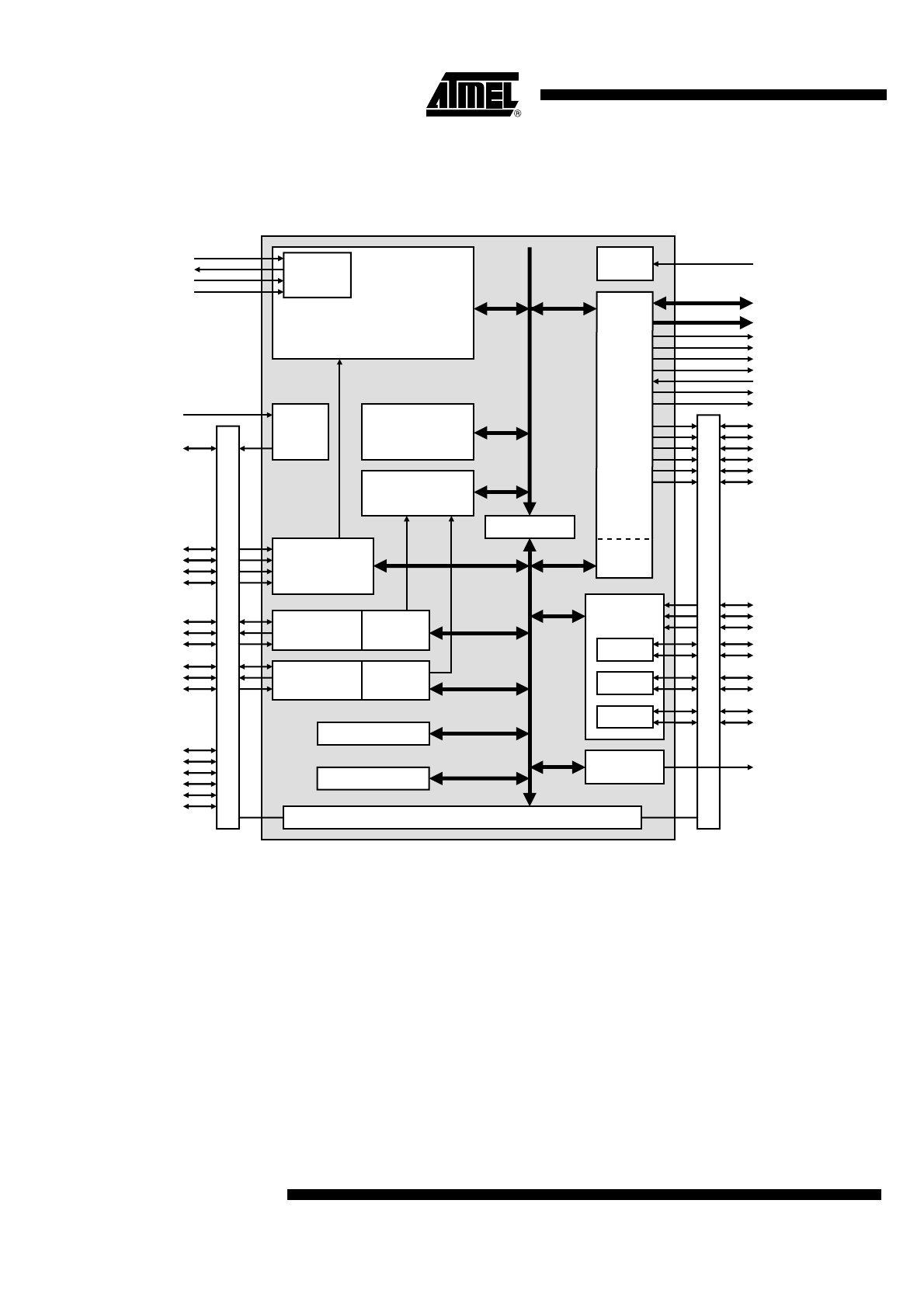
4.
Block Diagram
Figure 4-1.
AT91M40800
ARM7TDMI Core
Embedded
ICE
Reset
EBI: External Bus Interface
ASB
Controller
Clock
AIC: Advanced
Interrupt Controller
AMBA Bridge
EBI User
Interface
TC: Timer
Counter
TC0
TC1
TC2
USART0
USART1
2 PDC
Channels
2 PDC
Channels
PIO: Parallel I/O Controller
PS: Power Saving
Chip ID
WD: Watchdog
Timer
APB
ASB
P
I
O
P
I
O
NRST
D0-D15
A1-A19
A0/NLB
NRD/NOE
NWR0/NWE
NWR1/NUB
NWAIT
NCS0
NCS1
P26/NCS2
P27/NCS3
P28/A20/CS7
P29/A21/CS6
P30/A22/CS5
P31/A23/CS4
P0/TCLK0
P3/TCLK1
P6/TCLK2
P1/TIOA0
P2/TIOB0
P4/TIOA1
P5/TIOB1
P7/TIOA2
P8/TIOB2
NWDOVF
TMS
TDO
TDI
TCK
MCKI
P25/MCKO
P12/FIQ
P9/IRQ0
P10/IRQ1
P11/IRQ2
P13/SCK0
P14/TXD0
P15/RXD0
P20/SCK1
P21/TXD1/NTRI
P22/RXD1
P16
P17
P18
P19
P23
P24/BMS
8K-byte RAM

5
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
5.
Architectural Overview
The AT91M40800 microcontroller integrates an ARM7TDMI with Embedded ICE interface,
memories and peripherals. The architecture consists of two main buses, the Advanced System
Bus (ASB) and the Advanced Peripheral Bus (APB). Designed for maximum performance and
controlled by the memory controller, the ASB interfaces the ARM7TDMI processor with the on-
chip 32-bit memories, the External Bus Interface (EBI) and the AMBA
™
Bridge. The AMBA
Bridge drives the APB, which is designed for accesses to on-chip peripherals and optimized for
low power consumption.
The AT91M40800 microcontroller implements the ICE port of the ARM7TDMI processor on ded-
icated pins, offering a complete, low cost and easy-to-use debug solution for target debugging.
5.1
Memories
The AT91M40800 microcontroller embeds up to 8K bytes of internal SRAM. The internal mem-
ory is directly connected to the 32-bit data bus and is single-cycle accessible.
The AT91M40800 microcontroller features an External Bus Interface (EBI), which enables con-
nection of external memories and application-specific peripherals. The EBI supports 8- or 16-bit
devices and can use two 8-bit devices to emulate a single 16-bit device. The EBI implements the
early read protocol, enabling faster memory accesses than standard memory interfaces.
5.2
Peripherals
The AT91M40800 microcontrollers integrate several peripherals, which are classified as system
or user peripherals. All on-chip peripherals are 32-bit accessible by the AMBA Bridge, and can
be programmed with a minimum number of instructions. The peripheral register set is composed
of control, mode, data, status and enable/disable/status registers.
An on-chip Peripheral Data Controller (PDC) transfers data between the on-chip USARTs and
on- and off-chip memories address space without processor intervention. Most importantly, the
PDC removes the processor interrupt handling overhead, making it possible to transfer up to
64K contiguous bytes without reprogramming the start address, thus increasing the perfor-
mance of the microcontroller, and reducing the power consumption.
5.2.1
System Peripherals
The External Bus Interface (EBI) controls the external memory or peripheral devices via an 8- or
16-bit databus and is programmed through the APB. Each chip select line has its own program-
ming register.
The Power-saving (PS) module implements the Idle mode (ARM7TDMI core clock stopped until
the next interrupt) and enables the user to adapt the power consumption of the microcontroller to
application requirements (independent peripheral clock control).
The Advanced Interrupt Controller (AIC) controls the internal interrupt sources from the internal
peripherals and the four external interrupt lines (including the FIQ), to provide an interrupt and/or
fast interrupt request to the ARM7TDMI. It integrates an 8-level priority controller and, using the
Auto-vectoring feature, reduces the interrupt latency time.
The Parallel Input/Output Controller (PIO) controls up to 32 I/O lines. It enables the user to
select specific pins for on-chip peripheral input/output functions, and general-purpose input/out-
put signal pins. The PIO controller can be programmed to detect an interrupt on a signal change
from each line.
6
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
The Watchdog (WD) can be used to prevent system lock-up if the software becomes trapped in
a deadlock.
The Special Function (SF) module integrates the Chip ID, the Reset Status and the Protect
registers.
5.2.2
User Peripherals
Two USARTs, independently configurable, enable communication at a high baud rate in syn-
chronous or asynchronous mode. The format includes start, stop and parity bits and up to 8 data
bits. Each USART also features a Timeout and a Time Guard register, facilitating the use of the
two dedicated Peripheral Data Controller (PDC) channels.
The 3-channel, 16-bit Timer Counter (TC) is highly-programmable and supports capture or
waveform modes. Each TC channel can be programmed to measure or generate different kinds
of waves, and can detect and control two input/output signals. The TC has also three external
clock signals.
6.
Associated Documentation
The AT91M40800 is part of the AT91x40 Series microcontrollers, a member of the Atmel AT91 16/32-bit microcontroller
family which is based on the ARM7TDMI processor core.
Table 6-1
contains details of associated documentation for further
reference.
Table 6-1.
Associated Documentation
Product
Information
Document Title
AT91M40800
Internal architecture of processor
ARM/Thumb instruction sets
Embedded in-circuit-emulator
ARM7TDMI (Thumb) Datasheet
External memory interface mapping
Peripheral operations
Peripheral user interfaces
AT91x40 Series Datasheet
DC characteristics
Power consumption
Thermal and reliability considerations
AC characteristics
AT91M40800 Electrical Characteristics
Product overview
Ordering information
Packaging information
Soldering profile
AT91M40800 Summary Datasheet (this document)

