2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005859A-page 1
HV574
Features
• 5V CMOS Logic
• 80V Maximum Output Voltage
• Low-power Level Shifting
• 100 MHz Equivalent Data Rate using Four
Dynamic Shift Registers
• Latched Data Outputs
• Forward and Reverse Shifting Options (DIR Pin)
• Diode to V
PP
allows Efficient Power Recovery
• Outputs may be Hot Switched
Applications
• Display Driver
• Inkjet Driver
• Microelectromechanical Systems Applications
General Description
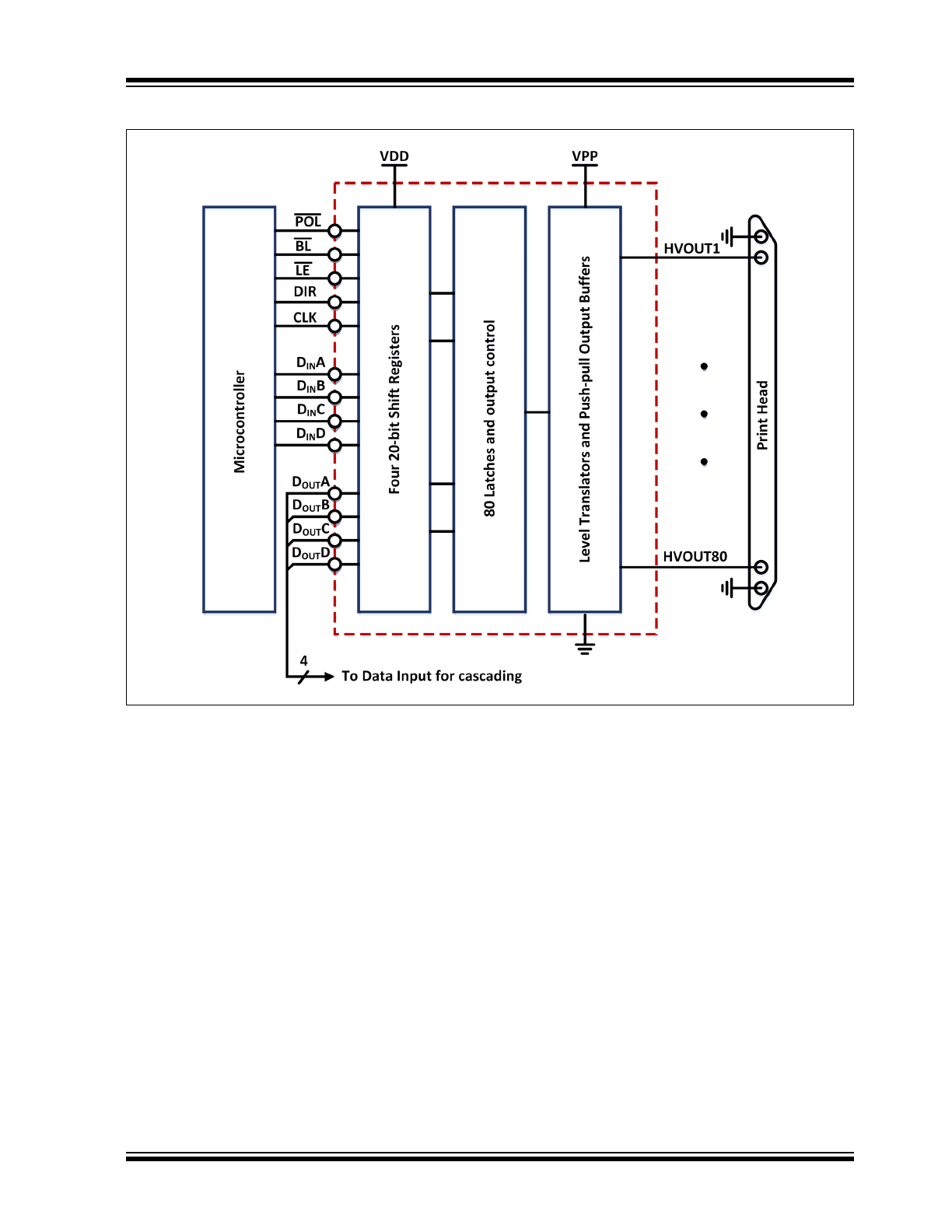
The HV574 is a low-voltage to high-voltage
serial-to-parallel converter with push-pull outputs. This
device is designed as a driver for printer applications. It
can also be used in any application requiring
multiple-output high-voltage current
sourcing-and-sinking capability such as driving plasma
panels, vacuum fluorescent displays and large matrix
LCD displays.
