2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21387C-page 1
TC1321
Features
• 10-Bit Digital-to-Analog Converter
• 2.7-5.5V Single Supply Operation
• Simple SMBus/I
2
C
TM
Serial Interface
• Low Power Operation
- Normal Mode: 350 µA
- Shutdown Mode: 0.5 µA
• Temperature Range: 40°C to +85°C
• 8-Pin SOIC and 8-Pin MSOP Packages
Applications
• Programmable Voltage Sources
• Digital Controlled Amplifiers/Attenuators
• Process Monitoring and Control
General Description
The TC1321 is a serially accessible, 10-bit voltage
output, digital-to-analog converter (DAC). The DAC
produces an output voltage that ranges from ground to
an externally supplied reference voltage. It operates
from a single power supply that can range from 2.7V to
5.5V, making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
Built into the part is a Power-on Reset (POR) function
that ensures that the device starts at a known condition.
Communication with the TC1321 is accomplished via a
simple 2-wire SMBus/I
2
C compatible serial port, with
the TC1321 acting as a slave only device. The host can
enable the SHDN bit in the CONFIG register to activate
the Low Power Standby mode.
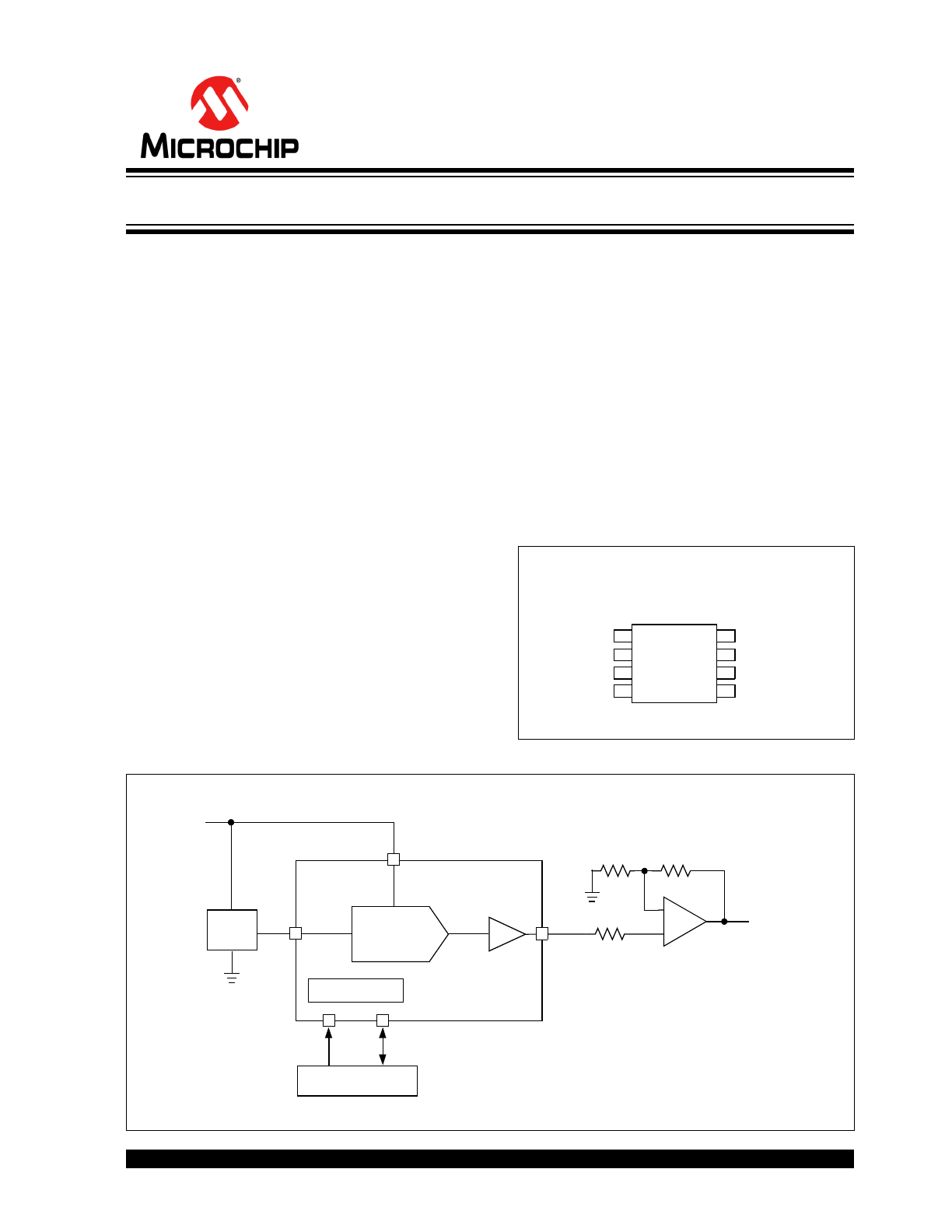
Package Type
Typical Application
V
SS
SDA
V
REF
SCL
NC
V
OUT
V
DD
DAC-OUT
1
8
2
7
3
6
4
5
TC1321
8-Pin MSOP and
8-Pin SOIC (Narrow)
