
M
1998 Microchip Technology Inc.
Preliminary
DS30453B-page 1
PIC16C5X
Devices Included in this Data Sheet:
• PIC16C52
• PIC16C54s
• PIC16CR54s
• PIC16C55s
• PIC16C56s
• PIC16CR56s
• PIC16C57s
• PIC16CR57s
• PIC16C58s
• PIC16CR58s
High-Performance RISC CPU:
• Only 33 single word instructions to learn
• All instructions are single cycle (200 ns) except for
program branches which are two-cycle
• Operating speed: DC - 20 MHz clock input
DC - 200 ns instruction cycle
Note:
The letter "s" used following the part
numbers throughout this document
indicate plural, meaning there is more
than one part variety for the indicated
device.
Device
Pins
I/O
EPROM/
ROM
RAM
PIC16C52
18
12
384
25
PIC16C54
18
12
512
25
PIC16C54A
18
12
512
25
PIC16C54B
18
12
512
25
PIC16C54C
18
12
512
25
PIC16CR54A
18
12
512
25
PIC16CR54B
18
12
512
25
PIC16CR54C
18
12
512
25
PIC16C55
28
20
512
24
PIC16C55A
28
20
512
24
PIC16C56
18
12
1K
25
PIC16C56A
18
12
1K
25
PIC16CR56A
18
12
1K
25
PIC16C57
28
20
2K
72
PIC16C57C
28
20
2K
72
PIC16CR57B
28
20
2K
72
PIC16CR57C
28
20
2K
72
PIC16C58A
18
12
2K
73
PIC16C58B
18
12
2K
73
PIC16CR58A
18
12
2K
73
PIC16CR58B
18
12
2K
73
• 12-bit wide instructions
• 8-bit wide data path
• Seven or eight special function hardware registers
• Two-level deep hardware stack
• Direct, indirect and relative addressing modes for
data and instructions
Peripheral Features:
• 8-bit real time clock/counter (TMR0) with 8-bit
programmable prescaler
• Power-On Reset (POR)
• Device Reset Timer (DRT)
• Watchdog Timer (WDT) with its own on-chip
RC oscillator for reliable operation
• Programmable code-protection
• Power saving SLEEP mode
• Selectable oscillator options:
- RC:
Low-cost RC oscillator
- XT:
Standard crystal/resonator
- HS:
High-speed crystal/resonator
- LP:
Power saving, low-frequency crystal
CMOS Technology:
• Low-power, high-speed CMOS EPROM/ROM
technology
• Fully static design
• Wide-operating voltage and temperature range:
- EPROM Commercial/Industrial 2.0V to 6.25V
- ROM Commercial/Industrial 2.0V to 6.25V
- EPROM Extended 2.5V to 6.0V
- ROM Extended 2.5V to 6.0V
• Low-power consumption
- < 2 mA typical @ 5V, 4 MHz
- 15
µ
A typical @ 3V, 32 kHz
- < 0.6
µ
A typical standby current
(with WDT disabled) @ 3V, 0
°
C to 70
°
C
Note:
In this document, figure and table titles
refer to all varieties of the part number
indicated, (i.e., The title "Figure 14-1:
Load Conditions - PIC16C54A", also
refers to PIC16LC54A and PIC16LV54A
parts).
