
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005767A-page 1
MD1820
Features
• Non-inverting, 4-channel MOSFET Driver
• 6 ns Rise and Fall Time
• 2A Peak Output Source and Sink Currents
• 1.8V to 5V Input CMOS Compatible
• 5V to 10V Total Supply Voltage
• Smart Logic Threshold
• Low-jitter Design
• Four Matched Channels
• Drives Two P-channel and Two N-channel
MOSFETs
• Outputs can Swing below Ground
• Low-inductance Quad Flat No-lead Package
• High-performance, Thermally Enhanced Package
Applications
• Medical Ultrasound Imaging
• Piezoelectric Transducer Drivers
• Non-destructive Testing (NDT)
• PIN Diode Driver
• CCD Clock Driver/buffer
• High-speed Level Translator
General Description
The MD1820 is a high-speed, 4-channel MOSFET
driver designed to drive high-voltage P-channel and
N-channel MOSFETs for medical ultrasound
applications and other applications requiring a high
output current for a capacitive load. The high-speed
input stage of the MD1820 can operate from a
1.8V to 5V logic interface with an optimum operating
input signal range of 1.8V to 3.3V. An adaptive
threshold circuit is used to set the level translator
switch threshold to the average of the input logic 0 and
logic 1 levels. The input logic levels may be ground
referenced, even though the driver is putting out bipolar
signals. The level translator uses a proprietary circuit,
which provides DC coupling together with high-speed
operation.
The output stage of the MD1820 has separate power
