2015-2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005463C-page 1
MCP2003B
Features
• The MCP2003B is Compliant with Local
Interconnect Network (LIN) Bus Specifications
1.3, 2.0, 2.1, 2.2, SAE J2602, and ISO17987
• Supports Baud Rates up to 20 Kbaud
with
LIN-Compatible Output Driver
• 60V Load Dump Protected
• Very High Electromagnetic Immunity (EMI) Meets
Stringent Original Equipment Manufacturers
(OEM) Requirements
• Direct Capacitor Coupling Robustness without
Transient Voltage Suppressor (TVS):
- ±35V on L
BUS
(SAE J2962-1)
- ±85V on L
BUS
(SAE J2962-1)
• High Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
Immunity without TVS:
- >25 kV on L
BUS
(SAE J2962-1)
- >15 kV on V
BB
(IEC 61000-4-2)
- >6 kV on L
BUS
(IEC 61000-4-2)
• Very High Immunity to RF Disturbances Meets
Stringent OEM Requirements
• Wide Supply Voltage: 5.5V – 30.0V Continuous
• Extended (E) Temperature Range: -40°C to +125°C
• High (H) Temperature Range: -40°C to +150°C
• Interfaces to PIC
®
MCU EUSART and Standard
USARTs
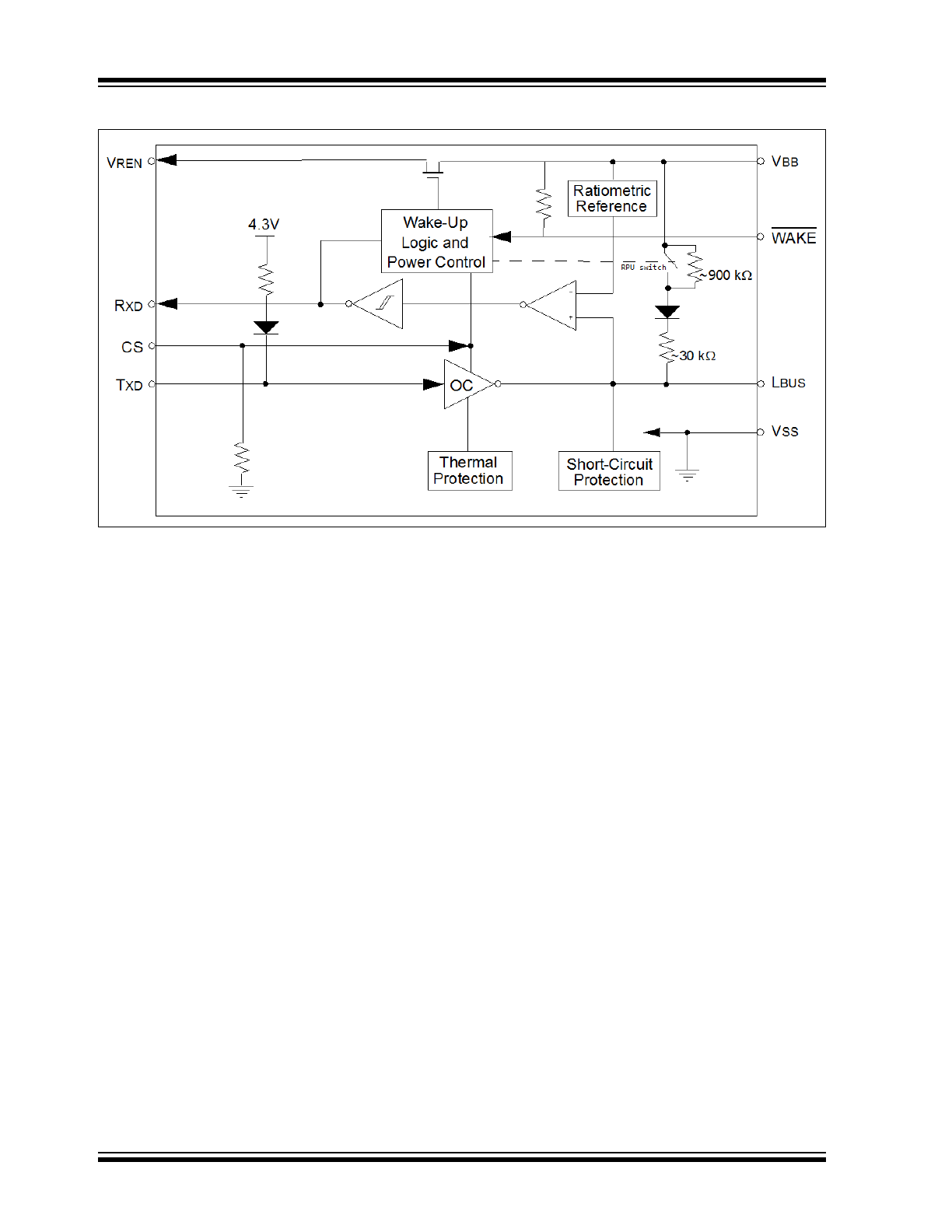
• LIN Bus Pin:
- Internal pull-up resistor and diode
- Protected against battery shorts
- Protected against loss of ground
- High current drive: >40 mA
• Automatic Thermal Shutdown
• Low-Power Mode:
- Receiver monitoring bus and transmitter off:
(
5 µA)
Description
This device provides a bidirectional, half-duplex
communication, physical interface to automotive and
industrial LIN systems to meet the LIN Bus
Specification Revision 2.2, SAE J2602, and ISO
17987. The device is both short-circuit and
overtemperature protected by internal circuitry. The
device has been specifically designed to operate in the
automotive operating environment and will survive all
specified transient conditions while meeting all of the
stringent quiescent current requirements.