EPROM/ROM-Based 8-Bit CMOS Microcontroller Series
PIC16C5X
DS30453B-page 2
Preliminary
1998 Microchip Technology Inc.
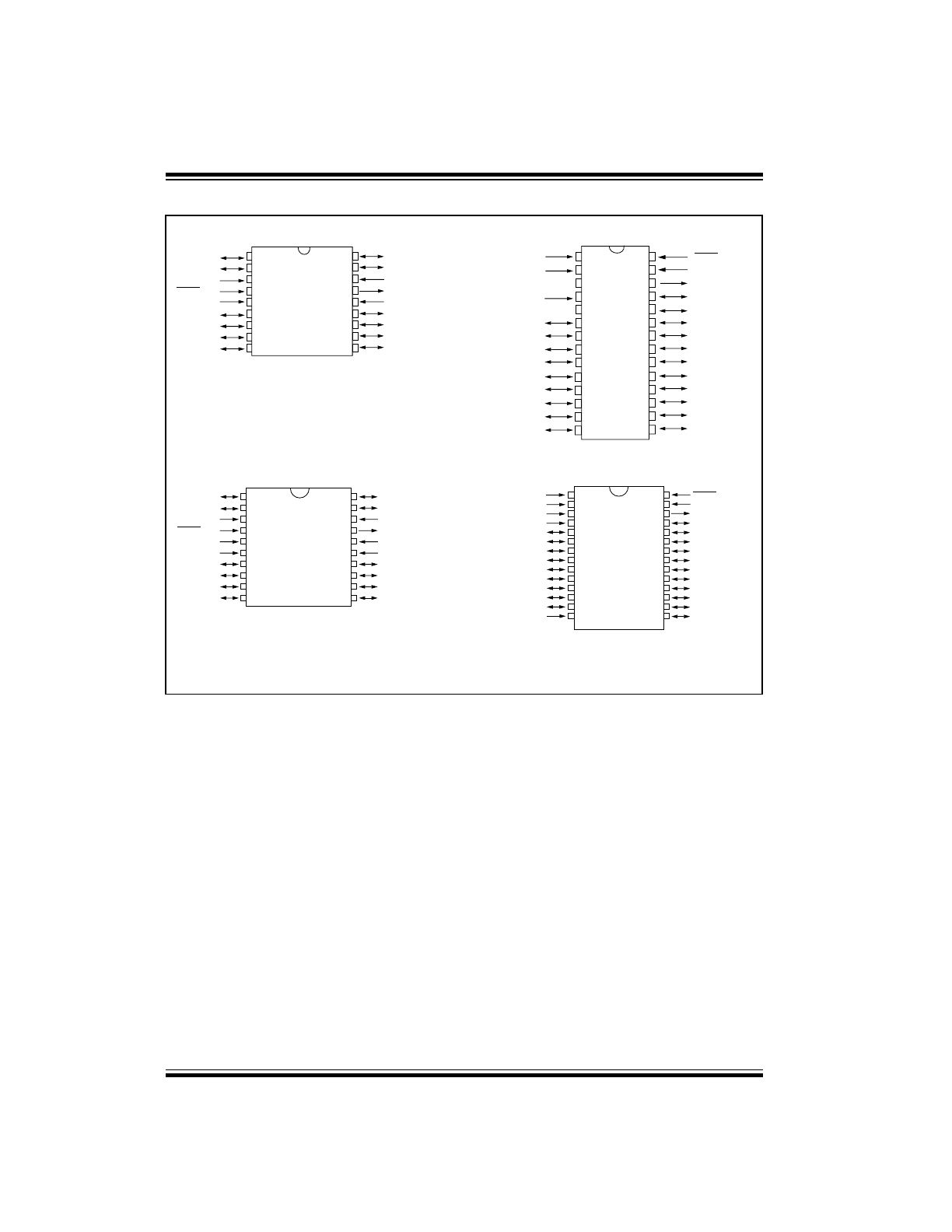
Pin Diagrams
PDIP, SOIC, Windowed CERDIP
PIC16CR54s
PIC16C58s
PIC16CR58s
PIC16C54s
RA1
RA0
OSC1/CLKIN
OSC2/CLKOUT
V
DD
V
DD
RB7
RB6
RB5
RB4
RA2
RA3
T0CKI
MCLR/V
PP
V
SS
V
SS
RB0
RB1
RB2
RB3
•
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
SSOP
PIC16C56s
PIC16CR56s
PIC16CR54s
PIC16C58s
PIC16CR58s
PIC16C54s
PIC16C56s
PIC16CR56s
RA2
RA3
T0CKI
MCLR/V
PP
V
SS
RB0
RB1
RB2
RB3
•
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
RA1
RA0
OSC1/CLKIN
OSC2/CLKOUT
V
DD
RB7
RB6
RB5
RB4
PIC16C52s
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
•1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
PDIP, SOIC, Windowed CERDIP
PIC16C57s
PIC16C55s
MCLR/V
PP
OSC1/CLKIN
OSC2/CLKOUT
RC7
RC6
RC5
RC4
RC3
RC2
RC1
RC0
RB7
RB6
RB5
T0CKI
V
DD
V
SS
RA0
RA1
RA2
RA3
RB0
RB1
RB2
RB3
RB4
•
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
PIC16C57s
SSOP
PIC16C55s
V
DD
V
SS
PIC16CR57s
PIC16CR57s
T0CKI
V
DD
N/C
V
SS
N/C
RA0
RA1
RA2
RA3