connections, enabling the output signal L and H levels
to be chosen independently from the supply voltages
used for the majority of the circuit. As an example, the
input logic levels may be 0V and 1.8V, the control logic
may be powered by +5V and –5V and the output L and
H levels may be varied anywhere over the range of
–5V to +5V. The output stage is capable of peak
currents of up to ±2A, depending on the supply
voltages used and load capacitance present. The PE
pin serves a dual purpose. First, its logic H level is used
to compute the threshold voltage level for the channel
input level translators. Second, when PE is low, the
outputs are High Z. This assists in properly precharging
the AC coupling capacitors that may be used in series
in the gate drive circuit of an external PMOS and
NMOS transistor pair.
Package Type
16-lead QFN
(Top view)
1
See
Table 2-1
for pin information.
High-Speed 4-Channel MOSFET Driver with Non-Inverting Outputs
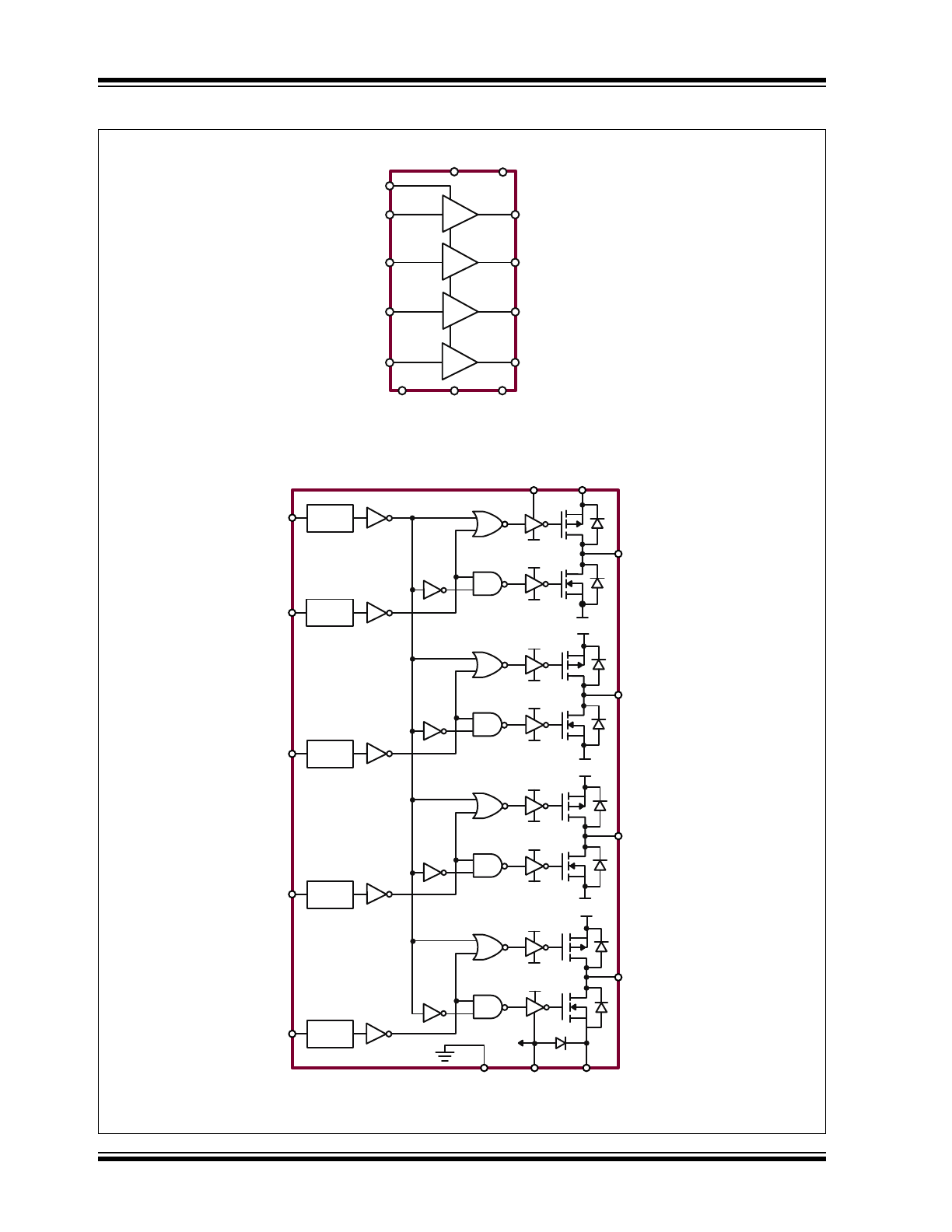
PE
INA
INB
OUTA
OUTB
VDD
VH
INC
IND
OUTC
OUTD
MD1820
GND
VSS
VL
INB
OUTC
OUTD
GND
VH
PE
INA
VL
OUTB
OUTA
VDD
VH
INC
IND
SUB
VSS
VL
VH
VL
VH
VL
MD1820
VSS
VDD
VSS
VDD
VSS
VDD
VSS
VDD
VSS
VDD
VSS
VDD
VSS
VDD
Level
Shifter
Level
Shifter
Level
Shifter
Level
Shifter
Level
Shifter
Simplified Block Diagram
Detailed Block Diagram
MD1820
DS20005767A-page 2
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
Functional Block Diagrams
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005767A-page 3
MD1820