Package Types
MCP2003B
SOIC
MCP2003B
2x3 DFN*
* Includes Exposed Thermal Pad (EP); see
Table 1-2
.
WAKE
CS
T
XD
V
BB
L
BUS
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5 V
SS
V
REN
R
XD
EP
9
WAKE
CS
T
XD
V
BB
L
BUS
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5 V
SS
V
REN
R
XD
EP
9
MCP2003B
3x3 DFN*
WAKE
CS
T
XD
V
BB
L
BUS
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5 V
SS
V
REN
R
XD
LIN Transceiver
MCP2003B
DS20005463C-page 2
2015-2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
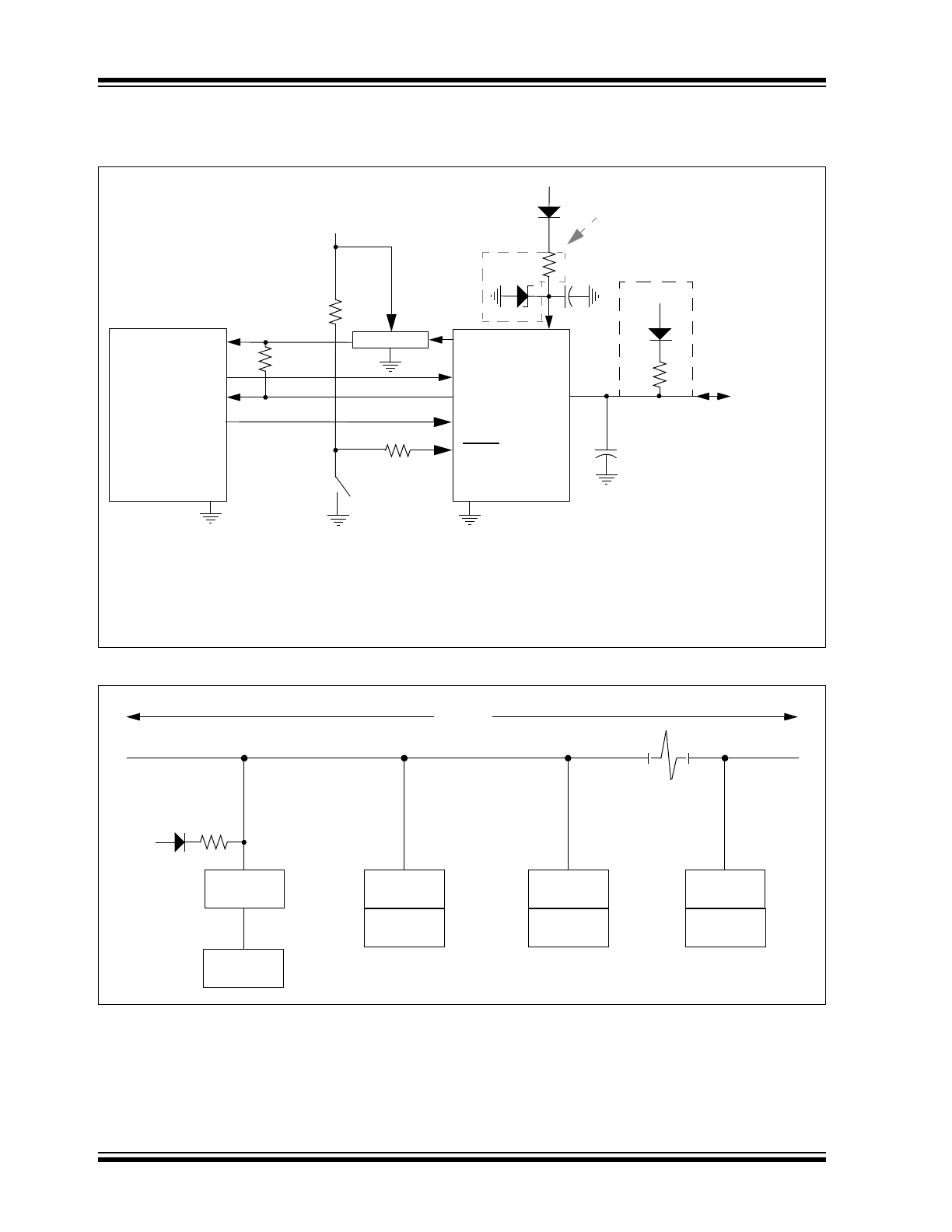
MCP2003B Block Diagram
2015-2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005463C-page 3
MCP2003B
1.0
DEVICE OVERVIEW
The MCP2003B devices provide a physical interface
between a microcontroller and a LIN bus. These
devices will translate the CMOS/TTL logic levels to LIN
logic level, and vice versa. It is intended for automotive
and industrial applications with serial bus speeds up to
20 Kbaud.
LIN Bus Specification Revision 2.2 requires that the
transceiver of all nodes in the system is connected via
the LIN pin, referenced to ground and with a maximum
external termination resistance load of 510
from LIN
bus to battery supply. The 510
corresponds to
1 master and 15 slave nodes.
