
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002134A-page 1
Target Applications
• Industrial Ethernet Applications that Employ IEEE
802.3-Compliant MACs. (Ethernet/IP, Profinet,
MODBUS TCP, etc.)
• VoIP Phone
• Set-Top/Game Box
• Automotive
• Industrial Control
• IPTV POF
• SOHO Residential Gateway with Full-Wire Speed
of Four LAN Ports
• Broadband Gateway/Firewall/VPN
• Integrated DSL/Cable Modem
• Wireless LAN Access Point + Gateway
• Standalone 10/100 Switch
• Networked Measurement and Control Systems
Features
• Management Capabilities
- The KSZ8794CNX Includes All the Functions
of a 10/100BASE-T/TX Switch System Which
Combines a Switch Engine, Frame Buffer
Management, Address Look-Up Table,
Queue Management, MIB Counters, Media
Access Controllers (MAC), and PHY Trans-
ceivers
- Non-Blocking Store-and-Forward Switch
Fabric Assures Fast Packet Delivery by Uti-
lizing a 1024-Entries Forwarding Table
- Port Mirroring/Monitoring/Sniffing: Ingress
and/or Egress Traffic to Any Port
- MIB Counters for Fully Compliant Statistics
Gathering (36 Counters per Port)
- Support Hardware for Port-Based Flush and
Freeze Command in MIB Counter.
- Multiple Loopback of Remote PHY, and MAC
Modes Support for the Diagnostics
- Rapid Spanning Tree Support (RSTP) for
Topology Management and Ring/Linear
Recovery
• Robust PHY Ports
- Four Integrated IEEE 802.3/802.3u-Compli-
ant Ethernet Transceivers Supporting
10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX
- IEEE 802.1az EEE Supported
- On-Chip Termination Resistors and Internal
Biasing for Differential Pairs to Reduce
Power
- HP Auto MDI/MDI-X Crossover Support Elim-
inates the Need to Differentiate Between
Straight or Crossover Cables in Applications
• MAC and GMAC Ports
- Three Internal Media Access Control (MAC1
to MAC3) Units and One Internal Gigabit
Media Access Control (GMAC4) Unit
- RGMII, MII, or RMII Interfaces Support for
the Port 4 GMAC4 with Uplink
- 2 KByte Jumbo Packet Support
- Tail Tagging Mode (One Byte Added Before
FCS) Support on Port 4 to Inform the Proces-
sor in which Ingress Port Receives the
Packet and its Priority
- Supports Reduced Media Independent Inter-
face (RMII) with 50 MHz Reference Clock
Output
- Supports Media Independent Interface (MII)
in Either PHY Mode or MAC Mode on Port 4
- LinkMD
®
Cable Diagnostic Capabilities for
Determining Cable Opens, Shorts, and
Length
• Advanced Switch Capabilities
- Non-Blocking Store-and-Forward Switch
Fabric Assures Fast Packet Delivery by Uti-
lizing a 1024-Entries Forwarding Table
- 64 KB Frame Buffer RAM
- IEEE 802.1q VLAN Support for up to 128
Active VLAN Groups (Full-Range 4096 of
VLAN IDs)
- IEEE 802.1p/Q Tag Insertion or Removal on
a Per Port Basis (Egress)
- VLAN ID Tag/Untag Options on Per Port
Basis
- Fully Compliant with IEEE 802.3/802.3u
Standards
- IEEE 802.3x Full-Duplex with Force-Mode
Option and Half-Duplex Back-Pressure Colli-
sion Flow Control
- IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
Support
- IGMP v1/v2/v3 Snooping for Multicast Packet
Filtering
KSZ8794CNX
Integrated 4-Port 10/100 Managed Ethernet
Switch with Gigabit RGMII/MII/RMII Interface

KSZ8794CNX
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002134A-page 2
- QoS/CoS Packets Prioritization Support:
802.1p, DiffServ-Based and Re-Mapping of
802.1p Priority Field Per Port Basis on Four
Priority Levels
- IPv4/IPv6 QoS Support
- IPv6 Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD)
Snooping
- Programmable Rate Limiting at the Ingress
and Egress Ports on a Per Port Basis
- Jitter-Free Per Packet Based Rate Limiting
Support
- Tail Tag Mode (1 byte Added before FCS)
Support on Port 4 to Inform the Processor
which Ingress Port Receives the Packet
- Broadcast Storm Protection with Percentage
Control (Global and Per Port Basis)
- 1K Entry Forwarding Table with 64 KB Frame
Buffer
- 4 Priority Queues with Dynamic Packet Map-
ping for IEEE 802.1P, IPv4 TOS (DIFF-
SERV), IPv6 Traffic Class, etc.
- Supports WoL Using AMD’s Magic Packet
- VLAN and Address Filtering
- Supports 802.1x Port-Based Security,
Authentication and MAC-Based Authentica-
tion via Access Control Lists (ACL)
- Provides Port-Based and Rule-Based ACLs
to Support Layer 2 MAC SA/DA Address,
Layer 3 IP Address and IP Mask, Layer 4
TCP/UDP Port Number, IP Protocol, TCP
Flag and Compensation for the Port Security
Filtering
- Ingress and Egress Rate Limit Based on Bit
per Second (bps) and Packet-Based Rate
Limiting (pps)
• Configuration Registers Access
- High-Speed SPI (4-Wire, up to 50 MHz) Inter-
face to Access All Internal Registers
- MII Management (MIIM, MDC/MDIO 2-Wire)
Interface to Access All PHY Registers per
Clause 22.2.4.5 of the IEEE 802.3 Specifica-
tion
- I/O Pin Strapping Facility to Set Certain Reg-
ister Bits from I/O Pins During Reset Time
- Control Registers Configurable On-the-Fly
• Power and Power Management
- Full-Chip Software Power-Down (All Register
Values are Not Saved and Strap-In Value Will
Re-Strap After it Releases the Power-Down)
- Per-Port Software Power-Down
- Energy Detect Power-Down (EDPD), which
Disables the PHY Transceiver When Cables
are Removed
- Supports IEEE P802.3az Energy Efficient
Ethernet (EEE) to Reduce Power Consump-
tion in Transceivers in LPI State Even
Though Cables are Not Removed
- Dynamic Clock Tree Control to Reduce
Clocking in Areas that are Not in Use
- Low Power Consumption without Extra
Power Consumption on Transformers
- Voltages: Using External LDO Power Sup-
plies
- Analog V
DDAT
3.3V or 2.5V
- V
DDIO
Support 3.3V, 2.5V, and 1.8V
- Low 1.2V Voltage for Analog and Digital Core
Power
- WoL Support with Configurable Packet Con-
trol
• Additional Features
- Single 25 MHz ±50 ppm Reference Clock
Requirement
- Comprehensive Programmable Two-LED
Indicator Support for Link, Activity, Full-/Half-
Duplex, and 10/100 Speed
• Packaging and Environmental
- Commercial Temperature Range: 0°C to
+70°C
- Industrial Temperature Range: –40°C to
+85°C
- Small Package Available in a Lead-Free,
RoHS-Compliant 64-Pin QFN
- 0.065 µm CMOS Technology for Lower
Power Consumption
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002134A-page 3
KSZ8794CNX
TO OUR VALUED CUSTOMERS
It is our intention to provide our valued customers with the best documentation possible to ensure successful use of your Microchip
products. To this end, we will continue to improve our publications to better suit your needs. Our publications will be refined and
enhanced as new volumes and updates are introduced.
If you have any questions or comments regarding this publication, please contact the Marketing Communications Department via
E-mail at
docerrors@microchip.com
. We welcome your feedback.
Most Current Data Sheet
To obtain the most up-to-date version of this data sheet, please register at our Worldwide Web site at:
http://www.microchip.com
You can determine the version of a data sheet by examining its literature number found on the bottom outside corner of any page.
The last character of the literature number is the version number, (e.g., DS30000000A is version A of document DS30000000).
Errata
An errata sheet, describing minor operational differences from the data sheet and recommended workarounds, may exist for cur-
rent devices. As device/documentation issues become known to us, we will publish an errata sheet. The errata will specify the
revision of silicon and revision of document to which it applies.
To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please check with one of the following:
• Microchip’s Worldwide Web site;
http://www.microchip.com
• Your local Microchip sales office (see last page)
When contacting a sales office, please specify which device, revision of silicon and data sheet (include -literature number) you are
using.
Customer Notification System
Register on our web site at
www.microchip.com
to receive the most current information on all of our products.

