
Features
•
High Performance, Low Power AVR
®
8-Bit Microcontroller
•
Advanced RISC Architecture
– 120 Powerful Instructions – Most Single Clock Cycle Execution
– 32 x 8 General Purpose Working Registers
– Fully Static Operation
– Up to 20 MIPS Througput at 20 MHz
•
High Endurance Non-volatile Memory segments
– 1K Bytes of In-System Self-programmable Flash program memory
– 64 Bytes EEPROM
– 64 Bytes Internal SRAM
– Write/Erase cyles: 10,000 Flash/100,000 EEPROM
– Data retention: 20 years at 85°C/100 years at 25°C (see
page 6
)
– Programming Lock for Self-Programming Flash & EEPROM Data Security
•
Peripheral Features
– One 8-bit Timer/Counter with Prescaler and Two PWM Channels
– 4-channel, 10-bit ADC with Internal Voltage Reference
– Programmable Watchdog Timer with Separate On-chip Oscillator
– On-chip Analog Comparator
•
Special Microcontroller Features
– debugWIRE On-chip Debug System
– In-System Programmable via SPI Port
– External and Internal Interrupt Sources
– Low Power Idle, ADC Noise Reduction, and Power-down Modes
– Enhanced Power-on Reset Circuit
– Programmable Brown-out Detection Circuit
– Internal Calibrated Oscillator
•
I/O and Packages
– 8-pin PDIP/SOIC: Six Programmable I/O Lines
– 20-pad MLF: Six Programmable I/O Lines
•
Operating Voltage:
– 1.8 - 5.5V for ATtiny13V
– 2.7 - 5.5V for ATtiny13
•
Speed Grade
– ATtiny13V: 0 - 4 MHz @ 1.8 - 5.5V, 0 - 10 MHz @ 2.7 - 5.5V