The V
REN
pin can be used to drive the logic input of an
external voltage regulator. This pin is high in all modes
except for Power-Down mode.
1.1
External Protection
1.1.1
REVERSE BATTERY PROTECTION
An external reverse-battery-blocking diode should be
used to provide polarity protection (see
Example 1-1
).
1.1.2
TRANSIENT VOLTAGE
PROTECTION (LOAD DUMP)
An external 60V transient suppressor (TVS) diode,
between V
BB
and ground, with a 50
transient
protection resistor (R
TP
) in series with the battery
supply and the V
BB
pin serve to protect the device from
power transients (see
Example 1-1
) and ESD events.
While this protection is optional, it is considered good
engineering practice.
1.2
Internal Protection
1.2.1
ESD PROTECTION
For component-level ESD ratings, please refer to the
maximum operation specifications.
1.2.2
GROUND LOSS PROTECTION
The LIN Bus specification states that the LIN pin must
transition to the recessive state when ground is
disconnected. Therefore, a loss of ground effectively
forces the LIN line to a high-impedance level.
1.2.3
THERMAL PROTECTION
The thermal protection circuit monitors the die
temperature and is able to shut down the
LIN
transmitter.
There are two causes for a thermal overload. A thermal
shutdown can be triggered by either, or both, of the
following thermal overload conditions.
• LIN bus output overload
• Increase in die temperature due to increase in
environment temperature
Driving the T
XD
and checking the R
XD
pin makes it
possible to determine whether there is a bus contention
(R
X
= low, T
X
= high) or a thermal overload condition
(R
X
= high, T
X
= low). After a thermal overload event,
the device will automatically recover once the die
temperature has fallen below the recovery temperature
threshold (see
Figure 1-1
).
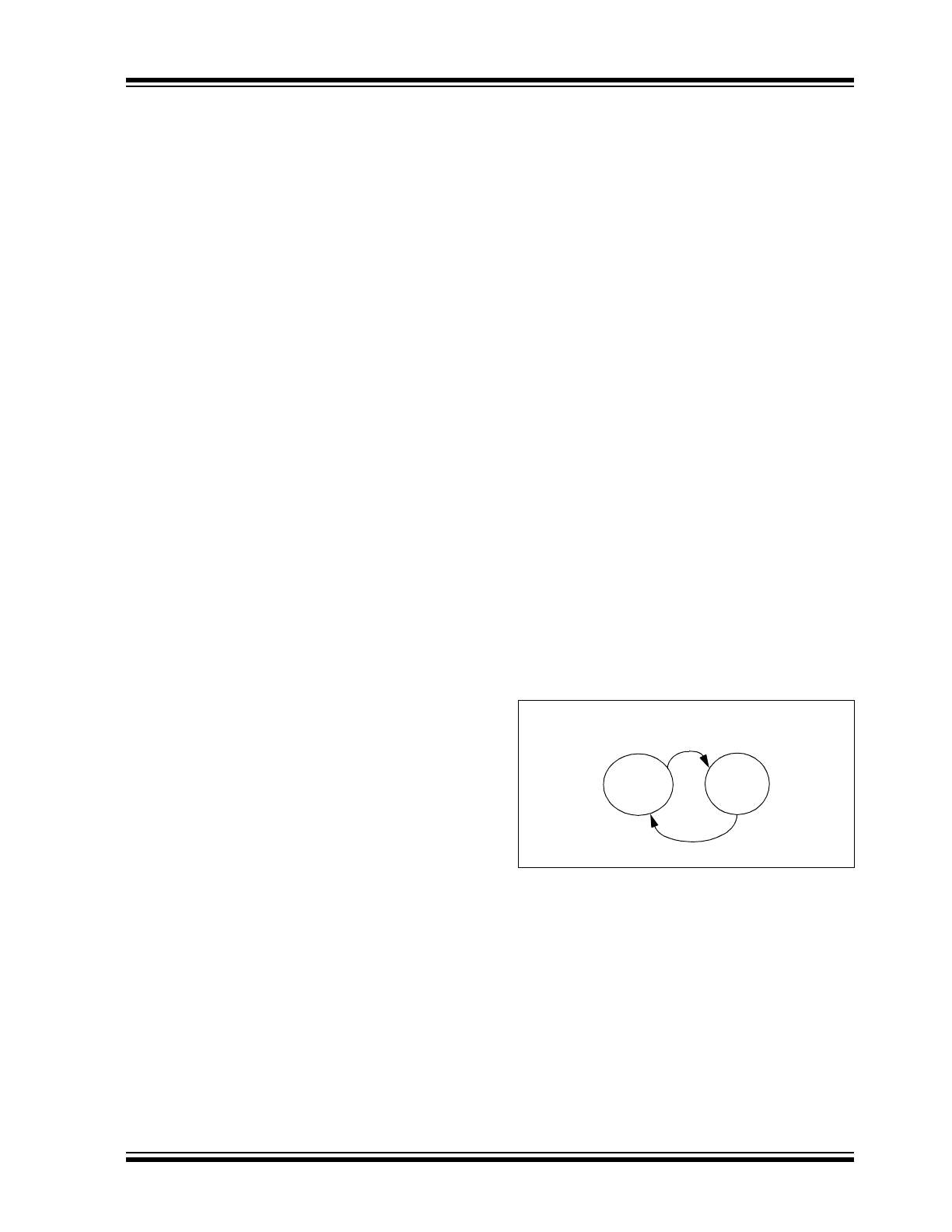
FIGURE 1-1:
THERMAL SHUTDOWN
STATE DIAGRAM
Operation
Mode
Transmitter
Shutdown
LIN bus
Shorted
to V
BB
Temp < Shutdown
TEMP

MCP2003B
DS20005463C-page 4
2015-2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.3
Modes of Operation
For an overview of all operational modes, refer to
Table 1-1
.