KSZ8794CNX
DS00002134A-page 4
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
Table of Contents
1.0 Introduction ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
2.0 Pin Description and Configuration ................................................................................................................................................... 6
3.0 Functional Description ................................................................................................................................................................... 12
4.0 Device Registers ........................................................................................................................................................................... 43
5.0 Operational Characteristics ......................................................................................................................................................... 106
6.0 Electrical Characteristics ............................................................................................................................................................. 107
7.0 Timing Diagrams .......................................................................................................................................................................... 109
8.0 Reset Circuit................................................................................................................................................................................. 117
9.0 Selection of Isolation Transformer ............................................................................................................................................... 118
10.0 Selection of Reference Crystal................................................................................................................................................... 118
11.0 Package Outlines ....................................................................................................................................................................... 119
Appendix A: Data Sheet Revision History ......................................................................................................................................... 120
The Microchip Web Site .................................................................................................................................................................... 121
Customer Change Notification Service ............................................................................................................................................. 121
Customer Support ............................................................................................................................................................................. 121
Product Identification System ............................................................................................................................................................ 122
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002134A-page 5
KSZ8794CNX
1.0
INTRODUCTION
1.1
General Description
The KSZ8794CNX is a highly integrated, Layer 2-managed, four-port switch with numerous features designed to reduce
system cost. It is intended for cost-sensitive applications requiring three 10/100 Mbps copper ports and one 10/100/
1000 Mbps Gigabit uplink port. The KSZ8794CNX incorporates a small package outline, lowest power consumption with
internal biasing, and on-chip termination. Its extensive features set includes enhanced power management, program-
mable rate limiting and priority ratio, tagged and port-based VLAN, port-based security and ACL rule-based packet fil-
tering technology, QoS priority with four queues, management interfaces, enhanced MIB counters, high-performance