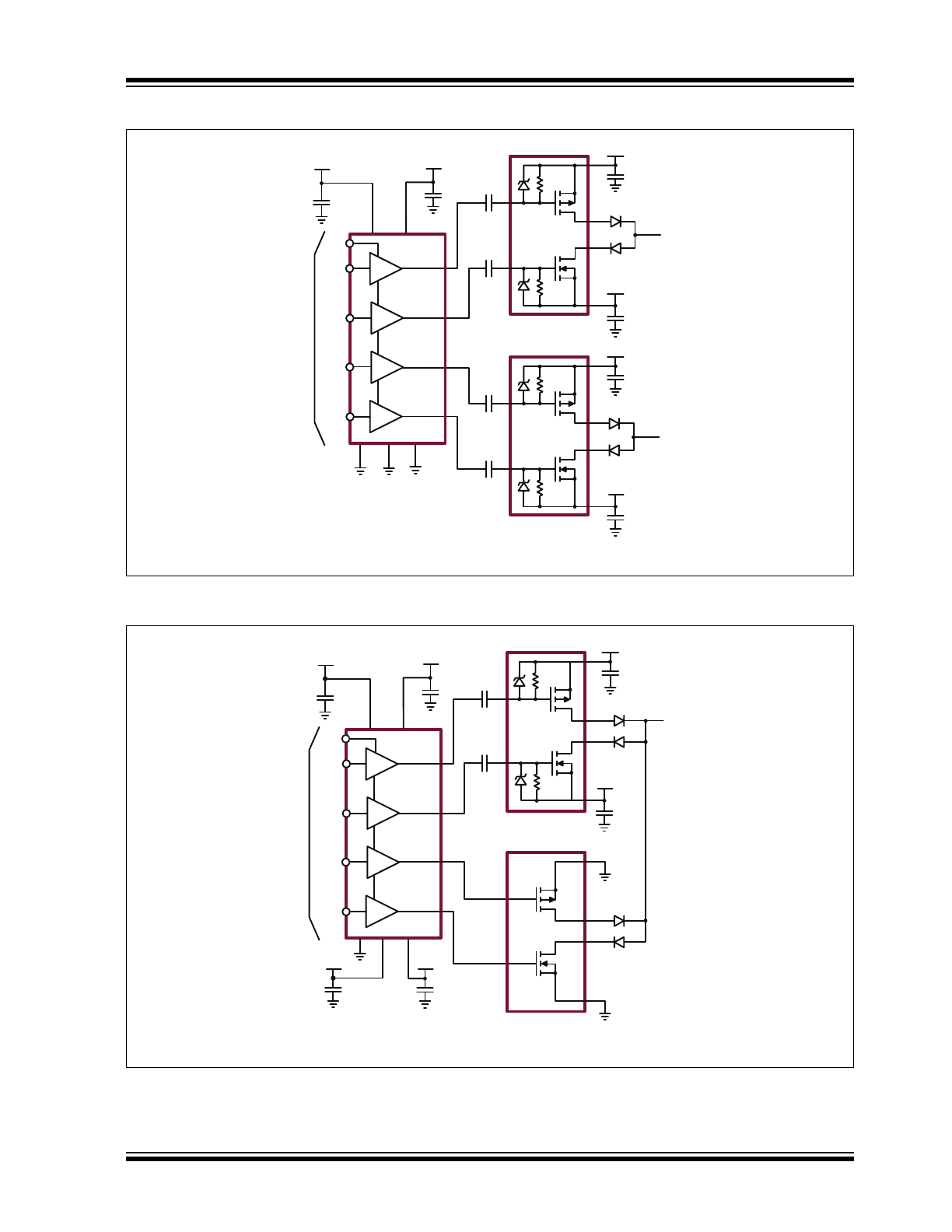
Typical Application Circuit
10nF
10nF
0.1μF
10nF
TC6320
10nF
To Piezoelectric
Transducer
VSS
VDD
VH
VL
PE
INA
GND
INB
INC
IND
OUTA
+10V
OUTB
OUTC
OUTD
0.47μF
0.47μF
+10V
+100V
0.1μF
+100V
0.1μF
-100V
0.1μF
-100V
TC6320
MD1820
3.3V CMOS
Logic Inputs
To Piezoelectric
Transducer
Typical 2-Channel +/–100V Application Diagram
s
TC6320
+100V
0.1μF
-100V
10nF
10nF
TC2320
VSS
VDD
VH
VL
PE
INA
GND
INB
INC
IND
OUTA
+5.0V
3.3V CMOS
Logic Inputs
OUTB
OUTC
OUTD
+5.0V
0.47μF
0.47μF
-5.0V
0.47μF
-5.0V
0.47μF
MD1820
0.1μF
To Piezoelectric
Transducer
Typical 1-Channel +/–100V RTZ Application Diagram
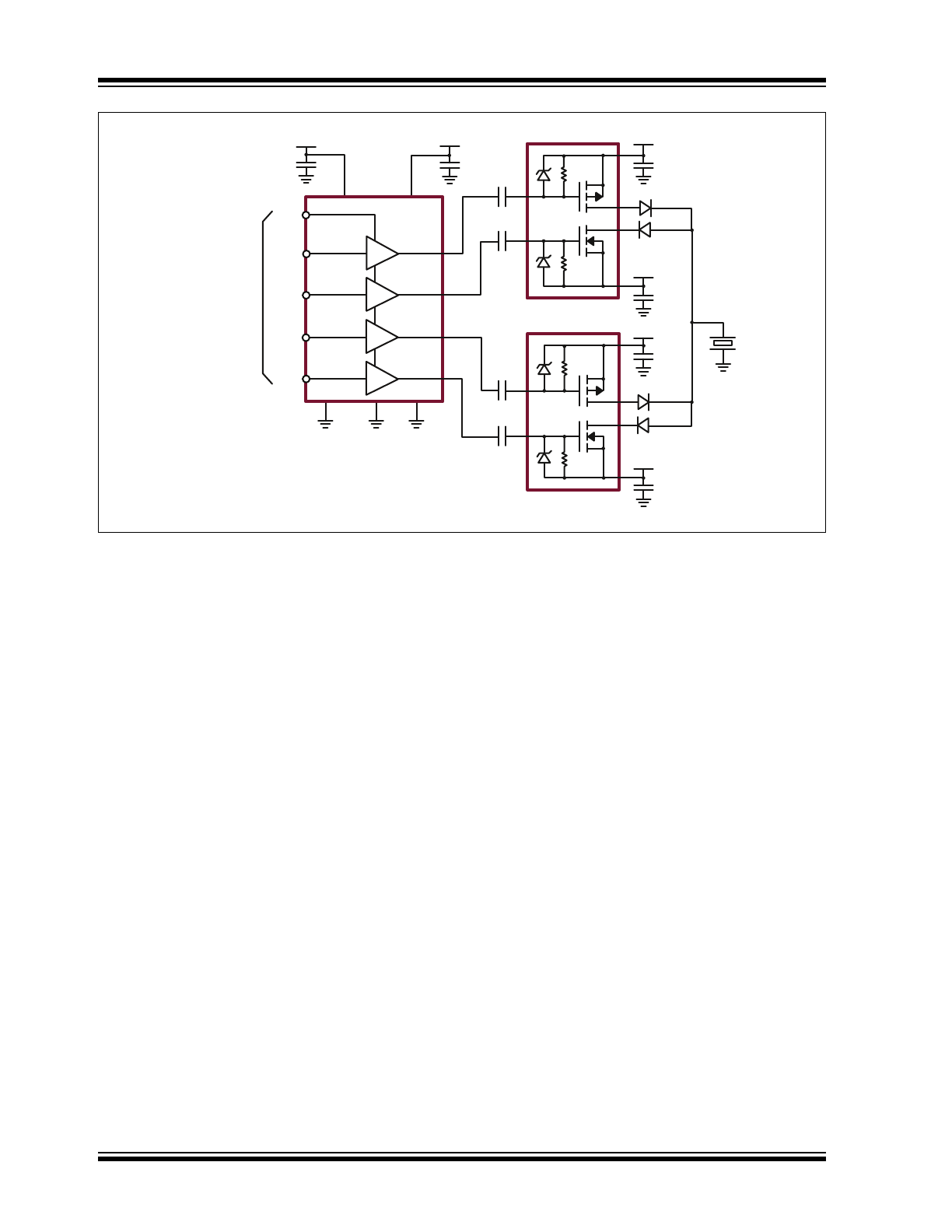
OUTA
OUTB
OUTC
OUTD
+10V
VDD
VH
+10V
VSS
VL
GND
INA
INB
INC
IND
PE
MD1820
10nF
10nF
+100V
HV
OUT
-100V
TC6320
0.47μF
TC6320
1.0μF
1.0μF
-10V
1.0μF
+10V
1.0μF
10nF
10nF
3.3V CMOS
Logic Inputs
0.47μF
MD1820
DS20005767A-page 4
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005767A-page 5
MD1820
1.0
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings†
Logic Supply Voltage, V
DD
–V
SS
............................................................................................................ –0.5V to +12.5V
Output High Supply Voltage, V
H
................................................................................................... V
L
–0.5V to V
DD
+0.5V
Output Low Supply Voltage, V
L
.................................................................................................... V
SS
–0.5V to V
H
+0.5V
Low-side Supply Voltage, V
SS
.................................................................................................................... –6V to +0.5V
Logic Input Levels
.................................................................................................................... V
SS
–0.5V to GND +5.5V
Maximum Junction Temperature, T
J
................................................................................................................... +125°C
Operating Ambient Temperature, T
A
..................................................................................................... –20°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature, T
S
..................................................................................................................... –65°C to +150°C
Package Power Dissipation:
16-lead QFN ............................................................................................................................................... 2.2W
ESD Rating (
Note 1
) ............................................................................................................................... ESD Sensitive
† Notice: Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the
device. This is a stress rating only, and functional operation of the device at those or any other conditions above those
indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not intended. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability.
