2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS22008E-page 1
MCP1702
Features:
• 2.0 µA Quiescent Current (typical)
• Input Operating Voltage Range: 2.7V to 13.2V
• 250 mA Output Current for Output Voltages
2.5V
• 200 mA Output Current for Output Voltages < 2.5V
• Low Dropout (LDO) Voltage
- 625 mV typical @ 250 mA (V
OUT
= 2.8V)
• 0.4% Typical Output Voltage Tolerance
• Standard Output Voltage Options:
- 1.2V, 1.5V, 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.8V,
3.0V, 3.3V, 4.0V, 5.0V
• Output Voltage Range 1.2V to 5.5V in 0.1V
Increments (50 mV increments available upon
request)
• Stable with 1.0 µF to 22 µF Output Capacitor
• Short-Circuit Protection
• Overtemperature Protection
Applications:
• Battery-powered Devices
• Battery-powered Alarm Circuits
• Smoke Detectors
• CO
2
Detectors
• Pagers and Cellular Phones
• Smart Battery Packs
• Low Quiescent Current Voltage Reference
• PDAs
• Digital Cameras
• Microcontroller Power
• Solar-Powered Instruments
• Consumer Products
• Battery Powered Data Loggers
Related Literature:
• AN765, “Using Microchip’s Micropower LDOs”,
DS00765, Microchip Technology Inc., 2002
• AN766, “Pin-Compatible CMOS Upgrades to
Bipolar LDOs”, DS00766,
Microchip Technology Inc., 2002
• AN792, “A Method to Determine How Much
Power a SOT-23 Can Dissipate in an Application”,
DS00792, Microchip Technology Inc., 2001
Description:
The MCP1702 is a family of CMOS low dropout (LDO)
voltage regulators that can deliver up to 250 mA of
current while consuming only 2.0 µA of quiescent
current (typical). The input operating range is specified
from 2.7V to 13.2V, making it an ideal choice for two to
six primary cell battery-powered applications, 9V
alkaline and one or two cell Li-Ion-powered
applications.
The MCP1702 is capable of delivering 250 mA with
only 625 mV (typical) of input to output voltage
differential (V
OUT
= 2.8V). The output voltage tolerance
of the MCP1702 is typically ±0.4% at +25°C and ±3%
maximum over the operating junction temperature
range of -40°C to +125°C. Line regulation is ±0.1%
typical at +25°C.
Output voltages available for the MCP1702 range from
1.2V to 5.0V. The LDO output is stable when using only
1 µF of output capacitance. Ceramic, tantalum or
aluminum electrolytic capacitors can all be used for
input and output. Overcurrent limit and
overtemperature shutdown provide a robust solution
for any application.
Package options include the SOT-23A, SOT-89-3, and
TO-92.
Package Types
1
3
2
V
IN
GND V
OUT
MCP1702
1
2
3
V
IN
GND
V
OUT
MCP1702
3-Pin SOT-23A
3-Pin SOT-89
V
IN
3-Pin TO-92
1 2
V
OUT
V
IN
GND
Bottom
View
3
250 mA Low Quiescent Current LDO Regulator
MCP1702
DS22008E-page 2
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
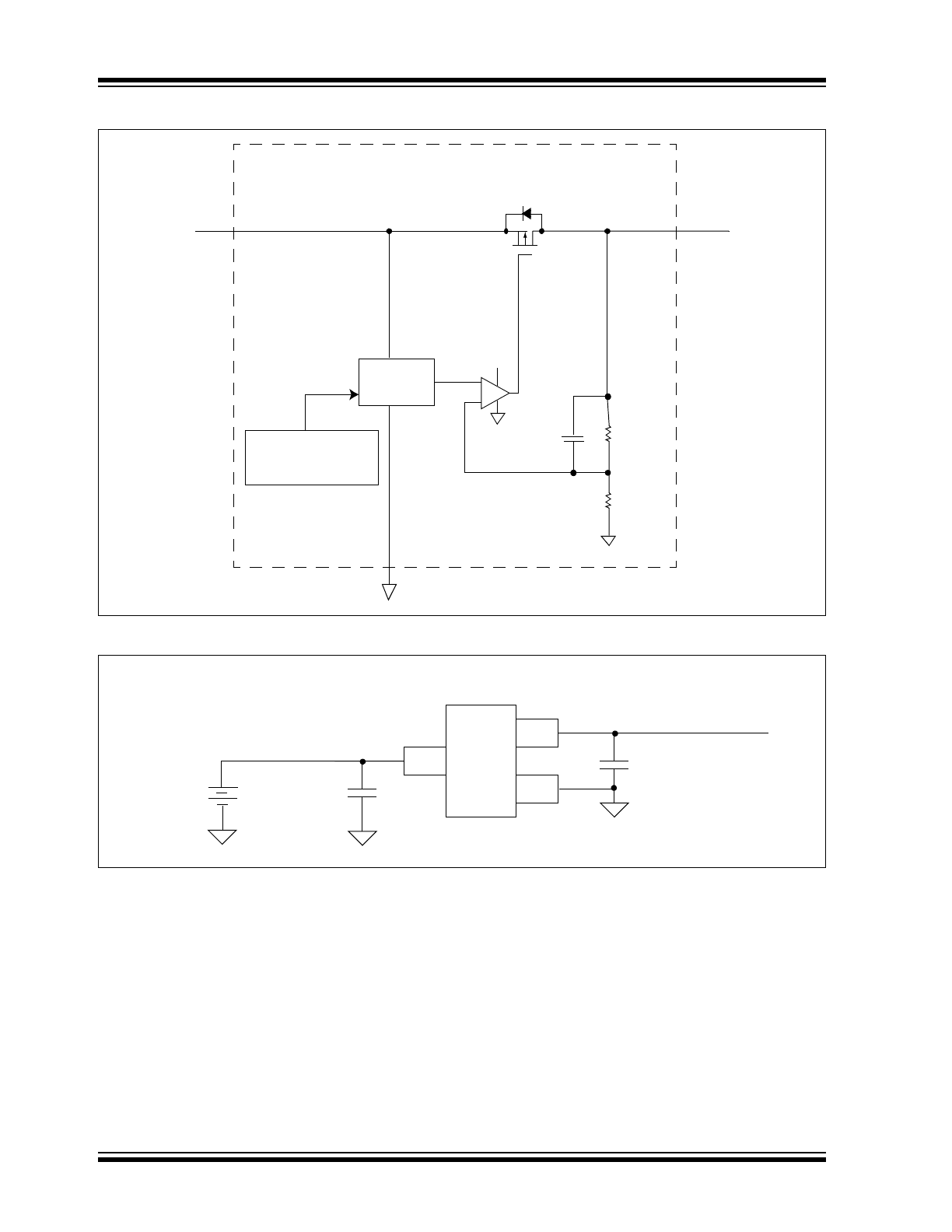