RB0
RB1
RB2
RB3
RB4
MCLR/V
PP
OSC1/CLKIN
OSC2/CLKOUT
RC7
RC6
RC5
RC4
RC3
RC2
RC1
RC0
RB7
RB6
RB5
1998 Microchip Technology Inc.
Preliminary
DS30453B-page 3
PIC16C5X
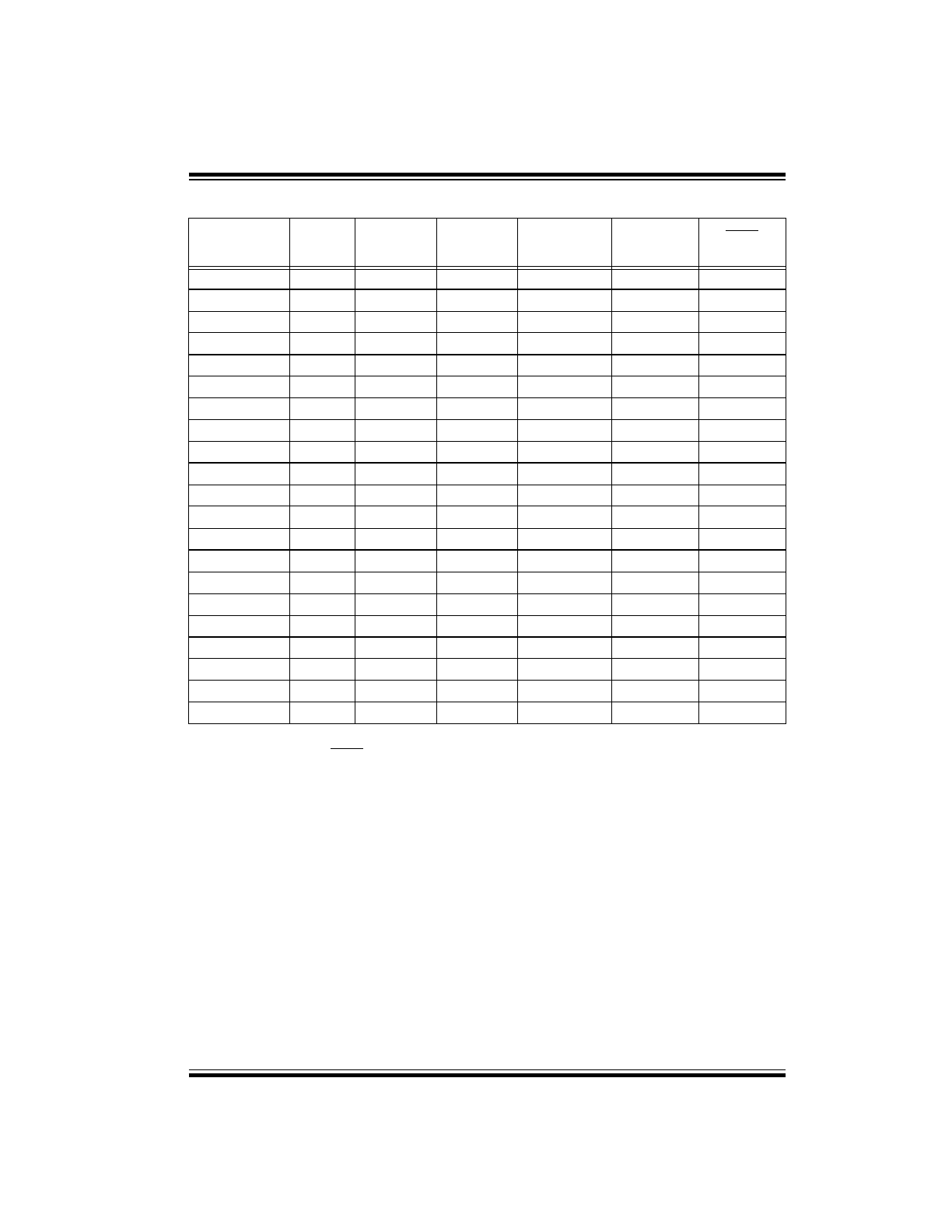
Device Differences
Note 1:
If you change from this device to another device, please verify oscillator characteristics in your application.
Note 2:
In PIC16LV58A, MCLR Filter = Yes
Device
Voltage
Range
Oscillator
Selection
(Program)
Oscillator
Process
Technology
(Microns)
ROM
Equivalent
MCLR
Filter
PIC16C52
3.0-6.25
User
See Note 1
0.9
—
No
PIC16C54
2.5-6.25
Factory
See Note 1
1.2
PIC16CR54A
No
PIC16C54A
2.0-6.25
User
See Note 1
0.9
—
No
PIC16C54B
2.5-5.5
User
See Note 1
0.7
PIC16CR54B
Yes
PIC16C54C
2.5-5.5
User
See Note 1
0.7
PIC16CR54C
Yes
PIC16C55
2.5-6.25
Factory
See Note 1
1.7
—
No
PIC16C55A
2.5-5.5
User
See Note 1
0.7
—
Yes
PIC16C56
2.5-6.25
Factory
See Note 1
1.7
—
No
PIC16C56A
2.5-5.5
User
See Note 1
0.7
PIC16CR56A
Yes
PIC16C57
2.5-6.25
Factory
See Note 1
1.2
—
No
PIC16C57C
2.5-5.5
User
See Note 1
0.7
PIC16CR57C
Yes
PIC16C58A
2.0-6.25
User
See Note 1
0.9
PIC16CR58A
No
(2)