Note 1: Device is ESD sensitive. Handling precautions are recommended.
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Specifications: V
H
= V
DD
= 10V, V
L
= V
SS
= GND = 0V, V
PE
= 3.3V, T
A
= 25°C
Parameter
Sym.
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Conditions
Logic Supply Voltage
V
DD
–V
SS
4.75
—
11.5
V
4V ≤ V
DD
≤ 11.5V
Low-side Supply Voltage
V
SS
–5.5
—
0
V
Output High Supply Voltage
V
H
V
SS
+2
—
V
DD
V
Output Low Supply Voltage
V
L
V
SS
—
V
DD
–4
V
V
DD
Quiescent Current
I
DDQ
—
60
μA
No input transitions, PE = 0
V
H
Quiescent Current
I
HQ
—
2
—
μA
V
DD
Quiescent Current
I
DDQ
—
0.8
—
mA
No input transitions, PE = 1
V
H
Quiescent Current
I
HQ
—
2
—
μA
V
DD
Average Current
I
DD
—
3.5
—
mA
One channel on at 5 MHz, no load
V
H
Average Current
I
H
—
10
—
mA
Input Logic Voltage High
V
IH
V
PE
–0.3
—
V
PE
V
For logic inputs INA, INB, INC and
IND
Input Logic Voltage Low
V
IL
0
—
0.3
V
Input Logic Current High
I
IH
—
—
1
μA
Input Logic Current Low
I
IL
—
—
1
μA
PE Input logic Voltage High
V
IH
1.7
3.3
5.25
V
For logic input PE
PE Input Logic Voltage Low
V
IL
0
—
0.3
V
PE Input Resistance
R
IN_PE
100
—
—
kΩ
Logic Input Capacitance
C
IN
—
5
10
pF
Output Sink Resistance
R
SINK
—
1.5
—
Ω
I
SINK
= 50 mA
Output Source Resistance
R
SOURCE
—
2
—
Ω
I
SOURCE
= 50 mA
Peak Output Sink Current
I
SINK
—
2
—
A
Peak Output Source Current
I
SOURCE
—
2
—
A
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Specifications: V
H
= V
DD
= 10V, V
L
= V
SS
= GND = 0V, V
PE
= 3.3V, T
A
= 25°C
Parameter
Sym.
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Conditions
Input or PE Rise and Fall Time
t
irf
—
—
10
ns
Logic input edge speed
requirement
Propagation Delay when Output is
from Low to High
t
PLH
—
6.5
—
ns
C
LOAD
= 1000 pF (See
Timing
Diagram
.), input signal rise/fall
time 2 ns
Propagation Delay when Output is
from High to Low
t
PHL
—
6.5
—
ns
Output Rise Time
t
r
—
7
—
ns
Output Fall Time
t
f
—
7
—
ns
Rise and Fall Time Matching
l t
r
–t
f
l
—
1
—
ns
For each channel
Propagation Low to High and High
to Low Matching
l t
PLH
–t
PHL
l
—
1
—
ns
Propagation Delay Matching
∆t
dm
—
±2
—
ns
Device-to-device delay match
PE On Time
t
PE–ON
—
—
5
µs
V
PE
= 1.7V~5.25V,
V
DD
= 7.5V~11.5V,
–20°C~85°C
PE Off-time
t
PE–OFF
—
—
4
µs
TEMPERATURE SPECIFICATIONS
Parameter
Sym.