Functional Block Diagrams
Typical Application Circuits
+
-
MCP1702
V
IN
V
OUT
GND
+V
IN
Error Amplifier
Voltage
Reference
Overcurrent
Overtemperature
MCP1702
V
IN
C
IN
1 µF Ceramic
C
OUT
1 µF Ceramic
V
OUT
V
IN
3.3V
I
OUT
50 mA
GND
V
OUT
9V
Battery
+
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS22008E-page 3
MCP1702
1.0
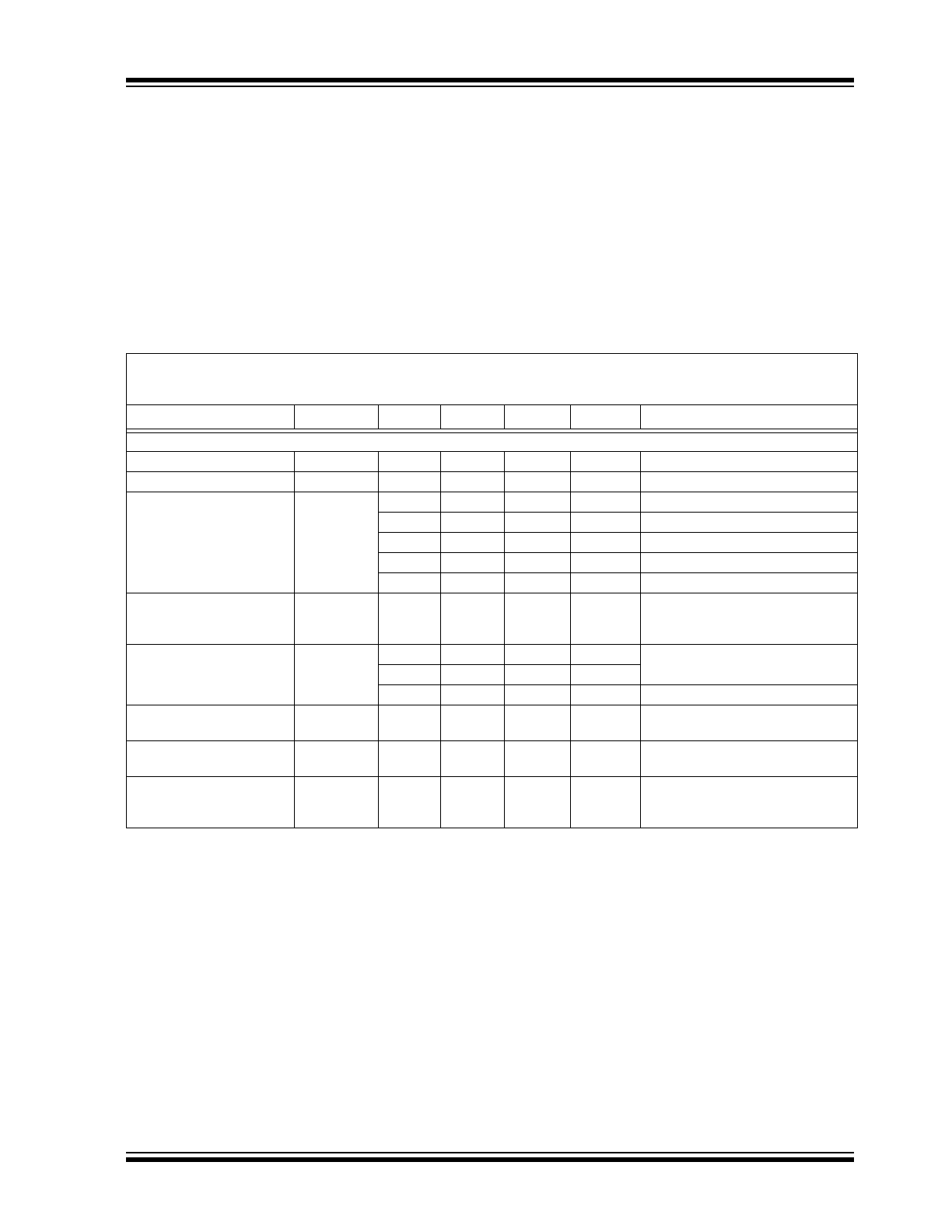
ELECTRICAL
CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings †
V
DD
...............................................................................+14.5V
All inputs and outputs w.r.t. .............(V
SS
-0.3V) to (V
IN
+0.3V)
Peak Output Current ...................................................500 mA
Storage temperature .....................................-65°C to +150°C
Maximum Junction Temperature ................................... 150°C
ESD protection on all pins (HBM;MM)
4 kV; 400V
† Notice: Stresses above those listed under “Maximum
Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is
a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at
those or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational listings of this specification is not implied.
Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended periods
may affect device reliability.
DC CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Specifications: Unless otherwise specified, all limits are established for V
IN
= V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
,
Note 1
,
I
LOAD
= 100 µA, C
OUT
= 1 µF (X7R), C
IN
= 1 µF (X7R), T
A
= +25°C.
Boldface type applies for junction temperatures, T
J
of -40°C to +125°C.
(
Note 7
)
Parameters
Sym
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
Input / Output Characteristics
Input Operating Voltage
V
IN
2.7
—
13.2
V
Note 1
Input Quiescent Current
I
q
—
2.0
5
µA
I
L
= 0 mA
Maximum Output Current
I
OUT_mA
250
—
—
mA
For V
R
2.5V
50
100
—
mA
For V
R
< 2.5V, V
IN
2.7V
100
130
—
mA
For V
R
< 2.5V, V
IN
2.95V
150
200
—
mA
For V
R
< 2.5V, V
IN
3.2V
200
250
—
mA
For V
R
< 2.5V, V
IN
3.45V
Output Short Circuit Current
I
OUT_SC
—
400
—
mA
V
IN
= V
IN(MIN)
(
Note 1
), V
OUT
= GND,
Current (average current) measured
10 ms after short is applied.
Output Voltage Regulation
V
OUT
V
R
-3.0%
V
R
±0.4%
V
R
+3.0%
V
Note 2
V
R
-2.0%
V
R
±0.4%
V
R
+2.0%
V
V
R
-1.0%
V
R
±0.4%
V
R
+1.0%
V
1% Custom
V
OUT
Temperature
Coefficient
TCV
OUT
—
50
—
ppm/°C
Note 3
Line Regulation
V
OUT
/
(V
OUT
X
V
IN
)
-0.3
±0.1
+0.3
%/V
(V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
)
V
IN
13.2V, (
Note 1
)
Load Regulation
V
OUT
/V
OUT
-2.5
±1.0
+2.5
%
I
L
= 1.0 mA to 250 mA for V
R
2.5V
I
L
= 1.0 mA to 200 mA for V
R
2.5V,
V
IN
= 3.45V (
Note 4
)
Note 1:
The minimum V
IN
must meet two conditions: V
IN
2.7V and V
IN
V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
.
