1999-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21034F-page 1
MCP3202
Features
• 12-bit resolution
• ±1 LSB maximum DNL
• ±1 LSB maximum INL (MCP3202-B)
• ±2 LSB maximum INL (MCP3202-C)
• Analog inputs programmable as single-ended or
pseudo-differential pairs
• On-chip sample and hold
• SPI Serial Interface (Modes 0,0 and 1,1)
• Single supply operation: 2.7V-5.5V
• 100 ksps maximum sampling rate at V
DD
= 5V
• 50 ksps maximum sampling rate at V
DD
= 2.7V
• Low power CMOS technology
• 500 nA typical standby current, 5 µA maximum
• 550 µA maximum active current at 5V
• Industrial temp range: -40°C to +85°C
• 8-pin MSOP, PDIP, SOIC and TSSOP packages
Applications
• Sensor Interface
• Process Control
• Data Acquisition
• Battery Operated Systems
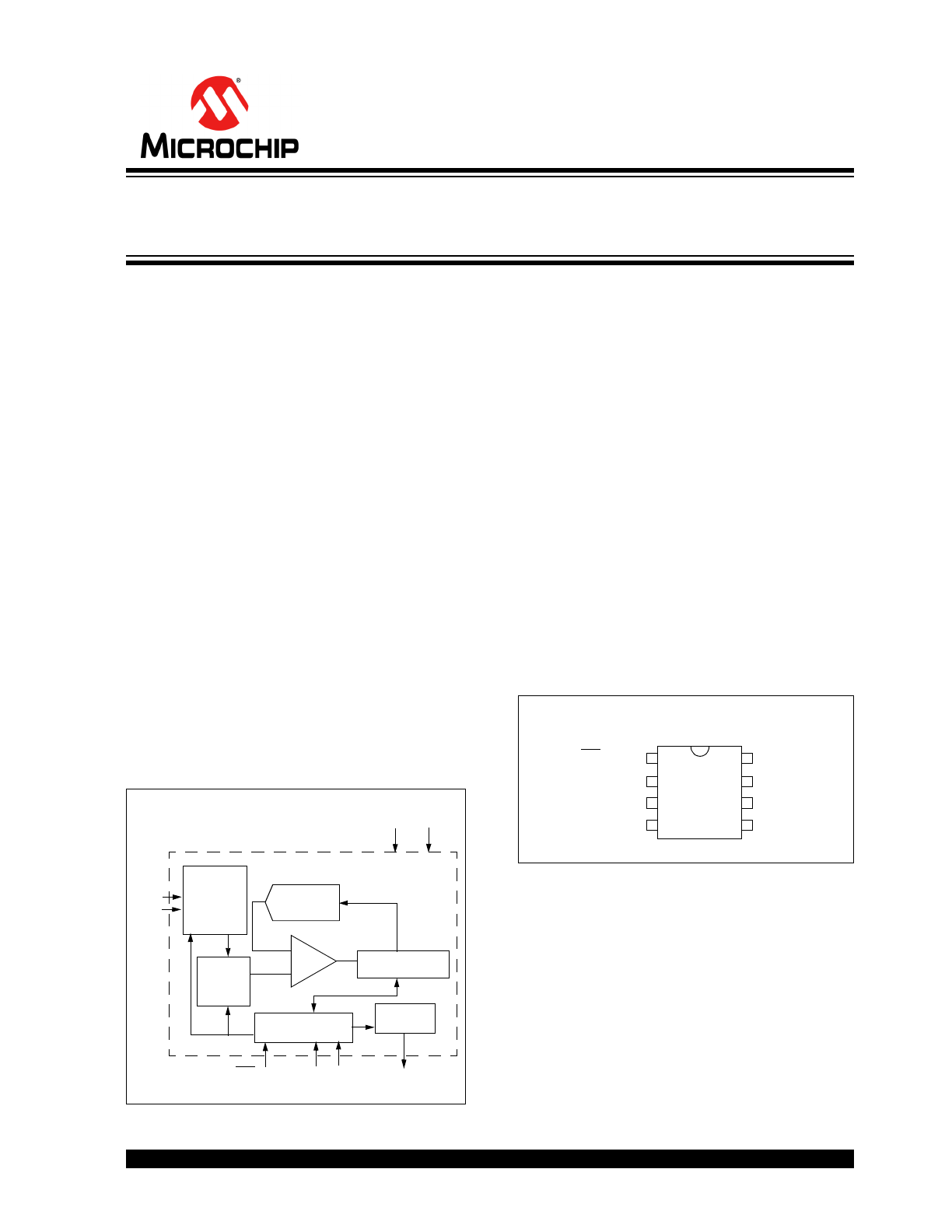
Functional Block Diagram
Description
The MCP3202 is a successive approximation 12-bit
analog-to-digital (A/D) converter with on-board sample
and hold circuitry.
The MCP3202 is programmable to provide a single
pseudo-differential input pair or dual single-ended
inputs. Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) is specified at
±1 LSB, and Integral Nonlinearity (INL) is offered in
±1 LSB (MCP3202-B) and ±2 LSB (MCP3202-C)
versions.
Communication with the device is done using a simple
serial interface compatible with the SPI protocol. The
device is capable of conversion rates of up to 100 ksps
at 5V and 50 ksps at 2.7V.
The MCP3202 operates over a broad voltage range,
2.7V to 5.5V. Low-current design permits operation with
typical standby and active currents of only 500 nA and
375 µA, respectively.
The MCP3202 is offered in 8-pin MSOP, PDIP, TSSOP
and 150 mil SOIC packages.