– ATtiny13: 0 - 10 MHz @ 2.7 - 5.5V, 0 - 20 MHz @ 4.5 - 5.5V
•
Industrial Temperature Range
•
Low Power Consumption
– Active Mode:
• 1 MHz, 1.8V: 240 µA
– Power-down Mode:
• < 0.1 µA at 1.8V
8-bit
Microcontroller
with 1K Bytes
In-System
Programmable
Flash
ATtiny13
ATtiny13V
Summary
Rev. 2535JS–AVR–08/10
2
2535JS–AVR–08/10
ATtiny13
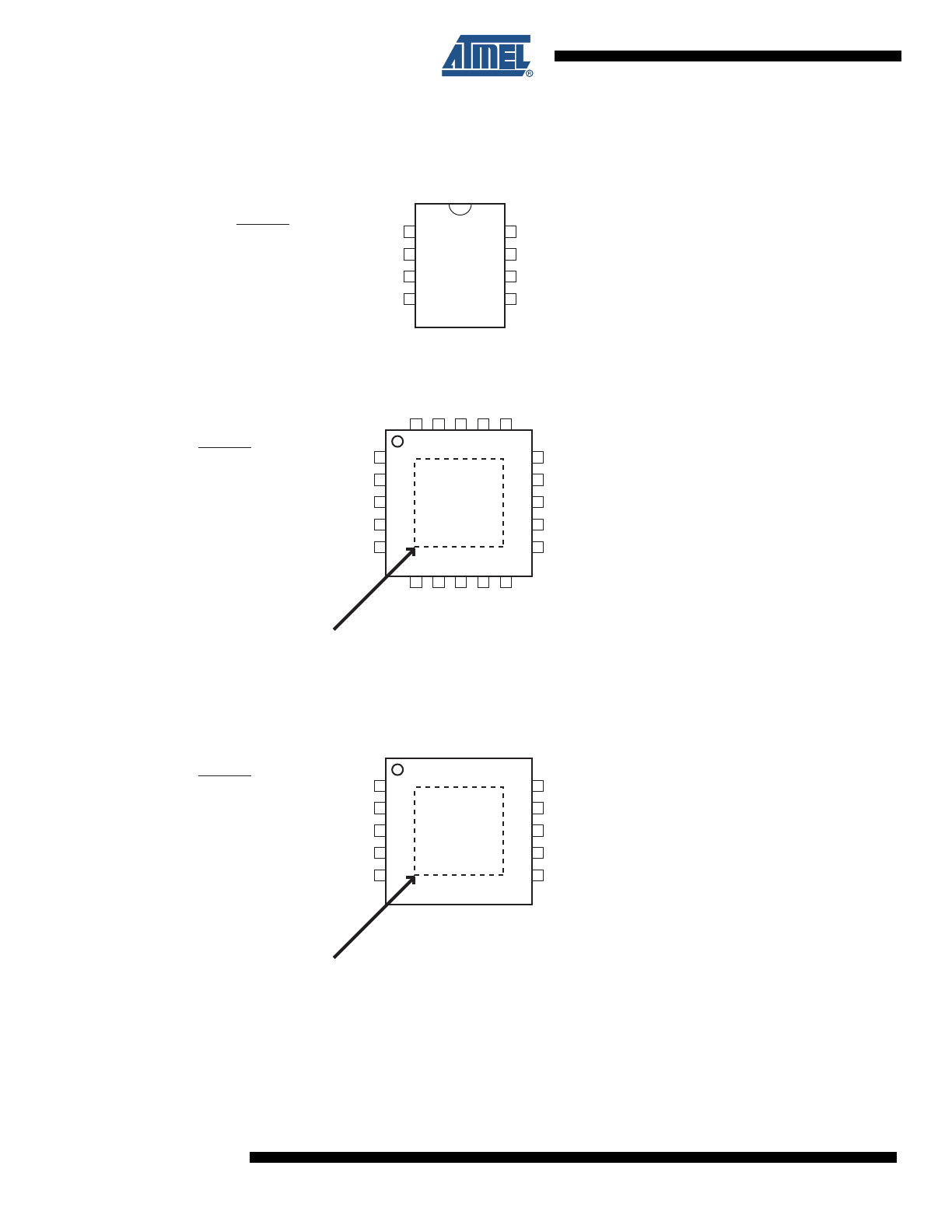
1. Pin Configurations
Figure 1-1.
Pinout ATtiny13/ATtiny13V
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
(PCINT5/RESET/ADC0/dW) PB5
(PCINT3/CLKI/ADC3) PB3
(PCINT4/ADC2) PB4
GND
VCC
PB2 (SCK/ADC1/T0/PCINT2)
PB1 (MISO/AIN1/OC0B/INT0/PCINT1)
PB0 (MOSI/AIN0/OC0A/PCINT0)
8-PDIP/SOIC
1
2
3
4
5
20-QFN/MLF
15
14
13
12
11
20
19
18
17
16
6
7
8
9
10
(PCINT5/RESET/ADC0/dW) PB5
(PCINT3/CLKI/ADC3) PB3
DNC
DNC
(PCINT4/ADC2) PB4
DNC
DNC
GND
DNC
DNC
VCC
PB2 (SCK/ADC1/T0/PCINT2)
DNC
PB1 (MISO/AIN1/OC0B/INT0/PCINT1)
PB0 (MOSI/AIN0/OC0A/PCINT0)
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
NOTE: Bottom pad should be soldered to ground.
DNC: Do Not Connect
1
2
3
4
5
10-QFN/MLF
10
9
8
7
6
(PCINT5/RESET/ADC0/dW) PB5
(PCINT3/CLKI/ADC3) PB3
DNC
(PCINT4/ADC2) PB4
GND
VCC
PB2 (SCK/ADC1/T0/PCINT2)
DNC
PB1 (MISO/AIN1/OC0B/INT0/PCINT1)
PB0 (MOSI/AIN0/OC0A/PCINT0)
NOTE: Bottom pad should be soldered to ground.
DNC: Do Not Connect

3
2535JS–AVR–08/10
ATtiny13
1.1
Pin Descriptions
1.1.1
VCC
Digital supply voltage.