7
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
7.
Product Overview
7.1
Power Supply
The AT91M40800 microcontroller has a unique type of power supply pin – VDD. The VDD pin
supplies the I/O pads and the device core. The supported voltage range on V
DD
is 1.8V to 3.6V.
7.2
Input/Output Considerations
The AT91M40800 microcontroller I/O pads are 5V-tolerant, enabling them to interface with
external 5V devices without any additional components. Thus, the devices accept 5V (3V) on the
inputs even if powered at 3V (2V). For further information, refer to the “AT91M40800 Electrical
Characteristics” datasheet.
After the reset, the peripheral I/Os are initialized as inputs to provide the user with maximum
flexibility. It is recommended that in any application phase, the inputs to the AT91M40800 micro-
controller be held at valid logic levels to minimize the power consumption.
7.3
Master Clock
The AT91M40800 microcontroller has a fully static design and works on the Master Clock
(MCK), provided on the MCKI pin from an external source.
The Master Clock is also provided as an output of the device on the pin MCKO, which is multi-
plexed with a general-purpose I/O line. While NRST is active, MCKO remains low. After the
reset, the MCKO is valid and outputs an image of the MCK signal. The PIO controller must be
programmed to use this pin as standard I/O line.
7.4
Reset
Reset restores the default states of the user interface registers (defined in the user interface of
each peripheral), and forces the ARM7TDMI to perform the next instruction fetch from address
zero. Except for the program counter the ARM7TDMI registers do not have defined reset states.
7.4.1
NRST Pin
NRST is active low-level input. It is asserted asynchronously, but exit from reset is synchronized
internally to the MCK. The signal presented on MCKI must be active within the specification for a
minimum of 10 clock cycles up to the rising edge of NRST, to ensure correct operation.
The first processor fetch occurs 80 clock cycles after the rising edge of NRST.
7.4.2
Watchdog Reset
The watchdog can be programmed to generate an internal reset. In this case, the reset has the
same effect as the NRST pin assertion, but the pins BMS and NTRI are not sampled. Boot Mode
and Tri-state Mode are not updated. If the NRST pin is asserted and the watchdog triggers the
internal reset, the NRST pin has priority.
7.5
Emulation Functions
7.5.1
Tri-state Mode
The AT91M40800 microcontroller provides a Tri-state mode, which is used for debug purposes.
This enables the connection of an emulator probe to an application board without having to des-
older the device from the target board. In Tri-state mode, all the output pin drivers of the
AT91M40800 microcontroller is disabled.

8
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
To enter Tri-state mode, the pin NTRI must be held low during the last 10 clock cycles before the
rising edge of NRST. For normal operation the pin NTRI must be held high during reset by a
resistor of up to 400K Ohm.
NTRI is multiplexed with I/O line P21 and USART1 serial data transmit line TXD1.
Standard RS232 drivers generally contain internal 400K Ohm pull-up resistors. If TXD1 is con-
nected to a device not including this pull-up, the user must make sure that a high level is tied on
NTRI while NRST is asserted.
7.5.2
JTAG/ICE Debug
ARM Standard Embedded In-circuit Emulation is supported via the JTAG/ICE port. The pins
TDI, TDO, TCK and TMS are dedicated to this debug function and can be connected to a host
computer via the external ICE interface.
In ICE Debug mode, the ARM7TDMI core responds with a non-JTAG chip ID that identifies the
microcontroller. This is not fully IEEE
®
1149.1 compliant.
7.6
Memory Controller
The ARM7TDMI processor address space is 4G bytes. The memory controller decodes the
internal 32-bit address bus and defines three address spaces:
• Internal memories in the four lowest megabytes
• Middle space reserved for the external devices (memory or peripherals) controlled by the EBI
• Internal peripherals in the four highest megabytes
In any of these address spaces, the ARM7TDMI operates in Little-Endian mode only.
7.6.1
Internal Memories
The AT91M40800 microcontroller integrates 8K bytes of internal SRAM. All internal memories
are 32 bits wide and single-clock cycle accessible. Byte (8-bit), half-word (16-bit) or word (32-bit)
accesses are supported and are executed within one cycle. Fetching Thumb or ARM instruc-
tions is supported and internal memory can store twice as many Thumb instructions as ARM
ones.
The SRAM is mapped at address 0x0 (after the remap command), allowing ARM7TDMI excep-
tion vectors between 0x0 and 0x20 to be modified by the software. The rest of the bank can be
used for stack allocation (to speed up context saving and restoring) or as data and program stor-
age for critical algorithms.
7.6.2
Boot Mode Select
The ARM reset vector is at address 0x0. After the NRST line is released, the ARM7TDMI exe-
cutes the instruction stored at this address. This means that this address must be mapped in
nonvolatile memory after the reset.
The input level on the BMS pin during the last 10 clock cycles before the rising edge of the
NRST selects the type of boot memory (see
Table 7-1
).
9
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
The pin BMS is multiplexed with the I/O line P24 that can be programmed after reset like any
standard PIO line.
7.6.3
Remap Command
The ARM vectors (Reset, Abort, Data Abort, Prefetch Abort, Undefined Instruction, Interrupt,
Fast Interrupt) are mapped from address 0x0 to address 0x20. In order to allow these vectors to
be redefined dynamically by the software, the AT91M40800 microcontroller uses a remap com-
mand that enables switching between the boot memory and the internal primary SRAM bank
addresses. The remap command is accessible through the EBI User Interface, by writing one in
RCB of EBI_RCR (Remap Control Register). Performing a remap command is mandatory if
access to the other external devices (connected to chip-selects 1 to 7) is required. The remap
operation can only be changed back by an internal reset or an NRST assertion.
7.6.4
Abort Control
The abort signal providing a Data Abort or a Prefetch Abort exception to the ARM7TDMI is
asserted when accessing an undefined address in the EBI address space.
No abort is generated when reading the internal memory or by accessing the internal peripher-
als, whether the address is defined or not.
7.6.5
External Bus Interface
The External Bus Interface handles the accesses between addresses 0x0040 0000 and 0xFFC0
0000. It generates the signals that control access to the external devices, and can be configured
from eight 1-Mbyte banks up to four 16-Mbyte banks. It supports byte-, half-word- and word-
aligned accesses.
For each of these banks, the user can program:
• Number of wait states
• Number of data float times (wait time after the access is finished to prevent any bus
contention in case the device is too long in releasing the bus)
• Data bus-width (8-bit or 16-bit).
• With a 16-bit wide data bus, the user can program the EBI to control one 16-bit device (Byte
Access Select mode) or two 8-bit devices in parallel that emulate a 16-bit memory (Byte
Write Access mode).
The External Bus Interface features also the Early Read Protocol, configurable for all the
devices, that significantly reduces access time requirements on an external device in the case of
single-clock cycle access.
Table 7-1.
Boot Mode Select
BMS
Boot Memory
1
External 8-bit memory on NCS0
0
External 16-bit memory on NCS0