memory bandwidth, and a shared memory-based switch fabric with non-blocking support. The KSZ8794CNX provides
support for multiple CPU data interfaces to effectively address both current and emerging fast Ethernet and Gigabit
Ethernet applications where the GMAC interface can be configured to any of RGMII, MII, and RMII modes. The
KSZ8794CNX is built on the latest industry-leading Ethernet analog and digital technology, with features designed to
offload host processing and streamline the overall design:
• Three integrated 10/100BASE-T/TX MAC/PHYs.
• One integrated 10/100/1000BASE-T/TX GMAC with selectable RGMII, MII, or RMII interfaces.
• Small 64-pin QFN package.
A robust assortment of power management features including Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE), PME, and WoL have
been designed in to satisfy energy efficient environments.
All registers in the MAC and PHY units can be managed through the SPI interface. MIIM PHY registers can be accessed
through the MDC/MDIO interface.
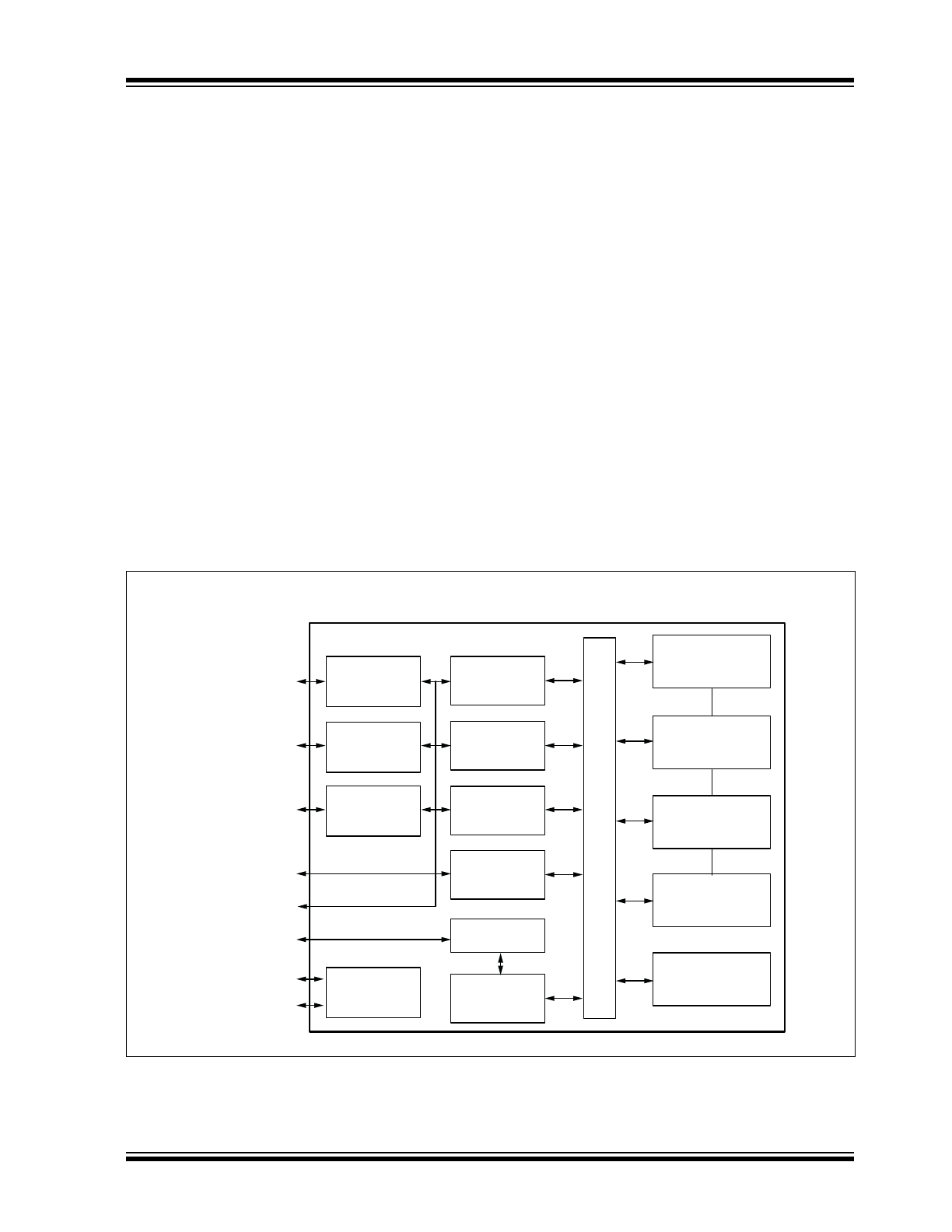
FIGURE 1-1:
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
KSZ8794
AUTO MDI/MDIX
AUTO MDI/MDIX
AUTO MDI/MDIX
SW4-RGMII/MII/RMII
MDC, MDI/O FOR MIIM
CONTROL REG SPI I/F
LED0 {3:1]
LED1 {3:1]
10/100
T/TX
EEE PHY1
10/100
T/TX
EEE PHY2
10/100
T/TX
EEE PHY3
LED I/F
10/100
MAC 1
10/100
MAC 2
10/100
MAC 3
10/100/1000
GMAC 4
SPI
CONTROL
REGISTERS
LOOK UP ENGINE
QUEUE MANAGEMENT
BUFFER MANAGEMENT
FRAME BUFFER
MIB COUNTERS
FIFO, FLOW CONTROL, VLAN
TAGGING, PRIORITY
KSZ8794CNX
DS00002134A-page 6
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
2.0
PIN DESCRIPTION AND CONFIGURATION
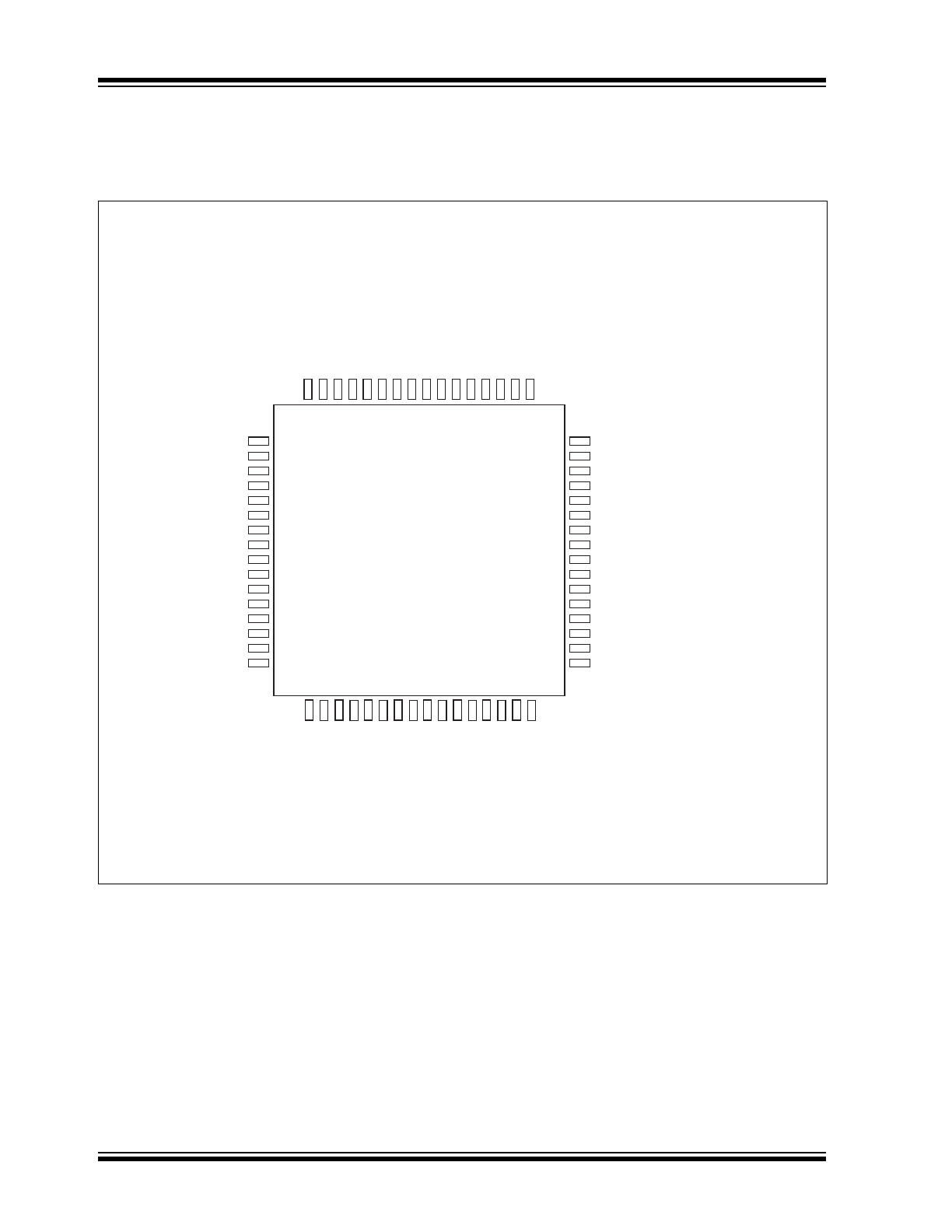
FIGURE 2-1:
64-QFN PIN ASSIGNMENT (TOP VIEW)
ISET
LED2_0
LED1_1
LED1_0
SPIQ
SCL_MDC
SDA_MDIO
SPIS_N
VDDIO
GNDD
RST_N
VDD12D
VDDA
T33
GNDA
XI
XO
VDD12A
VDDAT33
GNDA
RXP1
RXM1
TXP1
TXM1
RXP2
RXM2
TXP2
TXM2
VDDAT33
RXP3
RXM3
TXP3
TXM3
LED2_1
PME
REFCLKO
COL4
CRS4
RXER4
RXDV4/CRSDV4/RXD4_CTL
RXD4_3
RXD4_2
VDDIO
GNDD
RXD4_1
RXD4_0
RXC4/GRXC4
TXC4/REFCLKI4/GTXC4
VDD12D
64
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
KSZ8794
(Top View)
64-pin QFN
LED3_0
GNDD
NC
TXER4
TXD4_3
TXD4_2
VDDIO
GNDD
TXD4_1
TXD4_0
TXEN4
GNDD
VDD12D
LED3_1
INTR_N
GNDA
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002134A-page 7
KSZ8794CNX
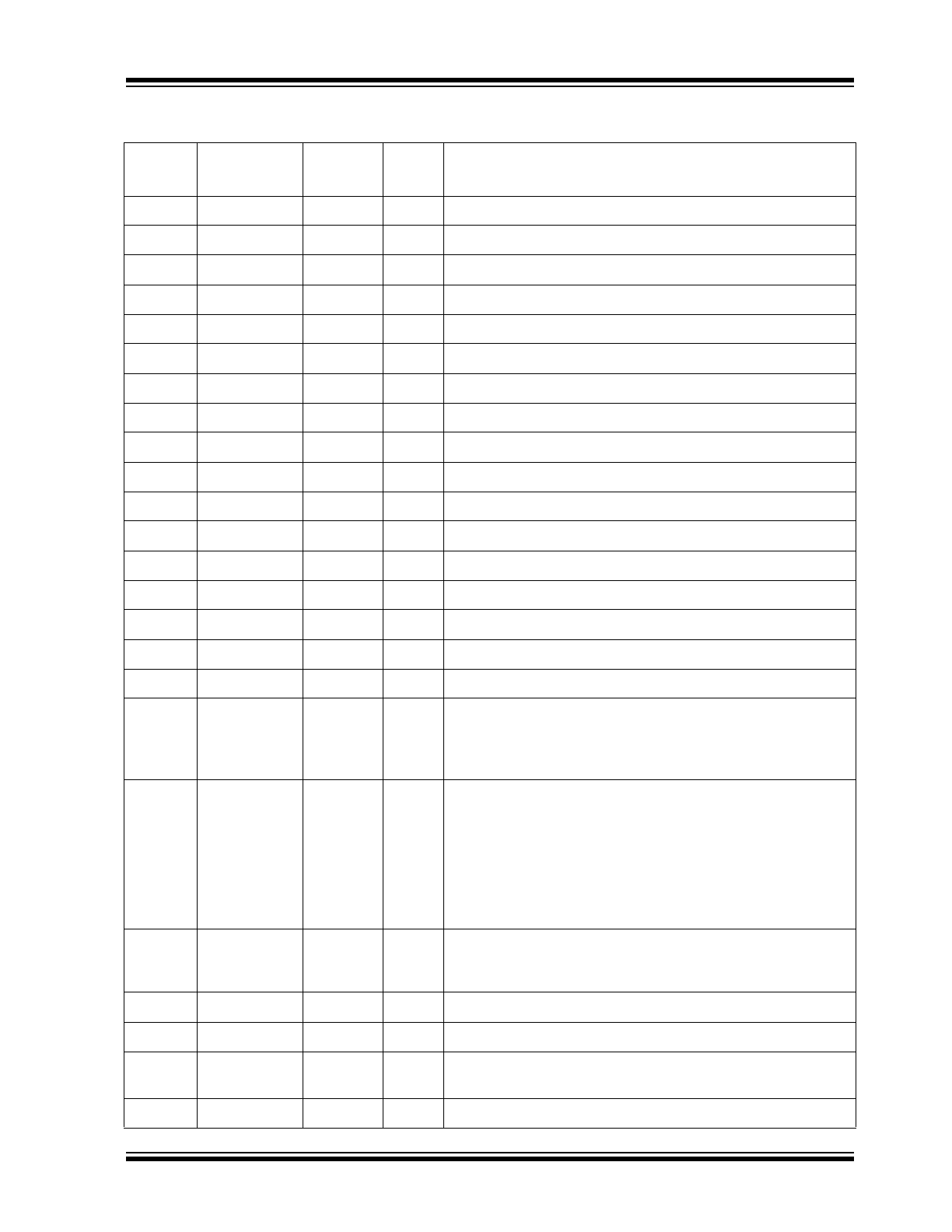
TABLE 2-1:
SIGNALS - KSZ8794CNX
Pin
Number
Pin
Name
Type
Note 2-1
Port
Description
1
VDD12A
P
—
1.2V Core Power
2
VDDAT
P
—
3.3V or 2.5V Analog Power.
3
GNDA
GND
—
Analog Ground.
4
RXP1
I
1
Port 1 Physical Receive Signal + (Differential).
5
RXM1
I
1
Port 1 Physical Receive Signal - (Differential).
6
TXP1
O
1
Port 1 Physical Transmit Signal + (Differential).
7
TXM1
O
1
Port 1 Physical Transmit Signal - (Differential).
8
RXP2
I
2
Port 2 Physical Receive Signal + (Differential).
9
RXM2
I
2
Port 2 Physical Receive Signal - (Differential).
10
TXP2
O
2
Port 2 Physical Transmit Signal + (Differential).
11
TXM2
O
2
Port 2 Physical Transmit Signal - (Differential).
12
VDDAT
P
—
3.3V or 2.5V Analog Power.
13
RXP3
I
3
Port 3 Physical Receive Signal + (Differential).
14
RXM3
I
3
Port 3 Physical Receive Signal - (Differential).
15
TXP3
O
3
Port 3 Physical Transmit Signal + (Differential).
16
TXM3
O
3
Port 3 Physical Transmit Signal – (Differential).
17
GNDA
GND
—
Analog Ground.
18
INTR_N
Opu
—
Interrupt: Active-Low
This pin is an open-drain output pin.
Note:
an external pull-up resistor is needed on this pin when it
is in use.
19
LED3_1
Ipu/O
3
Port 3 LED Indicator 1:
See Global Register 11 bits [5:4] for details.
Strap Option: Switch Port 4 GMAC4 interface mode select by
LED3[1:0]
00 = MII for SW4-MII
01 = RMII for SW4-RMII
10 = Reserved
11 = RGMII for SW4-RGMII (Default)
20
LED3_0
Ipu/O
3
Port 3 LED Indicator 0:
See Global Register 11 bits [5:4] for details.