1.1.2
GND
Ground.
1.1.3
Port B (PB5:PB0)
Port B is a 6-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port B output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port B pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port B pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port B also serves the functions of various special features of the ATtiny13 as listed on
page 54
.
1.1.4
RESET
Reset input. A low level on this pin for longer than the minimum pulse length will generate a
reset, even if the clock is not running. The minimum pulse length is given in
Table 18-1 on page
115
. Shorter pulses are not guaranteed to generate a reset.
The reset pin can also be used as a (weak) I/O pin.
4
2535JS–AVR–08/10
ATtiny13
2. Overview
The ATtiny13 is a low-power CMOS 8-bit microcontroller based on the AVR enhanced RISC
architecture. By executing powerful instructions in a single clock cycle, the ATtiny13 achieves
throughputs approaching 1 MIPS per MHz allowing the system designer to optimize power con-
sumption versus processing speed.
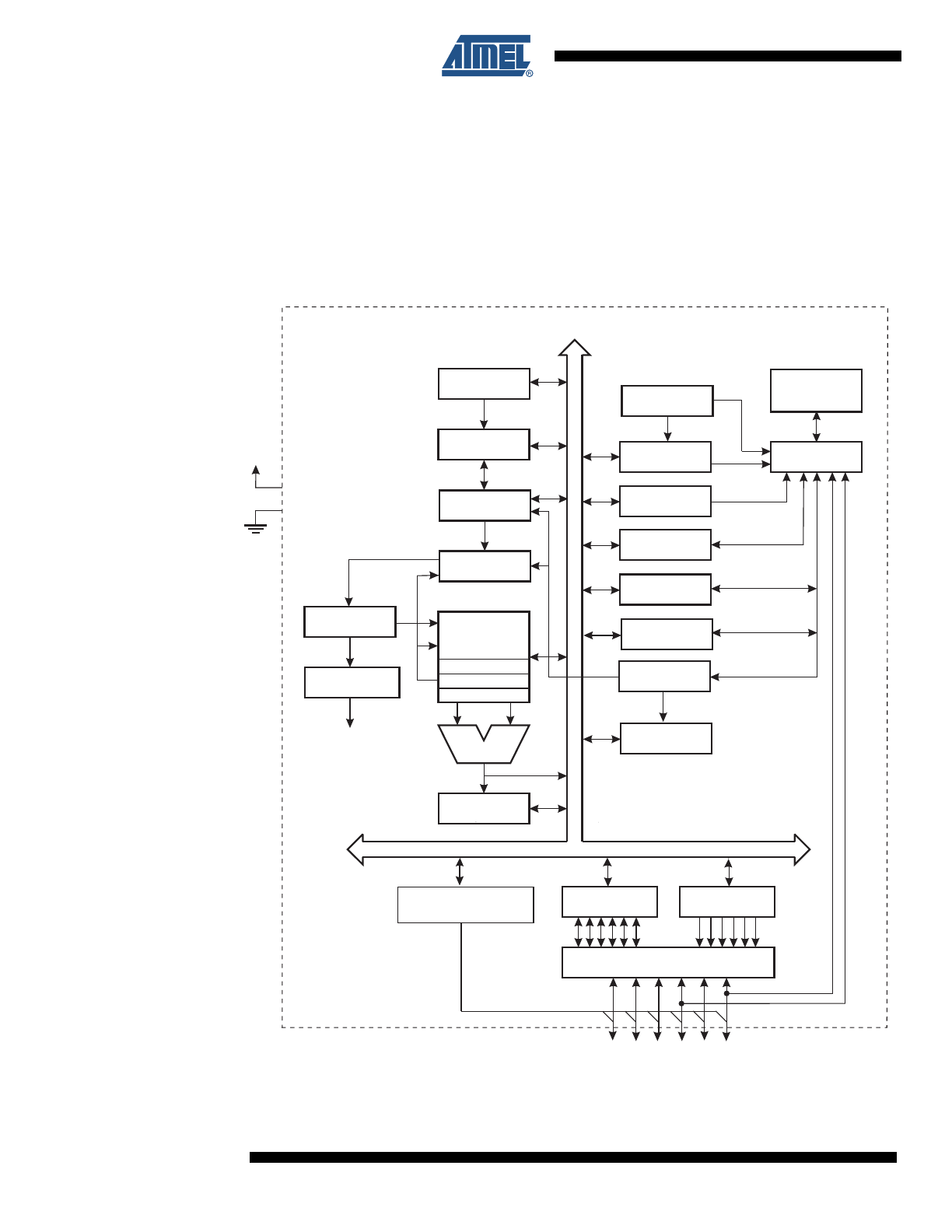
2.1
Block Diagram
Figure 2-1.