10
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
8.
Peripherals
The AT91M40800 microcontroller peripherals are connected to the 32-bit wide Advanced
Peripheral Bus. Peripheral registers are only word accessible – byte and half-word accesses are
not supported. If a byte or a half-word access is attempted, the memory controller automatically
masks the lowest address bits and generates an word access.
Each peripheral has a 16-Kbyte address space allocated (the AIC only has a 4-Kbyte address
space).
8.1
Peripheral Registers
The following registers are common to all peripherals:
• Control Register – write only register that triggers a command when a one is written to the
corresponding position at the appropriate address. Writing a zero has no effect.
• Mode Register – read/write register that defines the configuration of the peripheral. Usually
has a value of 0x0 after a reset.
• Data Registers – read and/or write register that enables the exchange of data between the
processor and the peripheral.
• Status Register – read only register that returns the status of the peripheral.
• Enable/Disable/Status Registers are shadow command registers. Writing a one in the Enable
Register sets the corresponding bit in the Status Register. Writing a one in the Disable
Register resets the corresponding bit and the result can be read in the Status Register.
Writing a bit to zero has no effect. This register access method maximizes the efficiency of bit
manipulation, and enables modification of a register with a single non-interruptible
instruction, replacing the costly read-modify-write operation.
Unused bits in the peripheral registers are shown as “–” and must be written at 0 for upward
compatibility. These bits read 0.
8.2
Peripheral Interrupt Control
The Interrupt Control of each peripheral is controlled from the status register using the interrupt
mask. The status register bits are ANDed to their corresponding interrupt mask bits and the
result is then ORed to generate the Interrupt Source signal to the Advanced Interrupt Controller.
The interrupt mask is read in the Interrupt Mask Register and is modified with the Interrupt
Enable Register and the Interrupt Disable Register. The enable/disable/status (or mask) makes
it possible to enable or disable peripheral interrupt sources with a non-interruptible single
instruction. This eliminates the need for interrupt masking at the AIC or Core level in real-time
and multi-tasking systems.
8.3
Peripheral Data Controller
The AT91M40800 microcontroller has a 4-channel PDC dedicated to the two on-chip USARTs.
One PDC channel is dedicated to the receiver and one to the transmitter of each USART.
The user interface of a PDC channel is integrated in the memory space of each USART. It con-
tains a 32-bit Address Pointer Register (RPR or TPR) and a 16-bit Transfer Counter Register
(RCR or TCR). When the programmed number of transfers are performed, a status bit indicating
the end of transfer is set in the USART Status Register and an interrupt can be generated.

NOTE: This is a summary document.
The complete document is available on
the Atmel website at www.atmel.com.
Features
•
Incorporates the ARM7TDMI
®
ARM
®
Thumb
®
Processor Core
– High-performance 32-bit RISC Architecture
– High-density 16-bit Instruction Set
– Leader in MIPS/Watt
– EmbeddedICE
™
•
8K Bytes On-chip SRAM
– 32-bit Data Bus
– Single-clock Cycle Access
•
Fully-programmable External Bus Interface (EBI)
– Maximum External Address Space of 64M Bytes
– Up to 8 Chip Selects
– Software Programmable 8/16-bit External Databus
•
8-level Priority, Individually Maskable, Vectored Interrupt Controller
– 4 External Interrupts, Including a High-priority Low-latency Interrupt Request
•
32 Programmable I/O Lines
•
3-channel 16-bit Timer/Counter
– 3 External Clock Inputs
– 2 Multi-purpose I/O Pins per Channel
•
2 USARTs
– 2 Dedicated Peripheral Data Controller (PDC) Channels per USART
•
Programmable Watchdog Timer
•
Advanced Power-saving Features
– CPU and Peripheral Can Be Deactivated Individually
•
Fully Static Operation:
– 0 Hz to 40 MHz Internal Frequency Range at 3.0V, 85
°
C
•
1.8V to 3.6V Operating Range
•
-40
°
C to +85
°
C Temperature Range
•
Available in a 100-lead LQFP Package (Green)
1.
Description
The AT91M40800 microcontroller is a member of the Atmel AT91 16/32-bit microcon-
troller family, which is based on the ARM7TDMI processor core. This processor has a
high-performance 32-bit RISC architecture with a high-density 16-bit instruction set
and very low power consumption. In addition, a large number of internally banked reg-
isters result in very fast exception handling, making the device ideal for real-time
control applications.
The AT91M40800 microcontroller features a direct connection to off-chip memory,
including Flash, through the fully-programmable External Bus Interface (EBI). An
eight-level priority vectored interrupt controller, in conjunction with the Peripheral Data
Controller, significantly improves the real-time performance of the device.
The device is manufactured using Atmel’s high-density CMOS technology. By com-
bining the ARM7TDMI processor core with on-chip high-speed memory and a wide
range of peripheral functions on a monolithic chip, the AT91M40800 is a powerful
microcontroller that offers a flexible, cost-effective solution to many compute-intensive
embedded control applications.
AT91 ARM
Thumb
Microcontrollers
AT91M40800
Summary
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06

2
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
2.
Pin Configuration
Figure 2-1.
AT91M40800 Pinout (Top View)
P21/TXD1/NTRI
P20/SCK1
P19
P18
P17
P16
P15/RXD0
P14/TXD0
P13/SCK0
P12/FIQ
GND
P11/IRQ2
P10/IRQ1
VDD
VDD
P9/IRQ0
P8/TIOB2
P7/TIOA2
P6/TCLK2
P5/TIOB1
P4/TIOA1
P3/TCLK1
GND
GND
P2/TIOB0
P1/TIOA0
P0/TCLK0
D15
D14
D13
D12
VDD
D11
D10
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
GND
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
P31/A23/CS4
P30/A22/CS5
VDD
VDD
P29/A21/CS6
P22/RXD1
NWR1/NUB
GND
NRST
NWDOVF
VDD
MCKI
P23
P24/BMS
P25/MCKO
GND
GND
TMS
TDO
TCK
NRD/NOE
NWR0/NWE
VDD
VDD
NWAIT
NCS0
NCS1
P26/NCS2
P27/NCS3
A0/NLB
A1
A2A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
VDD
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
GND
GND
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
P28/A20/CS7
GND
1
25
100-lead TQFP
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
116
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
26
50
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
75
51
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
100
76
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
TDI