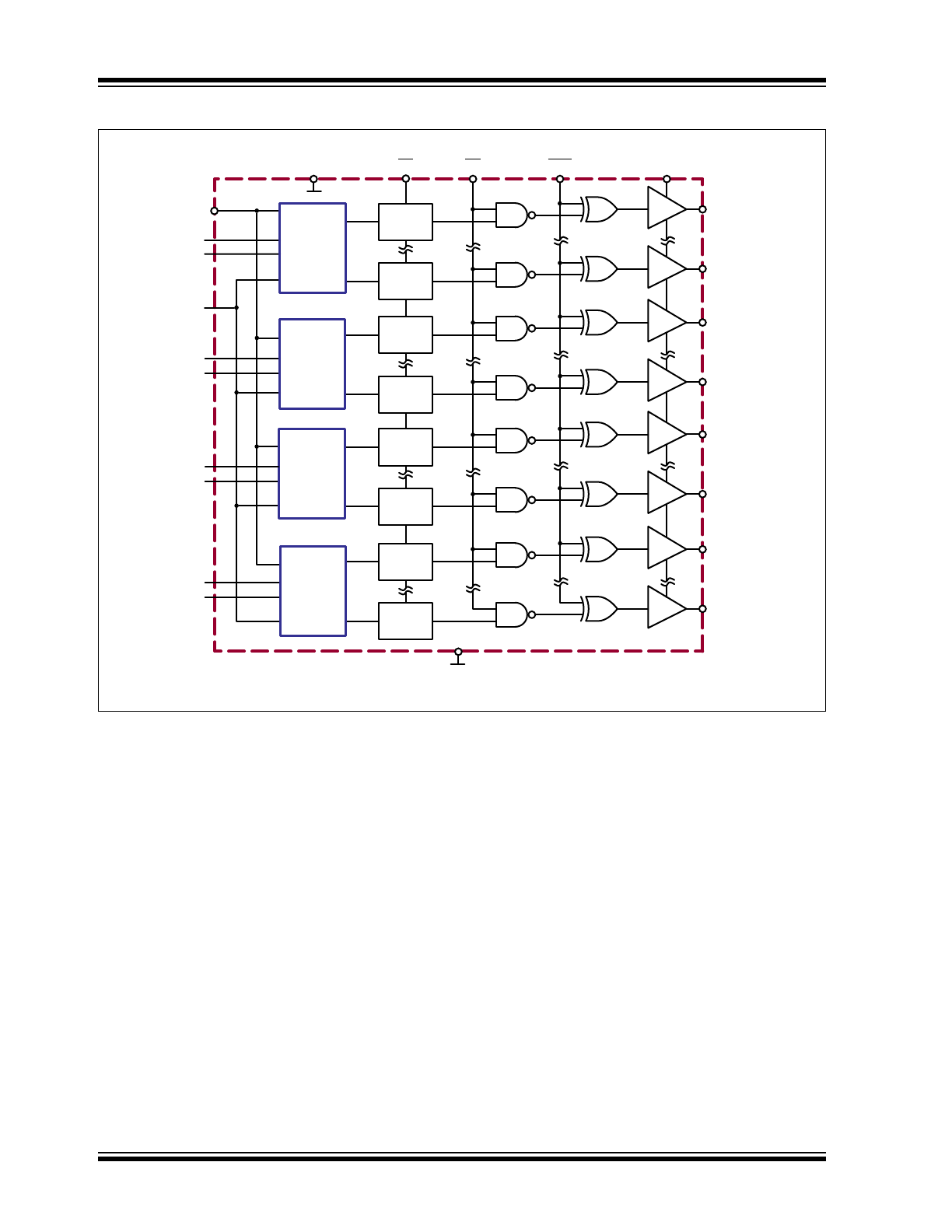
The device has four parallel 20-bit dynamic Shift
registers, permitting data rates four times the speed of
one in a single clock cycle. There are 80 static latches
and control logic to perform the polarity select and
blanking of the outputs. HV
OUT
1 is connected to the
first stage of the first Shift register through the polarity
and blanking logic. Data is shifted through the Shift
registers on the logic low-to-high transition of the clock.
The DIR pin causes counter-clockwise shifting when
connected to GND and clockwise shifting when
connected to V
DD
. A data output buffer is provided for
cascading devices. This output reflects the current
status of the last bit of the Shift register, HV
OUT
80. The
operation of the Shift register is not affected by the latch
enable (LE), blanking (BL) and polarity (POL) inputs.
Transfer of data from the Shift registers to the latches
occurs when the LE input is high. The data in the
latches is stored when LE is low.