1.3.1
POWER-DOWN MODE
In Power-Down mode, everything is off except the
wake-up section. The internal 30 k
pull-up resistor
switch is open, which enables the high ohmic pull-up
resistor (900 k
typical). This is the lowest power
mode. The receiver is off, thus its output is open-drain.
On CS going to a high level or a falling edge on WAKE,
the device will enter Ready mode as soon as internal
voltage stabilizes. Refer to
Section 2.4 “AC
Specifications”
for further information. In addition, LIN
bus activity will change the device from Power-Down
mode to Ready mode; The
MCP2003B
wakes up on a
rising edge on
L
BUS
preceded by a low level lasting at
least
70 µs typically.
See
Figure 1-2
about remote
wake-up. If CS is held high as the device transitions
from Power-Down to Ready mode, the device will
transition to either Operation or Transmitter Off mode,
depending on T
XD
input, as soon as internal voltages
stabilize.
1.3.2
READY MODE
Transitioning from POR into Ready mode is achieved
when V
BB
> V
BBUV_RISE
. Upon entering Ready mode,
V
REN
is enabled and the receiver detect circuit is
powered-up. The transmitter remains disabled and the
device is ready to receive data but not to transmit.
Upon V
BB
supply pin power-on, the device will remain
in Ready mode as long as CS is low. When CS
transitions high, the device will either enter Operation
mode if the T
XD
pin is held high, or the device will enter
Transmitter Off mode if the T
XD
pin is held low.
1.3.3
OPERATION MODE
In this mode, all internal modules are operational. Note
that the part cannot transmit if the pull-up resistance is
missing on R
X
pin. See
Section 1.5.1.1 “R
XD
Monitoring”
for details.
The device will go into Power-Down mode on the falling
edge of CS and the T
XD
pin is held high. The device will
enter Transmitter Off mode in the event of a Fault con-
dition such as thermal overload, bus contention or T
XD
timer expiration.
The V
BB
to L
BUS
~30 kΩ pull-up resistor
(
R
SLAVE
)
is
connected only in Operation mode.
1.3.4
TRANSMITTER OFF MODE