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Conditions
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Maximum Junction Temperature
T
J
—
—
+125
°C
Operating Ambient Temperature
T
A
–20
—
+85
°C
Storage Temperature
T
S
–65
—
+150
°C
PACKAGE THERMAL RESISTANCE
16-lead QFN
JA
—
55
—
°C/W
Note 1
MD1820
DS20005767A-page 6
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
Note 1: 1 oz four-layer 3” x 4” PCB
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005767A-page 7
MD1820
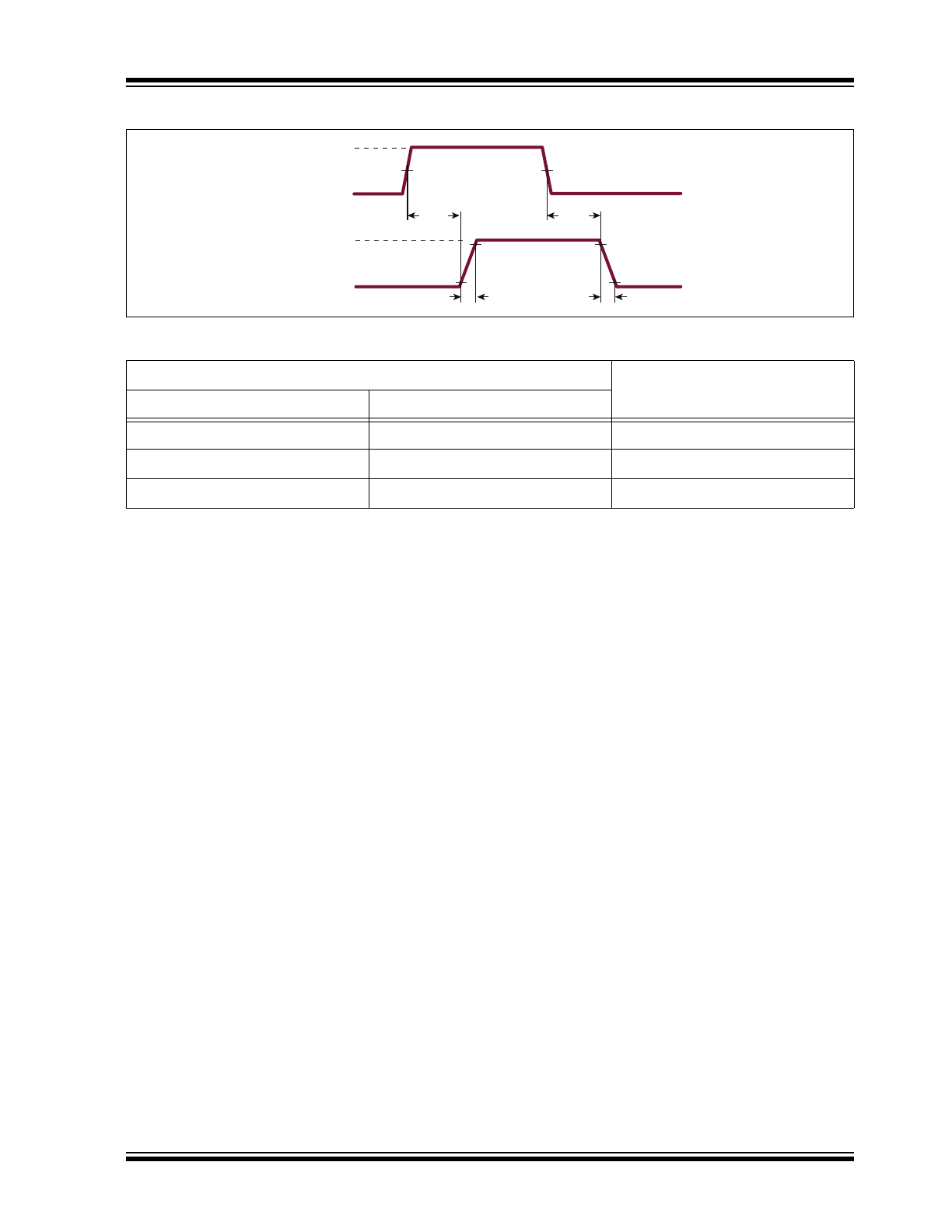
Timing Diagram
0V
3.3V
IN
t
PLH
10%
90%
50%
0V
10V
50%
OUT
t
PHL
t
r
90%
10%
t
f
TABLE 1-1:
TRUTH FUNCTION TABLE
Logic Inputs
Output
PE
IN
H
L
V
L
H
H
V
H
L
X
High Z
MD1820
DS20005767A-page 8
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
2.0
PIN DESCRIPTION
The details on the pins of MD1820 are listed on
Table 2-1
. See
Package Type
for the location of pins.