3
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
3.
Pin Description
Table 3-1.
AT91M40800 Pin Description
Module
Name
Function
Type
Active
Level
Comments
EBI
A0 - A23
Address Bus
Output
–
All valid after reset
D0 - D15
Data Bus
I/O
–
NCS0 - NCS3
Chip Select
Output
Low
CS4 - CS7
Chip Select
Output
High
A23 - A20 after reset
NWR0
Lower Byte 0 Write Signal
Output
Low
Used in Byte Write option
NWR1
Upper Byte 1 Write Signal
Output
Low
Used in Byte Write option
NRD
Read Signal
Output
Low
Used in Byte Write option
NWE
Write Enable
Output
Low
Used in Byte Select option
NOE
Output Enable
Output
Low
Used in Byte Select option
NUB
Upper Byte Select
Output
Low
Used in Byte Select option
NLB
Lower Byte Select
Output
Low
Used in Byte Select option
NWAIT
Wait Input
Input
Low
BMS
Boot Mode Select
Input
–
Sampled during reset
AIC
FIQ
Fast Interrupt Request
Input
–
PIO-controlled after reset
IRQ0 - IRQ2
External Interrupt Request
Input
–
PIO-controlled after reset
TC
TCLK0 - TCLK2
Timer External Clock
Input
–
PIO-controlled after reset
TIOA0 - TIOA2
Multipurpose Timer I/O pin A
I/O
–
PIO-controlled after reset
TIOB0 - TIOB2
Multipurpose Timer I/O pin B
I/O
–
PIO-controlled after reset
USART
SCK0 - SCK1
External Serial Clock
I/O
–
PIO-controlled after reset
TXD0 - TXD1
Transmit Data Output
Output
–
PIO-controlled after reset
RXD0 - RXD1
Receive Data Input
Input
–
PIO-controlled after reset
PIO
P0 - P31
Parallel IO line
I/O
–
WD
NWDOVF
Watchdog Overflow
Output
Low
Open-drain
Clock
MCKI
Master Clock Input
Input
–
Schmidt trigger
MCKO
Master Clock Output
Output
–
Reset
NRST
Hardware Reset Input
Input
Low
Schmidt trigger
NTRI
Tri-state Mode Select
Input
Low
Sampled during reset
ICE
TMS
Test Mode Select
Input
–
Schmidt trigger, internal pull-up
TDI
Test Data Input
Input
–
Schmidt trigger, internal pull-up
TDO
Test Data Output
Output
–
TCK
Test Clock
Input
–
Schmidt trigger, internal pull-up
Power
VDD
Power
Power
–
GND
Ground
Ground
–

4
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
4.
Block Diagram
Figure 4-1.
AT91M40800
ARM7TDMI Core
Embedded
ICE
Reset
EBI: External Bus Interface
ASB
Controller
Clock
AIC: Advanced
Interrupt Controller
AMBA Bridge
EBI User
Interface
TC: Timer
Counter
TC0
TC1
TC2
USART0
USART1
2 PDC
Channels
2 PDC
Channels
PIO: Parallel I/O Controller
PS: Power Saving
Chip ID
WD: Watchdog
Timer
APB
ASB
P
I
O
P
I
O
NRST
D0-D15
A1-A19
A0/NLB
NRD/NOE
NWR0/NWE
NWR1/NUB
NWAIT
NCS0
NCS1
P26/NCS2
P27/NCS3
P28/A20/CS7
P29/A21/CS6
P30/A22/CS5
P31/A23/CS4
P0/TCLK0
P3/TCLK1
P6/TCLK2
P1/TIOA0
P2/TIOB0
P4/TIOA1
P5/TIOB1
P7/TIOA2
P8/TIOB2
NWDOVF
TMS
TDO
TDI
TCK
MCKI
P25/MCKO
P12/FIQ
P9/IRQ0
P10/IRQ1
P11/IRQ2
P13/SCK0
P14/TXD0
P15/RXD0
P20/SCK1
P21/TXD1/NTRI
P22/RXD1
P16
P17
P18
P19
P23
P24/BMS
8K-byte RAM

5
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
5.
Architectural Overview
The AT91M40800 microcontroller integrates an ARM7TDMI with Embedded ICE interface,
memories and peripherals. The architecture consists of two main buses, the Advanced System
Bus (ASB) and the Advanced Peripheral Bus (APB). Designed for maximum performance and
controlled by the memory controller, the ASB interfaces the ARM7TDMI processor with the on-
chip 32-bit memories, the External Bus Interface (EBI) and the AMBA
™
Bridge. The AMBA
Bridge drives the APB, which is designed for accesses to on-chip peripherals and optimized for
low power consumption.
The AT91M40800 microcontroller implements the ICE port of the ARM7TDMI processor on ded-
icated pins, offering a complete, low cost and easy-to-use debug solution for target debugging.
5.1
Memories
The AT91M40800 microcontroller embeds up to 8K bytes of internal SRAM. The internal mem-
ory is directly connected to the 32-bit data bus and is single-cycle accessible.
The AT91M40800 microcontroller features an External Bus Interface (EBI), which enables con-
nection of external memories and application-specific peripherals. The EBI supports 8- or 16-bit
devices and can use two 8-bit devices to emulate a single 16-bit device. The EBI implements the
early read protocol, enabling faster memory accesses than standard memory interfaces.
5.2
Peripherals
The AT91M40800 microcontrollers integrate several peripherals, which are classified as system
or user peripherals. All on-chip peripherals are 32-bit accessible by the AMBA Bridge, and can
be programmed with a minimum number of instructions. The peripheral register set is composed
of control, mode, data, status and enable/disable/status registers.
An on-chip Peripheral Data Controller (PDC) transfers data between the on-chip USARTs and
on- and off-chip memories address space without processor intervention. Most importantly, the
PDC removes the processor interrupt handling overhead, making it possible to transfer up to
64K contiguous bytes without reprogramming the start address, thus increasing the perfor-
mance of the microcontroller, and reducing the power consumption.
5.2.1
System Peripherals
The External Bus Interface (EBI) controls the external memory or peripheral devices via an 8- or
16-bit databus and is programmed through the APB. Each chip select line has its own program-
ming register.
The Power-saving (PS) module implements the Idle mode (ARM7TDMI core clock stopped until
the next interrupt) and enables the user to adapt the power consumption of the microcontroller to
application requirements (independent peripheral clock control).
The Advanced Interrupt Controller (AIC) controls the internal interrupt sources from the internal
peripherals and the four external interrupt lines (including the FIQ), to provide an interrupt and/or
fast interrupt request to the ARM7TDMI. It integrates an 8-level priority controller and, using the
Auto-vectoring feature, reduces the interrupt latency time.
The Parallel Input/Output Controller (PIO) controls up to 32 I/O lines. It enables the user to
select specific pins for on-chip peripheral input/output functions, and general-purpose input/out-
put signal pins. The PIO controller can be programmed to detect an interrupt on a signal change
from each line.

6
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
The Watchdog (WD) can be used to prevent system lock-up if the software becomes trapped in
a deadlock.
The Special Function (SF) module integrates the Chip ID, the Reset Status and the Protect
registers.
5.2.2
User Peripherals
Two USARTs, independently configurable, enable communication at a high baud rate in syn-
chronous or asynchronous mode. The format includes start, stop and parity bits and up to 8 data
bits. Each USART also features a Timeout and a Time Guard register, facilitating the use of the
two dedicated Peripheral Data Controller (PDC) channels.
The 3-channel, 16-bit Timer Counter (TC) is highly-programmable and supports capture or
waveform modes. Each TC channel can be programmed to measure or generate different kinds
of waves, and can detect and control two input/output signals. The TC has also three external
clock signals.
6.
Associated Documentation
The AT91M40800 is part of the AT91x40 Series microcontrollers, a member of the Atmel AT91 16/32-bit microcontroller
family which is based on the ARM7TDMI processor core.
Table 6-1
contains details of associated documentation for further
reference.
Table 6-1.
Associated Documentation
Product
Information
Document Title
AT91M40800
Internal architecture of processor
ARM/Thumb instruction sets
Embedded in-circuit-emulator
ARM7TDMI (Thumb) Datasheet
External memory interface mapping
Peripheral operations
Peripheral user interfaces
AT91x40 Series Datasheet
DC characteristics
Power consumption
Thermal and reliability considerations
AC characteristics
AT91M40800 Electrical Characteristics
Product overview
Ordering information
Packaging information
Soldering profile
AT91M40800 Summary Datasheet (this document)