PIC16C58B
2.5-5.5
User
See Note 1
0.7
PIC16CR58B
Yes
PIC16CR54A
2.5-6.25
Factory
See Note 1
1.2
N/A
Yes
PIC16CR54B
2.5-5.5
Factory
See Note 1
0.7
N/A
Yes
PIC16CR54C
2.5-5.5
Factory
See Note 1
0.7
N/A
Yes
PIC16CR56A
2.5-5.5
Factory
See Note 1
0.7
N/A
Yes
PIC16CR57B
2.5-6.25
Factory
See Note 1
0.9
N/A
Yes
PIC16CR57C
2.5-5.5
Factory
See Note 1
0.7
N/A
Yes
PIC16CR58A
2.5-6.25
Factory
See Note 1
0.9
N/A
Yes
PIC16CR58B
2.5-5.5
Factory
See Note 1
0.7
N/A
Yes
PIC16C5X
DS30453B-page 4
Preliminary
1998 Microchip Technology Inc.
Table of Contents
1.0
General Description ............................................................................................................................................. 5
2.0
PIC16C5X Device Varieties................................................................................................................................. 7
3.0
Architectural Overview......................................................................................................................................... 9
4.0
Memory Organization ........................................................................................................................................ 15
5.0
I/O Ports............................................................................................................................................................. 25
6.0
Timer0 Module and TMR0 Register................................................................................................................... 27
7.0
Special Features of the CPU ............................................................................................................................. 31
8.0
Instruction Set Summary ................................................................................................................................... 43
9.0
Development Support ........................................................................................................................................ 55
10.0
Electrical Characteristics - PIC16C52................................................................................................................ 59
11.0
Electrical Characteristics - PIC16C54/55/56/57................................................................................................. 67
12.0
DC and AC Characteristics - PIC16C54/55/56/57 ............................................................................................. 81
13.0
Electrical Characteristics - PIC16CR54A........................................................................................................... 89
14.0
Electrical Characteristics - PIC16C54A ........................................................................................................... 103
15.0
Electrical Characteristics - PIC16CR57B......................................................................................................... 117
16.0
Electrical Characteristics - PIC16C58A ........................................................................................................... 131
17.0
Electrical Characteristics - PIC16CR58A......................................................................................................... 145
18.0
DC and AC Characteristics - PIC16C54A/CR57B/C58A/CR58A .................................................................... 159
19.0
Electrical Characteristics -
PIC16C54B/C54C/CR54B/CR54C/C55A/C56A/CR56A/C57C/CR57C/C58B/CR58B .................................... 171
20.0
DC and AC Characteristics -
PIC16C54B/C54C/CR54B/CR54C/C55A/C56A/CR56A/C57C/CR57C/C58B/CR58B .................................... 183
21.0
Packaging Information ..................................................................................................................................... 195
Appendix A: Compatibility ........................................................................................................................................... 207
Index ......................................................................................................................................................................... 209
On-Line Support .......................................................................................................................................................... 211
PIC16C5X Product Identification System.................................................................................................................... 213
PIC16C54/55/56/57 Product Identification System ..................................................................................................... 214
To Our Valued Customers
Most Current Data Sheet
To obtain the most up-to-date version of this data sheet, please check our Worldwide Web site at:
http://www.microchip.com
You can determine the version of a data sheet by examining its literature number found on the bottom outside corner of any page.
The last character of the literature number is the version number. e.g., DS30000A is version A of document DS30000.
Errata
An errata sheet may exist for current devices, describing minor operational differences (from the data sheet) and recommended
workarounds. As device/documentation issues become known to us, we will publish an errata sheet. The errata will specify the revi-
sion of silicon and revision of document to which it applies.
To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please check with one of the following:
• Microchip’s Worldwide Web site; http://www.microchip.com
• Your local Microchip sales office (see last page)
• The Microchip Corporate Literature Center; U.S. FAX: (602) 786-7277
When contacting a sales office or the literature center, please specify which device, revision of silicon and data sheet (include lit-
erature number) you are using.
Corrections to this Data Sheet
We constantly strive to improve the quality of all our products and documentation. We have spent a great deal of time to ensure
that this document is correct. However, we realize that we may have missed a few things. If you find any information that is missing
or appears in error, please:
• Fill out and mail in the reader response form in the back of this data sheet.
• E-mail us at webmaster@microchip.com.
We appreciate your assistance in making this a better document.