Microcontroller
Serial Port
SDA
SCL
V
IN
V
ADJUST
V
DD
DAC
V
REF
V
OUT
TC1321
+
–
5
8
1
3
2
V
REF
10-Bit Digital-to-Analog Converter with Two-Wire Interface
TC1321
DS21387C-page 2
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
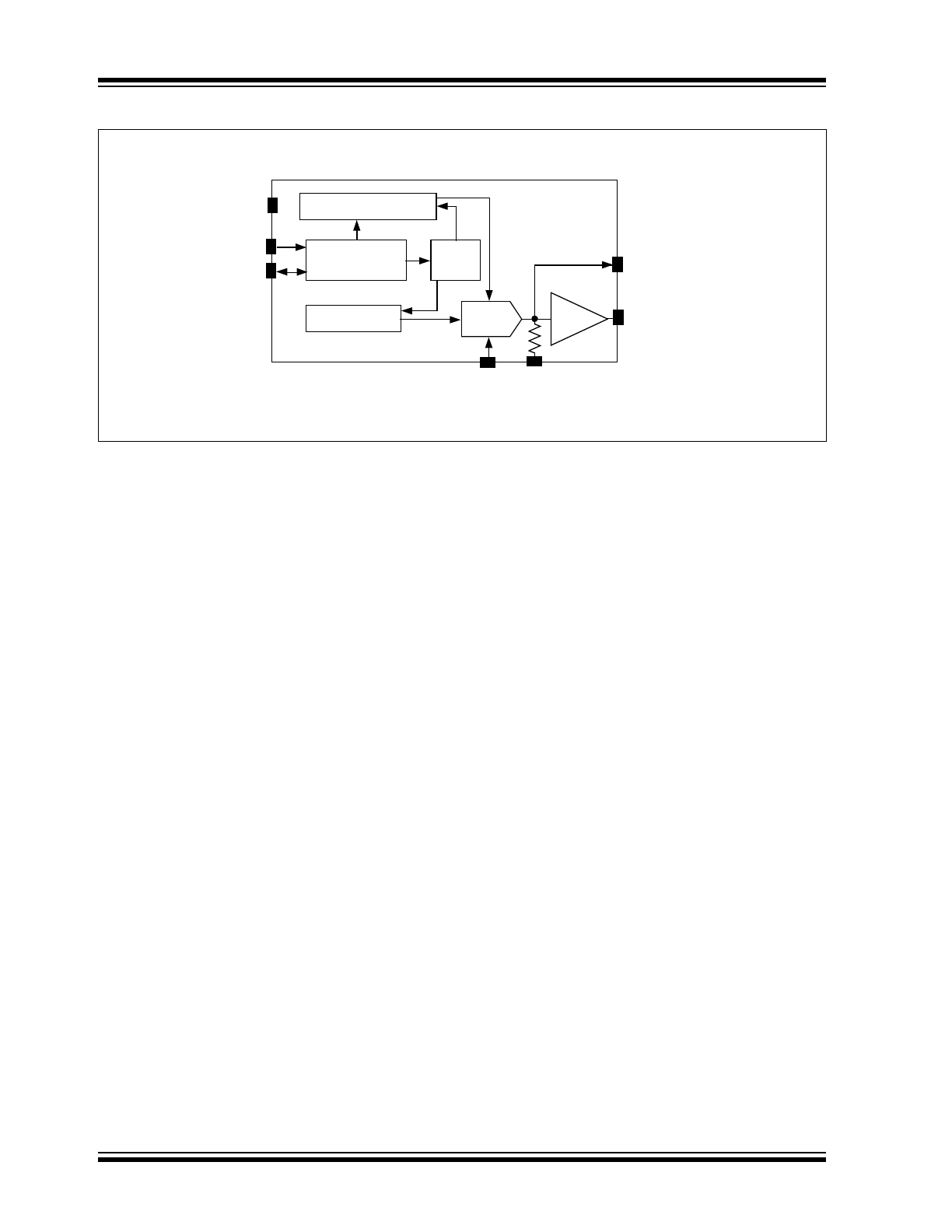
Functional Block Diagram
Serial Port
Interface
SDA
V
DD
DAC-OUT
V
OUT
Configuration Register
Data Register
Control
V
REF
V
SS
SCL
DAC
TC1321
Circuit
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21387C-page 3
TC1321
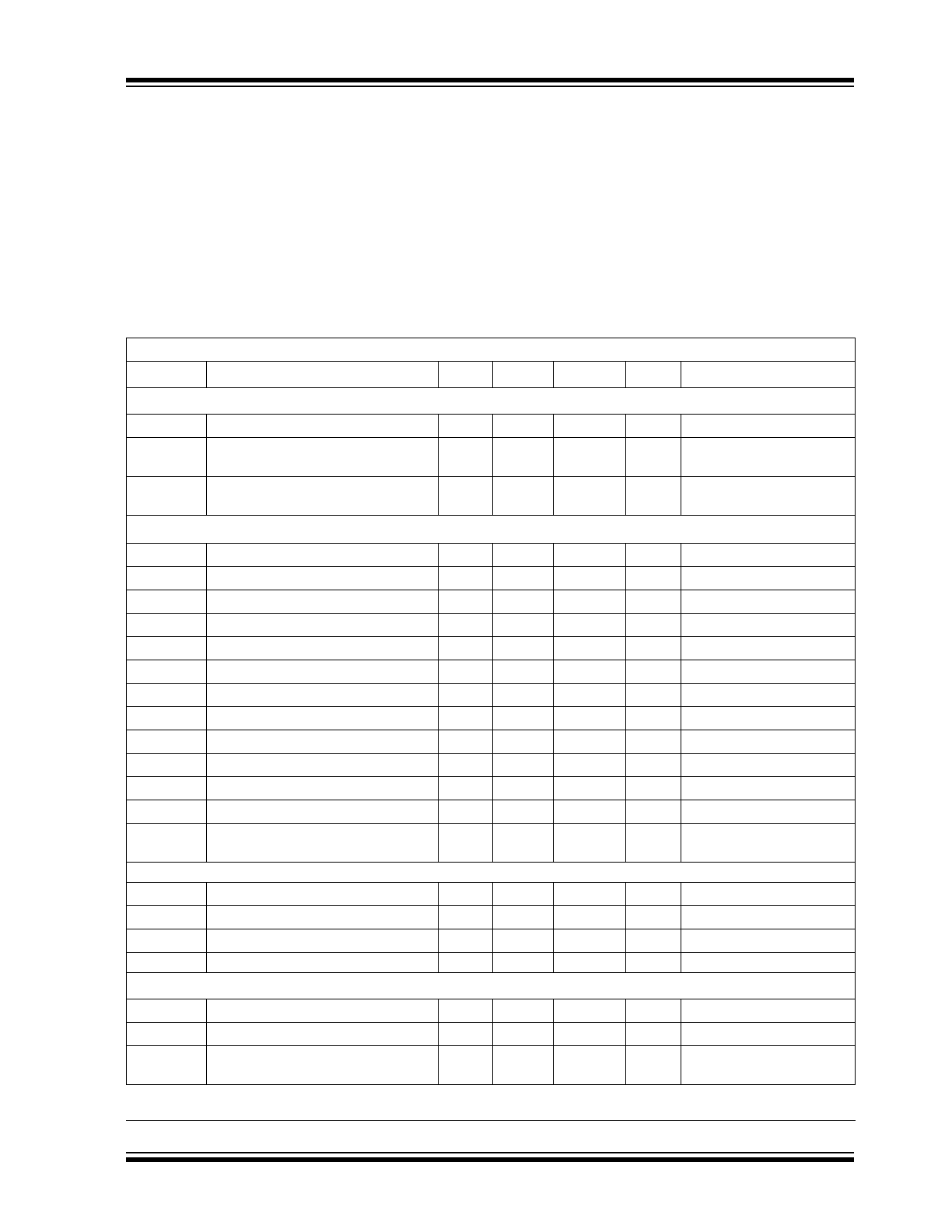
1.0
ELECTRICAL
CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings*
Supply Voltage (V
DD
) ........................................................+6V
Voltage on any Pin ....................(V
SS
– 0.3V) to (V
DD
+ 0.3V)
Current on any Pin ......................................................±50 mA
Package Thermal Resistance (
JA
)....................... 330°C C/W
Operating Temperature (T
A
)................................... See Below
Storage Temperature (T
STG
) .........................-65°C to +150°C
*Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum
Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These
are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device
at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operation sections of the specifications is not implied.
Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability.
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Electrical Characteristics: V
DD
= 2.7V to 5.5V, -40°C
T
A
+85°C, V
REF
= 1.2 V unless otherwise noted.
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Test Conditions
Power Supply
V
DD
Supply Voltage
2.7
—
5.5
V
I
DD
Operating Current
—
350
500
µA
V
DD
= 5.5V, V
REF
= 1.2V
Serial Port Inactive (
Note 1
)
I
DD-
STANDBY
Standby Supply Current
—
0.1
1
µA
V
DD
= 3.3V
Serial Port Inactive (
Note 1
)
Static Performance - Analog Section
Resolution
—
—
10
Bits
INL
Integral Non-Linearity at FS, T
A
= +25°C
—
—
±4.0
LSB
(
Note 2
)
FSE
Full Scale Error
—
—
±3
%FS
DNL
Differential Non-Linearity, T
A
= +25°C
-1
—
+2
LSB
All Codes (
Note 2
)
V
OS
Offset Error at V
OUT
—
±0.3
±8
mV
(
Note 2
)
TCV
OS
Offset Error Tempco at V
OUT
—
10
—
µv/°C
PSRR
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
—
80
—
dB
V
DD
at DC
V
REF
Voltage Reference Range
0
—
V
DD
– 1.2
V
I
REF
Reference Input Leakage Current
—
—
±1.0
µA
V
SW
Voltage Swing
0
—
V
REF
V
V
REF
(V
DD
– 1.2V)
R
OUT
Output Resistance @ V
OUT
—
5.0
—
R
OUT
(
)
I
OUT
Output Current (Source or Sink)
—
2
—
mA
I
SC
Output Short-Circuit Current
V
DD
= 5.5V
—
—
30
20
50
50
mA
mA
Source
Sink
Dynamic Performance
SR
Voltage Output Slew Rate
—
0.8
—
V/µs
t
SETTLE
Output Voltage Full Scale Settling Time
—
10
—
µs
t
WU
Wake-up Time
—
20
—
µs
Digital Feed Through and Crosstalk
—
5
—
nV-s
SDA = V
DD
, SCL = 100 kHz
Serial Port Interface
V
IH
Logic Input High
2.4
—
V
DD
V
V
IL
Logic Input Low
—
—
0.6
—
V
OL
SDA Output Low
—
—
—
—
0.4
0.6
V
V
I
OL
= 3 mA (Sinking Current)
I
OL
= 6 mA
Note 1: SDA and SCL must be connected to V
DD
or V
SS
.
2: Measured at V
OUT
50 mV referred to V
SS
to avoid output buffer clipping.