7
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
7.
Product Overview
7.1
Power Supply
The AT91M40800 microcontroller has a unique type of power supply pin – VDD. The VDD pin
supplies the I/O pads and the device core. The supported voltage range on V
DD
is 1.8V to 3.6V.
7.2
Input/Output Considerations
The AT91M40800 microcontroller I/O pads are 5V-tolerant, enabling them to interface with
external 5V devices without any additional components. Thus, the devices accept 5V (3V) on the
inputs even if powered at 3V (2V). For further information, refer to the “AT91M40800 Electrical
Characteristics” datasheet.
After the reset, the peripheral I/Os are initialized as inputs to provide the user with maximum
flexibility. It is recommended that in any application phase, the inputs to the AT91M40800 micro-
controller be held at valid logic levels to minimize the power consumption.
7.3
Master Clock
The AT91M40800 microcontroller has a fully static design and works on the Master Clock
(MCK), provided on the MCKI pin from an external source.
The Master Clock is also provided as an output of the device on the pin MCKO, which is multi-
plexed with a general-purpose I/O line. While NRST is active, MCKO remains low. After the
reset, the MCKO is valid and outputs an image of the MCK signal. The PIO controller must be
programmed to use this pin as standard I/O line.
7.4
Reset
Reset restores the default states of the user interface registers (defined in the user interface of
each peripheral), and forces the ARM7TDMI to perform the next instruction fetch from address
zero. Except for the program counter the ARM7TDMI registers do not have defined reset states.
7.4.1
NRST Pin
NRST is active low-level input. It is asserted asynchronously, but exit from reset is synchronized
internally to the MCK. The signal presented on MCKI must be active within the specification for a
minimum of 10 clock cycles up to the rising edge of NRST, to ensure correct operation.
The first processor fetch occurs 80 clock cycles after the rising edge of NRST.
7.4.2
Watchdog Reset
The watchdog can be programmed to generate an internal reset. In this case, the reset has the
same effect as the NRST pin assertion, but the pins BMS and NTRI are not sampled. Boot Mode
and Tri-state Mode are not updated. If the NRST pin is asserted and the watchdog triggers the
internal reset, the NRST pin has priority.
7.5
Emulation Functions
7.5.1
Tri-state Mode
The AT91M40800 microcontroller provides a Tri-state mode, which is used for debug purposes.
This enables the connection of an emulator probe to an application board without having to des-
older the device from the target board. In Tri-state mode, all the output pin drivers of the
AT91M40800 microcontroller is disabled.

8
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
To enter Tri-state mode, the pin NTRI must be held low during the last 10 clock cycles before the
rising edge of NRST. For normal operation the pin NTRI must be held high during reset by a
resistor of up to 400K Ohm.
NTRI is multiplexed with I/O line P21 and USART1 serial data transmit line TXD1.
Standard RS232 drivers generally contain internal 400K Ohm pull-up resistors. If TXD1 is con-
nected to a device not including this pull-up, the user must make sure that a high level is tied on
NTRI while NRST is asserted.
7.5.2
JTAG/ICE Debug
ARM Standard Embedded In-circuit Emulation is supported via the JTAG/ICE port. The pins
TDI, TDO, TCK and TMS are dedicated to this debug function and can be connected to a host
computer via the external ICE interface.
In ICE Debug mode, the ARM7TDMI core responds with a non-JTAG chip ID that identifies the
microcontroller. This is not fully IEEE
®
1149.1 compliant.
7.6
Memory Controller
The ARM7TDMI processor address space is 4G bytes. The memory controller decodes the
internal 32-bit address bus and defines three address spaces:
• Internal memories in the four lowest megabytes
• Middle space reserved for the external devices (memory or peripherals) controlled by the EBI
• Internal peripherals in the four highest megabytes
In any of these address spaces, the ARM7TDMI operates in Little-Endian mode only.
7.6.1
Internal Memories
The AT91M40800 microcontroller integrates 8K bytes of internal SRAM. All internal memories
are 32 bits wide and single-clock cycle accessible. Byte (8-bit), half-word (16-bit) or word (32-bit)
accesses are supported and are executed within one cycle. Fetching Thumb or ARM instruc-
tions is supported and internal memory can store twice as many Thumb instructions as ARM
ones.
The SRAM is mapped at address 0x0 (after the remap command), allowing ARM7TDMI excep-
tion vectors between 0x0 and 0x20 to be modified by the software. The rest of the bank can be
used for stack allocation (to speed up context saving and restoring) or as data and program stor-
age for critical algorithms.
7.6.2
Boot Mode Select
The ARM reset vector is at address 0x0. After the NRST line is released, the ARM7TDMI exe-
cutes the instruction stored at this address. This means that this address must be mapped in
nonvolatile memory after the reset.
The input level on the BMS pin during the last 10 clock cycles before the rising edge of the
NRST selects the type of boot memory (see
Table 7-1
).

9
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
The pin BMS is multiplexed with the I/O line P24 that can be programmed after reset like any
standard PIO line.
7.6.3
Remap Command
The ARM vectors (Reset, Abort, Data Abort, Prefetch Abort, Undefined Instruction, Interrupt,
Fast Interrupt) are mapped from address 0x0 to address 0x20. In order to allow these vectors to
be redefined dynamically by the software, the AT91M40800 microcontroller uses a remap com-
mand that enables switching between the boot memory and the internal primary SRAM bank
addresses. The remap command is accessible through the EBI User Interface, by writing one in
RCB of EBI_RCR (Remap Control Register). Performing a remap command is mandatory if
access to the other external devices (connected to chip-selects 1 to 7) is required. The remap
operation can only be changed back by an internal reset or an NRST assertion.
7.6.4
Abort Control
The abort signal providing a Data Abort or a Prefetch Abort exception to the ARM7TDMI is
asserted when accessing an undefined address in the EBI address space.
No abort is generated when reading the internal memory or by accessing the internal peripher-
als, whether the address is defined or not.
7.6.5
External Bus Interface
The External Bus Interface handles the accesses between addresses 0x0040 0000 and 0xFFC0
0000. It generates the signals that control access to the external devices, and can be configured
from eight 1-Mbyte banks up to four 16-Mbyte banks. It supports byte-, half-word- and word-
aligned accesses.
For each of these banks, the user can program:
• Number of wait states
• Number of data float times (wait time after the access is finished to prevent any bus
contention in case the device is too long in releasing the bus)
• Data bus-width (8-bit or 16-bit).
• With a 16-bit wide data bus, the user can program the EBI to control one 16-bit device (Byte
Access Select mode) or two 8-bit devices in parallel that emulate a 16-bit memory (Byte
Write Access mode).
The External Bus Interface features also the Early Read Protocol, configurable for all the
devices, that significantly reduces access time requirements on an external device in the case of
single-clock cycle access.
Table 7-1.
Boot Mode Select
BMS
Boot Memory
1
External 8-bit memory on NCS0
0
External 16-bit memory on NCS0