2:
V
R
is the nominal regulator output voltage. For example: V
R
= 1.2V, 1.5V, 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.8V, 3.0V, 3.3V, 4.0V, or 5.0V. The
input voltage V
IN
= V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
or V
IN
= 2.7V (whichever is greater); I
OUT
= 100 µA.
3:
TCV
OUT
= (V
OUT-HIGH
- V
OUT-LOW
) *10
6
/ (V
R
*
Temperature), V
OUT-HIGH
= highest voltage measured over the
temperature range. V
OUT-LOW
= lowest voltage measured over the temperature range.
4:
Load regulation is measured at a constant junction temperature using low duty cycle pulse testing. Changes in output
voltage due to heating effects are determined using thermal regulation specification TCV
OUT
.
5:
Dropout voltage is defined as the input to output differential at which the output voltage drops 2% below its measured
value with an applied input voltage of V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
or 2.7V, whichever is greater.
6:
The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of ambient temperature, the maximum allowable junction
temperature and the thermal resistance from junction to air (i.e., T
A
, T
J
,
JA
). Exceeding the maximum allowable power
dissipation will cause the device operating junction temperature to exceed the maximum 150°C rating. Sustained
junction temperatures above 150°C can impact the device reliability.
7:
The junction temperature is approximated by soaking the device under test at an ambient temperature equal to the
desired Junction temperature. The test time is small enough such that the rise in the Junction temperature over the
ambient temperature is not significant.
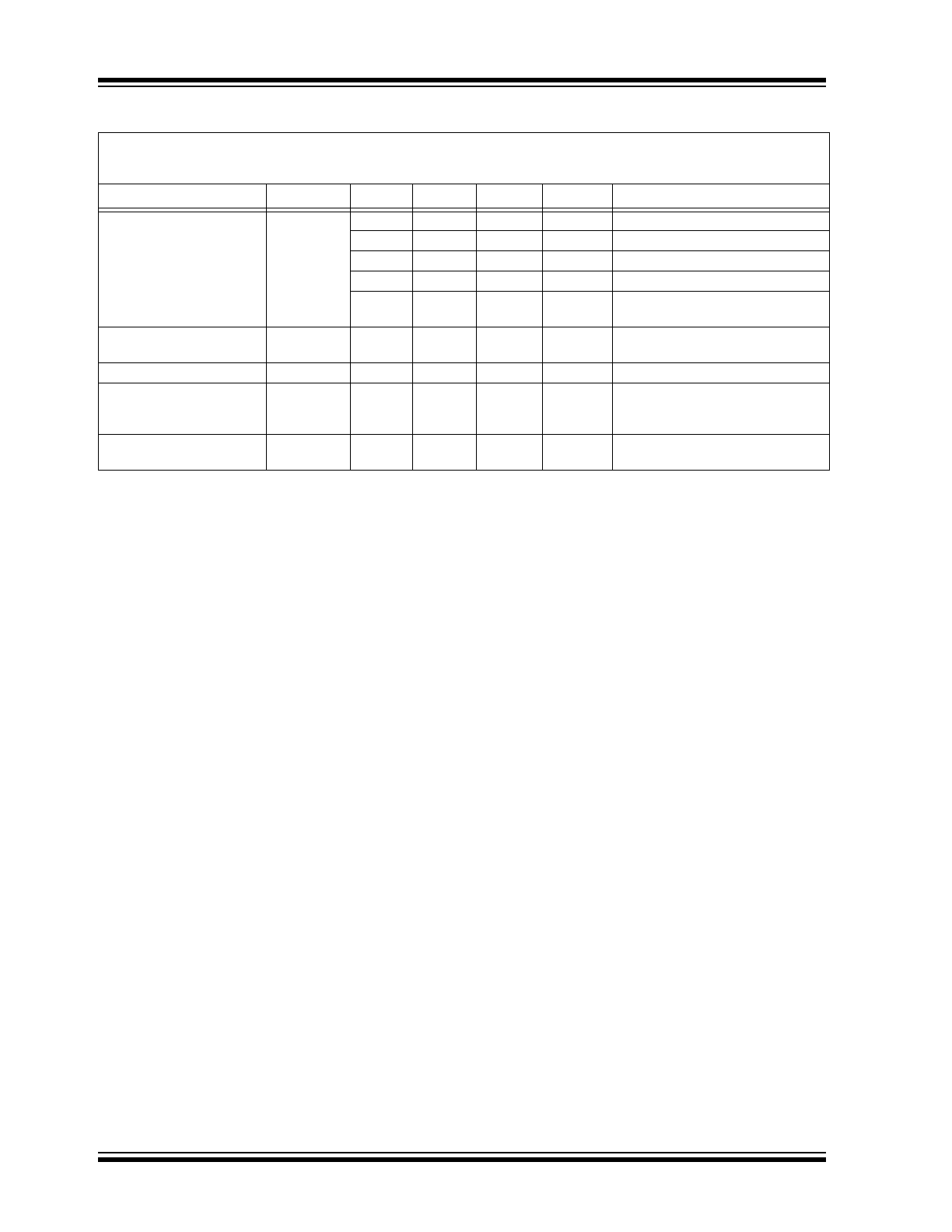
MCP1702
DS22008E-page 4
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
Dropout Voltage
(
Note 1
,
Note 5
)
V
DROPOUT
—
330
650
mV
I
L
= 250 mA, V
R
= 5.0V
—
525
725
mV
I
L
= 250 mA, 3.3V
V
R
< 5.0V
—
625
975
mV
I
L
= 250 mA, 2.8V
V
R
< 3.3V
—
750
1100
mV
I
L
= 250 mA, 2.5V
V
R
< 2.8V
—
—
—
mV
V
R
< 2.5V, See Maximum Output
Current Parameter
Output Delay Time
T
DELAY
—
1000
—
µs
V
IN
= 0V to 6V, V
OUT
= 90% V
R
R
L
= 50
resistive
Output Noise
e
N
—
8
—
µV/(Hz)
1/2
I
L
= 50 mA, f = 1 kHz, C
OUT
= 1 µF
Power Supply Ripple
Rejection Ratio
PSRR
—
44
—
dB
f = 100 Hz, C
OUT
= 1 µF, I
L
= 50 mA,
V
INAC
= 100 mV pk-pk, C
IN
= 0 µF,
V
R
= 1.2V
Thermal Shutdown
Protection
T
SD
—
150
—
°C
DC CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED)
Electrical Specifications: Unless otherwise specified, all limits are established for V
IN
= V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
,
Note 1
,
I
LOAD
= 100 µA, C
OUT
= 1 µF (X7R), C
IN
= 1 µF (X7R), T
A
= +25°C.