1998 Microchip Technology Inc.
Preliminary
DS30453B-page 5
PIC16C5X
1.0
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The PIC16C5X from Microchip Technology is a family
of low-cost, high performance, 8-bit, fully static,
EPROM/ ROM-based CMOS microcontrollers. It
employs a RISC architecture with only 33 single
word/single cycle instructions. All instructions are sin-
gle cycle (200 ns) except for program branches which
take two cycles. The PIC16C5X delivers performance
an order of magnitude higher than its competitors in the
same price category. The 12-bit wide instructions are
highly symmetrical resulting in 2:1 code compression
over other 8-bit microcontrollers in its class. The easy
to use and easy to remember instruction set reduces
development time significantly.
The PIC16C5X products are equipped with special fea-
tures that reduce system cost and power requirements.
The Power-On Reset (POR) and Device Reset Timer
(DRT) eliminate the need for external reset circuitry.
There are four oscillator configurations to choose from,
including the power-saving LP (Low Power) oscillator
and cost saving RC oscillator. Power saving SLEEP
mode, Watchdog Timer and code protection features
improve system cost, power and reliability.
The UV erasable CERDIP packaged versions are ideal
for code development, while the cost-effective One
Time Programmable (OTP) versions are suitable for
production in any volume. The customer can take full
advantage of Microchip’s price leadership in OTP
microcontrollers while benefiting from the OTP’s
flexibility.
The PIC16C5X products are supported by a
full-featured macro assembler, a software simulator, an
in-circuit emulator, a ‘C’ compiler, fuzzy logic support
tools, a low-cost development programmer, and a full
featured programmer. All the tools are supported on
IBM
PC and compatible machines.
1.1
Applications
The PIC16C5X series fits perfectly in applications rang-
ing from high-speed automotive and appliance motor
control to low-power remote transmitters/receivers,
pointing devices and telecom processors. The EPROM
technology makes customizing application programs
(transmitter codes, motor speeds, receiver frequen-
cies, etc.) extremely fast and convenient. The small
footprint packages, for through hole or surface mount-
ing, make this microcontroller series perfect for applica-
tions with space limitations. Low-cost, low-power, high
performance, ease of use and I/O flexibility make the
PIC16C5X series very versatile even in areas where no
microcontroller use has been considered before (e.g.,
timer functions, replacement of “glue” logic in larger