Package Types
Comparator
Sample
and
Hold
12-Bit SAR
DAC
Control Logic
CS/SHDN
V
SS
V
DD
CLK
D
OUT
Shift
Register
CH0
Channel
Mux
Input
CH1
D
IN
MC
P3
202
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
CH0
CH1
V
SS
CS/SHDN
V
DD
/V
REF
CLK
D
OUT
D
IN
PDIP, MSOP, SOIC, TSSOP
2.7V Dual Channel 12-Bit A/D Converter
with SPI Serial Interface
MCP3202
DS21034F-page 2
1999-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.0
ELECTRICAL
CHARACTERISTICS
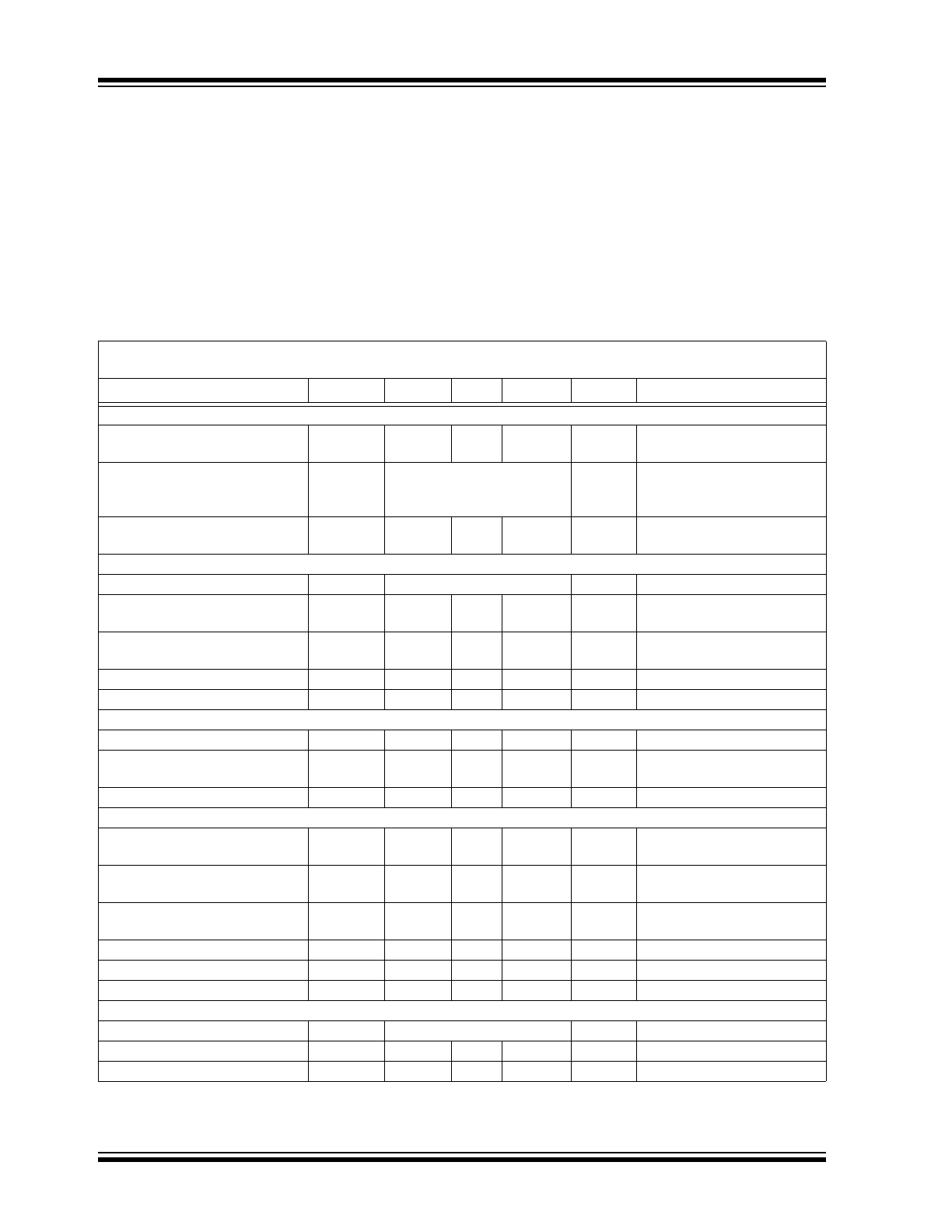
Absolute Maximum Ratings †
V
DD
- V
SS
.........................................................................7.0V
All Inputs and Outputs w.r.t. V
SS
............. -0.6V to V
DD
+ 0.6V
Storage Temperature.....................................-65°C to +150°C
Ambient temperature with power applied.......-65°C to +150°C
Maximum Junction Temperature (T
J
) ......................... .+150°C
ESD Protection On All Pins (HBM)
4 kV
† Notice: Stresses above those listed under “Absolute
Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the
device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of
the device at those or any other conditions above those
indicated in the operational listings of this specification is not
implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended
periods may affect device reliability.
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise noted, all parameters apply at V
DD
= 5.5V, V
SS
= 0V,
T
A
= -40°C to +85°C, f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps and f
CLK
= 18*f
SAMPLE
.
Parameter
Sym
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Conditions
Conversion Rate:
Conversion Time
t
CONV
—
—
12
clock
cycles
Analog Input Sample Time
t
SAMPLE
1.5
clock
cycles
Throughput Rate
f
SAMPL
—
—
—
—
100
50
ksps
ksps
V
DD
= V
REF
= 5V
V
DD
= V
REF
= 2.7V
DC Accuracy:
Resolution
12
bits
Integral Nonlinearity
INL
—
—
±0.75
±1
±1
±2
LSB
LSB
MCP3202-B
MCP3202-C
Differential Nonlinearity
DNL
—
±0.5
±1
LSB
No missing codes over
temperature
Offset Error
—
±1.25
±3
LSB
Gain Error
—
±1.25
±5
LSB
Dynamic Performance:
Total Harmonic Distortion
THD
—
-82
—
dB
V
IN
= 0.1V to 4.9V@1 kHz
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion
(SINAD)
SINAD
—
72
—
dB
V
IN
= 0.1V to 4.9V@1 kHz
Spurious Free Dynamic Range
SFDR
—
86
—
dB
V
IN
= 0.1V to 4.9V@1 kHz
Analog Inputs:
Input Voltage Range for CH0 or
CH1 in Single-Ended Mode
V
SS
—
V
DD
V
Input Voltage Range for IN+ in
Pseudo-Differential Mode
IN+
IN-
—
V
DD
+IN-
See Sections
3.1
and
4.1
Input Voltage Range for IN- in
Pseudo-Differential Mode
IN-
V
SS
-100
—
V
SS
+100
mV
See Sections
3.1
and
4.1
Leakage Current
—
.001
±1
A
Switch Resistance
R
SS
—
1 k
—
Ω
See
Figure 4-1
Sample Capacitor
C
SAMPLE
—
20
—
pF
See
Figure 4-1
Digital Input/Output:
Data Coding Format
Straight Binary
High Level Input Voltage
V
IH
0.7 V
DD
—
—
V
Low Level Input Voltage
V
IL
—
—
0.3 V
DD
V
Note 1: This parameter is established by characterization and not 100% tested.
2: Because the sample cap will eventually lose charge, effective clock rates below 10 kHz can affect linearity performance,
especially at elevated temperatures. See
Section 6.2 “Maintaining Minimum Clock Speed”
for more information.