Strap Option: See LED3_1.
21
VDD12D
P
—
1.2V Core Power.
22
GNDD
GND
—
Digital Ground.
23
TXEN4/
TXD4_CTL
Ipd
4
MII/RMII: Port 4 Switch transmit enable.
RGMII: Transmit data control.
24
TXD4_0
Ipd
4
RGMII/MII/RMII: Port 4 Switch transmit bit [0].
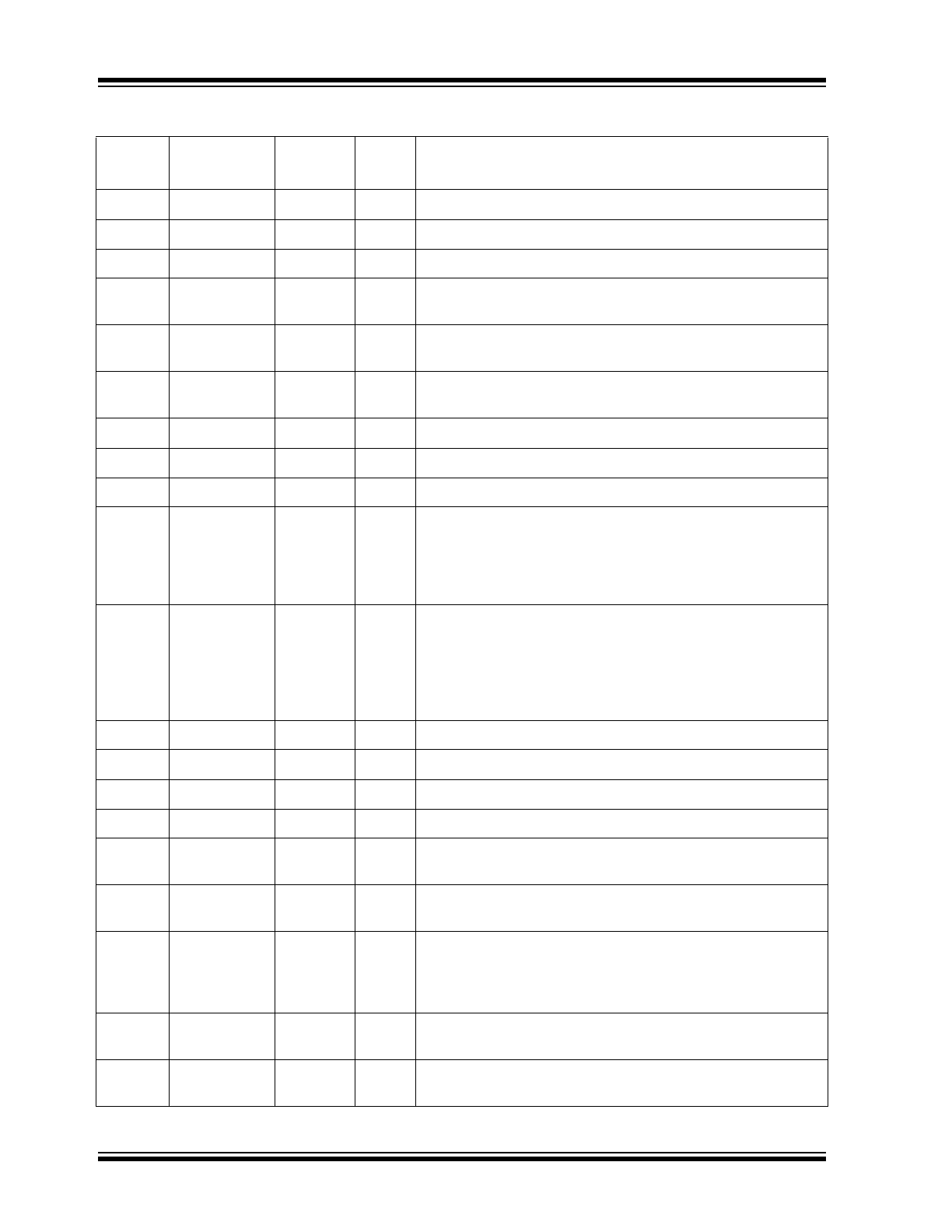
KSZ8794CNX
DS00002134A-page 8
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
25
TXD4_1
Ipd
4
RGMII/MII/RMII: Port 4 Switch transmit bit [1].
26
GNDD
GND
—
Digital Ground.
27
VDDIO
P
—
3.3V, 2.5V, or 1.8V digital V
DD
for digital I/O circuitry.
28
TXD4_2
Ipd
4
RGMII/MII: Port 4 Switch transmit bit [2].
RMII: No connection.
29
TXD4_3
Ipd
4
RGMII/MII: Port 4 Switch transmit bit [3].
RMII: No connection.
30
TXER4
Ipd
4
MII: Port 4 Switch transmit error.
RGMII/RMII: No connection.
31
NC
NC
—
No Connect.
32
GNDD
GND
—
Digital Ground.
33
VDD12D
P
—
1.2V Core Power.
34
TXC4/
REFCLKI4
/GTXC4
I/O
4
Port 4 Switch GMAC4 Clock Pin
MII: 2.5/25 MHz clock, PHY mode is output, MAC mode is input.
RMII: Input for receiving 50 MHz clock in normal mode
RGMII: Input 125 MHz clock with falling and rising edge to latch
data for the transmit.
35
RXC4/
GRXC4
I/O
4
Port 4 Switch GMAC4 Clock Pin
MII: 2.5/25 MHz clock, PHY mode is output, MAC mode is input.
RMII: Output 50 MHz reference clock for the receiving/transmit
in the clock mode.
RGMII: Output 125 MHz clock with falling and rising edge to
latch data for the receiving.
36
RXD4_0
Ipd/O
4
RGMII/MII/RMII: Port 4 Switch receive bit [0].
37
RXD4_1
Ipd/O
4
RGMII/MII/RMII: Port 4 Switch receive bit [1].
38
GNDD
GND
—
Digital Ground.
39
VDDIO
P
—
3.3V, 2.5V, or 1.8V digital V
DD
for digital I/O circuitry.
40
RXD4_2
Ipd/O
4
RGMII/MII: Port 4 Switch receive bit [2].
RMII: No connection.
41
RXD4_3
Ipd/O
4
RGMII/MII: Port 4 Switch receive bit [3].
RMII: No connection.
42
RXDV4/
CRSDV4
/RXD4_CTL
Ipd/O
4
MII: RXDV4 is for Port 4 Switch GMII/MII receive data valid.
RMII: CRSDV4 is for Port 4 RMII carrier sense/receive data
valid output.
RGMII: RXD4_CTL is for Port 4 RGMII receive data control
43
RXER
Ipd/O
4
MII: Port 4 Switch receives error.
RGMII/RMII: No connection.
44
CRS4
Ipd/O
4
MII: Port 4 Switch MII modes carrier sense.
RGMII/RMII: No connection.