Transmitter Off mode is reached whenever the
transmitter is disabled due to a Fault condition. Fault
conditions include thermal overload, bus contention,
R
XD
monitoring and T
XD
timer expiration.
The device will go into Power-Down mode on the falling
edge of CS, or return to Operation mode if all faults are
resolved.
2015-2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005463C-page 5
MCP2003B
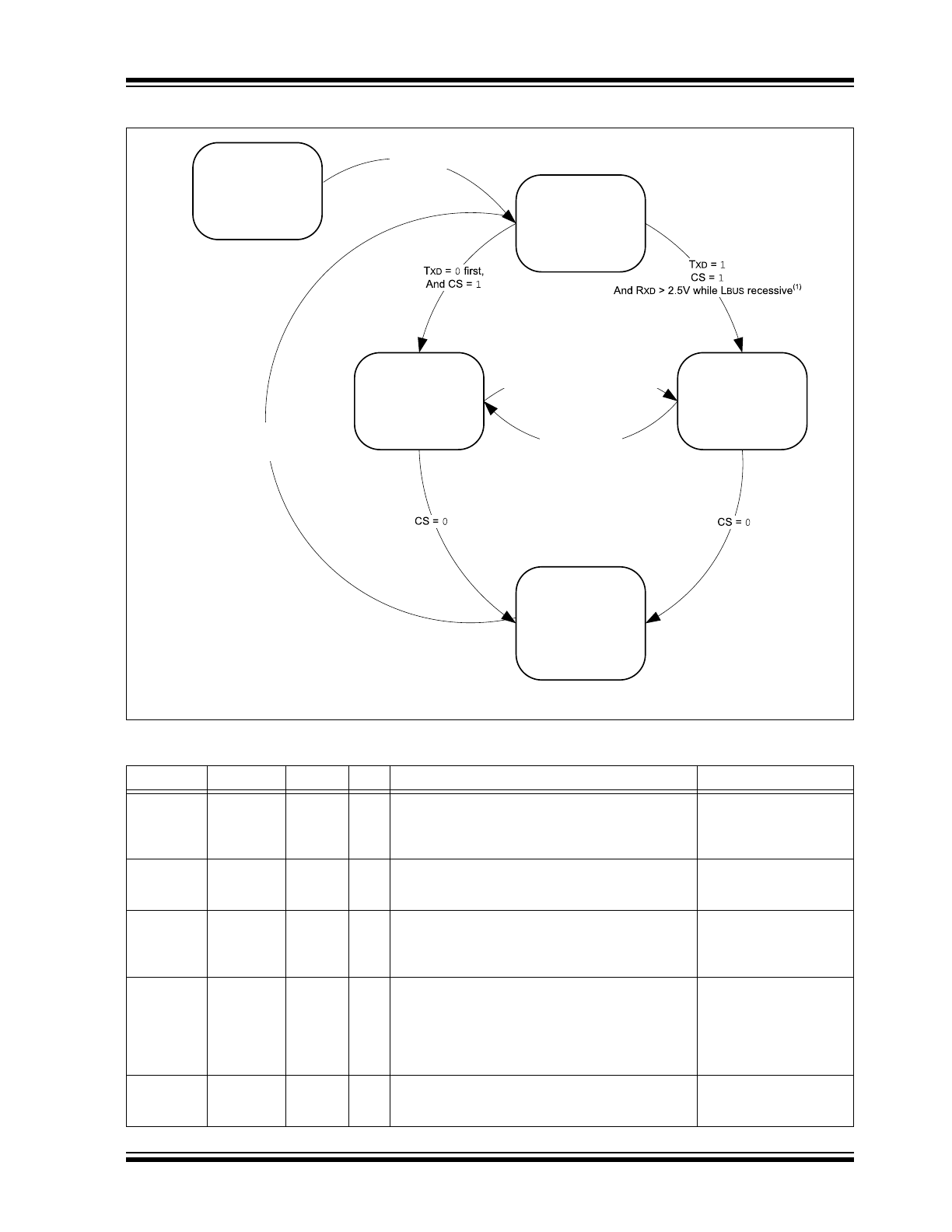
FIGURE 1-2:
OPERATIONAL MODES STATE DIAGRAM – MCP2003B
TABLE 1-1:
OVERVIEW OF OPERATIONAL MODES
State
Transmitter Receiver V
REN
Operation
Comments
POR
OFF
OFF
OFF Check CS: if low, then proceed to Ready mode;
If high, transition to either TOFF or Operation mode,
depending on T
XD
.
V
BB
> V
BB
(
MIN
) and
Internal Supply stable.
High ohmic pull-up resistor
enabled (900 k
typical).
Ready
OFF
ON
ON
On CS high level, proceed to Operation or TOFF mode.
Bus Off state.
High ohmic pull-up resistor
enabled (900 k
typical).
Operation
ON
ON
ON
On CS low level, proceed to Power-Down.
On a fault condition, proceed to TOFF mode.
Normal Operation mode.
R
XD
has to be at a high
level (>2.5V typical) while
L
BUS
is recessive.
Power-Down
OFF
Activity
Detect
OFF On CS high level, proceed to Ready mode then
proceed to either Operation or TOFF mode.
Falling edge on WAKE will put the device into
Ready mode.
Rising edge on LIN bus will put the device into
Ready mode.
Low-Power mode.
High ohmic pull-up resistor
enabled (900 k
typical).
Transmitter
Off
OFF
ON
ON
On CS low level, proceed to Power-Down mode;
On T
XD
high and no fault condition, proceed to
Operation mode.
High ohmic pull-up resistor
enabled (900k
typical).
Rising Edge on LBUS or
CS =
1 or
Falling Edge on WAKE pin
T
XD
=
1 And CS = 1
NO Fault,
And R
XD
> 2.5V while L
BUS
recessive
(1)
Fault:
Thermal or Timer
POR
V
REN
OFF
R
X
OFF
T
X
OFF
RPU switch OFF
Ready Mode
V
REN
ON
R
X
ON
T
X
OFF
RPU switch OFF
TOFF Mode
V
REN
ON
R
X
ON
T
X
OFF
RPU switch OFF
Operation Mode
V
REN
ON
R
X
ON
T
X
ON
RPU switch ON
Power-Down
Mode
V
REN
OFF
R
X
OFF
T
X
OFF
RPU switch OFF