10
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
8.
Peripherals
The AT91M40800 microcontroller peripherals are connected to the 32-bit wide Advanced
Peripheral Bus. Peripheral registers are only word accessible – byte and half-word accesses are
not supported. If a byte or a half-word access is attempted, the memory controller automatically
masks the lowest address bits and generates an word access.
Each peripheral has a 16-Kbyte address space allocated (the AIC only has a 4-Kbyte address
space).
8.1
Peripheral Registers
The following registers are common to all peripherals:
• Control Register – write only register that triggers a command when a one is written to the
corresponding position at the appropriate address. Writing a zero has no effect.
• Mode Register – read/write register that defines the configuration of the peripheral. Usually
has a value of 0x0 after a reset.
• Data Registers – read and/or write register that enables the exchange of data between the
processor and the peripheral.
• Status Register – read only register that returns the status of the peripheral.
• Enable/Disable/Status Registers are shadow command registers. Writing a one in the Enable
Register sets the corresponding bit in the Status Register. Writing a one in the Disable
Register resets the corresponding bit and the result can be read in the Status Register.
Writing a bit to zero has no effect. This register access method maximizes the efficiency of bit
manipulation, and enables modification of a register with a single non-interruptible
instruction, replacing the costly read-modify-write operation.
Unused bits in the peripheral registers are shown as “–” and must be written at 0 for upward
compatibility. These bits read 0.
8.2
Peripheral Interrupt Control
The Interrupt Control of each peripheral is controlled from the status register using the interrupt
mask. The status register bits are ANDed to their corresponding interrupt mask bits and the
result is then ORed to generate the Interrupt Source signal to the Advanced Interrupt Controller.
The interrupt mask is read in the Interrupt Mask Register and is modified with the Interrupt
Enable Register and the Interrupt Disable Register. The enable/disable/status (or mask) makes
it possible to enable or disable peripheral interrupt sources with a non-interruptible single
instruction. This eliminates the need for interrupt masking at the AIC or Core level in real-time
and multi-tasking systems.
8.3
Peripheral Data Controller
The AT91M40800 microcontroller has a 4-channel PDC dedicated to the two on-chip USARTs.
One PDC channel is dedicated to the receiver and one to the transmitter of each USART.
The user interface of a PDC channel is integrated in the memory space of each USART. It con-
tains a 32-bit Address Pointer Register (RPR or TPR) and a 16-bit Transfer Counter Register
(RCR or TCR). When the programmed number of transfers are performed, a status bit indicating
the end of transfer is set in the USART Status Register and an interrupt can be generated.

NOTE: This is a summary document.
The complete document is available on
the Atmel website at www.atmel.com.
Features
•
Incorporates the ARM7TDMI
®
ARM
®
Thumb
®
Processor Core
– High-performance 32-bit RISC Architecture
– High-density 16-bit Instruction Set
– Leader in MIPS/Watt
– EmbeddedICE
™
•
8K Bytes On-chip SRAM
– 32-bit Data Bus
– Single-clock Cycle Access
•
Fully-programmable External Bus Interface (EBI)
– Maximum External Address Space of 64M Bytes
– Up to 8 Chip Selects
– Software Programmable 8/16-bit External Databus
•
8-level Priority, Individually Maskable, Vectored Interrupt Controller
– 4 External Interrupts, Including a High-priority Low-latency Interrupt Request
•
32 Programmable I/O Lines
•
3-channel 16-bit Timer/Counter
– 3 External Clock Inputs
– 2 Multi-purpose I/O Pins per Channel
•
2 USARTs
– 2 Dedicated Peripheral Data Controller (PDC) Channels per USART
•
Programmable Watchdog Timer
•
Advanced Power-saving Features
– CPU and Peripheral Can Be Deactivated Individually
•
Fully Static Operation:
– 0 Hz to 40 MHz Internal Frequency Range at 3.0V, 85
°
C
•
1.8V to 3.6V Operating Range
•
-40
°
C to +85
°
C Temperature Range
•
Available in a 100-lead LQFP Package (Green)
1.
Description
The AT91M40800 microcontroller is a member of the Atmel AT91 16/32-bit microcon-
troller family, which is based on the ARM7TDMI processor core. This processor has a
high-performance 32-bit RISC architecture with a high-density 16-bit instruction set
and very low power consumption. In addition, a large number of internally banked reg-
isters result in very fast exception handling, making the device ideal for real-time
control applications.
The AT91M40800 microcontroller features a direct connection to off-chip memory,
including Flash, through the fully-programmable External Bus Interface (EBI). An
eight-level priority vectored interrupt controller, in conjunction with the Peripheral Data
Controller, significantly improves the real-time performance of the device.
The device is manufactured using Atmel’s high-density CMOS technology. By com-
bining the ARM7TDMI processor core with on-chip high-speed memory and a wide
range of peripheral functions on a monolithic chip, the AT91M40800 is a powerful
microcontroller that offers a flexible, cost-effective solution to many compute-intensive
embedded control applications.
AT91 ARM
Thumb
Microcontrollers
AT91M40800
Summary
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06

2
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
2.
Pin Configuration
Figure 2-1.
AT91M40800 Pinout (Top View)
P21/TXD1/NTRI
P20/SCK1
P19
P18
P17
P16
P15/RXD0
P14/TXD0
P13/SCK0
P12/FIQ
GND
P11/IRQ2
P10/IRQ1
VDD
VDD
P9/IRQ0
P8/TIOB2
P7/TIOA2
P6/TCLK2
P5/TIOB1
P4/TIOA1
P3/TCLK1
GND
GND
P2/TIOB0
P1/TIOA0
P0/TCLK0
D15
D14
D13
D12
VDD
D11
D10
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
GND
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
P31/A23/CS4
P30/A22/CS5
VDD
VDD
P29/A21/CS6
P22/RXD1
NWR1/NUB
GND
NRST
NWDOVF
VDD
MCKI
P23
P24/BMS
P25/MCKO
GND
GND
TMS
TDO
TCK
NRD/NOE
NWR0/NWE
VDD
VDD
NWAIT
NCS0
NCS1
P26/NCS2
P27/NCS3
A0/NLB
A1
A2A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
VDD
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
GND
GND
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
P28/A20/CS7
GND
1
25
100-lead TQFP
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
116
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
26
50
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
75
51
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
100
76
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
TDI

3
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
3.
Pin Description
Table 3-1.
AT91M40800 Pin Description
Module
Name
Function
Type
Active
Level
Comments
EBI
A0 - A23
Address Bus
Output
–
All valid after reset
D0 - D15
Data Bus
I/O
–
NCS0 - NCS3
Chip Select
Output
Low
CS4 - CS7
Chip Select
Output
High
A23 - A20 after reset
NWR0
Lower Byte 0 Write Signal
Output
Low
Used in Byte Write option
NWR1
Upper Byte 1 Write Signal
Output
Low
Used in Byte Write option
NRD
Read Signal
Output
Low
Used in Byte Write option
NWE
Write Enable
Output
Low
Used in Byte Select option
NOE
Output Enable
Output
Low
Used in Byte Select option
NUB
Upper Byte Select
Output
Low
Used in Byte Select option
NLB
Lower Byte Select
Output
Low
Used in Byte Select option
NWAIT
Wait Input
Input
Low
BMS
Boot Mode Select
Input
–
Sampled during reset
AIC
FIQ
Fast Interrupt Request
Input
–
PIO-controlled after reset
IRQ0 - IRQ2
External Interrupt Request
Input
–
PIO-controlled after reset
TC
TCLK0 - TCLK2
Timer External Clock
Input
–
PIO-controlled after reset
TIOA0 - TIOA2
Multipurpose Timer I/O pin A
I/O
–
PIO-controlled after reset
TIOB0 - TIOB2
Multipurpose Timer I/O pin B
I/O
–
PIO-controlled after reset
USART
SCK0 - SCK1
External Serial Clock
I/O
–
PIO-controlled after reset
TXD0 - TXD1
Transmit Data Output
Output
–
PIO-controlled after reset
RXD0 - RXD1
Receive Data Input
Input
–
PIO-controlled after reset
PIO
P0 - P31
Parallel IO line
I/O
–
WD
NWDOVF
Watchdog Overflow
Output
Low
Open-drain
Clock
MCKI
Master Clock Input
Input
–
Schmidt trigger
MCKO
Master Clock Output
Output
–
Reset
NRST
Hardware Reset Input
Input
Low
Schmidt trigger
NTRI
Tri-state Mode Select
Input
Low
Sampled during reset
ICE
TMS
Test Mode Select
Input
–
Schmidt trigger, internal pull-up
TDI
Test Data Input
Input
–
Schmidt trigger, internal pull-up
TDO
Test Data Output
Output
–
TCK
Test Clock
Input
–
Schmidt trigger, internal pull-up
Power
VDD
Power
Power
–
GND
Ground
Ground
–