TABLE 2-1:
PIN FUNCTION TABLE
Pin Number
Pin Name
Description
1
INB
Logic input
2
VDD
High-side supply voltage
3
VSS
Low-side supply voltage. VSS is also connected to the IC substrate. It is required to
connect to the most negative potential of voltage supplies.
4
INC
Logic input
5
IND
6
GND
Logic input ground reference
7
VL
Supply voltage for N-channel output stage
8
OUTC
Output drivers
9
OUTD
10, 11
VH
Supply voltage for P-channel output stage
12
OUTA
Output drivers
13
OUTB
14
VL
Supply voltage for N-channel output stage
15
PE
Power enable logic input. When PE is high, the input logic threshold is set. When PE is
low, all outputs are at default state and the IC is in Standby mode. (See
Table 1-1
and
Figure 3-1
.)
16
INA
Logic input
Substrate
The IC substrate is internally connected to the thermal pad. The thermal pad and VSS
must be connected externally.
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005767A-page 9
MD1820
3.0
APPLICATION INFORMATION
For proper operation of the MD1820, low-inductance
bypass capacitors should be used on the various
supply pins. The GND pin should be connected to the
logic ground. The INA, INB, INC, IND and PE pins
should be connected to a logic source with a swing of
GND to PE, where PE is 1.8V to 5V. Good trace
practices should be followed corresponding to the
desired operating speed. The internal circuitry of the
MD1820 is capable of operating up to 100 MHz, with
the primary speed limitation being the loading effects of
the load capacitance. Because of this speed and the
high transient currents due to capacitive loads, the
bypass capacitors should be as close to the chip pins
as possible. Unless the load specifically requires
bipolar drive, the V
SS
and V
L
pins should have a
low-inductance bypass capacitor to GND and supply
power connections. If these voltages are not zero, they
need bypass capacitors similar to the positive power
supplies. The power connection V
DD
should have a
ceramic bypass capacitor to the ground plane with
short leads and decoupling components to prevent
resonance in the powerleads.
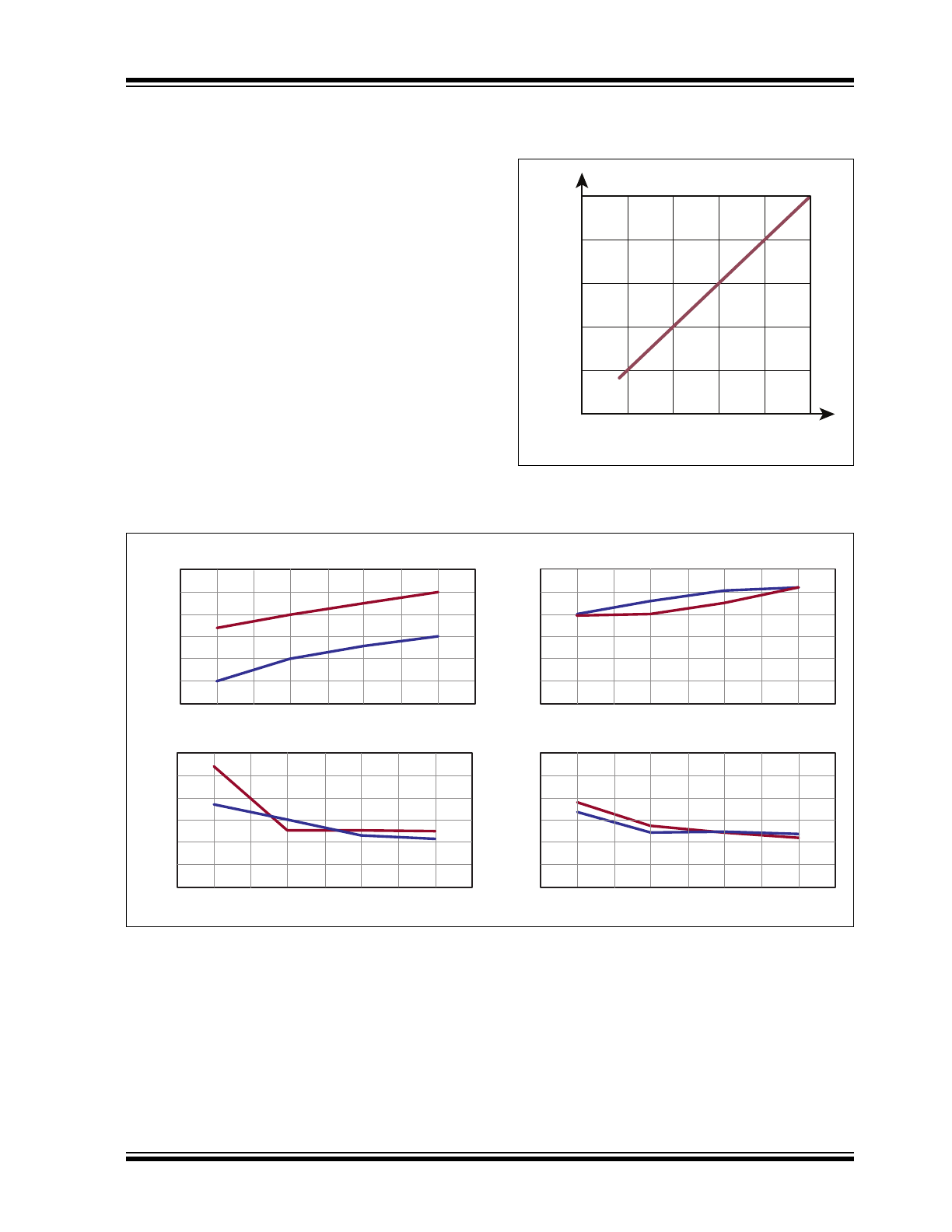
V
PE
V
TH
0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