systems, coprocessor applications).
PIC16C5X
DS30453B-page 6
Preliminary
1998 Microchip Technology Inc.
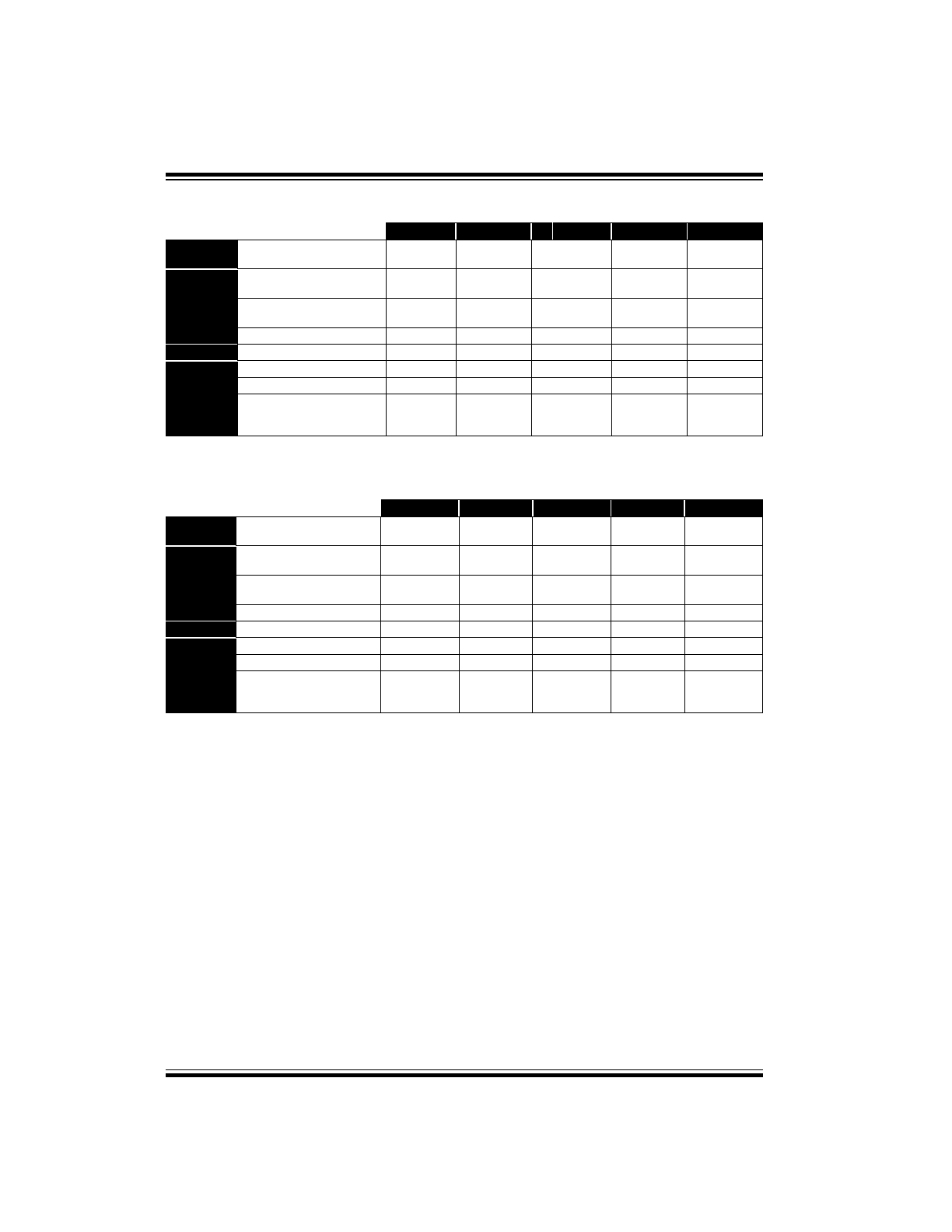
TABLE 1-1:
PIC16C5X FAMILY OF DEVICES
PIC16C52
PIC16C54s
PIC16CR54s
PIC16C55s
PIC16C56s
Clock
Maximum Frequency
of Operation (MHz)
4
20
20
20
20
Memory
EPROM Program Memory
(x12 words)
384
512
—
512
1K
ROM Program Memory
(x12 words)
—
—
512
—
—
RAM Data Memory (bytes)
25
25
25
24
25
Peripherals
Timer Module(s)
TMR0
TMR0
TMR0
TMR0
TMR0
Features
I/O Pins
12
12
12
20
12
Number of Instructions
33
33
33
33
33
Packages
18-pin DIP,
SOIC
18-pin DIP,
SOIC;
20-pin SSOP
18-pin DIP,
SOIC;
20-pin SSOP
28-pin DIP,
SOIC;
28-pin SSOP
18-pin DIP,
SOIC;
20-pin SSOP
All PICmicro™ Family devices have Power-on Reset, selectable Watchdog Timer (except PIC16C52), selectable code
protect and high I/O current capability.
PIC16CR56s
PIC16C57s
PIC16CR57s
PIC16C58s
PIC16CR58s
Clock
Maximum Frequency
of Operation (MHz)
20
20
20
20
20
Memory
EPROM Program Memory
(x12 words)
—
2K
—
2K
—
ROM Program Memory
(x12 words)
1K
—
2K
—
2K
RAM Data Memory (bytes)
25
72
72
73
73
Peripherals
Timer Module(s)
TMR0
TMR0
TMR0
TMR0
TMR0
Features
I/O Pins
12
20
20
12
12
Number of Instructions
33
33
33
33
33
Packages
18-pin DIP,
SOIC;
20-pin SSOP
28-pin DIP,
SOIC;
28-pin SSOP
28-pin DIP,
SOIC;
28-pin SSOP
18-pin DIP,
SOIC;
20-pin SSOP
18-pin DIP,
SOIC;
20-pin SSOP
All PICmicro™ Family devices have Power-on Reset, selectable Watchdog Timer (except PIC16C52), selectable code
protect and high I/O current capability.

1998 Microchip Technology Inc.
Preliminary
DS30453B-page 7
PIC16C5X
2.0
PIC16C5X DEVICE VARIETIES
A variety of frequency ranges and packaging options
are available. Depending on application and
production requirements, the proper device option can
be selected using the information in this section. When
placing orders, please use the PIC16C5X Product
Identification System at the back of this data sheet to
specify the correct part number.
For the PIC16C5X family of devices, there are four
device types, as indicated in the device number:
1.
C
, as in PIC16C54. These devices have
EPROM program memory and operate over the
standard voltage range.
2.
LC
, as in PIC16LC54A. These devices have
EPROM program memory and operate over an
extended voltage range.
3.
LV
, as in PIC16LV54A. These devices have
EPROM program memory and operate over a
2.0V to 3.8V range.
4.
CR
, as in PIC16CR54A. These devices have
ROM program memory and operate over the
standard voltage range.
5.
LCR
, as in PIC16LCR54B. These devices have
ROM program memory and operate over an
extended voltage range.