1999-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21034F-page 3
MCP3202
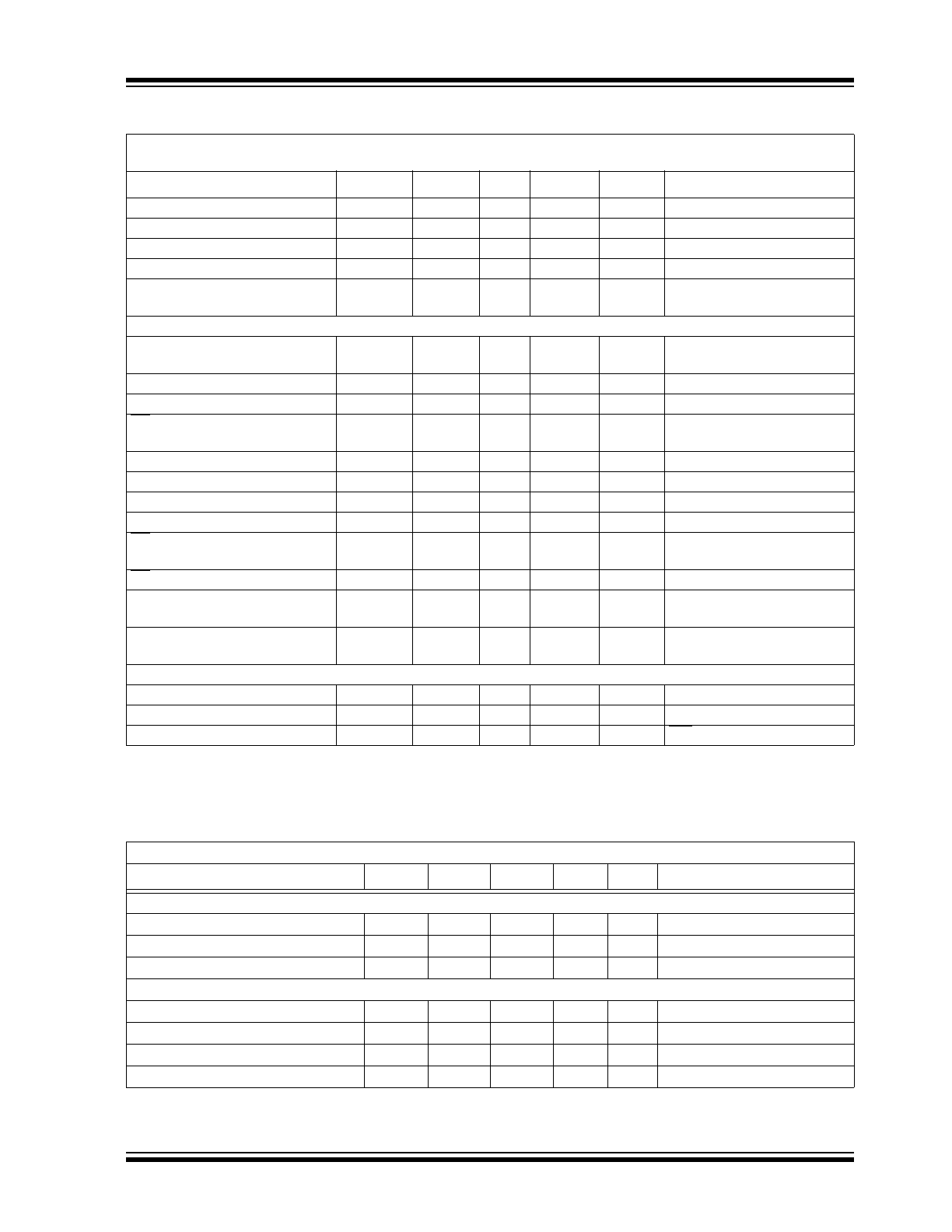
TEMPERATURE CHARACTERISTICS
High Level Output Voltage
V
OH
4.1
—
—
V
I
OH
= -1 mA, V
DD
= 4.5V
Low Level Output Voltage
V
OL
—
—
0.4
V
I
OL
= 1 mA, V
DD
= 4.5V
Input Leakage Current
I
LI
-10
—
10
µA
V
IN
= V
SS
or V
DD
Output Leakage Current
I
LO
-10
—
10
µA
V
OUT
= V
SS
or V
DD
Pin Capacitance
(All Inputs/Outputs)
C
IN
, C
OUT
—
—
10
pF
V
DD
= 5.0V (
Note 1
)
T
A
= +25°C, f = 1 MHz
Timing Parameters:
Clock Frequency
f
CLK
—
—
1.8
0.9
MHz
MHz
V
DD
= 5V (
Note 2
)
V
DD
= 2.7V (
Note 2
)
Clock High Time
t
HI
—
2
MHz
Clock Low Time
t
LO
—
2
MHz
CS Fall To First Rising CLK
Edge
t
SUCS
100
—
—
ns
Data Input Setup Time
t
SU
50
—
—
ns
Data Input Hold Time
t
HD
50
—
—
ns
CLK Fall To Output Data Valid
t
DO
—
—
200
ns
See Test Circuits,
Figure 1-2
CLK Fall To Output Enable
t
EN
—
—
200
ns
See Test Circuits,
Figure 1-2
CS Rise To Output Disable
t
DIS
—
—
100
ns
See Test Circuits,
Figure 1-2
Note 1
CS Disable Time
t
CSH
500
—
—
ns
D
OUT
Rise Time
t
R
—
—
100
ns
See Test Circuits,
Figure 1-2
Note 1
D
OUT
Fall Time
t
F
—
—
100
ns
See Test Circuits,
Figure 1-2
Note 1
Power Requirements:
Operating Voltage
V
DD
2.7
—
5.5
V
Operating Current
I
DD
—
375
550
µA
V
DD
= 5.0V, D
OUT
unloaded
Standby Current
I
DDS
—
0.5
5
µA
CS = V
DD
= 5.0V
Electrical Specifications: Unless otherwise indicated, V
DD
= +2.7V to +5.5V, V
SS
= GND.
Parameters
Sym
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
Temperature Ranges
Specified Temperature Range
T
A
-40
—
+85
°C
Operating Temperature Range
T
A
-40
—
+85
°C
Storage Temperature Range
T
A
-65
—
+150
°C
Thermal Package Resistances
Thermal Resistance, 8L-MSOP
JA
—
211
—
°C/W
Thermal Resistance, 8L-PDIP
JA
—
89.5
—
°C/W
Thermal Resistance, 8L-SOIC
JA
—
149.5
—
°C/W
Thermal Resistance, 8L-TSSOP
JA
—
139
—
°C/W
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED)
Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise noted, all parameters apply at V
DD
= 5.5V, V
SS
= 0V,
T
A
= -40°C to +85°C, f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps and f
CLK
= 18*f
SAMPLE
.
Parameter
Sym
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Conditions
Note 1: This parameter is established by characterization and not 100% tested.
2: Because the sample cap will eventually lose charge, effective clock rates below 10 kHz can affect linearity performance,
especially at elevated temperatures. See
Section 6.2 “Maintaining Minimum Clock Speed”
for more information.