TC1321
DS21387C-page 4
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
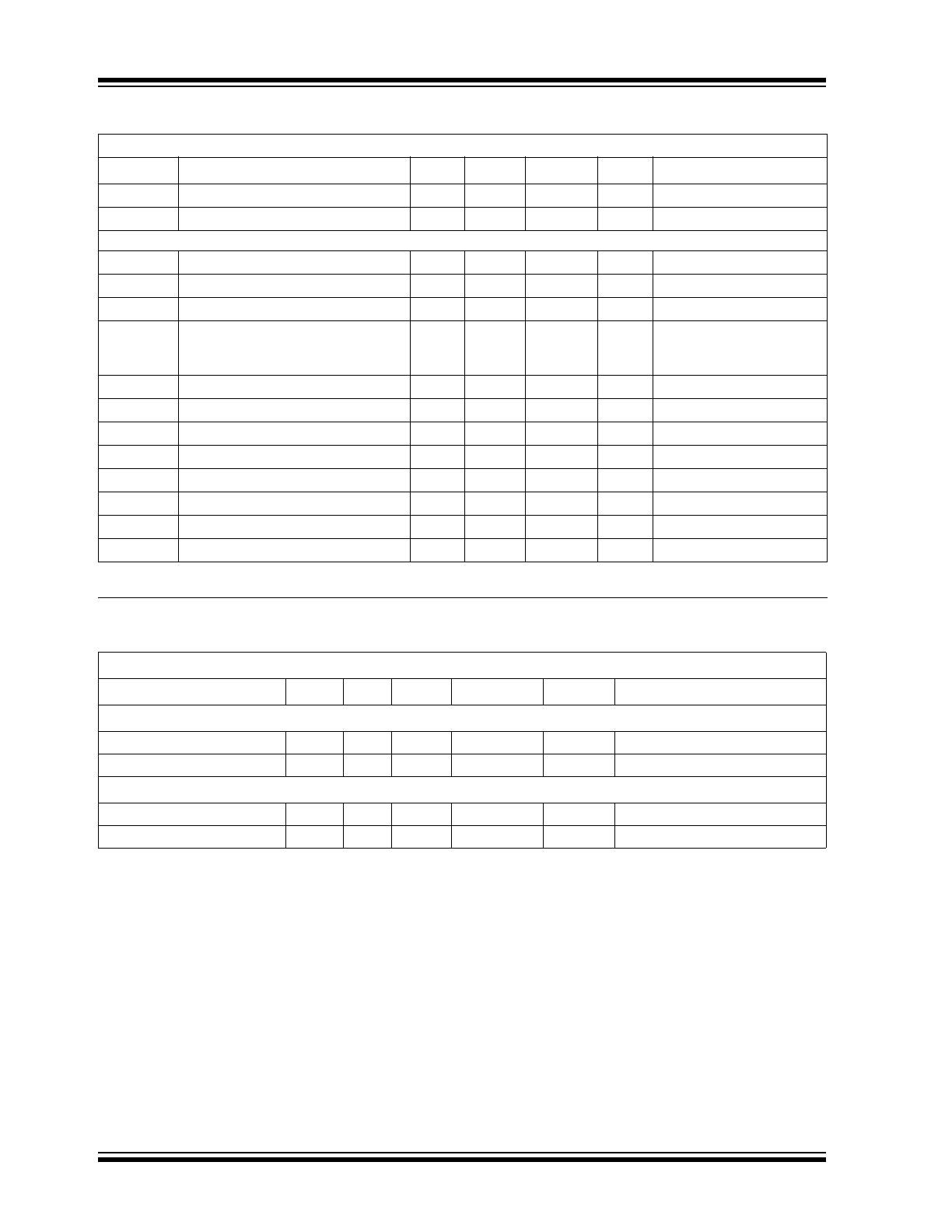
C
IN
Input Capacitance (SDA and SCL pins)
—
5
0.4
pF
I
LEAK
I/O Leakage
—
—
±1.0
µA
Serial Port AC Timing
f
SMB
SMBus Clock Frequency
10
—
100
kHz
t
IDLE
Bus Free Time Prior to New Transition
4.7
—
—
µs
t
H(START)
START Condition Hold Time
4.0
—
—
µs
t
SU(START)
START Condition Setup Time
4.7
—
—
µs
90% SCL to 10% SDA
(for Repeated START
Condition)
t
SU(STOP)
STOP Condition Setup Time
4.0
—
—
µs
t
H-DATA
Data In Hold Time
100
—
—
ns
t
SU-DATA
Data In Setup Time
100
—
—
ns
t
LOW
Low Clock Period
4.7
—
—
µs
10% to 10%
t
HIGH
High Clock Period
4
—
—
µs
90% to 90%
t
F
SMBus Fall Time
—
—
300
ns
90% to 10%
t
R
SMBus Rise Time
—
—
1000
ns
10% to 90%
t
POR
Power-on Reset Delay
—
500
—
µs
V
DD
V
POR
(Rising Edge)
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (CONTINUED)
Electrical Characteristics: V
DD
= 2.7V to 5.5V, -40°C
T
A
+85°C, V
REF
= 1.2 V unless otherwise noted.
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Test Conditions
Note 1: SDA and SCL must be connected to V
DD
or V
SS
.
2: Measured at V
OUT
50 mV referred to V
SS
to avoid output buffer clipping.
TEMPERATURE CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Specifications: V
DD
= 2.7V to 5.5V, -40°C
T
A
+85°C, V
REF
= 1.2V unless otherwise noted.
Parameters
Symbol
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
Temperature Ranges
Operating Temperature Range
T
A
-40
—
+85
°C
Storage Temperature Range
T
A
-65
—
150
°C
Thermal Package Resistances
Thermal Resistance, 8L SOIC
JA
—
149.5
—
°C/W
Thermal Resistance, 8L MSOP
JA
—
211
—
°C/W
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21387C-page 5
TC1321
2.0
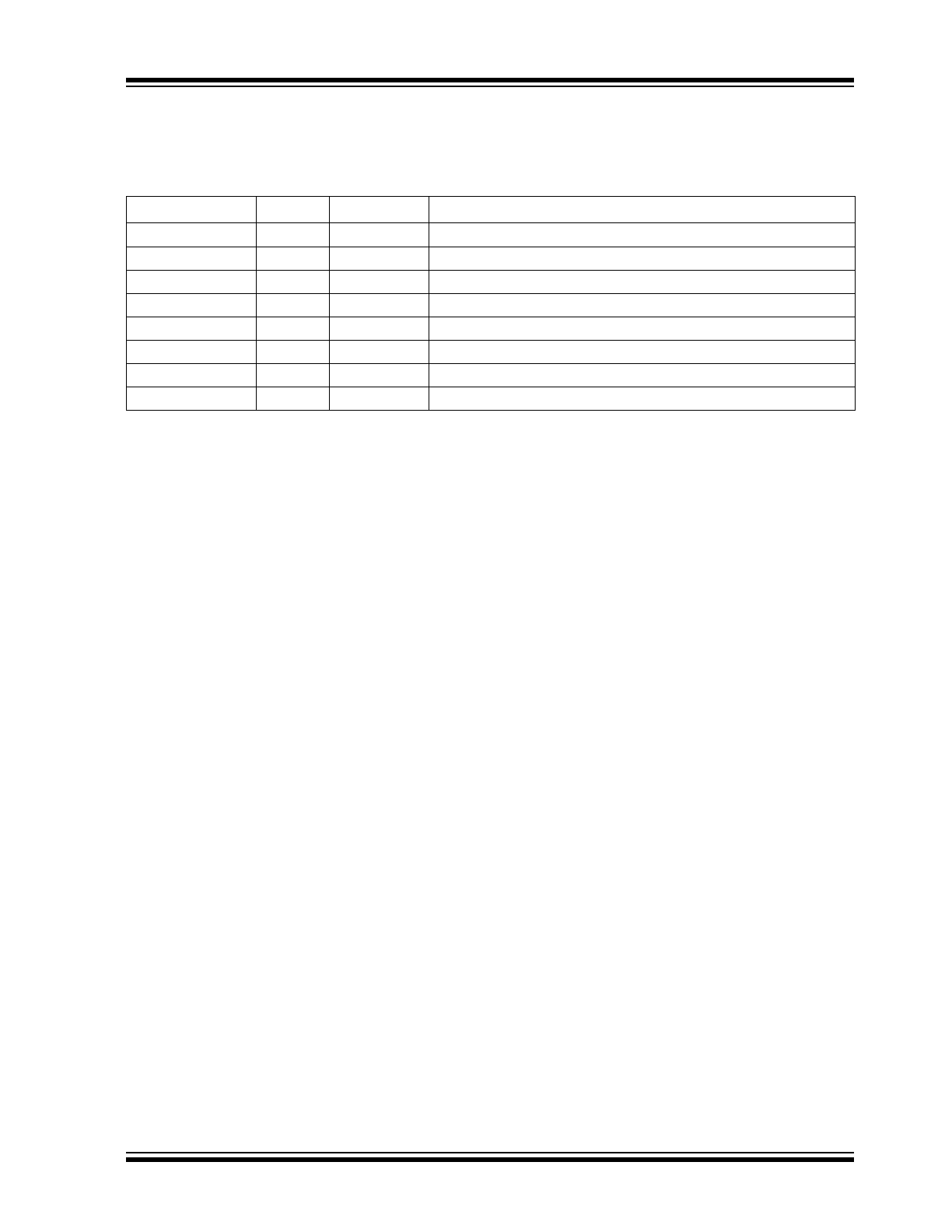
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
The descriptions of the pins are listed in
Table 2-1
.
TABLE 2-1:
PIN FUNCTION TABLE
2.1
External Voltage Reference Input
(V
REF
)
Voltage Reference Input can range from 0V to 1.2V
below V
DD
.
2.2
Bi-Directional Serial Data Input
and Output (SDA)
Serial data is transferred on the SMBus in both
directions using this pin.
2.3
Serial Clock Input (SCL)
SMBus/I
2
C serial clock. Clocks data into and out of the
TC1321.
2.4
Supply Power Ground (V
SS
)
The ground reference pin.
2.5
Output (V
OUT
)
Buffered DAC output voltage. This voltage is a function
of the reference voltage and the contents of the DATA
register.
2.6
No Connection (NC)
There is not a connection at this pin.
2.7
Output (DAC-OUT)
Unbuffered DAC output voltage. This voltage is a