Boldface type applies for junction temperatures, T
J
of -40°C to +125°C.
(
Note 7
)
Parameters
Sym
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
Note 1:
The minimum V
IN
must meet two conditions: V
IN
2.7V and V
IN
V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
.
2:
V
R
is the nominal regulator output voltage. For example: V
R
= 1.2V, 1.5V, 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.8V, 3.0V, 3.3V, 4.0V, or 5.0V. The
input voltage V
IN
= V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
or V
IN
= 2.7V (whichever is greater); I
OUT
= 100 µA.
3:
TCV
OUT
= (V
OUT-HIGH
- V
OUT-LOW
) *10
6
/ (V
R
*
Temperature), V
OUT-HIGH
= highest voltage measured over the
temperature range. V
OUT-LOW
= lowest voltage measured over the temperature range.
4:
Load regulation is measured at a constant junction temperature using low duty cycle pulse testing. Changes in output
voltage due to heating effects are determined using thermal regulation specification TCV
OUT
.
5:
Dropout voltage is defined as the input to output differential at which the output voltage drops 2% below its measured
value with an applied input voltage of V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
or 2.7V, whichever is greater.
6:
The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of ambient temperature, the maximum allowable junction
temperature and the thermal resistance from junction to air (i.e., T
A
, T
J
,
JA
). Exceeding the maximum allowable power
dissipation will cause the device operating junction temperature to exceed the maximum 150°C rating. Sustained
junction temperatures above 150°C can impact the device reliability.
7:
The junction temperature is approximated by soaking the device under test at an ambient temperature equal to the
desired Junction temperature. The test time is small enough such that the rise in the Junction temperature over the
ambient temperature is not significant.
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS22008E-page 5
MCP1702
TEMPERATURE SPECIFICATIONS (
Note 1
)
Parameters
Sym
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
Temperature Ranges
Operating Junction Temperature Range
T
J
-40
+125
°C
Steady State
Maximum Junction Temperature
T
J
—
+150
°C
Transient
Storage Temperature Range
T
A
-65
+150
°C
Thermal Package Resistance (
Note 2
)
Thermal Resistance, 3L-SOT-23A
JA
—
336
—
°C/W
EIA/JEDEC JESD51-7
FR-4 0.063 4-Layer Board
JC
—
110
—
°C/W
Thermal Resistance, 3L-SOT-89
JA
—
153.3
—
°C/W
EIA/JEDEC JESD51-7
FR-4 0.063 4-Layer Board
JC
—
100
—
°C/W
Thermal Resistance, 3L-TO-92
JA
—
131.9
—
°C/W
JC
—
66.3
—
°C/W
Note 1:
The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of ambient temperature, the maximum allowable junction
temperature and the thermal resistance from junction to air (i.e., T
A
, T
J
,
JA
). Exceeding the maximum allowable power
dissipation will cause the device operating junction temperature to exceed the maximum 150°C rating. Sustained