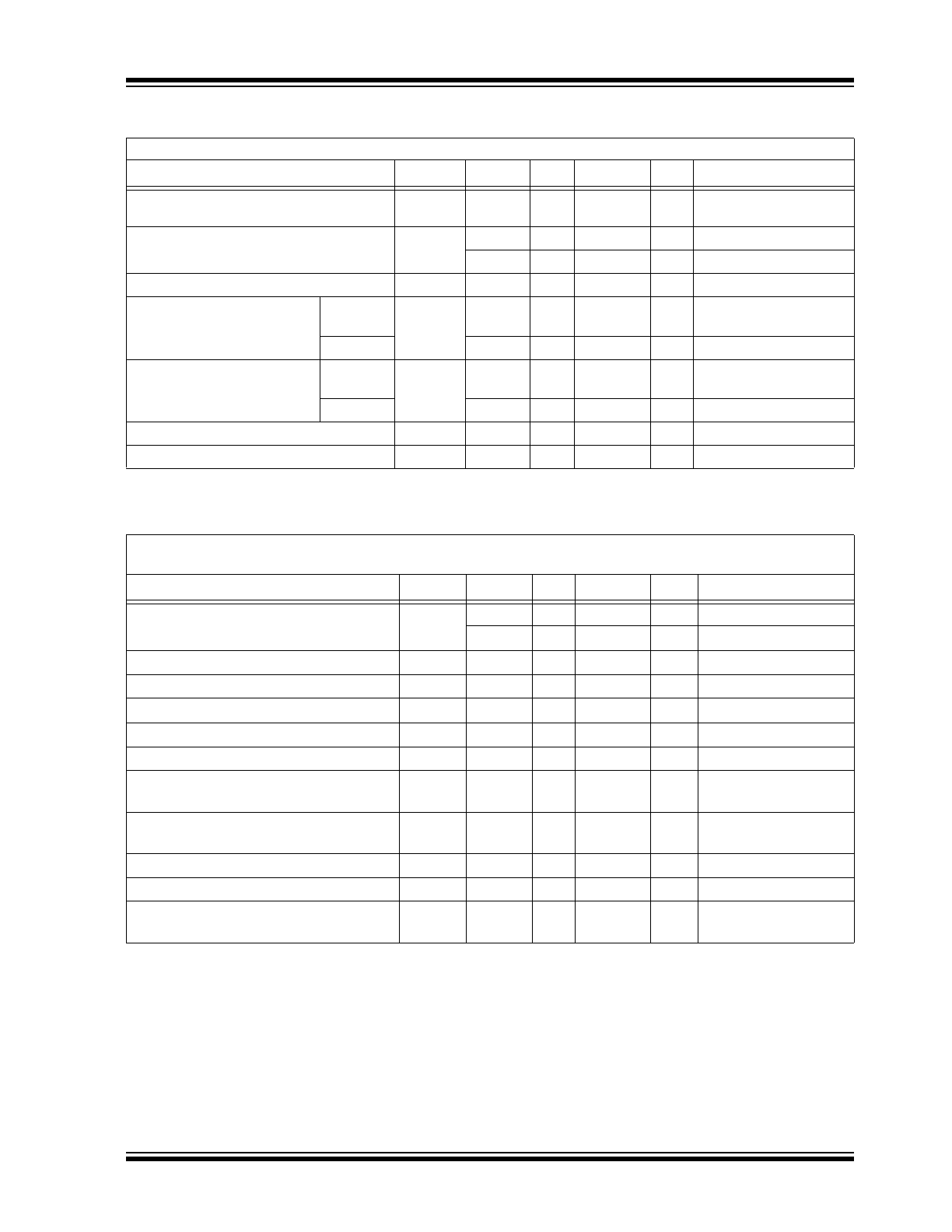
Package Type
See
Table 2-1
for pin information.
100-lead PQFP
(Top view)
100
1
80-Channel 100 MHz Serial-to-Parallel Converter with Push-Pull Outputs
HV
OUT
1
HV
OUT
20
HV
OUT
21
HV
OUT
40
HV
OUT
41
HV
OUT
60
HV
OUT
61
HV
OUT
80
POL
BL
LE
D
IN
A
D
OUT
A
DIR
CLK
GND
VDD
20-bit
Shift
Register
20-bit
Shift
Register
20-bit
Shift
Register
20-bit
Shift
Register
D
IN
B
D
OUT
B
D
IN
C
D
OUT
C
D
IN
D
D
OUT
D
VPP
HV574
DS20005859A-page 2
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
Functional Block Diagram
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005859A-page 3
HV574
Typical Application Circuit
HV574
DS20005859A-page 4
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
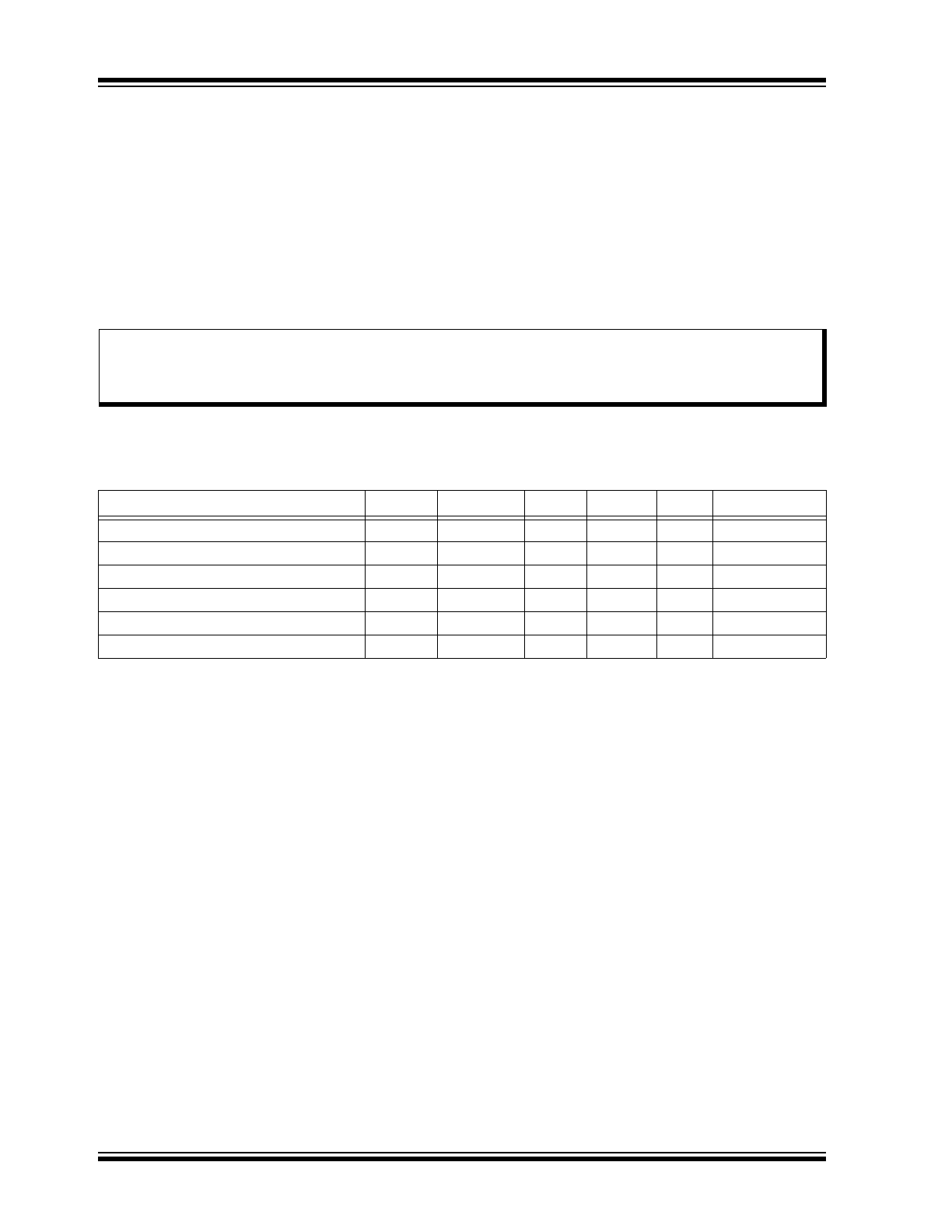
1.0
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings†
Low-voltage Supply Voltage, V
DD
........................................................................................................... –0.5V to +7.5V
High-voltage Supply Voltage, V
PP
........................................................................................................... –0.5V to +90V
Logic Input Levels ........................................................................................................................... –0.3V to V
DD
+0.3V
Ground Current (
Note 1
) ......................................................................................................................................... 1.5A
Maximum Junction Temperature, T
J(MAX)
........................................................................................................... +125°C
Storage Temperature, T
S
.................................................................................................................... –65°C to +150°C
Continuous Total Power Dissipation:
100-lead PQFP (
Note 2