V
BAT
>
V
BBUV_RISE
Note 1: Achieved via pull-up resistor on R
XD
(See
Example 1-1
)
MCP2003B
DS20005463C-page 6
2015-2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.4
Typical Applications
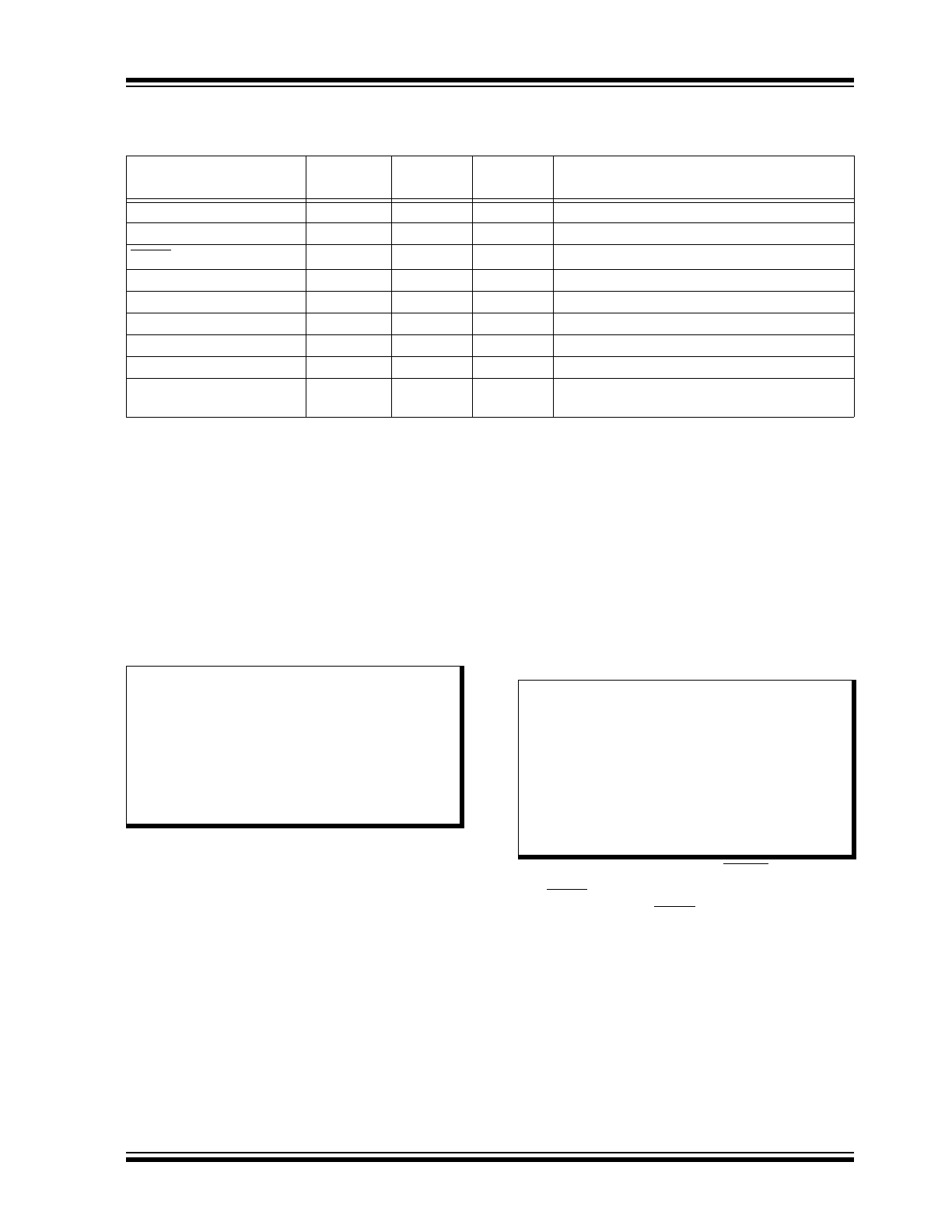
EXAMPLE 1-1:
TYPICAL MCP2003B APPLICATION
EXAMPLE 1-2:
TYPICAL LIN NETWORK CONFIGURATION
LIN Bus
V
BB
L
BUS
V
REN
T
XD
R
XD
V
SS
V
DD
T
XD
R
XD
V
BAT
1.0 µF
CS
I/O
WAKE
50
60V
1 k
V
BAT
Master Node Only
V
BAT
3.9 k
Wake-up
Voltage Reg
4.7 k
optional resistor and transient suppressor
33 k
220 pF
Note 1: For applications with current requirements of less than 20 mA, the connection to V
BAT
can be
deleted, and voltage to the regulator supplied directly from the V
REN
pin.
2: Required for transmission.
3: A Transient Voltage Suppressor on the LIN Bus is not required to sustain SAE J2962-1 ESD
and Direct Capacitor Coupling tests.
(
Note 1
)
(
2
)
Master
(MCU)
1 k
V
BB
Slave 1
(MCU)
Slave 2
(MCU)
Slave n <23
(MCU)
40m
+ Return
LIN bus
LIN bus
MCP2003B
LIN bus
MCP2003B
LIN bus
MCP2003B
LIN bus
MCP2003B
2015-2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005463C-page 7
MCP2003B
1.5
Pin Descriptions
1.5.1
RECEIVE DATA OUTPUT (R
XD
)
The Receive Data Output pin is an open-drain (OD)
output and follows the state of the LIN pin, except in
Power-Down mode.
1.5.1.1
R
XD
Monitoring
The
R
XD
pin is internally monitored. It has to be at a
high level (> 2.5V typical) while
L
BUS
is recessive
in
Operation mode
. Otherwise, an internal fault will be
created and the device will transition to Transmitter Off
mode.
1.5.2
CHIP SELECT (CS)
This is the Chip Select Input pin. An internal pull-down
resistor will keep the CS pin low. This is done to ensure
that no disruptive data will be present on the bus while
the microcontroller is executing a Power-on Reset and
an I/O initialization sequence. The pin must detect a
high level to activate the transmitter. An internal Low-
Pass filter, with a typical time constant of 10 µs,
prevents unwanted wake-up (or transition to Power-
Down mode) on glitches.