junction temperatures above 150°C can impact the device reliability.
2:
Thermal Resistance values are subject to change. Please visit the Microchip web site for the latest packaging
information.
MCP1702
DS22008E-page 6
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
2.0
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
Note: Unless otherwise indicated: V
R
= 2.8V, C
OUT
= 1 µF Ceramic (X7R), C
IN
= 1 µF Ceramic (X7R), I
L
= 100 µA,
T
A
= +25°C, V
IN
= V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
.
Note: Junction Temperature (T
J
) is approximated by soaking the device under test to an ambient temperature equal to the desired junction
temperature. The test time is small enough such that the rise in Junction temperature over the Ambient temperature is not significant.
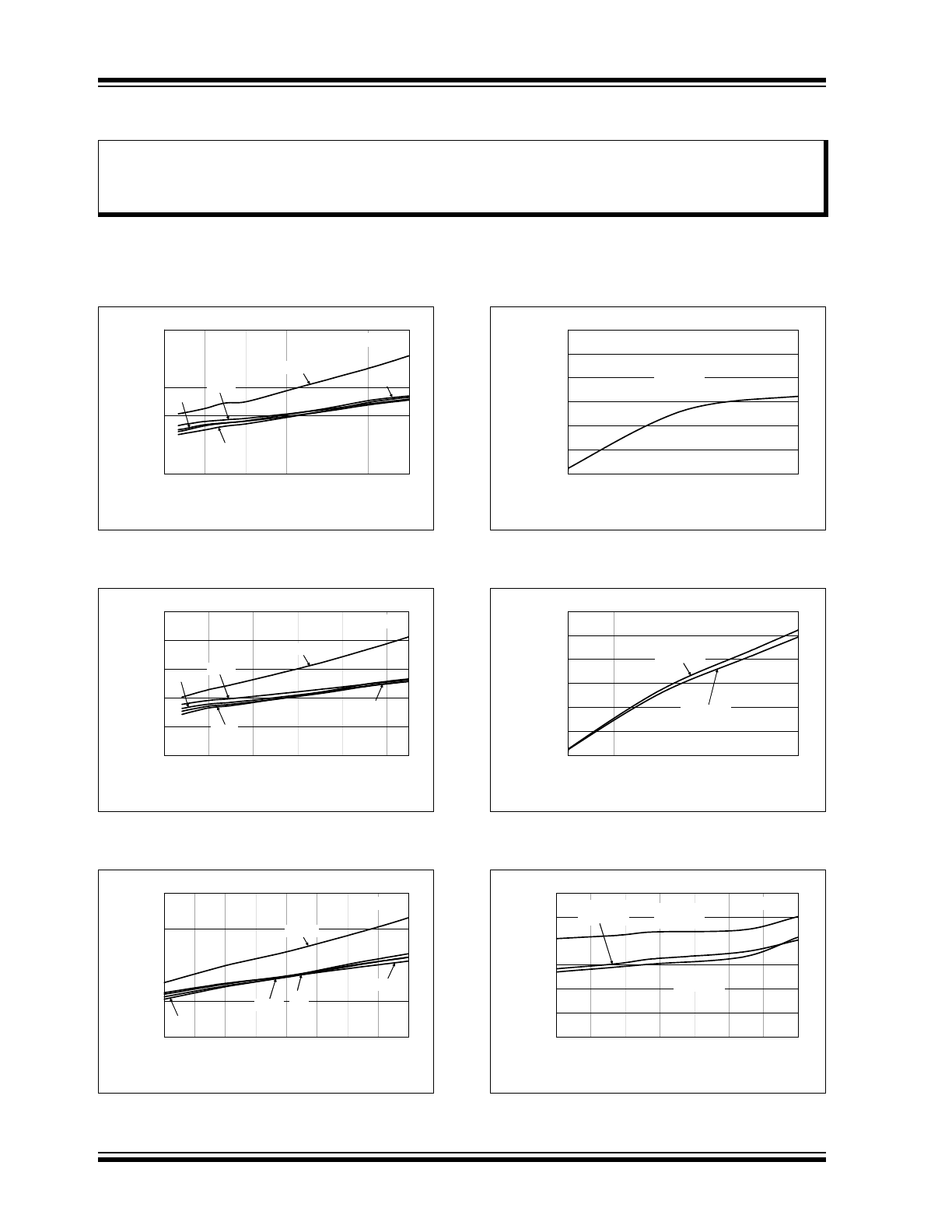
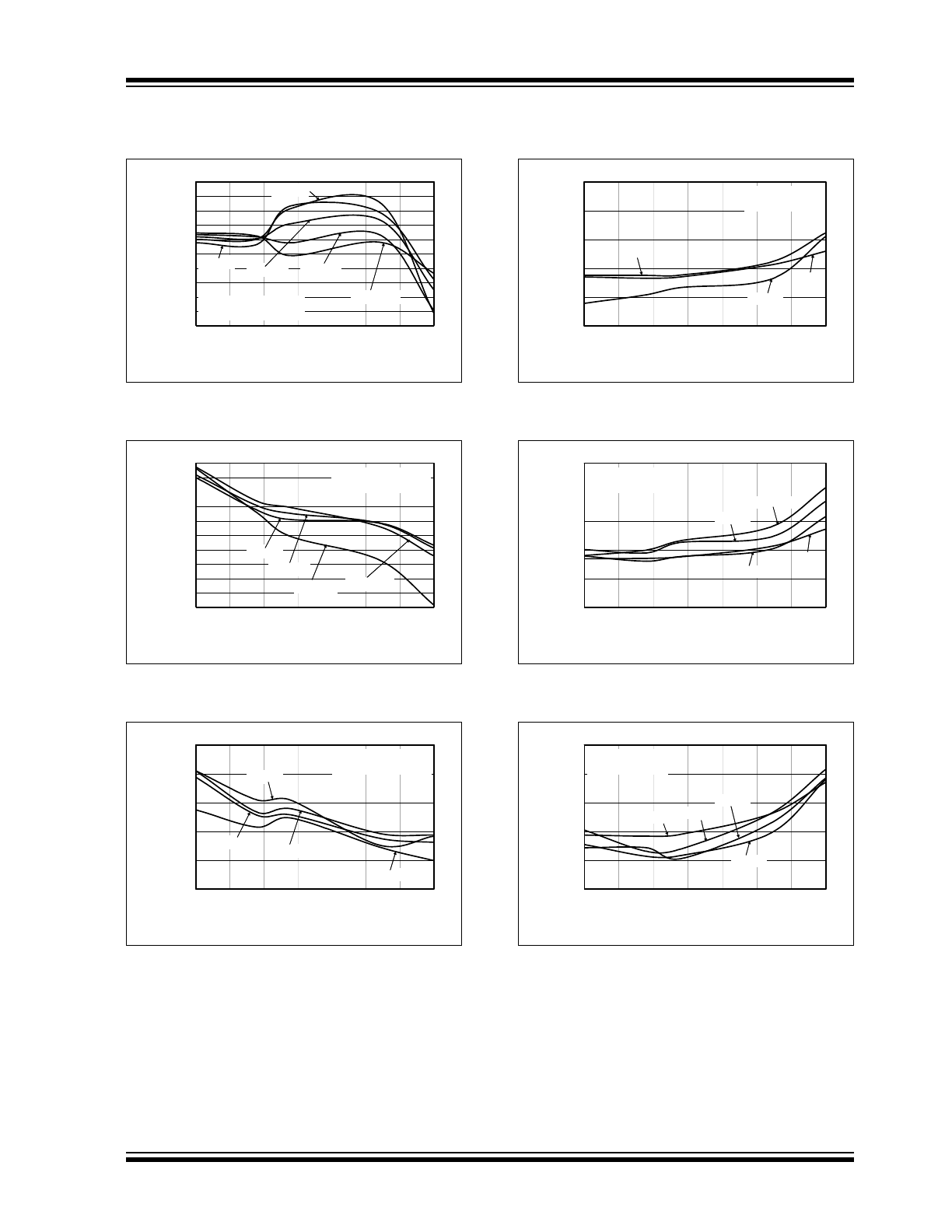
FIGURE 2-1:
Quiescent Current vs. Input
Voltage.
FIGURE 2-2:
Quiescent Current vs.Input
Voltage.
FIGURE 2-3:
Quiescent Current vs.Input
Voltage.
FIGURE 2-4:
Ground Current vs. Load
Current.
FIGURE 2-5:
Ground Current vs. Load
Current.
FIGURE 2-6:
Quiescent Current vs.
Junction Temperature.
Note:
The graphs and tables provided following this note are a statistical summary based on a limited number of
samples and are provided for informational purposes only. The performance characteristics listed herein
are not tested or guaranteed. In some graphs or tables, the data presented may be outside the specified
operating range (e.g., outside specified power supply range) and therefore outside the warranted range.
0.00
1.00
2.00
3.00
4.00
5.00
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
Input Voltage (V)
Q
u
iesc
en
t C
u
rr
en
t
(µ
A
)
V
OUT
= 1.2V
+25°C
+130°C
-45°C
0°C
+90°C
0.00
1.00
2.00
3.00
4.00
5.00
3
5
7
9
11
13
Input Voltage (V)
Quie
s
c
ent C
u
rr
en
t (µA)
V
OUT
= 2.8V
+25°C
+130°C
-45°C
0°C
+90°C
1.00
2.00
3.00
4.00
5.00
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Input Voltage (V)
Q
u
ie
sc
ent
C
u
rr
e
nt
(
µ
A
)
V
OUT
= 5.0V
+25°C
+130°C
-45°C
0°C
+90°C
0.00
20.00
40.00
60.00
80.00
100.00
120.00
0
40
80
120
160
200
Load Current (mA)
GND Cu
rre
n
t (µ
A
)
Temperature = +25°C
V
OUT
= 1.2V
V
IN
= 2.7V
0.00
20.00
40.00
60.00
80.00
100.00
120.00
0
50
100
150
200
250
Load Current (mA)
GND Cu
rre
n
t (µ
A)
Temperature = +25°C
V
OUT
= 5.0V
V
IN
= 6.0V
V
OUT
= 2.8V
V
IN
= 3.8V
0.00
0.50
1.00
1.50
2.00
2.50
3.00
-45
-20
5
30
55
80
105
130
Junction Temperature (°C)
Qu
ie
sc
e
n
t Cu
rre
n
t (
µ
A)
I
OUT
= 0 mA
V
OUT
= 5.0V
V
IN
= 6.0V
V
OUT
= 1.2V
V
IN
= 2.7V
V
OUT
= 2.8V
V
IN
= 3.8V
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS22008E-page 7
MCP1702
Note: Unless otherwise indicated: V
R
= 2.8V, C
OUT
= 1 µF Ceramic (X7R), C
IN
= 1 µF Ceramic (X7R), I
L
= 100 µA,
T
A
= +25°C, V
IN
= V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
.