) ....................................................................................................................... 1200 mW
† Notice: Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the
device. This is a stress rating only, and functional operation of the device at those or any other conditions above those
indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not intended. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability.
Note 1: Limited by the total power dissipated in the package
2: For operations above 25°C ambient, derate linearly to 85°C at 20 mW/°C.
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Parameter
Sym.
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Conditions
Logic Supply Voltage
V
DD
4.5
—
5.5
V
Output Voltage
V
PP
12
—
80
V
High-level Input Voltage
V
IH
V
DD
–0.5V
—
—
V
Low-level Input Voltage
V
IL
0
—
0.5
V
Clock Frequency per Register
f
CLK
0.001
—
25
MHz
Operating Ambient Temperature
T
A
–40
—
+85
°C
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Specifications: Over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted
Parameter
Sym.
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Conditions
V
DD
Supply Current
I
DD
—
—
30
mA
V
DD
= V
DD
maximum
f
CLK
= 25 MHz
Quiescent V
PP
Supply Current
I
PP
—
—
100
µA
Outputs high
—
—
100
µA
Outputs low
Quiescent V
DD
Supply Current
I
DDQ
—
—
100
µA
All V
IN
= V
DD
High-level Output
HV
OUT
V
OH
V
PP
–9
—
—
V
I
O
= –30 mA,
V
PP
= +80V
Data Out
V
DD
–0.5
—
—
V
I
O
= –100 µA
Low-level Output
HV
OUT
V
OL
—
—
3.75
V
I
O
= +15 mA,
V
DD
= +5V
Data Out
—
—
0.5
V
I
O
= +100 µA
High-level Logic Input Current
I
IH
—
—
1
µA
V
IH
= V
DD
Low-level Logic Input Current
I
IL
—
—
–1
µA
V
IL
= 0V
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Specifications: T
A
= 85°C maximum. Logic signal inputs and data inputs have t
r
, t
f
≤ 5 ns (10% and 90%
points).
Parameter
Sym.