4
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
4.
Block Diagram
Figure 4-1.
AT91M40800
ARM7TDMI Core
Embedded
ICE
Reset
EBI: External Bus Interface
ASB
Controller
Clock
AIC: Advanced
Interrupt Controller
AMBA Bridge
EBI User
Interface
TC: Timer
Counter
TC0
TC1
TC2
USART0
USART1
2 PDC
Channels
2 PDC
Channels
PIO: Parallel I/O Controller
PS: Power Saving
Chip ID
WD: Watchdog
Timer
APB
ASB
P
I
O
P
I
O
NRST
D0-D15
A1-A19
A0/NLB
NRD/NOE
NWR0/NWE
NWR1/NUB
NWAIT
NCS0
NCS1
P26/NCS2
P27/NCS3
P28/A20/CS7
P29/A21/CS6
P30/A22/CS5
P31/A23/CS4
P0/TCLK0
P3/TCLK1
P6/TCLK2
P1/TIOA0
P2/TIOB0
P4/TIOA1
P5/TIOB1
P7/TIOA2
P8/TIOB2
NWDOVF
TMS
TDO
TDI
TCK
MCKI
P25/MCKO
P12/FIQ
P9/IRQ0
P10/IRQ1
P11/IRQ2
P13/SCK0
P14/TXD0
P15/RXD0
P20/SCK1
P21/TXD1/NTRI
P22/RXD1
P16
P17
P18
P19
P23
P24/BMS
8K-byte RAM

5
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
5.
Architectural Overview
The AT91M40800 microcontroller integrates an ARM7TDMI with Embedded ICE interface,
memories and peripherals. The architecture consists of two main buses, the Advanced System
Bus (ASB) and the Advanced Peripheral Bus (APB). Designed for maximum performance and
controlled by the memory controller, the ASB interfaces the ARM7TDMI processor with the on-
chip 32-bit memories, the External Bus Interface (EBI) and the AMBA
™
Bridge. The AMBA
Bridge drives the APB, which is designed for accesses to on-chip peripherals and optimized for
low power consumption.
The AT91M40800 microcontroller implements the ICE port of the ARM7TDMI processor on ded-
icated pins, offering a complete, low cost and easy-to-use debug solution for target debugging.
5.1
Memories
The AT91M40800 microcontroller embeds up to 8K bytes of internal SRAM. The internal mem-
ory is directly connected to the 32-bit data bus and is single-cycle accessible.
The AT91M40800 microcontroller features an External Bus Interface (EBI), which enables con-
nection of external memories and application-specific peripherals. The EBI supports 8- or 16-bit
devices and can use two 8-bit devices to emulate a single 16-bit device. The EBI implements the
early read protocol, enabling faster memory accesses than standard memory interfaces.
5.2
Peripherals
The AT91M40800 microcontrollers integrate several peripherals, which are classified as system
or user peripherals. All on-chip peripherals are 32-bit accessible by the AMBA Bridge, and can
be programmed with a minimum number of instructions. The peripheral register set is composed
of control, mode, data, status and enable/disable/status registers.
An on-chip Peripheral Data Controller (PDC) transfers data between the on-chip USARTs and
on- and off-chip memories address space without processor intervention. Most importantly, the
PDC removes the processor interrupt handling overhead, making it possible to transfer up to
64K contiguous bytes without reprogramming the start address, thus increasing the perfor-
mance of the microcontroller, and reducing the power consumption.
5.2.1
System Peripherals
The External Bus Interface (EBI) controls the external memory or peripheral devices via an 8- or
16-bit databus and is programmed through the APB. Each chip select line has its own program-
ming register.
The Power-saving (PS) module implements the Idle mode (ARM7TDMI core clock stopped until
the next interrupt) and enables the user to adapt the power consumption of the microcontroller to
application requirements (independent peripheral clock control).
The Advanced Interrupt Controller (AIC) controls the internal interrupt sources from the internal
peripherals and the four external interrupt lines (including the FIQ), to provide an interrupt and/or
fast interrupt request to the ARM7TDMI. It integrates an 8-level priority controller and, using the
Auto-vectoring feature, reduces the interrupt latency time.
The Parallel Input/Output Controller (PIO) controls up to 32 I/O lines. It enables the user to
select specific pins for on-chip peripheral input/output functions, and general-purpose input/out-
put signal pins. The PIO controller can be programmed to detect an interrupt on a signal change
from each line.

6
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
The Watchdog (WD) can be used to prevent system lock-up if the software becomes trapped in
a deadlock.
The Special Function (SF) module integrates the Chip ID, the Reset Status and the Protect
registers.
5.2.2
User Peripherals
Two USARTs, independently configurable, enable communication at a high baud rate in syn-
chronous or asynchronous mode. The format includes start, stop and parity bits and up to 8 data
bits. Each USART also features a Timeout and a Time Guard register, facilitating the use of the
two dedicated Peripheral Data Controller (PDC) channels.
The 3-channel, 16-bit Timer Counter (TC) is highly-programmable and supports capture or
waveform modes. Each TC channel can be programmed to measure or generate different kinds
of waves, and can detect and control two input/output signals. The TC has also three external
clock signals.
6.
Associated Documentation
The AT91M40800 is part of the AT91x40 Series microcontrollers, a member of the Atmel AT91 16/32-bit microcontroller
family which is based on the ARM7TDMI processor core.
Table 6-1
contains details of associated documentation for further
reference.
Table 6-1.
Associated Documentation
Product
Information
Document Title
AT91M40800
Internal architecture of processor
ARM/Thumb instruction sets
Embedded in-circuit-emulator
ARM7TDMI (Thumb) Datasheet
External memory interface mapping
Peripheral operations
Peripheral user interfaces
AT91x40 Series Datasheet
DC characteristics
Power consumption
Thermal and reliability considerations
AC characteristics
AT91M40800 Electrical Characteristics
Product overview
Ordering information
Packaging information
Soldering profile
AT91M40800 Summary Datasheet (this document)

7
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
7.
Product Overview
7.1
Power Supply
The AT91M40800 microcontroller has a unique type of power supply pin – VDD. The VDD pin
supplies the I/O pads and the device core. The supported voltage range on V
DD
is 1.8V to 3.6V.
7.2
Input/Output Considerations
The AT91M40800 microcontroller I/O pads are 5V-tolerant, enabling them to interface with
external 5V devices without any additional components. Thus, the devices accept 5V (3V) on the
inputs even if powered at 3V (2V). For further information, refer to the “AT91M40800 Electrical
Characteristics” datasheet.
After the reset, the peripheral I/Os are initialized as inputs to provide the user with maximum
flexibility. It is recommended that in any application phase, the inputs to the AT91M40800 micro-
controller be held at valid logic levels to minimize the power consumption.
7.3
Master Clock
The AT91M40800 microcontroller has a fully static design and works on the Master Clock
(MCK), provided on the MCKI pin from an external source.
The Master Clock is also provided as an output of the device on the pin MCKO, which is multi-
plexed with a general-purpose I/O line. While NRST is active, MCKO remains low. After the
reset, the MCKO is valid and outputs an image of the MCK signal. The PIO controller must be
programmed to use this pin as standard I/O line.
7.4
Reset
Reset restores the default states of the user interface registers (defined in the user interface of
each peripheral), and forces the ARM7TDMI to perform the next instruction fetch from address
zero. Except for the program counter the ARM7TDMI registers do not have defined reset states.
7.4.1
NRST Pin
NRST is active low-level input. It is asserted asynchronously, but exit from reset is synchronized
internally to the MCK. The signal presented on MCKI must be active within the specification for a
minimum of 10 clock cycles up to the rising edge of NRST, to ensure correct operation.
The first processor fetch occurs 80 clock cycles after the rising edge of NRST.
7.4.2
Watchdog Reset
The watchdog can be programmed to generate an internal reset. In this case, the reset has the
same effect as the NRST pin assertion, but the pins BMS and NTRI are not sampled. Boot Mode
and Tri-state Mode are not updated. If the NRST pin is asserted and the watchdog triggers the
internal reset, the NRST pin has priority.
7.5
Emulation Functions
7.5.1
Tri-state Mode
The AT91M40800 microcontroller provides a Tri-state mode, which is used for debug purposes.
This enables the connection of an emulator probe to an application board without having to des-
older the device from the target board. In Tri-state mode, all the output pin drivers of the
AT91M40800 microcontroller is disabled.