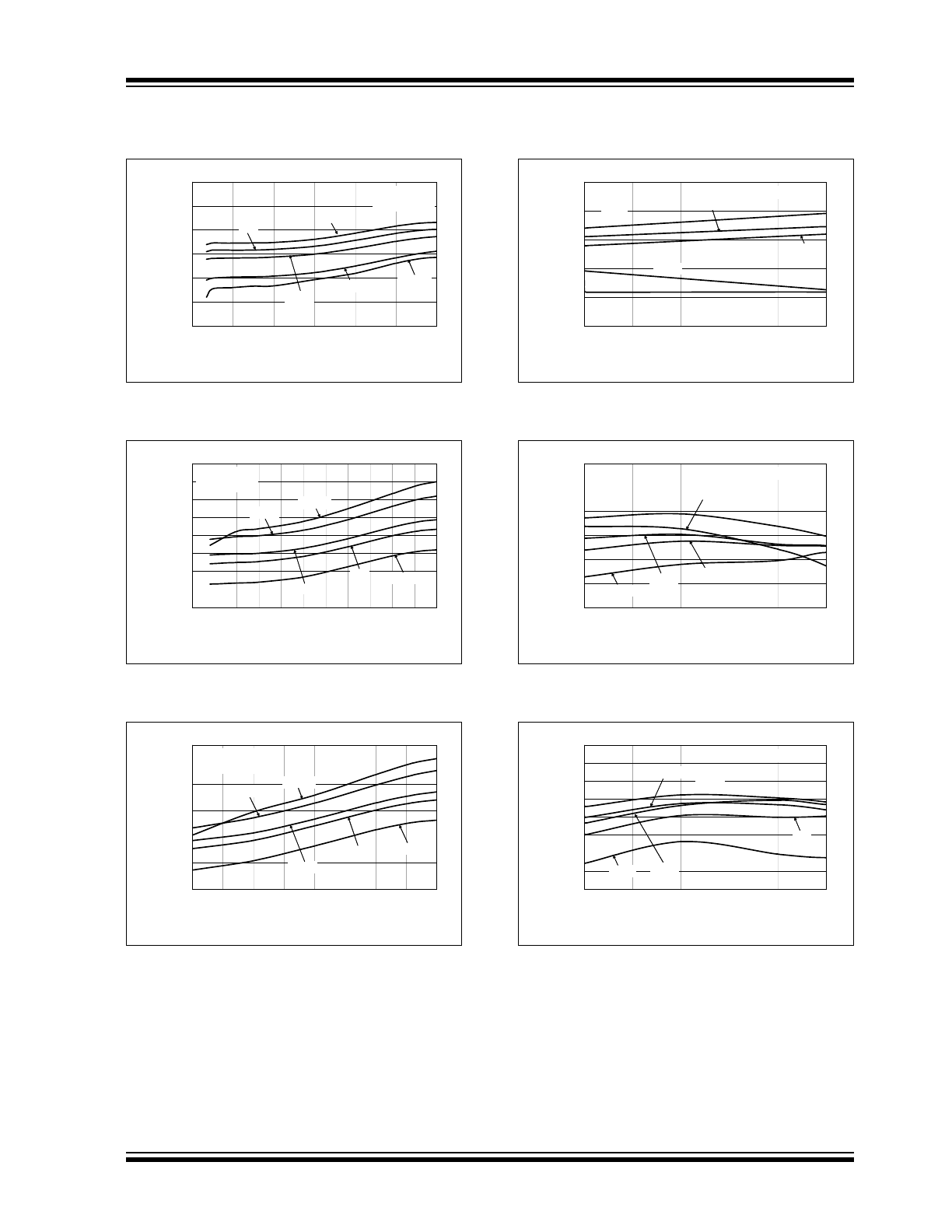
FIGURE 2-7:
Output Voltage vs. Input
Voltage.
FIGURE 2-8:
Output Voltage vs. Input
Voltage.
FIGURE 2-9:
Output Voltage vs. Input
Voltage.
FIGURE 2-10:
Output Voltage vs. Load
Current.
FIGURE 2-11:
Output Voltage vs. Load
Current.
FIGURE 2-12:
Output Voltage vs. Load
Current.
1.18
1.19
1.20
1.21
1.22
1.23
1.24
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
Input Voltage (V)
O
u
tput
Volt
age
(V)
V
OUT
= 1.2V
I
LOAD
= 0.1 mA
+25°C
+130°C
-45°C
0°C
+90°C
2.77
2.78
2.79
2.80
2.81
2.82
2.83
2.84
2.85
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11 12 13 14
Input Voltage (V)
O
u
tput V
o
lta
g
e
(V)
V
OUT
= 2.8V
I
LOAD
= 0.1 mA
+25°C
+130°C
-45°C
0°C
+90°C
4.96
4.98
5.00
5.02
5.04
5.06
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Input Voltage (V)
O
u
tput
Volt
age
(V)
V
OUT
= 5.0V
I
LOAD
= 0.1 mA
+25°C
+130°C
-45°C
0°C
+90°C
1.18
1.19
1.20
1.21
1.22
1.23
0
20
40
60
80
100
Load Current (mA)
O
u
tput
Volt
age
(V)
V
OUT
= 1.2V
+25°C
+130°C
-45°C
0°C
+90°C
2.77
2.78
2.79
2.80
2.81
2.82
2.83
0
50
100
150
200
250
Load Current (mA)
O
u
tput V
o
lta
g
e
(V)
V
OUT
= 2.8V
+25°C
+130°C
-45°C
0°C
+90°C
4.96
4.97
4.98
4.99
5.00
5.01
5.02
5.03
5.04
0
50
100
150
200
250
Load Current (mA)
O
u
tput
Volt
age
(V)
V
OUT
= 5.0V
+25°C
+130°C
-45°C
0°C
+90°C
MCP1702
DS22008E-page 8
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
Note: Unless otherwise indicated: V
R
= 2.8V, C
OUT
= 1 µF Ceramic (X7R), C
IN
= 1 µF Ceramic (X7R), I
L
= 100 µA,
T
A
= +25°C, V
IN
= V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
.