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Conditions
Clock Frequency
f
CLK
0.001
—
25
MHz V
DD
= 4.5V, T
J
= 25°C
0.001
—
20
MHz V
DD
= 4.5V, T
J
= 125°C
Clock Width High or Low
t
WL
, t
WH
20
—
—
ns
Data Set-up Time before Clock Rises
t
SU
0
—
—
ns
Data Hold Time after Clock Rises
t
H
15
—
—
ns
Time from Latch Enable to HV
OUT
t
ON
, t
OFF
—
—
500
ns
C
L
= 15 pF
Latch Enable Pulse Width
t
WLE
25
—
—
ns
Delay Time Clock to Latch Enable Low to
High
t
DLE
25
—
—
ns
Note 1
Latch Enable Set-up Time before Clock
Rises
t
SLE
0
—
—
ns
Delay Time Clock to Data Low to High
t
DLH
—
—
38
ns
C
L
= 15 pF, V
DD
= 5V
Delay Time Clock to Data High to Low
t
DHL
—
—
38
ns
C
L
= 15 pF, V
DD
= 5V
Output Rise and Fall Time
t
r
, t
f
—
—
1
ns
C
L
= 600 pF,
HV
OUT
from 0V–60V
Note 1: t
DLE
is not required but is recommended to produce stable HV outputs and minimize power dissipation and
current spikes. t
DLE
allows the internal SR output to stabilize.
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005859A-page 5
HV574