TABLE 2-1:
SIGNALS - KSZ8794CNX (CONTINUED)
Pin
Number
Pin
Name
Type
Note 2-1
Port
Description
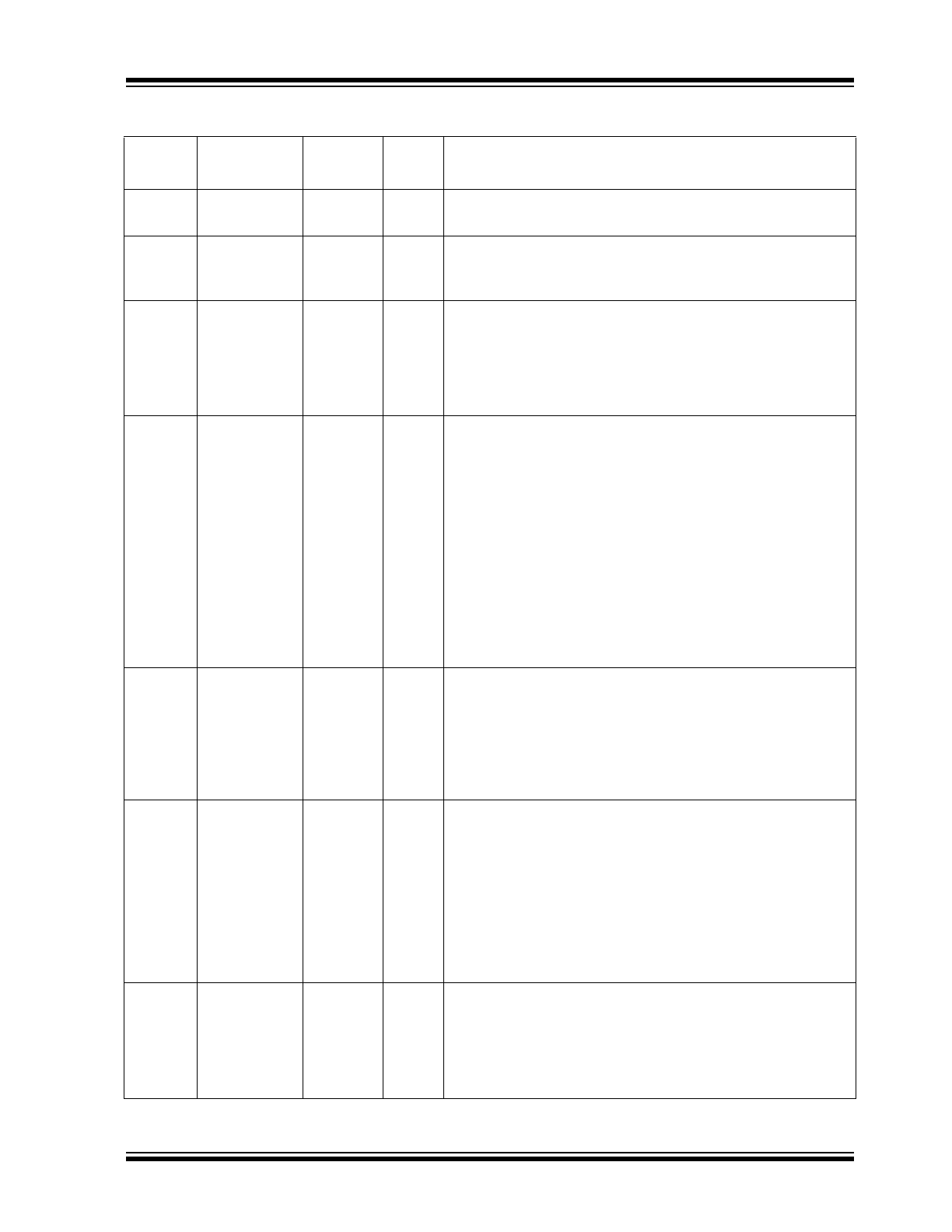
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002134A-page 9
KSZ8794CNX
45
COL4
Ipd/O
4
MII: Port 4 Switch MII collision detects.
RGMII/RMII: No connection.
46
REFCLKO
Ipu/O
—
25 MHz Clock Output (Option)
Controlled by the strap pin LED2_0.
Default is enabled, it is better to disable it if it’s not being used.
47
PME_N
I/O
—
Power Management Event
This output signal indicates that a Wake On LAN event has
been detected as a result of a Wake-Up frame being detected.
The KSZ8794CNX is requesting the system to wake up from
low power mode. Its assertion polarity is programmable with the
default polarity to be active low.
48
LED2_1
Ipu/O
2
Port 2 LED Indicator 1
See Global Register 11 bits [5:4] for details.
Strap Option: Port 4 MII and RMII Modes Select
When Port 4 is MII mode:
PU = MAC mode.
PD = PHY mode.
When Port 4 is RMII mode:
PU = Clock mode in RMII, using 25 MHz OSC clock and provide
50 MHz RMII clock from pin RXC4.
PD = Normal mode in RMII, the TXC4/REFCLKI4 pin on the
Port 4 RMII will receive an external 50 MHz clock.
Note:
Port 4 also can use either an internal or external clock in
RMII mode based on this strap pin or the setting of the Register
86 (0x56) bit [7].
49
LED2_0
Ipu/O
2
Port 2 LED Indicator 0
See Global Register 11 bits [5:4] for details.
Strap Option: REFCLKO Enable
PU = REFCLK_O (25 MHz) is enabled. (Default)
PD = REFCLK_O is disabled
Note:
It is better to disable this 25 MHz clock if not providing an
extra 25 MHz clock for system.
50
LED1_1
Ipu/O
1
Port 1 LED Indicator 1.
See Global Register 11 bits [5:4] for details.
Strap Option: PLL Clock Source Select
PU = Still use 25 MHz clock from XI/XO pin even though it is in
Port 4 RMII normal mode.
PD = Use external clock from TXC4 in Port 4 RMII normal
mode.
Note:
If received clock in Port 4 RMII normal mode has bigger
clock jitter, one can still select the 25 MHz Crystal/Oscillator as
switch’s clock source.
51
LED1_0
Ipu/O
1
Port 1 LED Indicator 0
See Global Register 11 bits [5:4] for details.
Strap Option: Speed Select in RGMII
PU = 1 Gbps in RGMII. (Default)
PD = 10/100 Mbps in RGMII.
Note:
Programmable through internal registers also.
TABLE 2-1:
SIGNALS - KSZ8794CNX (CONTINUED)
Pin
Number
Pin
Name
Type
Note 2-1
Port
Description
KSZ8794CNX
DS00002134A-page 10
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
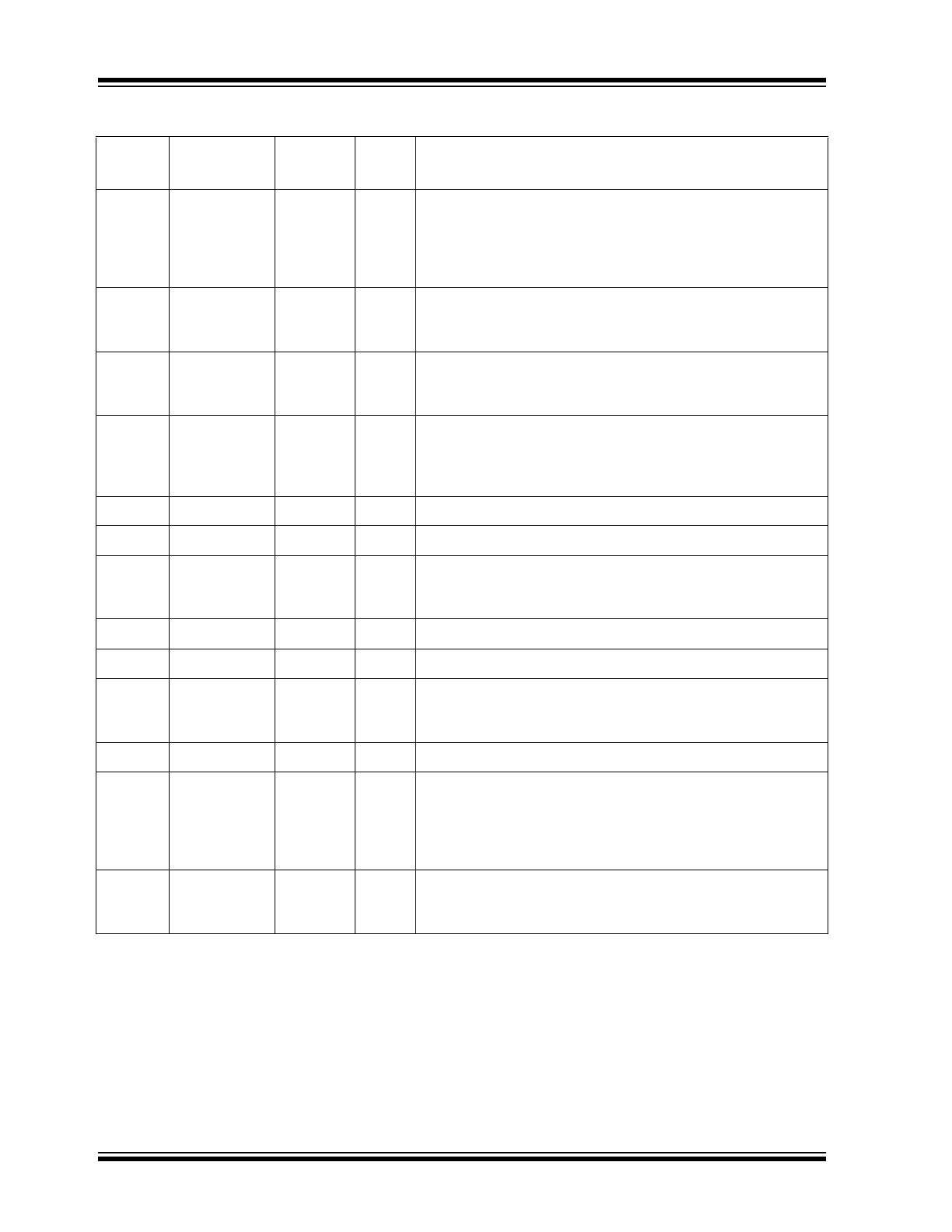
Note 2-1
P = power supply; GND = ground; I = input; O = output
I/O = bi-directional
Ipu = Input w/internal pull-up.
Ipd = Input w/internal pull-down.
Ipd/O = Input w/internal pull-down during reset, output pin otherwise.