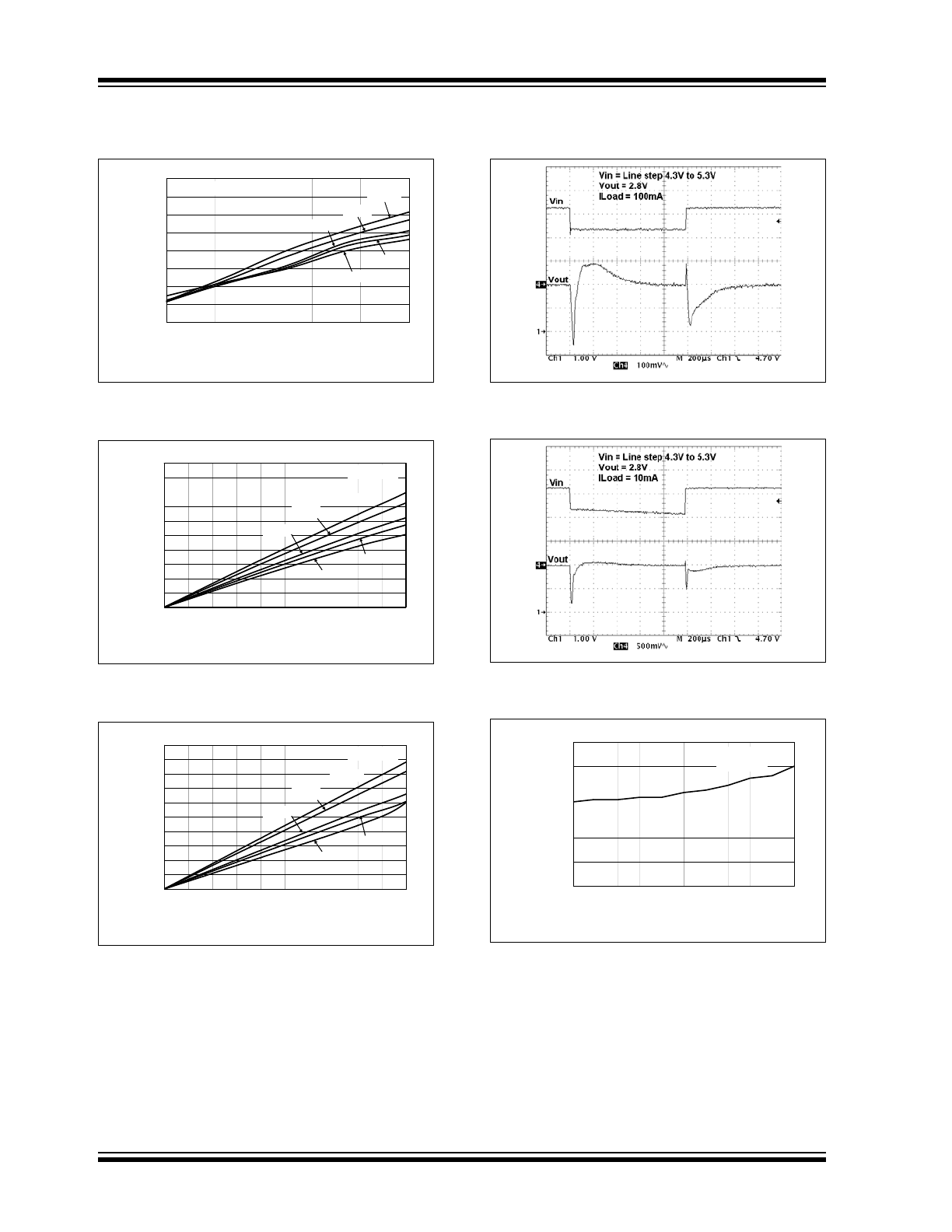
FIGURE 2-13:
Dropout Voltage vs. Load
Current.
FIGURE 2-14:
Dropout Voltage vs. Load
Current.
FIGURE 2-15:
Dropout Voltage vs. Load
Current.
FIGURE 2-16:
Dynamic Line Response.
FIGURE 2-17:
Dynamic Line Response.
FIGURE 2-18:
Short Circuit Current vs.
Input Voltage.
0.60
0.70
0.80
0.90
1.00
1.10
1.20
1.30
1.40
100
120
140
160
180
200
Load Current (mA)
D
ropou
t Vol
tage
(V)
V
OUT
= 1.8V
+25°C
+130°C
-45°C
0°C
+90°C
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.50
0.60
0.70
0.80
0.90
1.00
0
25
50
75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
Load Current (mA)
D
ropou
t Vol
tage
(V)
V
OUT
= 2.8V
+25°C
+130°C
+0°C
-45°C
+90°C
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
0.45
0.50
0
25
50
75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
Load Current (mA)
D
ropou
t Vol
tage
(V)
V
OUT
= 5.0V
+25°C
+130°C
+0°C
-45°C
+90°C
0.00
100.00
200.00
300.00
400.00
500.00
600.00
4
6
8
10
12
14
Input Voltage (V)
Short Circuit Current (mA)
V
OUT
= 2.8V
R
OUT
< 0.1
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS22008E-page 9
MCP1702
Note: Unless otherwise indicated: V
R
= 2.8V, C
OUT
= 1 µF Ceramic (X7R), C
IN
= 1 µF Ceramic (X7R), I
L
= 100 µA,
T
A
= +25°C, V
IN
= V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
.
FIGURE 2-19:
Load Regulation vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-20:
Load Regulation vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-21:
Load Regulation vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-22:
Line Regulation vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-23:
Line Regulation vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-24:
Line Regulation vs.
Temperature.