TEMPERATURE SPECIFICATIONS
Parameter
Sym.
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Conditions
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Operating Ambient Temperature
T
A
–40
—
+85
°C
Maximum Junction Temperature
T
J(MAX)
—
—
+125
°C
Storage Temperature
T
S
–65
—
+150
°C
PACKAGE THERMAL RESISTANCE
100-lead PQFP
JA
—
39
—
°C/W
HV574
DS20005859A-page 6
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
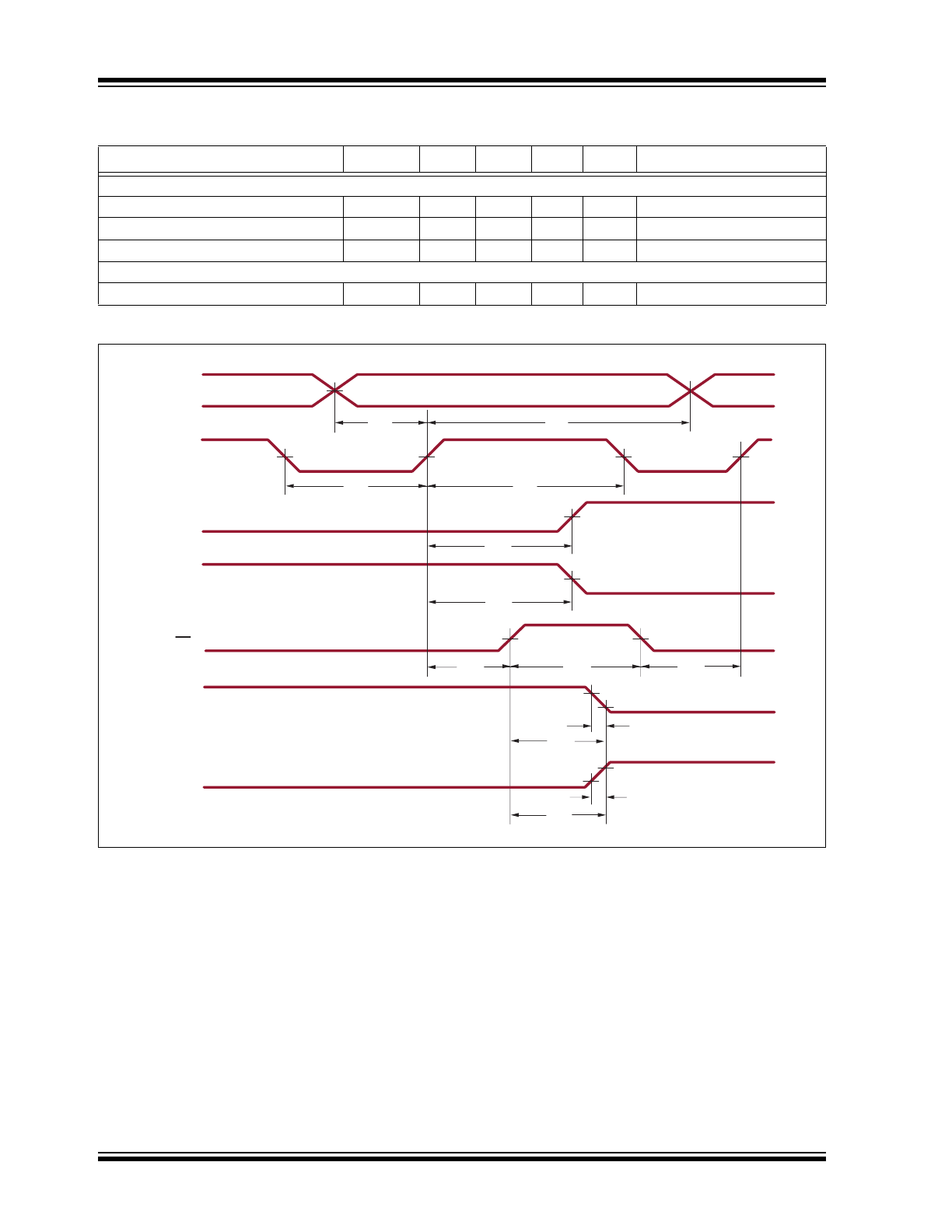
Timing Waveforms
LE
HV
OUT
w/ S/R LOW
Data Valid Data Valid
50%
DATA
INPUT
CLOCK
DATA
OUT
50%
50%
50%
t
SU
t
H
t
WL
t
WH
50%
t
DLH
t
DHL
50%
t
WLE
t
DLE
t
SLE
50%
50%
t
ON
10%
90%
90%
10%
t
OFF
t
f
t
r
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
OH
V
OL
V
OH
V
OL
V
IH
V
IL
V
OH
V
OL
V
OH
V
OL
50%
HV
OUT
w/ S/R HIGH
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005859A-page 7
HV574
2.0
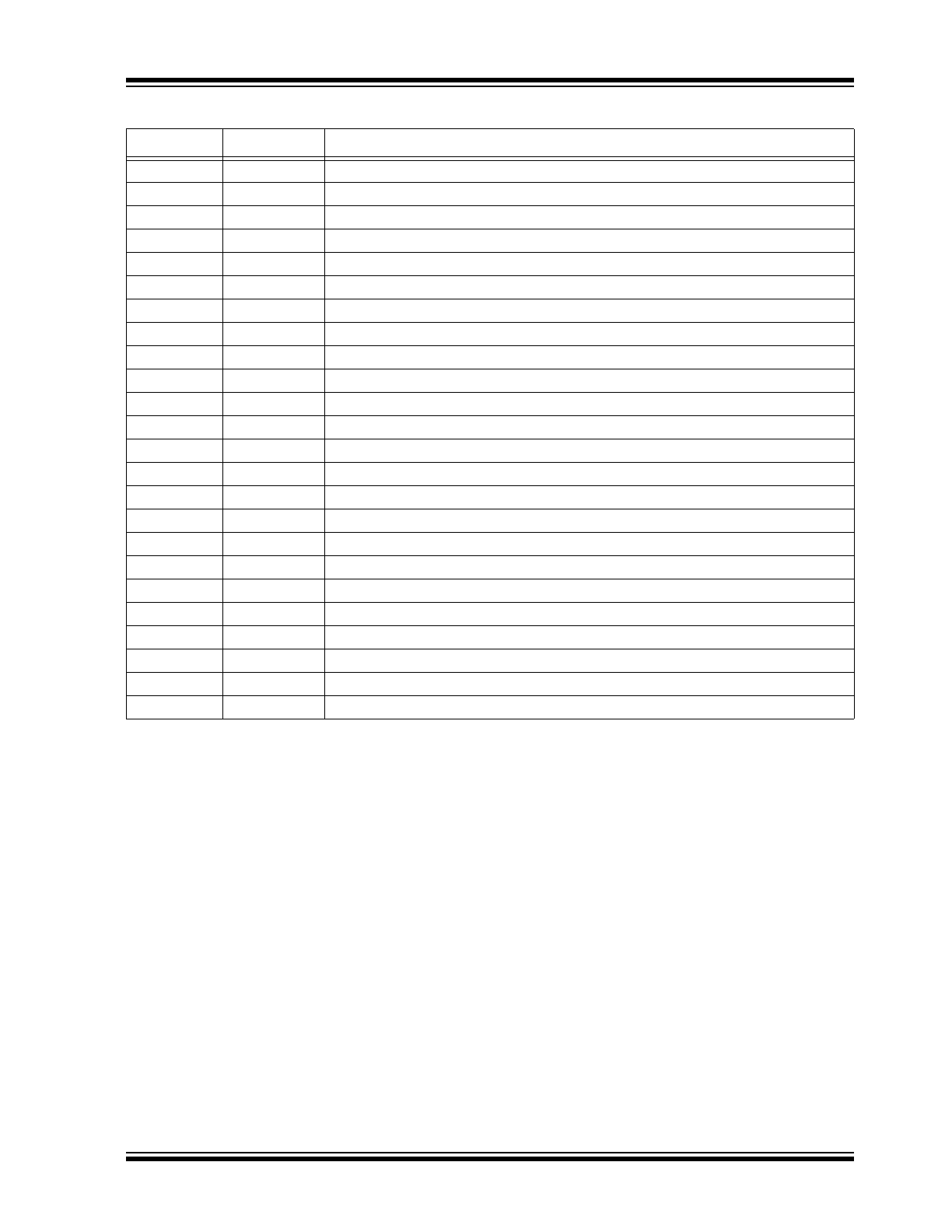
PIN DESCRIPTION
The details on the pins of HV574 are listed on
Table 2-1
. Refer to
Package Type
for the location of
pins.