MCP3202
DS21034F-page 4
1999-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
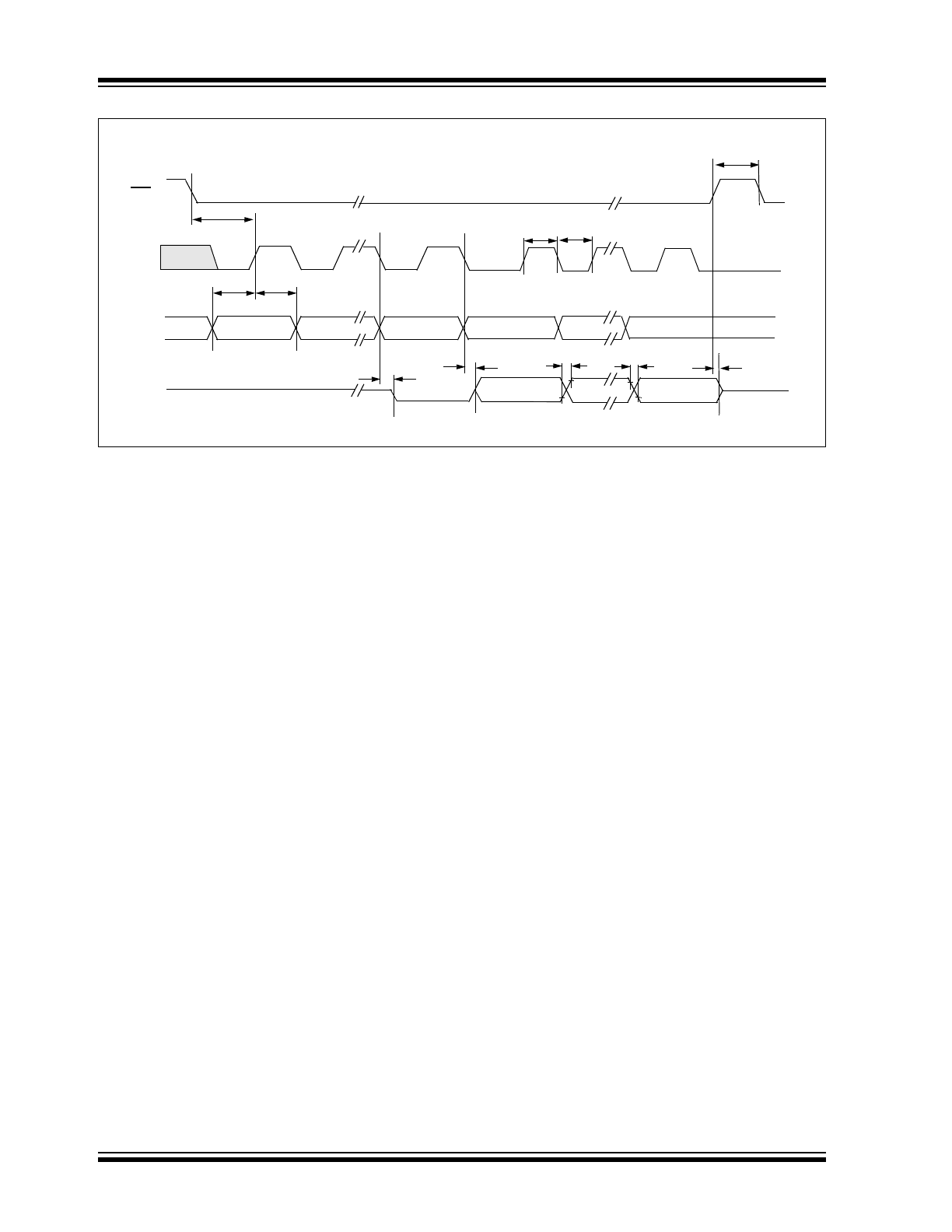
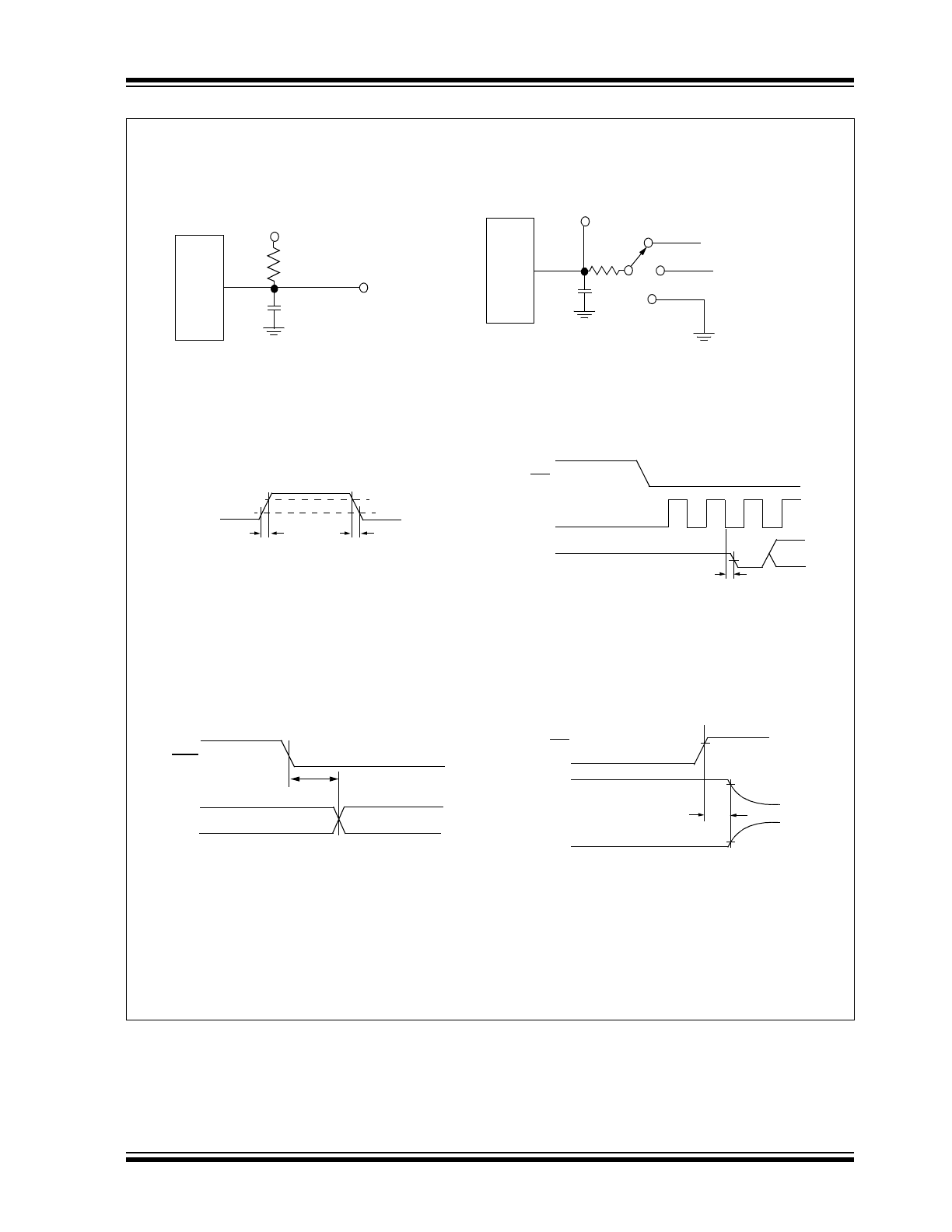
FIGURE 1-1:
Serial Timing.