-0.30
-0.25
-0.20
-0.15
-0.10
-0.05
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
-45
-20
5
30
55
80
105
130
Temperature (°C)
Lo
ad R
egul
atio
n
(%
)
V
OUT
= 1.2V
I
LOAD
= 0.1 mA to 200 mA
V
IN
= 4V
V
IN
= 13.2V
V
IN
= 6V
V
IN
= 12V
V
IN
= 10V
-0.60
-0.50
-0.40
-0.30
-0.20
-0.10
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
-45
-20
5
30
55
80
105
130
Temperature (°C)
Lo
ad R
egul
atio
n
(%
)
V
OUT
= 2.8V
I
LOAD
= 1 mA to 250 mA
V
IN
= 3.8V
V
IN
= 13.2V
V
IN
= 10V
V
IN
= 6V
-0.10
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
-45
-20
5
30
55
80
105
130
Temperature (°C)
Lo
ad R
egul
atio
n
(%
)
V
OUT
= 5.0V
I
LOAD
= 1 mA to 250 mA
V
IN
= 6V
V
IN
= 13.2V
V
IN
= 8V
V
IN
= 10V
0.00
0.04
0.08
0.12
0.16
0.20
-45
-20
5
30
55
80
105
130
Temperature (°C)
Line
R
e
gu
lati
on
(%/
V
)
V
OUT
= 1.2V
V
IN
= 2.7V to 13.2V
1 mA
100 mA
0 mA
0.00
0.04
0.08
0.12
0.16
0.20
-45
-20
5
30
55
80
105
130
Temperature (°C)
Li
ne R
egula
tion
(%
/V)
V
OUT
= 2.8V
V
IN
= 3.8V to 13.2V
200 mA
100 mA
0 mA
250 mA
0.06
0.08
0.10
0.12
0.14
0.16
-45
-20
5
30
55
80
105
130
Temperature (°C)
Li
ne R
egula
tion
(%
/V)
V
OUT
= 5.0V
V
IN
= 6.0V to 13.2V
200 mA
100 mA
0 mA
250 mA
MCP1702
DS22008E-page 10
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
Note: Unless otherwise indicated: V
R
= 2.8V, C
OUT
= 1 µF Ceramic (X7R), C
IN
= 1 µF Ceramic (X7R), I
L
= 100 µA,
T
A
= +25°C, V
IN
= V
OUT(MAX)
+ V
DROPOUT(MAX)
.
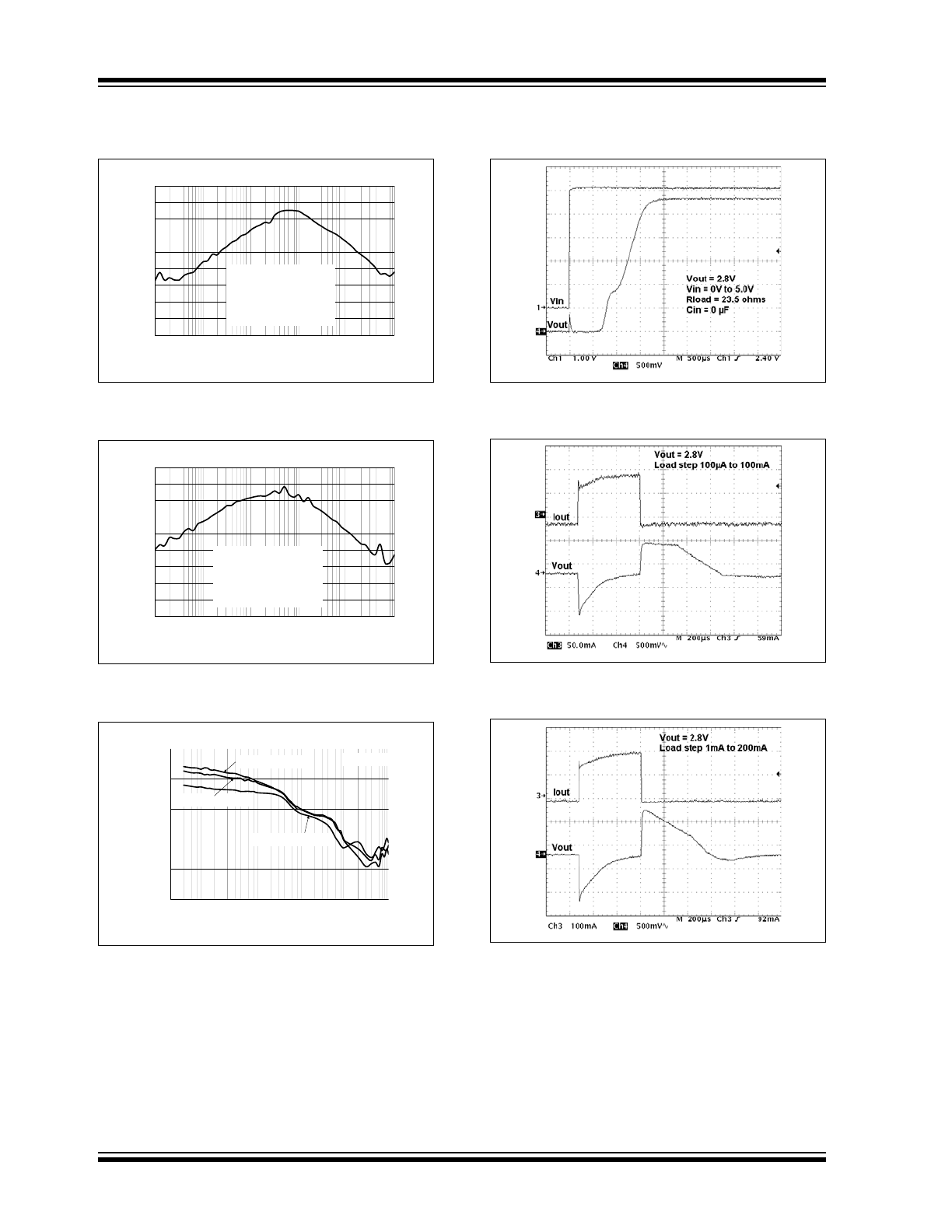
FIGURE 2-25:
Power Supply Ripple
Rejection vs. Frequency.
FIGURE 2-26:
Power Supply Ripple
Rejection vs. Frequency.
FIGURE 2-27:
Output Noise vs. Frequency.
FIGURE 2-28:
Power Up Timing.
FIGURE 2-29:
Dynamic Load Response.
FIGURE 2-30:
Dynamic Load Response.
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
1000
Frequency (kHz)
PS
RR
(d
B)
V
R
=1.2V
C
OUT
=1.0 μF ceramic X7R
V
IN
=2.7V
C
IN
=0 μF
I
OUT
=1.0 mA
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
1000
Frequency (kHz)
PS
RR
(d
B)
V
R
=5.0V
C
OUT
=1.0 μF ceramic X7R
V
IN
=6.0V
C
IN
=0 μF
I
OUT
=1.0 mA
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
1000
Frequency (kHz)
Noise (μV/Hz)
V
R
=5.0V, V
IN
=6.0V
I
OUT
=50 mA
V
R
=2,8V, V
IN
=3.8V
V
R
=1.2V, V
IN
=2.7V