If CS = 0 when the V
BB
supply is turned on, the device
goes to Ready mode as soon as internal voltages sta-
bilize, and stays there as long as the CS pin is held low
(0). In Ready mode, the receiver is on and the LIN
transmitter driver is off.
If CS = 1 when the V
BB
supply is turned on, the device
will proceed to Operation mode, or T
XOFF
(refer to
Figure 1-2
), as soon as internal voltages stabilize.
This pin may also be used as a local wake-up input
(refer to
Example 1-1
). In this implementation, the
microcontroller I/O controlling the CS should be
converted to a high-impedance input allowing the
internal pull-down resistor to keep CS low. An external
switch, or other source, can then wake-up both the
transceiver and the microcontroller (if powered). Refer
to
Section 1.3 “Modes of Operation”
, for detailed
operation of CS.
1.5.3
WAKE-UP INPUT (WAKE)
The WAKE pin has an internal 800 kΩ pull-up to V
BB
.
A falling edge on the WAKE pin causes the device to
wake from Power-Down mode. Upon waking, the
MCP2003B will enter Ready mode.
1.5.4
TRANSMIT DATA INPUT (T
XD
)
The Transmit Data Input pin has an internal pull-up.
The LIN pin is low (dominant) when T
XD
is low, and high
(recessive) when T
XD
is high.
For extra bus security, T
XD
is internally forced to ‘1’
whenever the transmitter is disabled, regardless of
external T
XD
voltage.
TABLE 1-2:
PINOUT DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Name
8-Lead
SOIC
2x3 DFN
3x3 DFN
Normal Operation
R
XD
1
1
1
Receive Data Output (OD), HV tolerant
CS
2
2
2
Chip Select (TTL), HV tolerant
WAKE
3
3
3
Wake-up, HV tolerant
T
XD
4
4
4
Transmit Data Input (TTL), HV tolerant
V
SS
5
5
5
Ground
L
BUS
6
6
6
LIN Bus (bidirectional)
V
BB
7
7
7
Battery Positive
V
REN
8
8
8
Voltage Regulator Enable Output
EP
—
9
9
Exposed Thermal Pad. Do not electrically
connect or connect to Vss.
Legend: TTL = TTL Input Buffer; OD = Open-Drain Output
Note:
A voltage regulator sensing circuit is
connected to R
XD
. This sensing circuit
internally monitors the RXD pin when
LBUS is recessive (RXD = 1). It will not
allow the device to switch (or stay) in
Operation Mode if the RXD pin is left
open. The RXD pin must be connected to
a valid supply through a pull-up resistor as
RXD is an open drain pin.
Note:
It is not recommended to tie CS high, as
this can result in the device entering
Operation mode before the
microcontroller is initialized and may
result in unintentional LIN traffic. The CS
pin is internally pulled down to ground with
190 k
when CS is less than V
IL
, and
2 M
when CS is greater than V
IH
. The
current on CS is limited to about 2 µA
when CS is greater than V
IH
.

MCP2003B
DS20005463C-page 8
2015-2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.5.4.1
T
XD
Dominant Timeout
If T
XD
is driven low for longer than approximately
25 ms, the L
BUS
pin is switched to Recessive mode and
the part enters TOFF Mode. This is to prevent the LIN
node from permanently driving the LIN Bus dominant.
The transmitter is reenabled on T
XD
rising edge.
1.5.5
GROUND (V
SS
)
This is the Ground pin.
1.5.6
LIN BUS (L
BUS
)
The bidirectional LIN Bus pin (L
BUS
) is controlled by the
T
XD
input. L
BUS
has a current limited open collector
output. To reduce EMI, the edges during the signal
changes are slope controlled and include corner
rounding control for both falling and rising edges.
The internal LIN receiver observes the activities on the
LIN bus, and matches the output signal R
XD
to follow
the state of the L
BUS
pin.
1.5.6.1
Bus Dominant Timer
The Bus Dominant Timer is an internal timer that
deactivates the L
BUS
transmitter after approximately
25 ms of dominant state on the L
BUS
pin. The timer is
reset on any recessive L
BUS
state.
The LIN bus transmitter will be reenabled after a
recessive state on the L
BUS
pin as long as CS is high.
Disabling can be caused by the LIN bus being
externally held dominant, or by T
XD
being driven low.
1.5.7
BATTERY (V
BB
)
This is the Battery Positive Supply Voltage pin.
1.5.8
VOLTAGE REGULATOR ENABLE
OUTPUT (V
REN
)
This is the External Voltage Regulator Enable pin.
Open-drain output is pulled high to V
BB
in all modes
except Power-Down.
1.5.9
EXPOSED THERMAL PAD (EP)
Do not electrically connect, or connect to V
SS
.