0
V
PE
/2
V
TH
vs V
PE
FIGURE 3-1:
V
TH
/V
PE
Curve.
MD1820 Delay vs Temperature
MD1820 t
r
& t
f
vs Temperature
MD1820 Delay vs V
DD
MD1820 t
r
& t
f
vs V
DD
De
la
y T
im
e
(
n
s)
t
PLH
t
PHL
Temperature (
O
C)
-50 0 50 125
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
Ti
me
(
n
s
)
t
r
t
f
Temperature (
O
C)
-50 0 50 125
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
Delay T
ime (ns)
t
PLH
t
PHL
V
DD
Voltage (V)
5 8 10 12
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
Ti
m
e
(
n
s
)
t
r
t
f
V
DD
Voltage (V)
5 8 10 12
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
FIGURE 3-2:
Timing Characteristics vs.Temperature and V
DD
.
The voltages of V
H
and V
L
decide the output signal
levels. These two pins can draw fast transient currents
of up to 2A, so they should be provided with an
appropriate bypass capacitor located next to the chip
pins. A ceramic capacitor of up to 1 µF may be
appropriate, with a series ferrite bead to prevent
resonance in the power supply lead going to the
capacitor. Pay particular attention to minimizing trace
lengths, current loop area and using sufficient trace
width to reduce inductance. Surface-mount
components are highly recommended. Since the
output impedance of this driver is very low, in some
cases, it may be desirable to add a small series resistor
in series with the output signal to obtain better
waveform transitions at the load terminals. This will
reduce the output voltage slew rate at the terminals of
a capacitive load.

MD1820
DS20005767A-page 10
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
Make sure that parasitic couplings are minimized from
the output to the input signal terminals. The parasitic
feedback may cause oscillations or spurious waveform
shapes on the edges of signal transitions. Since the
input operates with signals down to 1.8V, even small
coupled voltages may cause problems. The use of a
solid ground plane and good power and signal layout
practices will prevent this problem. Make sure that the
circulating ground return current from a capacitive load
will not react with common inductance to cause noise
voltages in the input logic circuitry.