function of the reference voltage and the contents of
the DATA register. This output is unbuffered and care
must be taken that the pin is connected only to a
high-impedance node.
2.8
Positive Power Supply Input (V
DD
)
See the
Electrical Specifications
table.
Pin Number
Pin Name
Type
Description
1
V
REF
Input
Voltage Reference Input Pin
2
SDA
Bi-Directional
Serial Data Input/Output Pin
3
SCL
Input
Serial Clock Input Pin
4
V
SS
Power
Ground Reference Pin
5
V
OUT
Output
Buffered Analog Voltage Output Pin
6
NC
None
No connection
7
DAC-OUT
Output
Unbuffered Analog Voltage Output Pin
8
V
DD
Power
Positive Power Supply Input Pin

TC1321
DS21387C-page 6
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
NOTES:

2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21387C-page 7
TC1321
3.0
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The TC1321 is a monolithic 10-bit digital-to-analog
converter that is designed to operate from a single
supply that can range from 2.7V to 5.5V. The DAC
consists of a data register (DATA), a configuration
register (CONF), and a current output amplifier. The
TC1321 uses an external reference which also
determines the maximum output voltage.
The TC1321 uses a current steering DAC based on an
array of matched current sources. This current, along
with a precision resistor, converts the contents of the
DATA Register and V
REF
into an output voltage, V
OUT
,
that is given by:
3.1
Reference Input
The reference pin, V
REF
, is a buffered high-impedance
input. Because of this, the load regulation of the
reference source needs only to be able to tolerate
leakage levels of current (less than 1 µA). V
REF
accepts a voltage range from 0 to (V
DD
– 1.2V). Input
capacitance is typically 10 pF.
3.2
Output Amplifier
The TC1321 DAC output is buffered with an internal
unity gain rail-to-rail input/output amplifier with a typical
slew rate of 0.8V/µs. Maximum full scale transition
settling time is 10 µsec to within ±1/2LSB when loaded
with 1 k
in parallel with 100 pF.
3.3
Standby Mode
The TC1321 allows the host to put it into a Low Power
(I
DD
= 0.5 µA, typically) Standby mode.
In this mode, the D/A conversion is halted. The SMBus
port operates normally. Standby mode is enabled by
setting the SHDN bit in the CONFIG register.
Table 3-1
summarizes this operation.
TABLE 3-1:
STANDBY MODE OPERATION
3.4
SMBus Slave Address
The TC1321 is internally programmed to have a default
SMBus address value of 1001 000b. Seven other
addresses are available by custom order (contact
Microchip
Worldwide Sales and Service
). See
Figure 3-1
for the location of address bits in SMBus
protocol.