2.1
UV Erasable Devices (EPROM)
The UV erasable versions, offered in CERDIP
packages, are optimal for prototype development and
pilot programs
UV erasable devices can be programmed for any of
the four oscillator configurations. Microchip's
PICSTART
and PRO MATE
programmers both
support programming of the PIC16C5X. Third party
programmers also are available; refer to the Third
Party Guide for a list of sources.
2.2
One-Time-Programmable (OTP)
Devices
The availability of OTP devices is especially useful for
customers expecting frequent code changes and
updates.
The OTP devices, packaged in plastic packages,
permit the user to program them once. In addition to
the program memory, the configuration bits must be
programmed.
2.3
Quick-Turnaround-Production (QTP)
Devices
Microchip offers a QTP Programming Service for
factory production orders. This service is made
available for users who choose not to program a
medium to high quantity of units and whose code
patterns have stabilized. The devices are identical to
the OTP devices but with all EPROM locations and
configuration bit options already programmed by the
factory. Certain code and prototype verification
procedures apply before production shipments are
available. Please contact your Microchip Technology
sales office for more details.
2.4
Serialized
Quick-Turnaround-Production
(SQTP ) Devices
Microchip offers the unique programming service
where a few user-defined locations in each device are
programmed with different serial numbers. The serial
numbers may be random, pseudo-random or
sequential. The devices are identical to the OTP
devices but with all EPROM locations and
configuration bit options already programmed by the
factory.
Serial programming allows each device to have a
unique number which can serve as an entry code,
password or ID number.
2.5
Read Only Memory (ROM) Devices
Microchip offers masked ROM versions of several of
the highest volume parts, giving the customer a low
cost option for high volume, mature products.
SM

PIC16C5X
DS30453B-page 8
Preliminary
1998 Microchip Technology Inc.
NOTES:

1998 Microchip Technology Inc.
Preliminary
DS30453B-page 9
PIC16C5X
3.0
ARCHITECTURAL OVERVIEW
The high performance of the PIC16C5X family can be
attributed to a number of architectural features
commonly found in RISC microprocessors. To begin
with, the PIC16C5X uses a Harvard architecture in
which program and data are accessed on separate
buses. This improves bandwidth over traditional von
Neumann architecture where program and data are
fetched on the same bus. Separating program and
data memory further allows instructions to be sized
differently than the 8-bit wide data word. Instruction
opcodes are 12-bits wide making it possible to have all
single word instructions. A 12-bit wide program
memory access bus fetches a 12-bit instruction in a
single cycle. A two-stage pipeline overlaps fetch and
execution of instructions. Consequently, all instructions
(33) execute in a single cycle (200ns @ 20MHz)
except for program branches.
The PIC16C52 addresses 384 x 12 of program
memory, the PIC16C54s/CR54s and PIC16C55s
address 512
x
12 of program memory, the
PIC16C56s/CR56s address 1K X 12 of program
memory, and the PIC16C57s/CR57s and
PIC16C58s/CR58s address 2K
x
12 of program
memory. All program memory is internal.
The PIC16C5X can directly or indirectly address its
register files and data memory. All special function
registers including the program counter are mapped in
the data memory. The PIC16C5X has a highly
orthogonal (symmetrical) instruction set that makes it
possible to carry out any operation on any register
using any addressing mode. This symmetrical nature
and lack of ‘special optimal situations’ make
programming with the PIC16C5X simple yet efficient.
In addition, the learning curve is reduced significantly.
The PIC16C5X device contains an 8-bit ALU and
working register. The ALU is a general purpose
arithmetic unit. It performs arithmetic and Boolean
functions between data in the working register and any
register file.
The ALU is 8-bits wide and capable of addition,
subtraction, shift and logical operations. Unless
otherwise mentioned, arithmetic operations are two's
complement in nature. In two-operand instructions,
typically one operand is the W (working) register. The
other operand is either a file register or an immediate
constant. In single operand instructions, the operand
is either the W register or a file register.
The W register is an 8-bit working register used for
ALU operations. It is not an addressable register.
Depending on the instruction executed, the ALU may
affect the values of the Carry (C), Digit Carry (DC),
and Zero (Z) bits in the STATUS register. The C and
DC bits operate as a borrow and digit borrow out bit,
respectively, in subtraction. See the
SUBWF
and
ADDWF
instructions for examples.
A simplified block diagram is shown in Figure 3-1, with
the corresponding device pins described in Table 3-1.