CS
CLK
D
IN
MSB IN
t
SU
t
HD
t
SUCS
t
CSH
t
HI
t
LO
D
OUT
t
EN
t
DO
t
R
t
F
LSB
MSB OUT
t
DIS
NULL BIT
1999-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21034F-page 5
MCP3202
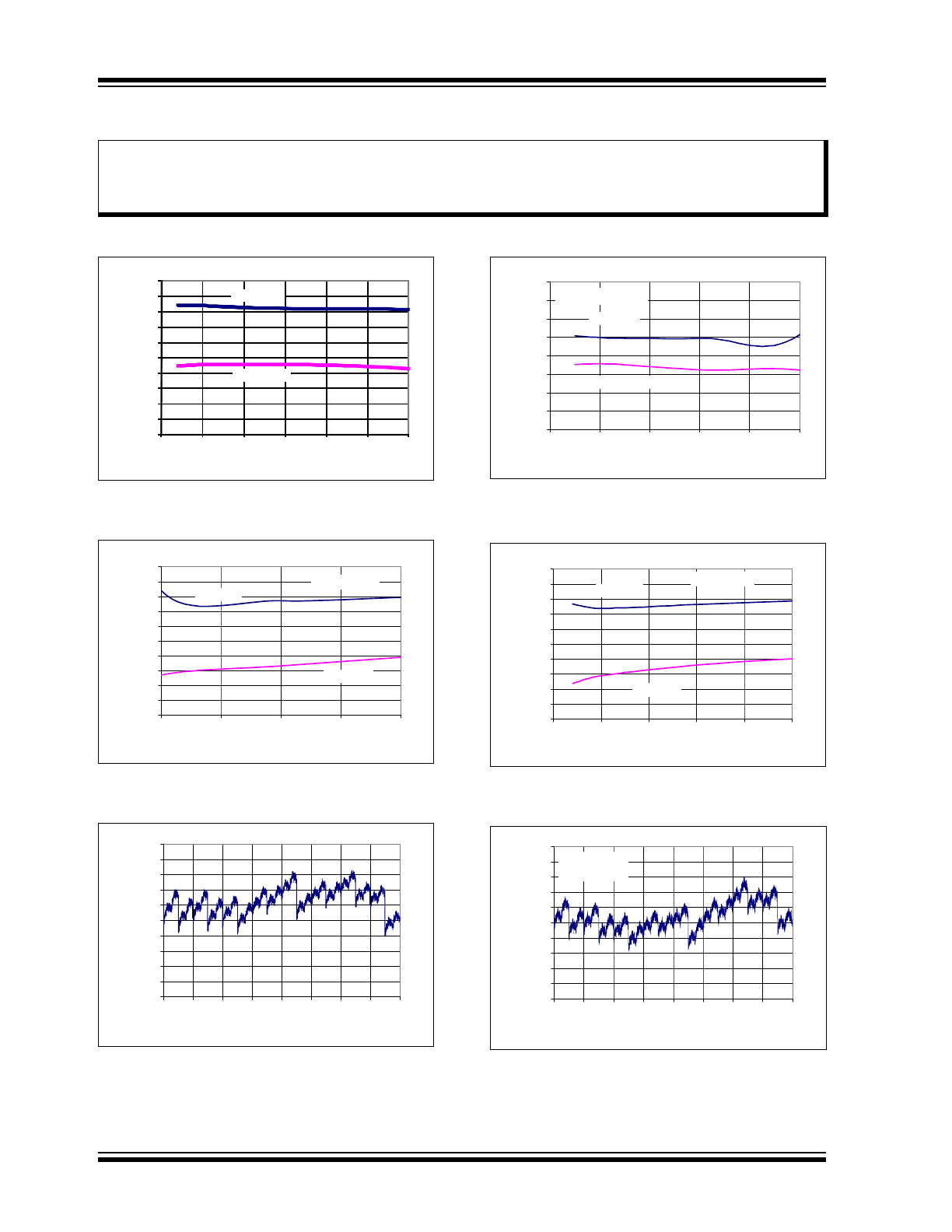
FIGURE 1-2:
Test Circuits.
V
IH
T
DIS
CS
D
OUT
Waveform 1*
D
OUT
Waveform 2†
90%
10%
* Waveform 1 is for an output with internal conditions
such that the output is high, unless disabled by the
output control.
† Waveform 2 is for an output with internal conditions
such that the output is low, unless disabled by the
output control.
Voltage Waveforms for t
DIS
Test Point
1.4V
D
OUT
Load Circuit for t
R
, t
F
, t
DO
3 kΩ
C
L
= 100 pF
Test Point
D
OUT
Load Circuit for t
DIS
and t
EN
3 kΩ
100 pF
t
DIS
Waveform 2
t
DIS
Waveform 1
CS
CLK
D
OUT
t
EN
1
2
B11
Voltage Waveforms for t
EN
t
EN
Waveform
V
DD
V
DD
/2
V
SS
3
4
D
OUT
t
R
Voltage Waveforms for t
R
, t
F
CLK
D
OUT
t
DO
Voltage Waveforms for t
DO
t
F
V
OH
V
OL
MCP3202
DS21034F-page 6
1999-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
2.0
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
DD
= 5V, V
SS
= 0V, f
SAMPLE =
100 ksps,
f
CLK
= 18* f
SAMPLE
, T
A
= +25°C.
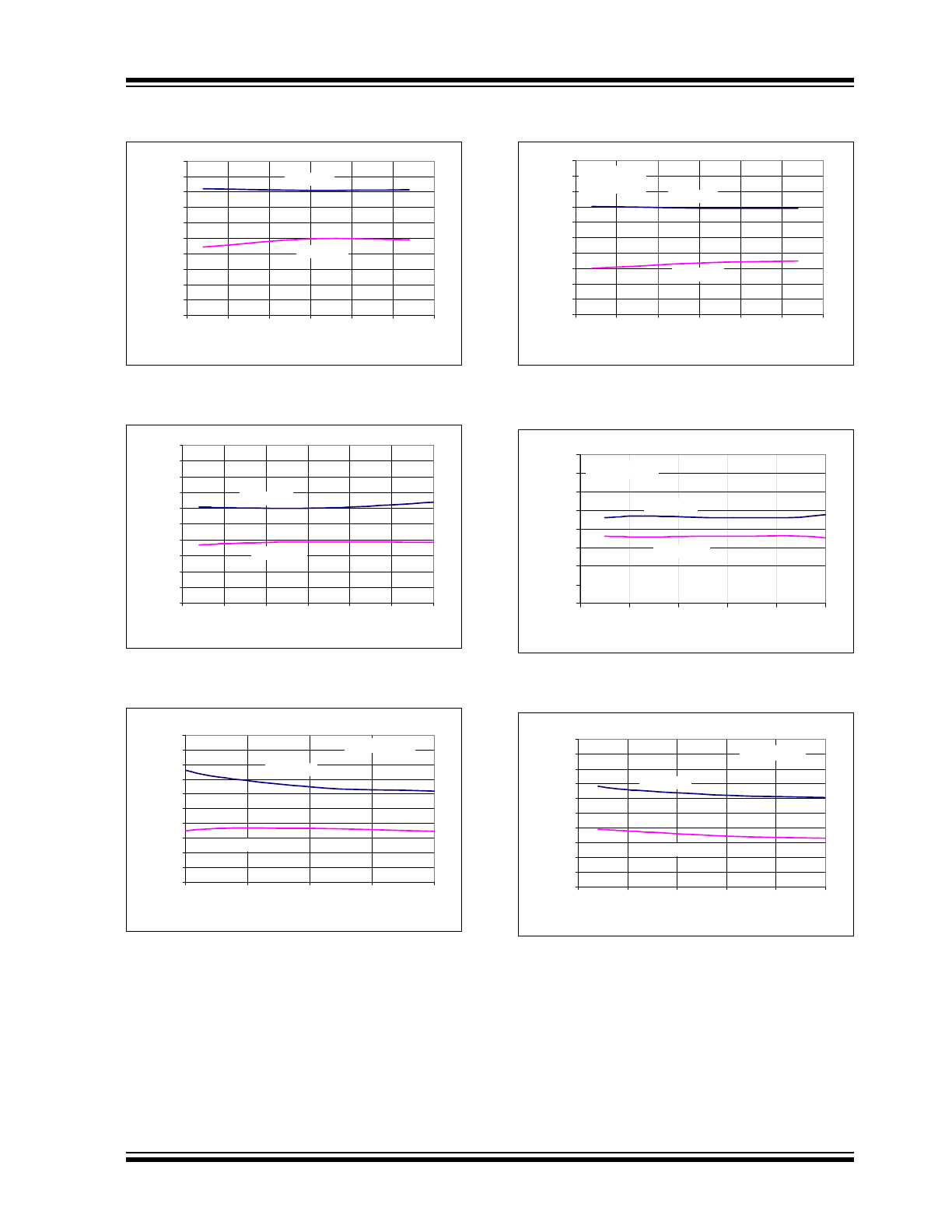
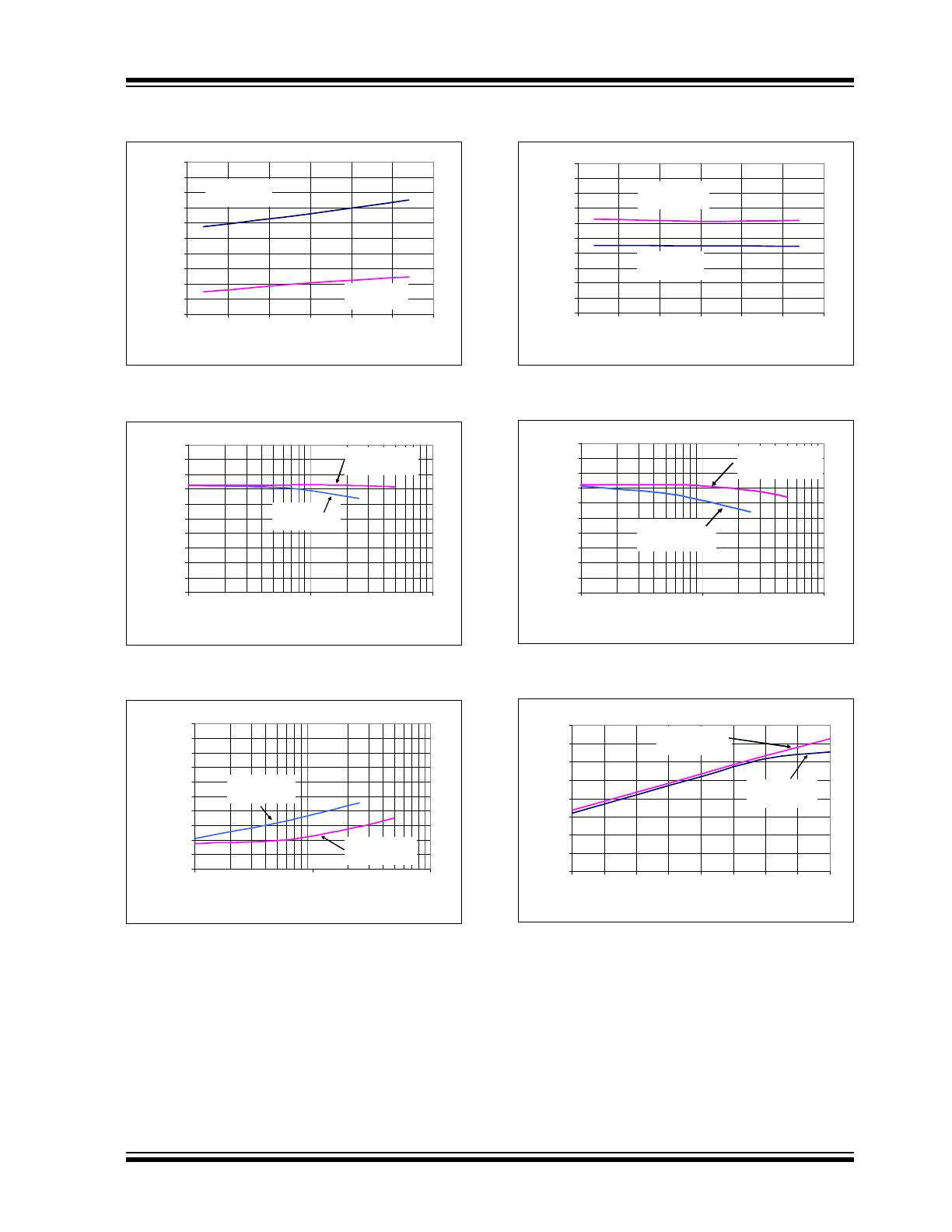
FIGURE 2-1:
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
vs. Sample Rate.
FIGURE 2-2:
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
vs. V
DD
.
FIGURE 2-3:
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
vs. Code (Representative Part).
FIGURE 2-4:
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
vs. Sample Rate (V
DD
= 2.7V).
FIGURE 2-5:
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
vs. V
DD
.
FIGURE 2-6:
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
vs. Code (Representative Part, V
DD
= 2.7V).
Note:
The graphs provided following this note are a statistical summary based on a limited number of samples
and are provided for informational purposes only. The performance characteristics listed herein are not
tested or guaranteed. In some graphs, the data presented may be outside the specified operating range
(e.g., outside specified power supply range) and therefore outside the warranted range.
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
0
25
50
75
100
125
150
IN
L
(L
S
B
)
Sample Rate (ksps)
Positive INL
Negative INL
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
V
DD
(V)
IN
L
(
L
S
B
)
Positive INL
Negative INL
f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
0
512
1024 1536 2048 2560 3072 3584 4096
Digital Code
INL (
L
SB)
-2.0
-1.5
-1.0
-0.5
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
0
20
40
60
80
100
Sample Rate (ksps)
INL (
L
S
B
)
V
DD
= 2.7V
Positive INL
Negative INL
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
V
DD
(V)
IN
L
(
L
S
B
)
Positive INL
Negative INL
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
0
512
1024
1536
2048 2560
3072 3584
4096
Digital Code
IN
L
(
L
S
B
)
V
DD
= 2.7V
F
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
1999-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21034F-page 7
MCP3202
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
DD
= 5V, V
SS
= 0V, f
SAMPLE =
100 ksps,
f
CLK
= 18* f
SAMPLE
, T
A
= +25°C.