TABLE 2-1:
PIN FUNCTION TABLE
Pin Number
Pin Name
Description
1
HVOUT30
High-voltage output
2
HVOUT29
High-voltage output
3
HVOUT28
High-voltage output
4
HVOUT27
High-voltage output
5
HVOUT26
High-voltage output
6
HVOUT25
High-voltage output
7
HVOUT24
High-voltage output
8
HVOUT23
High-voltage output
9
HVOUT22
High-voltage output
10
HVOUT21
High-voltage output
11
HVOUT20
High-voltage output
12
HVOUT19
High-voltage output
13
HVOUT18
High-voltage output
14
HVOUT17
High-voltage output
15
HVOUT16
High-voltage output
16
HVOUT15
High-voltage output
17
HVOUT14
High-voltage output
18
HVOUT13
High-voltage output
19
HVOUT12
High-voltage output
20
HVOUT11
High-voltage output
21
HVOUT10
High-voltage output
22
HVOUT9
High-voltage output
23
HVOUT8
High-voltage output
24
HVOUT7
High-voltage output
25
HVOUT6
High-voltage output
26
HVOUT5
High-voltage output
27
HVOUT4
High-voltage output
28
HVOUT3
High-voltage output
29
HVOUT2
High-voltage output
30
HVOUT1
High-voltage output
31
NC
No connection
32
VPP
High-voltage supply pin
33
HVGND
High-voltage supply ground
34
DINA
Data Input A pin
35
DINB
Data Input B pin
36
DINC
Data Input C pin
HV574
DS20005859A-page 8
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
37
DIND
Data Input D pin
38
VDD
Low-voltage supply pin
39
POL
Polarity pin
40
LE
Latch Enable pin
41
CLK
Clock pin
42
DIR
Direction pin
43
BL
Blanking pin
44
GND
Low-voltage supply ground
45
DOUTD
Data Output D pin
46
DOUTC
Data Output C pin
47
DOUTB
Data Output B pin
48
DOUTA
Data Output A pin
49
HVGND
High-voltage supply ground
50
VPP
High-voltage supply pin
51
HVOUT80
High-voltage output
52
HVOUT79
High-voltage output
53
HVOUT78
High-voltage output
54
HVOUT77
High-voltage output
55
HVOUT76
High-voltage output
56
HVOUT75
High-voltage output
57
HVOUT74
High-voltage output
58
HVOUT73
High-voltage output
59
HVOUT72
High-voltage output
60
HVOUT71
High-voltage output
61
HVOUT70
High-voltage output
62
HVOUT69
High-voltage output
63
HVOUT68
High-voltage output
64
HVOUT67
High-voltage output
65
HVOUT66
High-voltage output
66
HVOUT65
High-voltage output
67
HVOUT64
High-voltage output
68
HVOUT63
High-voltage output
69
HVOUT62
High-voltage output
70
HVOUT61
High-voltage output
71
HVOUT60
High-voltage output
72
HVOUT59
High-voltage output
73
HVOUT58
High-voltage output
74
HVOUT57
High-voltage output
75
HVOUT56
High-voltage output
76
HVOUT55
High-voltage output
TABLE 2-1:
PIN FUNCTION TABLE (CONTINUED)
Pin Number
Pin Name