2015-2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005463C-page 9
MCP2003B
2.0
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
2.1
Absolute Maximum Ratings†
V
IN
DC Voltage on R
XD
, T
XD
, CS ...................................................................................................................-0.3 to +50V
V
IN
DC Voltage on WAKE and V
REN
..............................................................................................................-0.3 to +V
BB
V
BB
Battery Voltage, continuous, non-operating
(
1
)
........................................................................................-0.3 to +50V
V
BB
Battery Voltage, non-operating (LIN bus recessive)
(
2
)
............................................................................-0.3 to +60V
V
BB
Battery Voltage, transient ISO 7637 Test 1 ......................................................................................................-200V
V
BB
Battery Voltage, transient ISO 7637 Test 2a ...................................................................................................+150V
V
BB
Battery Voltage, transient ISO 7637 Test 3a ....................................................................................................-300V
V
BB
Battery Voltage, transient ISO 7637 Test 3b ...................................................................................................+200V
V
LBUS
Bus Voltage, continuous.......................................................................................................................-18 to +50V
V
LBUS
Bus Voltage, transient
(
3
)
.......................................................................................................................-27 to +60V
V
LBUS
Bus Voltage, Direct Capacitor Coupling without TVS (SAE J2962-1) ........................................... ±35V and ±85V
I
LBUS
Bus Short-Circuit Current Limit....................................................................................................................200 mA
ESD protection on LIN, without TVS (SAE J2962-1) ............................................................................................. ±25 kV
ESD protection on LIN, V
BB
, WAKE (IEC 61000-4-2)
(
4
)
.......................................................................................... ±6 kV
ESD protection on LIN, V
BB
, WAKE, CS (Human Body Model)
(
5
)
........................................................................... ±8 kV
ESD protection on all other pins (Human Body Model)
(
5
)
........................................................................................ ±4 kV
ESD protection on all pins (Charge Device Model)
(
6
)
.............................................................................................. ±2 kV
ESD protection on all pins (Machine Model)
(
7
)
.......................................................................................................±400V
Maximum Junction Temperature........................................................................................................................... +150
C
Storage Temperature ..................................................................................................................................-65 to +150
C
Note 1: LIN 2.x compliant specification.
2: SAE J2602 compliant specification.
3: ISO 7637/1 load dump compliant (t < 500 ms).
4: According to IEC 61000-4-2, 330
, 150 pF and Transceiver EMC Test Specifications [2] to [4]. For WAKE
pin to meet the specification, series resistor must be in place (refer to
Example 1-2
).
5: According to AEC-Q100-002/JESD22-A114.
6: According to AEC-Q100-011B.
7: According to AEC-Q100-003/JESD22-A115.
† NOTICE: Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the
device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device, at those or any other conditions above those
indicated in the operational listings of this specification, is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability.
MCP2003B
DS20005463C-page 10
2015-2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
2.2
Nomenclature Used in This Document
Some terms and names used in this data sheet deviate from those referred to in the LIN specifications. Equivalent
values are shown in
Table 2-1
.
TABLE 2-1:
EQUIVALENT VALUES
LIN specifications Name
Term used in the following tables
Definition
V
BAT
not used
ECU operating voltage
V
SUP
V
BB
Supply voltage at device pin
I
BUS
_
LIM
I
SC
Current Limit of driver
V
BUSREC
V
IH
(L
BUS
)
Recessive state
V
BUSDOM
V
IL
(L
BUS
)
Dominant state
2.3
DC Specifications
DC Specifications
Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise indicated, all limits are specified for
V
BB
= 5.5V to 30.0V
Extended (E): T
A
= -40°C to +125°C
High (H): T
A
= -40°C to +150°C
Parameter
Sym.
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Conditions
Power
V
BB
Quiescent Operating
Current
I
BBQ
—
65
150
µA
Operating Mode,
bus recessive
—
—
160
µA
V
BB
> 18V
V
BB
Transmitter-off Current
I
BBTO
—
60
120
µA
Transmitter off,
bus recessive
—
—
130
µA
V
BB
> 18V
V
BB
Power-Down Current
I
BBPD
—
6
15
µA
—
—
20
µA
V
BB
> 18V
—
14
20
µA
LIN bus shorted to GND
V
LIN
= 0V, V
BB
< 12V
V
BB
Current
with V
SS
Floating
I
BBNOGND
-1
—
1
mA
V
BB
= 12V, GND to V
BB
,
V
LIN
= 0-27V
V
BB
Undervoltage
Threshold (switching from
Operation mode to TOFF
and V
REN
OFF)
V
BB
UV_FALL
3.8
4
4.4
V
V
BB
falling (
Note 3
)
V
BB
Undervoltage
Recovery Threshold
(switching from POR to
Ready mode)
V
BB
UV_RISE
5.5
5.6
6.0
V
V
BB
rising (
Note 3
)
Microcontroller Interface
High-Level Input Voltage
(T
XD
)
V
IH
2.0 —
30
V
Low-Level Input Voltage
(T
XD
)
V
IL
-0.3
—
0.8
V
High-Level Input Current
(T
XD
)
I
IH
-5
—
—
µA
Input voltage = 4.0V
Note 1:
Internal current limited. 2.0 ms maximum recovery time (R
LBUS
= 0
, T
X
= 0.4 V
REG
, V
LBUS
= V
BB
).
2:
Node has to sustain the current that can flow under this condition; bus must be operational under this
condition.
3:
Characterized; not 100% tested.