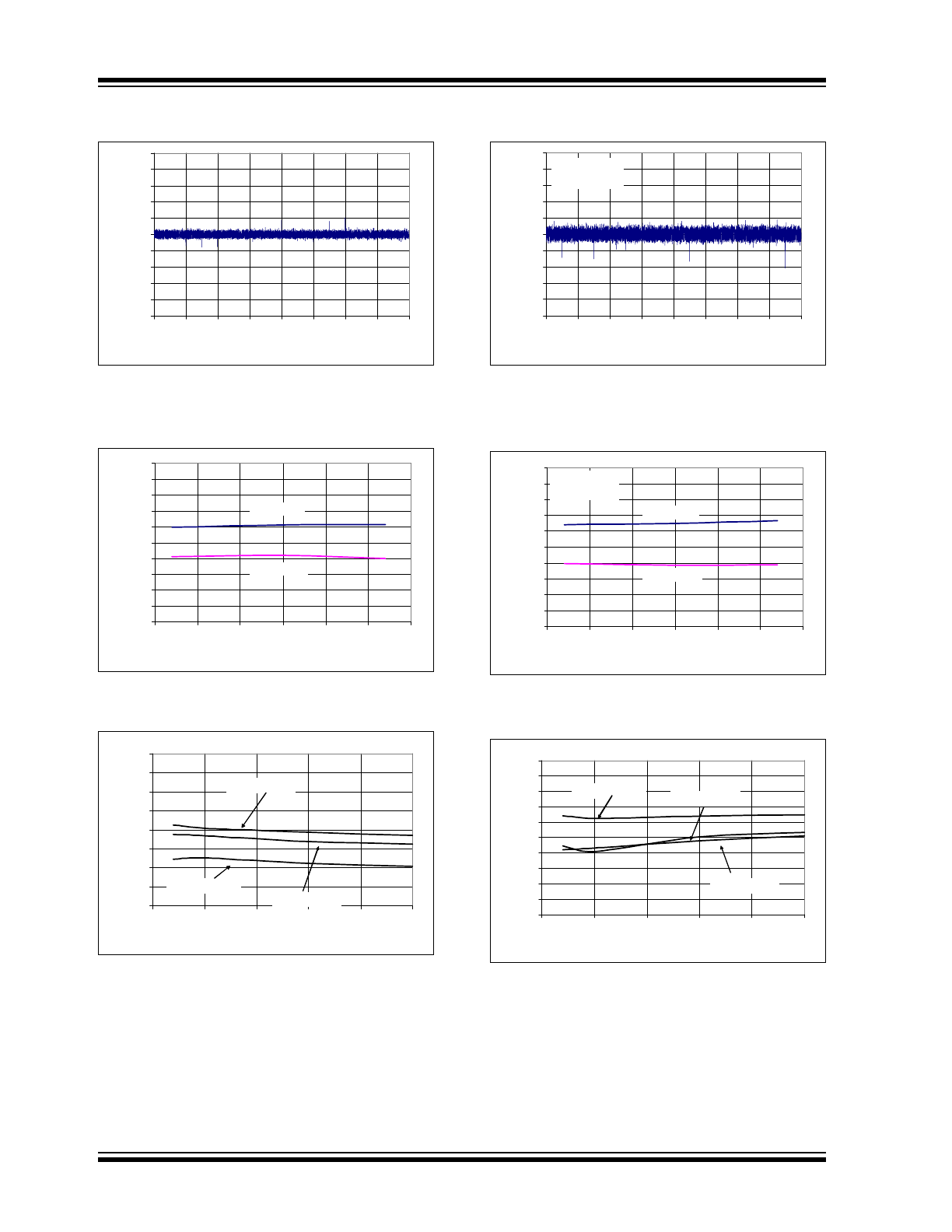
FIGURE 2-7:
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
vs. Temperature.
FIGURE 2-8:
Differential Nonlinearity
(DNL) vs. Sample Rate.
FIGURE 2-9:
Differential Nonlinearity
(DNL) vs. V
DD
.
FIGURE 2-10:
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
vs. Temperature (V
DD
= 2.7V).
FIGURE 2-11:
Differential Nonlinearity
(DNL) vs. Sample Rate (V
DD
= 2.7V).
FIGURE 2-12:
Differential Nonlinearity
(DNL) vs. V
DD
.
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
-50
-25
0
25
50
75
100
Temperature (°C)
INL
(
L
SB)
Positive INL
Negative INL
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
0
25
50
75
100
125
150
Sample Rate (ksps)
D
N
L
(L
SB
)
Positive DNL
Negative DNL
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
V
DD
(V)
DN
L
(
L
S
B
)
Positive DNL
Negative DNL
f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
-50
-25
0
25
50
75
100
Temperature (°C)
IN
L
(
L
S
B
)
Positive INL
V
DD
= 2.7V
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
Negative INL
-2.0
-1.5
-1.0
-0.5
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
0
20
40
60
80
100
Sample Rate (ksps)
DNL (
L
S
B
)
V
DD
= 2.7V
Positive DNL
Negative DNL
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
V
DD
(V)
DN
L
(
L
S
B
)
Positive DNL
Negative DNL
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
MCP3202
DS21034F-page 8
1999-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
DD
= 5V, V
SS
= 0V, f
SAMPLE =
100 ksps,
f
CLK
= 18* f
SAMPLE
, T
A
= +25°C.
FIGURE 2-13:
Differential Nonlinearity
(DNL) vs. Code (Representative Part).
FIGURE 2-14:
Differential Nonlinearity
(DNL) vs. Temperature.
FIGURE 2-15:
Gain Error vs. V
DD
.
FIGURE 2-16:
Differential Nonlinearity
(DNL) vs. Code (Representative Part, V
DD
=
2.7V).
FIGURE 2-17:
Differential Nonlinearity
(DNL) vs. Temperature (V
DD
= 2.7V).
FIGURE 2-18:
Offset Error vs. V
DD
.
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
0
512
1024 1536
2048
2560
3072
3584
4096
Digital Code
DNL
(
L
S
B
)
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
-50
-25
0
25
50
75
100
Temperature (°C)
DNL (
L
S
B
)
Positive DNL
Negative DNL
-2.0
-1.5
-1.0
-0.5
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
V
DD
(V)
Ga
in E
rror
(L
S
B
)
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
f
SAMPLE
= 10 ksps
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
0
512
1024 1536
2048
2560
3072
3584
4096
Digital Code
DNL
(
L
S
B
)
V
DD
= 2.7V
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
-50
-25
0
25
50
75
100
Temperature (°C)
DNL (
L
S
B
)
Positive DNL
V
DD
= 2.7V
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
Negative DNL
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
V
DD
(V)
Of
fs
et
E
rro
r (
L
S
B
)
f
SAMPLE
= 10 ksps
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
1999-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21034F-page 9
MCP3202
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
DD
= 5V, V
SS
= 0V, f
SAMPLE =
100 ksps,
f
CLK
= 18* f
SAMPLE
, T
A
= +25°C.