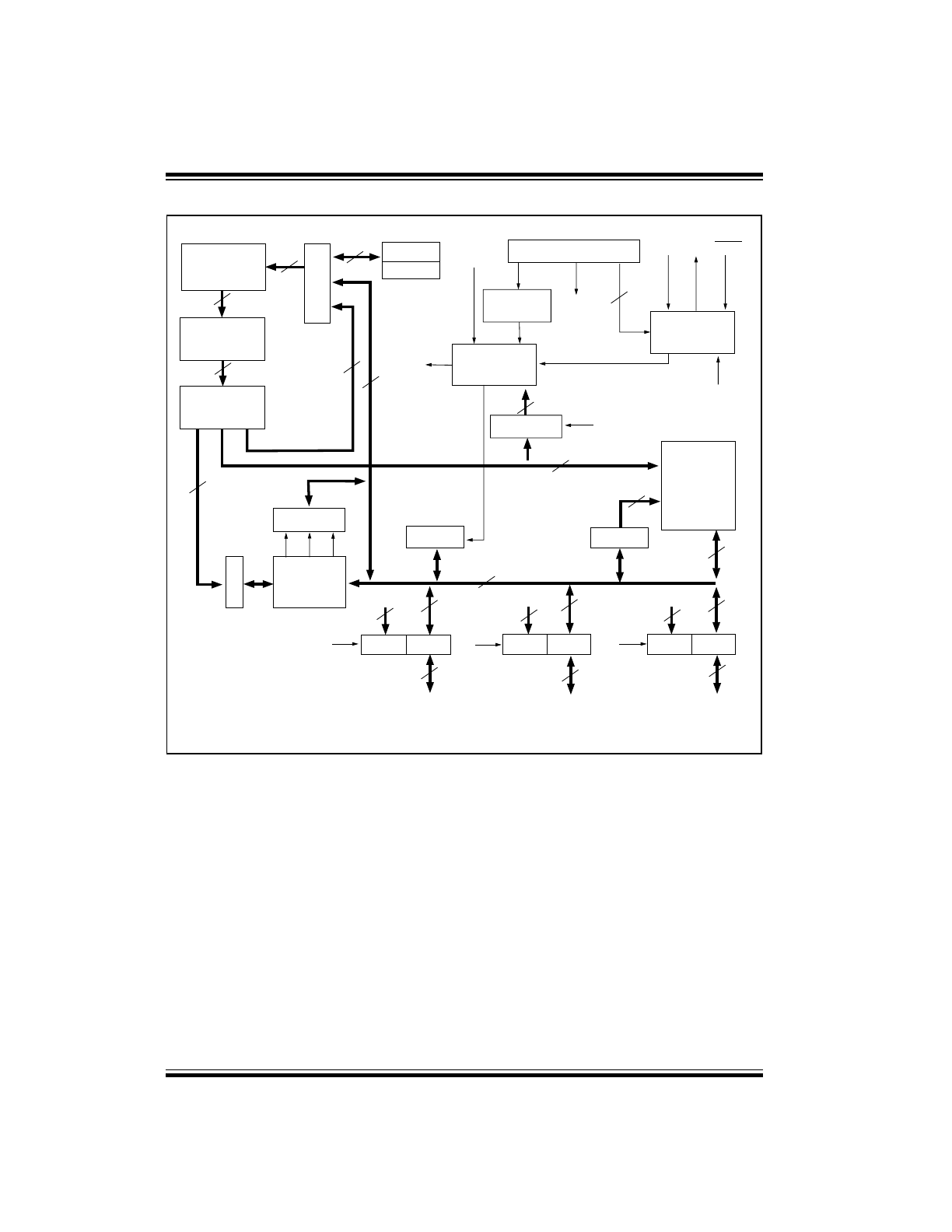
PIC16C5X
DS30453B-page 10
Preliminary
1998 Microchip Technology Inc.
FIGURE 3-1:
PIC16C5X SERIES BLOCK DIAGRAM
WDT TIME
OUT
8
STACK 1
STACK 2
EPROM/ROM
384 X 12 TO
2048 X 12
INSTRUCTION
REGISTER
INSTRUCTION
DECODER
WATCHDOG
TIMER
CONFIGURATION WORD
OSCILLATOR/
TIMING &
CONTROL
GENERAL
PURPOSE
REGISTER
FILE
(SRAM)
24, 25, 72 or
73 Bytes
WDT/TMR0
PRESCALER
OPTION REG.
“OPTION”
“SLEEP”
“CODE
PROTECT”
“OSC
SELECT”
DIRECT ADDRESS
TMR0
FROM W
FROM W
“TRIS 5”
“TRIS 6”
“TRIS 7”
FSR
TRISA
PORTA
TRISB
PORTC
TRISC
PORTB
FROM W
T0CKI
PIN
9-11
9-11
12
12
8
W
4
4
4
DATA BUS
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
ALU
STATUS
FROM W
CLKOUT
8
9
6
5
5-7
OSC1 OSC2 MCLR
LITERALS
PC
“DISABLE”
2
RA3:RA0
RB7:RB0
RC7:RC0
(28-Pin
Devices Only)
DIRECT RAM
ADDRESS