Ipu/O = Input w/internal pull-up during reset, output pin otherwise.
OTRI = Output tri-stated.
PU = Strap pin pull-up.
PD = Strap pin pull-down.
NC = No connect or tie-to-ground for this product.
52
SPIQ
Ipd/O
All
SPI Serial Data Output in SPI Slave Mode
Strap Option: Serial Bus Configuration
PD = SPI slave mode.
PU = MDC/MDIO mode.
Note:
An external pull-up or pull-down resistor is required.
53
SCL_MDC
Ipu
All
Clock for SPI or MDC/MDIO Interfaces
Input clock up to 50 MHz in SPI slave mode.
Input clock up to 25 MHz in MDC/MDIO for MIIM access.
54
SDA_MDIO
Ipu/O
All
Data Line for SPI or MDC/MDIO Interfaces
Serial data input in SPI slave mode.
MDC/MDIO interface input/output data line.
55
SPIS_N
Ipu
All
SPI Interface Chip Select
When SPIS_N is high, the KSZ8794CNX is deselected and
SPIQ is held in the high impedance state. A high-to-low transi-
tion initiates the SPI data transfer. This pin is active-low.
56
VDDIO
P
—
3.3V, 2.5V, or 1.8V digital V
DD
for digital I/O circuitry.
57
GNDD
GND
—
Digital Ground.
58
RST_N
Ipu
—
Reset
This active-low signal resets the hardware in the device. See
the timing requirements in the Timing Diagram Section.
59
VDD12D
P
—
1.2V Core Power.
60
VDDAT
P
—
3.3V or 2.5V Analog Power.
61
ISET
—
—
Transmit Output Current Set
This pin configures the physical transmit output current.
It should be connected to GND through a 12.4 kΩ 1% resistor.
62
GNDA
GND
—
Analog Ground.
63
XI
I
—
Crystal Clock Input/Oscillator Input
When using a 25 MHz crystal, this input is connected to one end
of the crystal circuit. When using a 3.3V oscillator, this is the
input from the oscillator.
The crystal or oscillator should have a tolerance of ±50 ppm.
64
XO
O
—
Crystal Clock Output.
When using a 25 MHz crystal, this output is connected to one
end of the crystal circuit.
TABLE 2-1:
SIGNALS - KSZ8794CNX (CONTINUED)
Pin
Number
Pin
Name
Type
Note 2-1
Port
Description

2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002134A-page 1
Target Applications
• Industrial Ethernet Applications that Employ IEEE
802.3-Compliant MACs. (Ethernet/IP, Profinet,
MODBUS TCP, etc.)
• VoIP Phone
• Set-Top/Game Box
• Automotive
• Industrial Control
• IPTV POF
• SOHO Residential Gateway with Full-Wire Speed
of Four LAN Ports
• Broadband Gateway/Firewall/VPN
• Integrated DSL/Cable Modem
• Wireless LAN Access Point + Gateway
• Standalone 10/100 Switch
• Networked Measurement and Control Systems
Features
• Management Capabilities
- The KSZ8794CNX Includes All the Functions
of a 10/100BASE-T/TX Switch System Which
Combines a Switch Engine, Frame Buffer
Management, Address Look-Up Table,
Queue Management, MIB Counters, Media
Access Controllers (MAC), and PHY Trans-
ceivers
- Non-Blocking Store-and-Forward Switch
Fabric Assures Fast Packet Delivery by Uti-
lizing a 1024-Entries Forwarding Table
- Port Mirroring/Monitoring/Sniffing: Ingress
and/or Egress Traffic to Any Port
- MIB Counters for Fully Compliant Statistics
Gathering (36 Counters per Port)
- Support Hardware for Port-Based Flush and
Freeze Command in MIB Counter.
- Multiple Loopback of Remote PHY, and MAC
Modes Support for the Diagnostics
- Rapid Spanning Tree Support (RSTP) for
Topology Management and Ring/Linear
Recovery
• Robust PHY Ports
- Four Integrated IEEE 802.3/802.3u-Compli-
ant Ethernet Transceivers Supporting
10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX
- IEEE 802.1az EEE Supported
- On-Chip Termination Resistors and Internal
Biasing for Differential Pairs to Reduce
Power
- HP Auto MDI/MDI-X Crossover Support Elim-
inates the Need to Differentiate Between
Straight or Crossover Cables in Applications
• MAC and GMAC Ports
- Three Internal Media Access Control (MAC1
to MAC3) Units and One Internal Gigabit
Media Access Control (GMAC4) Unit
- RGMII, MII, or RMII Interfaces Support for
the Port 4 GMAC4 with Uplink
- 2 KByte Jumbo Packet Support
- Tail Tagging Mode (One Byte Added Before
FCS) Support on Port 4 to Inform the Proces-
sor in which Ingress Port Receives the
Packet and its Priority
- Supports Reduced Media Independent Inter-
face (RMII) with 50 MHz Reference Clock
Output
- Supports Media Independent Interface (MII)
in Either PHY Mode or MAC Mode on Port 4
- LinkMD
®
Cable Diagnostic Capabilities for
Determining Cable Opens, Shorts, and
Length
• Advanced Switch Capabilities
- Non-Blocking Store-and-Forward Switch
Fabric Assures Fast Packet Delivery by Uti-
lizing a 1024-Entries Forwarding Table
- 64 KB Frame Buffer RAM
- IEEE 802.1q VLAN Support for up to 128
Active VLAN Groups (Full-Range 4096 of
VLAN IDs)
- IEEE 802.1p/Q Tag Insertion or Removal on
a Per Port Basis (Egress)
- VLAN ID Tag/Untag Options on Per Port
Basis
- Fully Compliant with IEEE 802.3/802.3u
Standards
- IEEE 802.3x Full-Duplex with Force-Mode
Option and Half-Duplex Back-Pressure Colli-
sion Flow Control
- IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
Support
- IGMP v1/v2/v3 Snooping for Multicast Packet
Filtering
KSZ8794CNX
Integrated 4-Port 10/100 Managed Ethernet
Switch with Gigabit RGMII/MII/RMII Interface

KSZ8794CNX
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002134A-page 2
- QoS/CoS Packets Prioritization Support:
802.1p, DiffServ-Based and Re-Mapping of
802.1p Priority Field Per Port Basis on Four
Priority Levels
- IPv4/IPv6 QoS Support
- IPv6 Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD)
Snooping
- Programmable Rate Limiting at the Ingress
and Egress Ports on a Per Port Basis
- Jitter-Free Per Packet Based Rate Limiting
Support
- Tail Tag Mode (1 byte Added before FCS)
Support on Port 4 to Inform the Processor
which Ingress Port Receives the Packet
- Broadcast Storm Protection with Percentage
Control (Global and Per Port Basis)
- 1K Entry Forwarding Table with 64 KB Frame
Buffer
- 4 Priority Queues with Dynamic Packet Map-
ping for IEEE 802.1P, IPv4 TOS (DIFF-
SERV), IPv6 Traffic Class, etc.
- Supports WoL Using AMD’s Magic Packet
- VLAN and Address Filtering
- Supports 802.1x Port-Based Security,
Authentication and MAC-Based Authentica-
tion via Access Control Lists (ACL)
- Provides Port-Based and Rule-Based ACLs
to Support Layer 2 MAC SA/DA Address,
Layer 3 IP Address and IP Mask, Layer 4
TCP/UDP Port Number, IP Protocol, TCP
Flag and Compensation for the Port Security
Filtering
- Ingress and Egress Rate Limit Based on Bit
per Second (bps) and Packet-Based Rate
Limiting (pps)
• Configuration Registers Access
- High-Speed SPI (4-Wire, up to 50 MHz) Inter-
face to Access All Internal Registers
- MII Management (MIIM, MDC/MDIO 2-Wire)
Interface to Access All PHY Registers per
Clause 22.2.4.5 of the IEEE 802.3 Specifica-
tion
- I/O Pin Strapping Facility to Set Certain Reg-
ister Bits from I/O Pins During Reset Time
- Control Registers Configurable On-the-Fly
• Power and Power Management
- Full-Chip Software Power-Down (All Register
Values are Not Saved and Strap-In Value Will
Re-Strap After it Releases the Power-Down)
- Per-Port Software Power-Down
- Energy Detect Power-Down (EDPD), which
Disables the PHY Transceiver When Cables
are Removed
- Supports IEEE P802.3az Energy Efficient
Ethernet (EEE) to Reduce Power Consump-
tion in Transceivers in LPI State Even
Though Cables are Not Removed
- Dynamic Clock Tree Control to Reduce
Clocking in Areas that are Not in Use
- Low Power Consumption without Extra
Power Consumption on Transformers
- Voltages: Using External LDO Power Sup-
plies
- Analog V
DDAT
3.3V or 2.5V
- V
DDIO
Support 3.3V, 2.5V, and 1.8V
- Low 1.2V Voltage for Analog and Digital Core
Power
- WoL Support with Configurable Packet Con-
trol
• Additional Features
- Single 25 MHz ±50 ppm Reference Clock
Requirement
- Comprehensive Programmable Two-LED
Indicator Support for Link, Activity, Full-/Half-
Duplex, and 10/100 Speed
• Packaging and Environmental
- Commercial Temperature Range: 0°C to
+70°C
- Industrial Temperature Range: –40°C to
+85°C
- Small Package Available in a Lead-Free,
RoHS-Compliant 64-Pin QFN
- 0.065 µm CMOS Technology for Lower
Power Consumption

2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002134A-page 3
KSZ8794CNX
TO OUR VALUED CUSTOMERS
It is our intention to provide our valued customers with the best documentation possible to ensure successful use of your Microchip
products. To this end, we will continue to improve our publications to better suit your needs. Our publications will be refined and
enhanced as new volumes and updates are introduced.