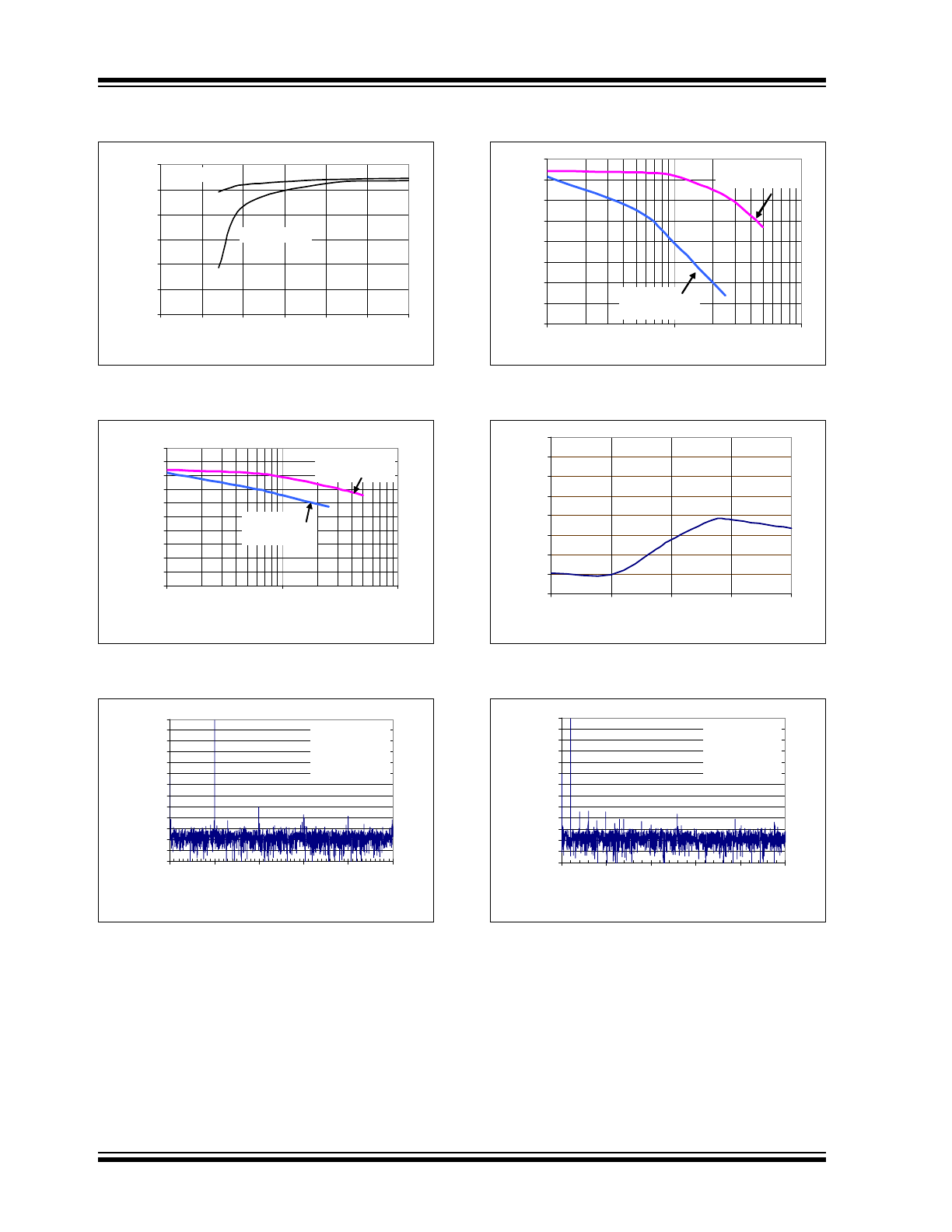
FIGURE 2-19:
Gain Error vs. Temperature.
FIGURE 2-20:
Signal-to-Noise Ratio
(SNR) vs. Input Frequency.
FIGURE 2-21:
Total Harmonic Distortion
(THD) vs. Input Frequency.
FIGURE 2-22:
Offset Error vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-23:
Signal-to-Noise and
Distortion (SINAD) vs. Input Frequency.
FIGURE 2-24:
Signal-to-Noise and
Distortion (SINAD) vs. Signal Level.
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
-50
-25
0
25
50
75
100
Temperature (°C)
G
ai
n
Error
(
L
S
B
)
V
DD
= 5V
f
SAMPLE
= 100
V
DD
= 2.7V
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
1
10
100
Input Frequency (kHz)
S
NR (dB)
V
DD
= 2.7V
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
V
DD
= 5V
f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
1
10
100
Input Frequency (kHz)
TH
D (
d
B)
V
DD
= 2.7V
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
V
DD
= 5V
f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
-50
-25
0
25
50
75
100
Temperature (°C)
O
ffs
et Er
ro
r
(L
S
B
)
V
DD
= 5V
f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
V
DD
= 2.7V
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
1
10
100
Input Frequency (kHz)
S
INAD (
d
B)
V
DD
= 2.7V
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
V
DD
= 5V
f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
-40
-35
-30
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
Input Signal Level (dB)
S
INA
D (
d
B)
V
DD
= 2.7V
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
V
DD
= 5V
f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
MCP3202
DS21034F-page 10
1999-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
DD
= 5V, V
SS
= 0V, f
SAMPLE =
100 ksps,
f
CLK
= 18* f
SAMPLE
, T
A
= +25°C.
FIGURE 2-25:
Effective Number of Bits
(ENOB) vs. V
DD
.
FIGURE 2-26:
Spurious Free Dynamic
Range (SFDR) vs. Input Frequency.
FIGURE 2-27:
Frequency Spectrum of
10 kHz input (Representative Part).
FIGURE 2-28:
Effective Number of Bits
(ENOB) vs. Input Frequency.
FIGURE 2-29:
Power Supply Rejection
(PSR) vs. Ripple Frequency.
FIGURE 2-30:
Frequency Spectrum of
1 kHz input (Representative Part, V
DD
= 2.7V).
9.0
9.5
10.0
10.5
11.0
11.5
12.0
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
V
DD
(V)
EN
O
B
(
rm
s)
f
SAMPLE
= 50ksps
f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
1
10
100
Input Frequency (kHz)
SF
D
R
(
d
B
)
V
DD
= 2.7V
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
V
DD
= 5V
f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
-130
-120
-110
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
0
10000
20000
30000
40000
50000
Frequency (Hz)
Am
pl
itude
(
d
B)
V
DD
= 5V
f
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
f
INPUT
= 9.985 kHz
4096 points
8.0
8.5
9.0
9.5
10.0
10.5
11.0
11.5
12.0
1
10
100
Input Frequency (kHz)
EN
O
B
(
rm
s)
V
DD
= 5V
F
SAMPLE
= 100 ksps
V
DD
= 2.7V
F
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
1
10
100
1000
10000
Ripple Frequency (kHz)
P
o
we
r S
uppl
y Re
je
ct
ion (dB)
-130
-120
-110
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
25000
Frequency (Hz)
A
m
pl
it
ude
(d
B
)
V
DD
= 2.7V
f
SAMPLE
= 50 ksps
f
INPUT
= 998.76 Hz
4096 points