Description
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005859A-page 9
HV574
77
HVOUT54
High-voltage output
78
HVOUT53
High-voltage output
79
HVOUT52
High-voltage output
80
HVOUT51
High-voltage output
81
HVOUT50
High-voltage output
82
HVOUT49
High-voltage output
83
HVOUT48
High-voltage output
84
HVOUT47
High-voltage output
85
HVOUT46
High-voltage output
86
HVOUT45
High-voltage output
87
HVOUT44
High-voltage output
88
HVOUT43
High-voltage output
89
HVOUT42
High-voltage output
90
HVOUT41
High-voltage output
91
HVOUT40
High-voltage output
92
HVOUT39
High-voltage output
93
HVOUT38
High-voltage output
94
HVOUT37
High-voltage output
95
HVOUT36
High-voltage output
96
HVOUT35
High-voltage output
97
HVOUT34
High-voltage output
98
HVOUT33
High-voltage output
99
HVOUT32
High-voltage output
100
HVOUT31
High-voltage output
TABLE 2-1:
PIN FUNCTION TABLE (CONTINUED)
Pin Number
Pin Name
Description
HV574
DS20005859A-page 10
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
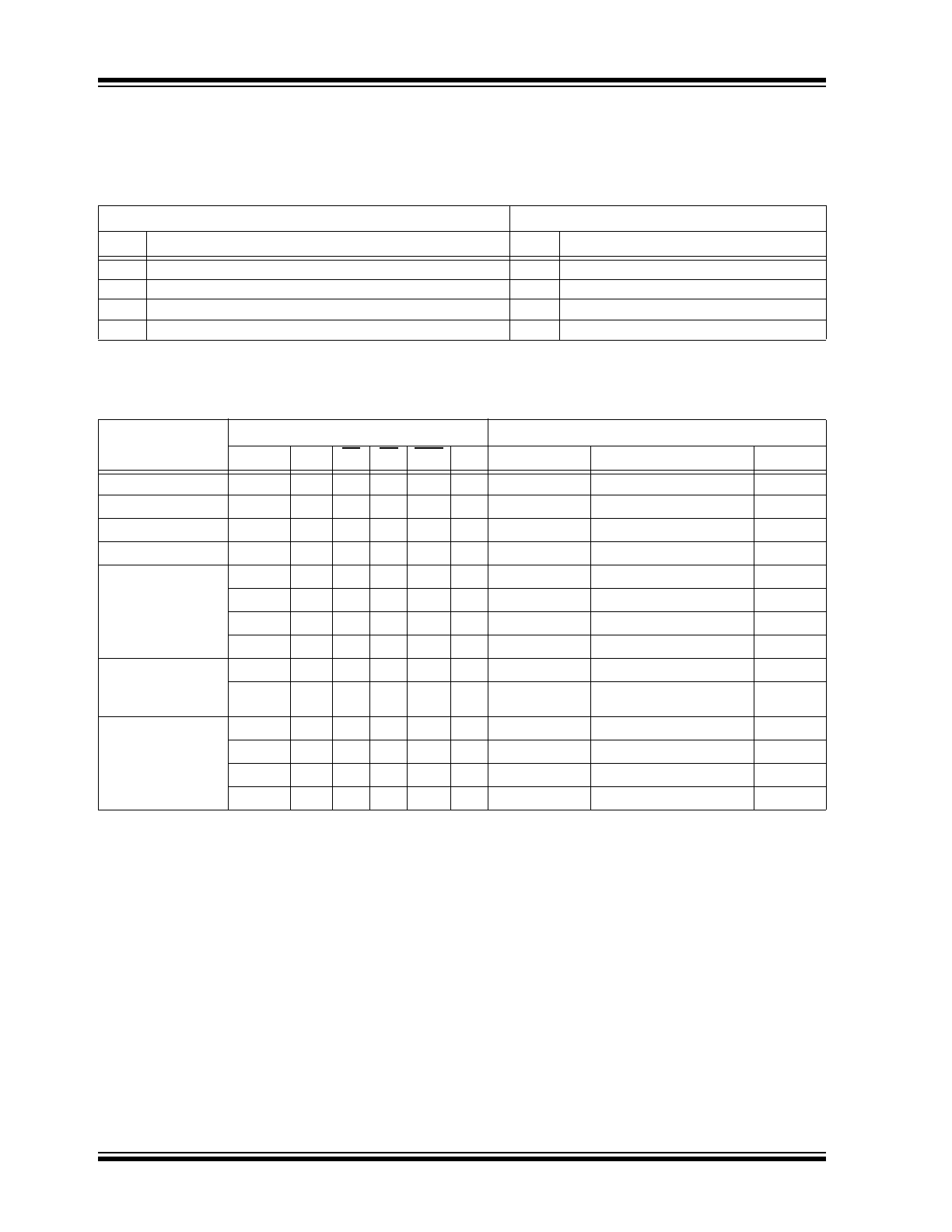
3.0
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Follow the steps in
Table 3-1
to power up and power
down the HV574.
TABLE 3-1:
POWER-UP AND POWER-DOWN SEQUENCE
Power-up
Power-down
Step
Description
Step
Description
1
Connect ground.
1
Remove V
PP.
(
Note 1
)
2
Apply V
DD.
2
Remove all inputs.
3
Set all inputs (Data, CLK, Enable, etc.) to a known state.
3
Remove V
DD.
4
Apply V
PP.
(
Note 1
)
4
Disconnect ground.
Note 1: The V
PP
should not drop below V
DD
or float during operation.
TABLE 3-2:
Function
Inputs
Outputs
Data
CLK
LE
BL
POL DIR Shift Register
High-voltage Output
Data Out
All O/P High
X
X
X
L
L
X
—
H
—
All O/P Low
X
X
X
L
H
X
—
L
—
O/P Normal
X
X
X
H
H
X
—
No inversion
—
O/P Inverted
X
X
X
H
L
X
—
Inversion
—
Data Falls through
Latches (Latches
Transparent)
L
↑
H
H
H
X
L
L
—
H
↑
H
H
H
X
H
H
—
L
↑
H
H
L
X
L
H
—
H
↑
H
H
L
X
H
L
—
Data
Stored/Latches
Loaded
X
X
L
H
H
X
*
Stored data
—
X
X
L
H
L
X
*
Inversion of stored data
—
I/O Relation
D
IN
X
↑
H
H
H
H
Q
n
→Q
n+1
New H or L
D
OUT
X
D
IN
X
↑
L
H
H
H
Q
n
→Q
n+1
Previous H or L
D
OUT
X
D
OUT
X
↑
L
H
H
L
Q
n
→Q
n-1
Previous H or L
D
IN
X
D
OUT
X
↑
H
H
H
L
Q
n
→Q
n-1
New H or L
D
IN
X
Note:
H = High-logic level
L = Low-logic level
X = Irrelevant
↑ = Low-to-high transition
* = Dependent on the previous stage’s state. See
Package Type
for D
IN
and D
OUT
pin designation for
clockwise and counter-clockwise shifts.
TRUTH FUNCTION TABLE