If you have any questions or comments regarding this publication, please contact the Marketing Communications Department via
E-mail at
docerrors@microchip.com
. We welcome your feedback.
Most Current Data Sheet
To obtain the most up-to-date version of this data sheet, please register at our Worldwide Web site at:
http://www.microchip.com
You can determine the version of a data sheet by examining its literature number found on the bottom outside corner of any page.
The last character of the literature number is the version number, (e.g., DS30000000A is version A of document DS30000000).
Errata
An errata sheet, describing minor operational differences from the data sheet and recommended workarounds, may exist for cur-
rent devices. As device/documentation issues become known to us, we will publish an errata sheet. The errata will specify the
revision of silicon and revision of document to which it applies.
To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please check with one of the following:
• Microchip’s Worldwide Web site;
http://www.microchip.com
• Your local Microchip sales office (see last page)
When contacting a sales office, please specify which device, revision of silicon and data sheet (include -literature number) you are
using.
Customer Notification System
Register on our web site at
www.microchip.com
to receive the most current information on all of our products.

KSZ8794CNX
DS00002134A-page 4
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
Table of Contents
1.0 Introduction ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
2.0 Pin Description and Configuration ................................................................................................................................................... 6
3.0 Functional Description ................................................................................................................................................................... 12
4.0 Device Registers ........................................................................................................................................................................... 43
5.0 Operational Characteristics ......................................................................................................................................................... 106
6.0 Electrical Characteristics ............................................................................................................................................................. 107
7.0 Timing Diagrams .......................................................................................................................................................................... 109
8.0 Reset Circuit................................................................................................................................................................................. 117
9.0 Selection of Isolation Transformer ............................................................................................................................................... 118
10.0 Selection of Reference Crystal................................................................................................................................................... 118
11.0 Package Outlines ....................................................................................................................................................................... 119
Appendix A: Data Sheet Revision History ......................................................................................................................................... 120
The Microchip Web Site .................................................................................................................................................................... 121
Customer Change Notification Service ............................................................................................................................................. 121
Customer Support ............................................................................................................................................................................. 121
Product Identification System ............................................................................................................................................................ 122

2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002134A-page 5
KSZ8794CNX
1.0
INTRODUCTION
1.1
General Description
The KSZ8794CNX is a highly integrated, Layer 2-managed, four-port switch with numerous features designed to reduce
system cost. It is intended for cost-sensitive applications requiring three 10/100 Mbps copper ports and one 10/100/
1000 Mbps Gigabit uplink port. The KSZ8794CNX incorporates a small package outline, lowest power consumption with
internal biasing, and on-chip termination. Its extensive features set includes enhanced power management, program-
mable rate limiting and priority ratio, tagged and port-based VLAN, port-based security and ACL rule-based packet fil-
tering technology, QoS priority with four queues, management interfaces, enhanced MIB counters, high-performance
memory bandwidth, and a shared memory-based switch fabric with non-blocking support. The KSZ8794CNX provides
support for multiple CPU data interfaces to effectively address both current and emerging fast Ethernet and Gigabit
Ethernet applications where the GMAC interface can be configured to any of RGMII, MII, and RMII modes. The
KSZ8794CNX is built on the latest industry-leading Ethernet analog and digital technology, with features designed to
offload host processing and streamline the overall design:
• Three integrated 10/100BASE-T/TX MAC/PHYs.
• One integrated 10/100/1000BASE-T/TX GMAC with selectable RGMII, MII, or RMII interfaces.
• Small 64-pin QFN package.
A robust assortment of power management features including Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE), PME, and WoL have
been designed in to satisfy energy efficient environments.
All registers in the MAC and PHY units can be managed through the SPI interface. MIIM PHY registers can be accessed
through the MDC/MDIO interface.
FIGURE 1-1:
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
KSZ8794
AUTO MDI/MDIX
AUTO MDI/MDIX
AUTO MDI/MDIX
SW4-RGMII/MII/RMII
MDC, MDI/O FOR MIIM
CONTROL REG SPI I/F
LED0 {3:1]
LED1 {3:1]
10/100
T/TX
EEE PHY1
10/100
T/TX
EEE PHY2
10/100
T/TX
EEE PHY3
LED I/F
10/100
MAC 1
10/100
MAC 2
10/100
MAC 3
10/100/1000
GMAC 4
SPI
CONTROL
REGISTERS
LOOK UP ENGINE
QUEUE MANAGEMENT
BUFFER MANAGEMENT
FRAME BUFFER
MIB COUNTERS
FIFO, FLOW CONTROL, VLAN
TAGGING, PRIORITY

KSZ8794CNX
DS00002134A-page 6
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
2.0
PIN DESCRIPTION AND CONFIGURATION
FIGURE 2-1:
64-QFN PIN ASSIGNMENT (TOP VIEW)
ISET
LED2_0
LED1_1
LED1_0
SPIQ
SCL_MDC
SDA_MDIO
SPIS_N
VDDIO
GNDD
RST_N
VDD12D
VDDA
T33
GNDA
XI
XO
VDD12A
VDDAT33
GNDA
RXP1
RXM1
TXP1
TXM1
RXP2
RXM2
TXP2
TXM2
VDDAT33
RXP3
RXM3
TXP3
TXM3
LED2_1
PME
REFCLKO
COL4
CRS4
RXER4
RXDV4/CRSDV4/RXD4_CTL
RXD4_3
RXD4_2
VDDIO
GNDD
RXD4_1
RXD4_0
RXC4/GRXC4
TXC4/REFCLKI4/GTXC4
VDD12D
64
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
KSZ8794
(Top View)
64-pin QFN
LED3_0
GNDD
NC
TXER4
TXD4_3
TXD4_2
VDDIO
GNDD
TXD4_1
TXD4_0
TXEN4
GNDD
VDD12D
LED3_1
INTR_N
GNDA

2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002134A-page 7
KSZ8794CNX
TABLE 2-1:
SIGNALS - KSZ8794CNX
Pin
Number
Pin
Name
Type
Note 2-1
Port
Description
1
VDD12A
P
—
1.2V Core Power
2
VDDAT
P
—
3.3V or 2.5V Analog Power.
3
GNDA
GND
—
Analog Ground.
4
RXP1
I
1
Port 1 Physical Receive Signal + (Differential).
5
RXM1
I
1
Port 1 Physical Receive Signal - (Differential).
6
TXP1
O
1
Port 1 Physical Transmit Signal + (Differential).
7
TXM1
O
1
Port 1 Physical Transmit Signal - (Differential).
8
RXP2
I
2
Port 2 Physical Receive Signal + (Differential).
9
RXM2
I
2
Port 2 Physical Receive Signal - (Differential).
10
TXP2
O
2
Port 2 Physical Transmit Signal + (Differential).
11
TXM2
O
2
Port 2 Physical Transmit Signal - (Differential).
12
VDDAT
P
—
3.3V or 2.5V Analog Power.
13
RXP3
I
3
Port 3 Physical Receive Signal + (Differential).
14
RXM3
I
3
Port 3 Physical Receive Signal - (Differential).
15
TXP3
O
3
Port 3 Physical Transmit Signal + (Differential).
16
TXM3
O
3
Port 3 Physical Transmit Signal – (Differential).
17
GNDA
GND
—
Analog Ground.
18
INTR_N
Opu
—
Interrupt: Active-Low
This pin is an open-drain output pin.
Note:
an external pull-up resistor is needed on this pin when it
is in use.
19
LED3_1
Ipu/O
3
Port 3 LED Indicator 1:
See Global Register 11 bits [5:4] for details.
Strap Option: Switch Port 4 GMAC4 interface mode select by
LED3[1:0]
00 = MII for SW4-MII
01 = RMII for SW4-RMII
10 = Reserved
11 = RGMII for SW4-RGMII (Default)
20
LED3_0
Ipu/O
3
Port 3 LED Indicator 0:
See Global Register 11 bits [5:4] for details.