8
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
To enter Tri-state mode, the pin NTRI must be held low during the last 10 clock cycles before the
rising edge of NRST. For normal operation the pin NTRI must be held high during reset by a
resistor of up to 400K Ohm.
NTRI is multiplexed with I/O line P21 and USART1 serial data transmit line TXD1.
Standard RS232 drivers generally contain internal 400K Ohm pull-up resistors. If TXD1 is con-
nected to a device not including this pull-up, the user must make sure that a high level is tied on
NTRI while NRST is asserted.
7.5.2
JTAG/ICE Debug
ARM Standard Embedded In-circuit Emulation is supported via the JTAG/ICE port. The pins
TDI, TDO, TCK and TMS are dedicated to this debug function and can be connected to a host
computer via the external ICE interface.
In ICE Debug mode, the ARM7TDMI core responds with a non-JTAG chip ID that identifies the
microcontroller. This is not fully IEEE
®
1149.1 compliant.
7.6
Memory Controller
The ARM7TDMI processor address space is 4G bytes. The memory controller decodes the
internal 32-bit address bus and defines three address spaces:
• Internal memories in the four lowest megabytes
• Middle space reserved for the external devices (memory or peripherals) controlled by the EBI
• Internal peripherals in the four highest megabytes
In any of these address spaces, the ARM7TDMI operates in Little-Endian mode only.
7.6.1
Internal Memories
The AT91M40800 microcontroller integrates 8K bytes of internal SRAM. All internal memories
are 32 bits wide and single-clock cycle accessible. Byte (8-bit), half-word (16-bit) or word (32-bit)
accesses are supported and are executed within one cycle. Fetching Thumb or ARM instruc-
tions is supported and internal memory can store twice as many Thumb instructions as ARM
ones.
The SRAM is mapped at address 0x0 (after the remap command), allowing ARM7TDMI excep-
tion vectors between 0x0 and 0x20 to be modified by the software. The rest of the bank can be
used for stack allocation (to speed up context saving and restoring) or as data and program stor-
age for critical algorithms.
7.6.2
Boot Mode Select
The ARM reset vector is at address 0x0. After the NRST line is released, the ARM7TDMI exe-
cutes the instruction stored at this address. This means that this address must be mapped in
nonvolatile memory after the reset.
The input level on the BMS pin during the last 10 clock cycles before the rising edge of the
NRST selects the type of boot memory (see
Table 7-1
).

9
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
The pin BMS is multiplexed with the I/O line P24 that can be programmed after reset like any
standard PIO line.
7.6.3
Remap Command
The ARM vectors (Reset, Abort, Data Abort, Prefetch Abort, Undefined Instruction, Interrupt,
Fast Interrupt) are mapped from address 0x0 to address 0x20. In order to allow these vectors to
be redefined dynamically by the software, the AT91M40800 microcontroller uses a remap com-
mand that enables switching between the boot memory and the internal primary SRAM bank
addresses. The remap command is accessible through the EBI User Interface, by writing one in
RCB of EBI_RCR (Remap Control Register). Performing a remap command is mandatory if
access to the other external devices (connected to chip-selects 1 to 7) is required. The remap
operation can only be changed back by an internal reset or an NRST assertion.
7.6.4
Abort Control
The abort signal providing a Data Abort or a Prefetch Abort exception to the ARM7TDMI is
asserted when accessing an undefined address in the EBI address space.
No abort is generated when reading the internal memory or by accessing the internal peripher-
als, whether the address is defined or not.
7.6.5
External Bus Interface
The External Bus Interface handles the accesses between addresses 0x0040 0000 and 0xFFC0
0000. It generates the signals that control access to the external devices, and can be configured
from eight 1-Mbyte banks up to four 16-Mbyte banks. It supports byte-, half-word- and word-
aligned accesses.
For each of these banks, the user can program:
• Number of wait states
• Number of data float times (wait time after the access is finished to prevent any bus
contention in case the device is too long in releasing the bus)
• Data bus-width (8-bit or 16-bit).
• With a 16-bit wide data bus, the user can program the EBI to control one 16-bit device (Byte
Access Select mode) or two 8-bit devices in parallel that emulate a 16-bit memory (Byte
Write Access mode).
The External Bus Interface features also the Early Read Protocol, configurable for all the
devices, that significantly reduces access time requirements on an external device in the case of
single-clock cycle access.
Table 7-1.
Boot Mode Select
BMS
Boot Memory
1
External 8-bit memory on NCS0
0
External 16-bit memory on NCS0

10
1348FS–ATARM–13-Apr-06
AT91M40800
8.
Peripherals
The AT91M40800 microcontroller peripherals are connected to the 32-bit wide Advanced
Peripheral Bus. Peripheral registers are only word accessible – byte and half-word accesses are
not supported. If a byte or a half-word access is attempted, the memory controller automatically
masks the lowest address bits and generates an word access.
Each peripheral has a 16-Kbyte address space allocated (the AIC only has a 4-Kbyte address
space).
8.1
Peripheral Registers
The following registers are common to all peripherals:
• Control Register – write only register that triggers a command when a one is written to the
corresponding position at the appropriate address. Writing a zero has no effect.
• Mode Register – read/write register that defines the configuration of the peripheral. Usually
has a value of 0x0 after a reset.
• Data Registers – read and/or write register that enables the exchange of data between the
processor and the peripheral.
• Status Register – read only register that returns the status of the peripheral.
• Enable/Disable/Status Registers are shadow command registers. Writing a one in the Enable
Register sets the corresponding bit in the Status Register. Writing a one in the Disable
Register resets the corresponding bit and the result can be read in the Status Register.
Writing a bit to zero has no effect. This register access method maximizes the efficiency of bit
manipulation, and enables modification of a register with a single non-interruptible
instruction, replacing the costly read-modify-write operation.
Unused bits in the peripheral registers are shown as “–” and must be written at 0 for upward
compatibility. These bits read 0.
8.2
Peripheral Interrupt Control
The Interrupt Control of each peripheral is controlled from the status register using the interrupt
mask. The status register bits are ANDed to their corresponding interrupt mask bits and the
result is then ORed to generate the Interrupt Source signal to the Advanced Interrupt Controller.
The interrupt mask is read in the Interrupt Mask Register and is modified with the Interrupt
Enable Register and the Interrupt Disable Register. The enable/disable/status (or mask) makes
it possible to enable or disable peripheral interrupt sources with a non-interruptible single
instruction. This eliminates the need for interrupt masking at the AIC or Core level in real-time
and multi-tasking systems.
8.3
Peripheral Data Controller
The AT91M40800 microcontroller has a 4-channel PDC dedicated to the two on-chip USARTs.
One PDC channel is dedicated to the receiver and one to the transmitter of each USART.
The user interface of a PDC channel is integrated in the memory space of each USART. It con-
tains a 32-bit Address Pointer Register (RPR or TPR) and a 16-bit Transfer Counter Register
(RCR or TCR). When the programmed number of transfers are performed, a status bit indicating
the end of transfer is set in the USART Status Register and an interrupt can be generated.