V
OUT
V
=
REF
DATA
1024
----------------
SHDN Bit
Operating Mode
0
Normal
1
Standby
TC1321
DS21387C-page 8
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
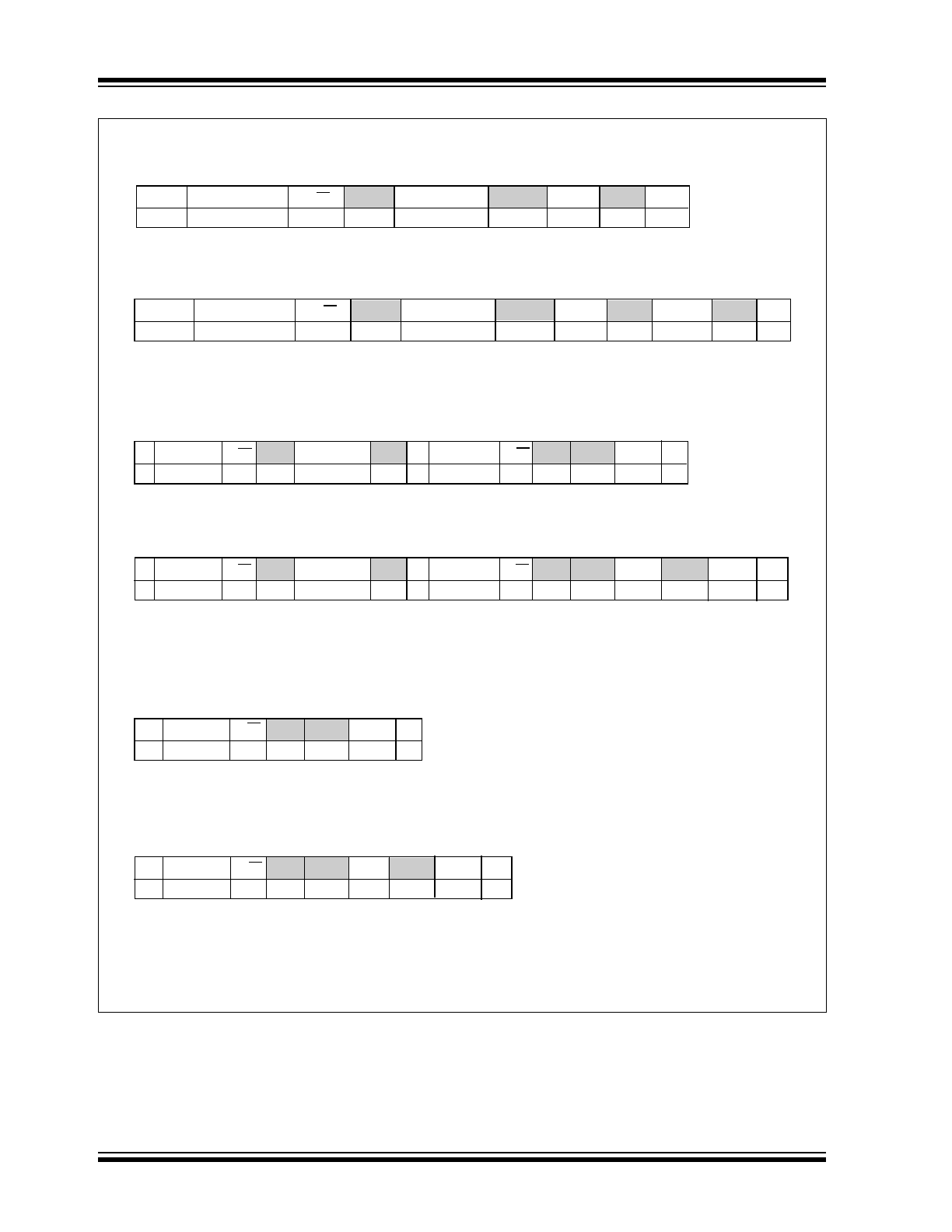
FIGURE 3-1:
SMBus/I
2
C Protocols.
S
Address
R/W
ACK
Command
ACK
Data
ACK
P
8-Bits
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
7-Bits
8-Bits
Slave Address
Command Byte: selects
which register you are
writing to.
Data Byte: data goes
into the register set
by the command byte.
Write 1-Byte Format
S
Address
R/W
ACK
Command
ACK
Data
ACK
Data
ACK
P
8-Bits
7-Bits
8-Bits
8-Bits
Slave Address
Command Byte: selects
which register you are
writing to.
Data Byte: data goes
into the register set
by the command byte.
Write 2-Byte Format
Read 1-Byte Format
S
Address
R/W
ACK
Command
ACK
S
Address
R/W ACK Data
NACK
P
7-Bits
8-Bits
7-Bits
8-Bits
Slave Address
Command Byte: selects
which register you are
reading from.
Slave Address: repeated
due to change in data
flow direction.
Data Byte: reads from
the register set by the
command byte.
Read 2-Byte Format
S
Address
R/W
ACK
Command
ACK
S
Address
R/W ACK Data
ACK
NACK
P
Data
7-Bits
8-Bits
7-Bits
8-Bits
8-Bits
Slave Address
Command Byte: selects
which register you are
reading from.
Slave Address: repeated
due to change in data
flow direction.
Data Byte: reads from
the register set by the
command byte.
Receive 1-Byte Format
S
Address
R/W ACK
Data
NACK
NACK
P
7-Bits
8-Bits
Data Byte: reads data from
the register commanded by
the last read-byte or write-
byte transmission.
S = START Condition
P = STOP Condition
Shaded = Slave Transmission
Receive 1-Byte Format
S
Address
R/W ACK
Data
Data
ACK
P
7-Bits
8-Bits
8-Bits
Data Byte: reads data from
the register commanded by
the last read-byte or write-
byte transmission.
S = START Condition
P = STOP Condition
Shaded = Slave Transmission
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21387C-page 9
TC1321
4.0
SERIAL PORT OPERATION
The Serial Clock input (SCL) and bi-directional data
port (SDA) form a 2-wire bi-directional serial port for
programming and interrogating the TC1321. The
following conventions are used in this bus architecture.