Strap Option: See LED3_1.
21
VDD12D
P
—
1.2V Core Power.
22
GNDD
GND
—
Digital Ground.
23
TXEN4/
TXD4_CTL
Ipd
4
MII/RMII: Port 4 Switch transmit enable.
RGMII: Transmit data control.
24
TXD4_0
Ipd
4
RGMII/MII/RMII: Port 4 Switch transmit bit [0].

KSZ8794CNX
DS00002134A-page 8
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
25
TXD4_1
Ipd
4
RGMII/MII/RMII: Port 4 Switch transmit bit [1].
26
GNDD
GND
—
Digital Ground.
27
VDDIO
P
—
3.3V, 2.5V, or 1.8V digital V
DD
for digital I/O circuitry.
28
TXD4_2
Ipd
4
RGMII/MII: Port 4 Switch transmit bit [2].
RMII: No connection.
29
TXD4_3
Ipd
4
RGMII/MII: Port 4 Switch transmit bit [3].
RMII: No connection.
30
TXER4
Ipd
4
MII: Port 4 Switch transmit error.
RGMII/RMII: No connection.
31
NC
NC
—
No Connect.
32
GNDD
GND
—
Digital Ground.
33
VDD12D
P
—
1.2V Core Power.
34
TXC4/
REFCLKI4
/GTXC4
I/O
4
Port 4 Switch GMAC4 Clock Pin
MII: 2.5/25 MHz clock, PHY mode is output, MAC mode is input.
RMII: Input for receiving 50 MHz clock in normal mode
RGMII: Input 125 MHz clock with falling and rising edge to latch
data for the transmit.
35
RXC4/
GRXC4
I/O
4
Port 4 Switch GMAC4 Clock Pin
MII: 2.5/25 MHz clock, PHY mode is output, MAC mode is input.
RMII: Output 50 MHz reference clock for the receiving/transmit
in the clock mode.
RGMII: Output 125 MHz clock with falling and rising edge to
latch data for the receiving.
36
RXD4_0
Ipd/O
4
RGMII/MII/RMII: Port 4 Switch receive bit [0].
37
RXD4_1
Ipd/O
4
RGMII/MII/RMII: Port 4 Switch receive bit [1].
38
GNDD
GND
—
Digital Ground.
39
VDDIO
P
—
3.3V, 2.5V, or 1.8V digital V
DD
for digital I/O circuitry.
40
RXD4_2
Ipd/O
4
RGMII/MII: Port 4 Switch receive bit [2].
RMII: No connection.
41
RXD4_3
Ipd/O
4
RGMII/MII: Port 4 Switch receive bit [3].
RMII: No connection.
42
RXDV4/
CRSDV4
/RXD4_CTL
Ipd/O
4
MII: RXDV4 is for Port 4 Switch GMII/MII receive data valid.
RMII: CRSDV4 is for Port 4 RMII carrier sense/receive data
valid output.
RGMII: RXD4_CTL is for Port 4 RGMII receive data control
43
RXER
Ipd/O
4
MII: Port 4 Switch receives error.
RGMII/RMII: No connection.
44
CRS4
Ipd/O
4
MII: Port 4 Switch MII modes carrier sense.
RGMII/RMII: No connection.
TABLE 2-1:
SIGNALS - KSZ8794CNX (CONTINUED)
Pin
Number
Pin
Name
Type
Note 2-1
Port
Description

2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS00002134A-page 9
KSZ8794CNX
45
COL4
Ipd/O
4
MII: Port 4 Switch MII collision detects.
RGMII/RMII: No connection.
46
REFCLKO
Ipu/O
—
25 MHz Clock Output (Option)
Controlled by the strap pin LED2_0.
Default is enabled, it is better to disable it if it’s not being used.
47
PME_N
I/O
—
Power Management Event
This output signal indicates that a Wake On LAN event has
been detected as a result of a Wake-Up frame being detected.
The KSZ8794CNX is requesting the system to wake up from
low power mode. Its assertion polarity is programmable with the
default polarity to be active low.
48
LED2_1
Ipu/O
2
Port 2 LED Indicator 1
See Global Register 11 bits [5:4] for details.
Strap Option: Port 4 MII and RMII Modes Select
When Port 4 is MII mode:
PU = MAC mode.
PD = PHY mode.
When Port 4 is RMII mode:
PU = Clock mode in RMII, using 25 MHz OSC clock and provide
50 MHz RMII clock from pin RXC4.
PD = Normal mode in RMII, the TXC4/REFCLKI4 pin on the
Port 4 RMII will receive an external 50 MHz clock.
Note:
Port 4 also can use either an internal or external clock in
RMII mode based on this strap pin or the setting of the Register
86 (0x56) bit [7].
49
LED2_0
Ipu/O
2
Port 2 LED Indicator 0
See Global Register 11 bits [5:4] for details.
Strap Option: REFCLKO Enable
PU = REFCLK_O (25 MHz) is enabled. (Default)
PD = REFCLK_O is disabled
Note:
It is better to disable this 25 MHz clock if not providing an
extra 25 MHz clock for system.
50
LED1_1
Ipu/O
1
Port 1 LED Indicator 1.
See Global Register 11 bits [5:4] for details.
Strap Option: PLL Clock Source Select
PU = Still use 25 MHz clock from XI/XO pin even though it is in
Port 4 RMII normal mode.
PD = Use external clock from TXC4 in Port 4 RMII normal
mode.
Note:
If received clock in Port 4 RMII normal mode has bigger
clock jitter, one can still select the 25 MHz Crystal/Oscillator as
switch’s clock source.
51
LED1_0
Ipu/O
1
Port 1 LED Indicator 0
See Global Register 11 bits [5:4] for details.
Strap Option: Speed Select in RGMII
PU = 1 Gbps in RGMII. (Default)
PD = 10/100 Mbps in RGMII.
Note:
Programmable through internal registers also.
TABLE 2-1:
SIGNALS - KSZ8794CNX (CONTINUED)
Pin
Number
Pin
Name
Type
Note 2-1
Port
Description

KSZ8794CNX
DS00002134A-page 10
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
Note 2-1
P = power supply; GND = ground; I = input; O = output
I/O = bi-directional
Ipu = Input w/internal pull-up.
Ipd = Input w/internal pull-down.
Ipd/O = Input w/internal pull-down during reset, output pin otherwise.
Ipu/O = Input w/internal pull-up during reset, output pin otherwise.
OTRI = Output tri-stated.
PU = Strap pin pull-up.
PD = Strap pin pull-down.
NC = No connect or tie-to-ground for this product.
52
SPIQ
Ipd/O
All
SPI Serial Data Output in SPI Slave Mode
Strap Option: Serial Bus Configuration
PD = SPI slave mode.
PU = MDC/MDIO mode.
Note:
An external pull-up or pull-down resistor is required.
53
SCL_MDC
Ipu
All
Clock for SPI or MDC/MDIO Interfaces
Input clock up to 50 MHz in SPI slave mode.
Input clock up to 25 MHz in MDC/MDIO for MIIM access.
54
SDA_MDIO
Ipu/O
All
Data Line for SPI or MDC/MDIO Interfaces
Serial data input in SPI slave mode.
MDC/MDIO interface input/output data line.
55
SPIS_N
Ipu
All
SPI Interface Chip Select
When SPIS_N is high, the KSZ8794CNX is deselected and
SPIQ is held in the high impedance state. A high-to-low transi-
tion initiates the SPI data transfer. This pin is active-low.
56
VDDIO
P
—
3.3V, 2.5V, or 1.8V digital V
DD
for digital I/O circuitry.
57
GNDD
GND
—
Digital Ground.
58
RST_N
Ipu
—
Reset
This active-low signal resets the hardware in the device. See
the timing requirements in the Timing Diagram Section.
59
VDD12D
P
—
1.2V Core Power.
60
VDDAT
P
—
3.3V or 2.5V Analog Power.
61
ISET
—
—
Transmit Output Current Set
This pin configures the physical transmit output current.
It should be connected to GND through a 12.4 kΩ 1% resistor.
62
GNDA
GND
—
Analog Ground.
63
XI
I
—
Crystal Clock Input/Oscillator Input
When using a 25 MHz crystal, this input is connected to one end
of the crystal circuit. When using a 3.3V oscillator, this is the
input from the oscillator.
The crystal or oscillator should have a tolerance of ±50 ppm.
64
XO
O
—
Crystal Clock Output.
When using a 25 MHz crystal, this output is connected to one
end of the crystal circuit.
TABLE 2-1:
SIGNALS - KSZ8794CNX (CONTINUED)
Pin
Number
Pin
Name
Type
Note 2-1
Port
Description