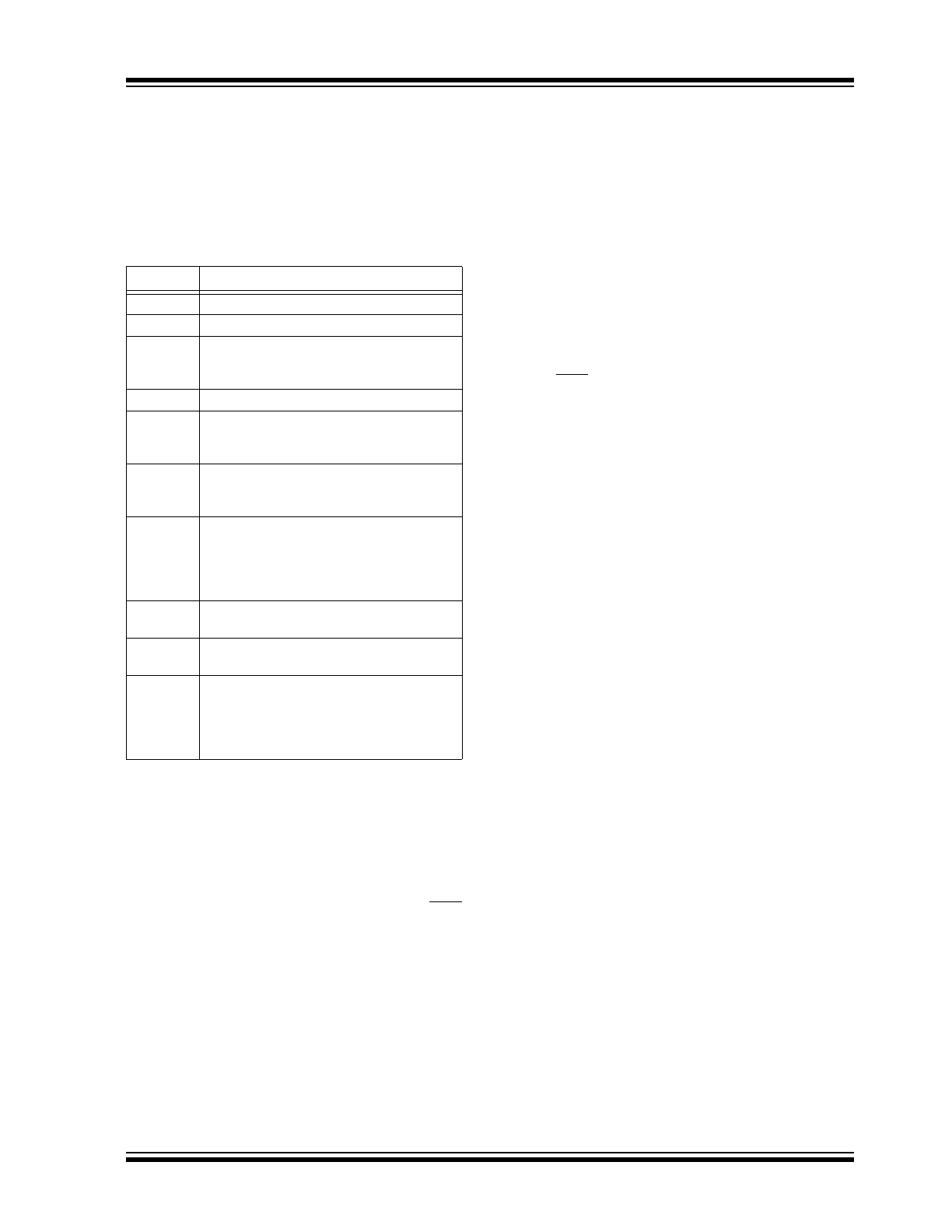
TABLE 4-1:
TC1321 SERIAL BUS
CONVENTIONS
All transfers take place under control of a host, usually
a CPU or microcontroller, acting as the master, which
provides the clock signal for all transfers. The TC1321
always operates as a slave. The serial protocol is
illustrated in
Figure 4-1
. All data transfers have two
phases; all bytes are transferred MSB first. Accesses
are initiated by a START condition (START), followed
by a device-address byte and one or more data bytes.
The device-address byte includes a Read/Write
selection bit. Each access must be terminated by a
STOP Condition (STOP). A convention called
Acknowledge (ACK) confirms receipt of each byte.
Note that SDA can change only during periods when
SCL is LOW (SDA changes while SCL is HIGH are
reserved for START and STOP conditions).
4.1
START Condition (START)
The TC1321 continuously monitors the SDA and SCL
lines for a START condition (a HIGH to LOW transition
of SDA while SCL is HIGH), and will not respond until
this condition is met.
4.2
Address Byte
Immediately following the START condition, the host
must transmit the address byte to the TC1321. The
7-bit SMBus address for the TC1321 is 1001000. The
7-bit address transmitted in the serial bit stream must
match for the TC1321 to respond with an Acknowledge
(indicating the TC1321 is on the bus and ready to
accept data). The eighth bit in the Address Byte is a
Read-Write bit. This bit is a 1 for a read operation or 0
for a write operation. During the first phase of any
transfer, this bit will be set = 0 to indicate that the
command byte is being written.
4.3
Acknowledge (ACK)
Acknowledge (ACK) provides a positive handshake
between the host and the TC1321. The host releases
SDA after transmitting eight bits, then generates a ninth
clock cycle to allow the TC1321 to pull the SDA line
LOW to Acknowledge that it successfully received the
previous eight bits of data or address.
4.4
Data Byte
After a successful ACK of the address byte, the host
must transmit the data byte to be written or clock out
the data to be read. (See the appropriate timing
diagrams.) ACK will be generated after a successful
write of a data byte into the TC1321.
4.5
Stop Condition (STOP)
Communications must be terminated by a STOP
condition (a LOW to HIGH transition of SDA while SCL
is HIGH). The STOP condition must be communicated
by the transmitter to the TC1321. Refer to
Figure 4-1
,
for serial bus timing.
Term
Explanation
Transmitter The device sending data to the bus.
Receiver
The device receiving data from the bus.
Master
The device that controls the bus: initiating
transfers (START), generating the clock, and
terminating transfers (STOP)
Slave
The device addressed by the master.
START
A unique condition signaling the beginning of
a transfer, indicated by SDA falling (High -
Low) while SCL is high.
STOP
A unique condition signaling the end of a
transfer, indicated by SDA rising (Low - High)
while SCL is high.
ACK
A receiver acknowledges the receipt of each
byte with this unique condition. The receiver
drives SDA low during SCL, high of the ACK
clock pulse.The master provides the clock
pulse for the ACK cycle.
Busy
Communication is not possible because the
bus is in use.
Not Busy
When the bus is IDLE, both SDA and SCL will
remain high.
Data Valid
The state of SDA must remain stable during
the High period of SCL in order for a data bit
to be considered valid. SDA only changes
state while SCL is low during normal data
transfers. See START and STOP conditions.
TC1321
DS21387C-page 10
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
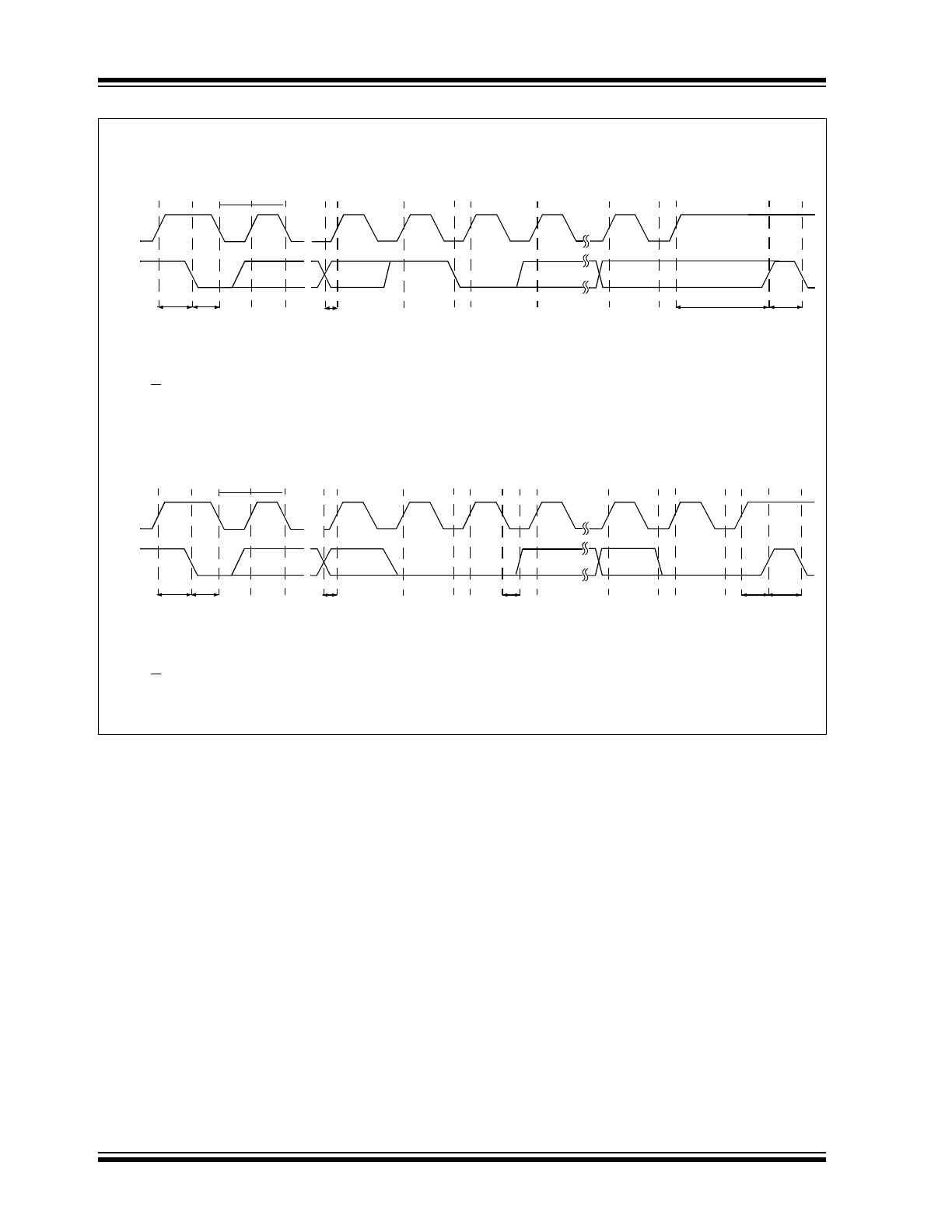
FIGURE 4-1:
SMBus/I
2
CTiming Diagrams.
t
SU(START)
t
H(START)
t
SU-DATA
t
SU(STOP)
t
IDLE
A = START Condition
B = MSB of Address Clocked into Slave
C = LSB of Address Clocked into Slave
D = R/W Bit Clocked into Slave
A
Write Timing Diagram
Read Timing Diagram
B
C
D
E F
G
H
I
J
K
E = Slave Pulls SDA Line Low
F = Acknowledge Bit Clocked into Master
G = MSB of Data Clocked into Master
H = LSB of Data Clocked into Master
I
LOW
I
HIGH
I = Acknowledge Clock Pulse
J = STOP Condition
K = New START Condition
SCL
SDA
t
SU(START)
t
H(START)
t
SU-DATA
t
H-DATA
t
SU(STOP)
t
IDLE
A = START Condition
B = MSB of Address Clocked into Slave
C = LSB of Address Clocked into Slave
D = R/W Bit Clocked into Slave
E = Slave Pulls SDA Line Low
A
B
C
D
E F
G
H
I J
K
L
M
F = Acknowledge Bit Clocked into Master
G = MSB of Data Clocked into Slave
H = LSB of Data Clocked into Slave
I = Slave Pulls SDA Line Low
J = Acknowledge Clocked into Master
K = Acknowledge Clock Pulse
L = STOP Condition, Data Executed by Slave
M = New START Condition
I
LOW
I
HIGH
SCL
SDA