Block Diagram
PROGRAM
COUNTER
INTERNAL
OSCILLATOR
WATCHDOG
TIMER
STACK
POINTER
PROGRAM
FLASH
SRAM
MCU CONTROL
REGISTER
GENERAL
PURPOSE
REGISTERS
INSTRUCTION
REGISTER
TIMER/
COUNTER0
INSTRUCTION
DECODER
DATA DIR.
REG.PORT B
DATA REGISTER
PORT B
PROGRAMMING
LOGIC
TIMING AND
CONTROL
MCU STATUS
REGISTER
STATUS
REGISTER
ALU
PORT B DRIVERS
PB0-PB5
VCC
GND
CONTROL
LINES
8-BIT DATABUS
Z
ADC /
ANALOG COMPARATOR
INTERRUPT
UNIT
CALIBRATED
Y
X
RESET
CLKI
WATCHDOG
OSCILLATOR
DATA
EEPROM

5
2535JS–AVR–08/10
ATtiny13
The AVR core combines a rich instruction set with 32 general purpose working registers. All 32
registers are directly connected to the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), allowing two independent
registers to be accessed in one single instruction executed in one clock cycle. The resulting
architecture is more code efficient while achieving throughputs up to ten times faster than con-
ventional CISC microcontrollers.
The ATtiny13 provides the following features: 1K byte of In-System Programmable Flash, 64
bytes EEPROM, 64 bytes SRAM, 6 general purpose I/O lines, 32 general purpose working reg-
isters, one 8-bit Timer/Counter with compare modes, Internal and External Interrupts, a 4-
channel, 10-bit ADC, a programmable Watchdog Timer with internal Oscillator, and three soft-
ware selectable power saving modes. The Idle mode stops the CPU while allowing the SRAM,
Timer/Counter, ADC, Analog Comparator, and Interrupt system to continue functioning. The
Power-down mode saves the register contents, disabling all chip functions until the next Inter-
rupt or Hardware Reset. The ADC Noise Reduction mode stops the CPU and all I/O modules
except ADC, to minimize switching noise during ADC conversions.
The device is manufactured using Atmel’s high density non-volatile memory technology. The
On-chip ISP Flash allows the Program memory to be re-programmed In-System through an SPI
serial interface, by a conventional non-volatile memory programmer or by an On-chip boot code
running on the AVR core.
The ATtiny13 AVR is supported with a full suite of program and system development tools
including: C Compilers, Macro Assemblers, Program Debugger/Simulators, and Evaluation kits.

6
2535JS–AVR–08/10
ATtiny13
3. General Information
3.1
Resources
A comprehensive set of drivers, application notes, data sheets and descriptions on development
tools are available for download at http://www.atmel.com/avr.
3.2
Code Examples
This documentation contains simple code examples that briefly show how to use various parts of
the device. These code examples assume that the part specific header file is included before
compilation. Be aware that not all C compiler vendors include bit definitions in the header files
and interrupt handling in C is compiler dependent. Please confirm with the C compiler documen-
tation for more details.
3.3
Data Retention
Reliability Qualification results show that the projected data retention failure rate is much less
than 1 PPM over 20 years at 85°C or 100 years at 25
°C.
7
2535JS–AVR–08/10
ATtiny13
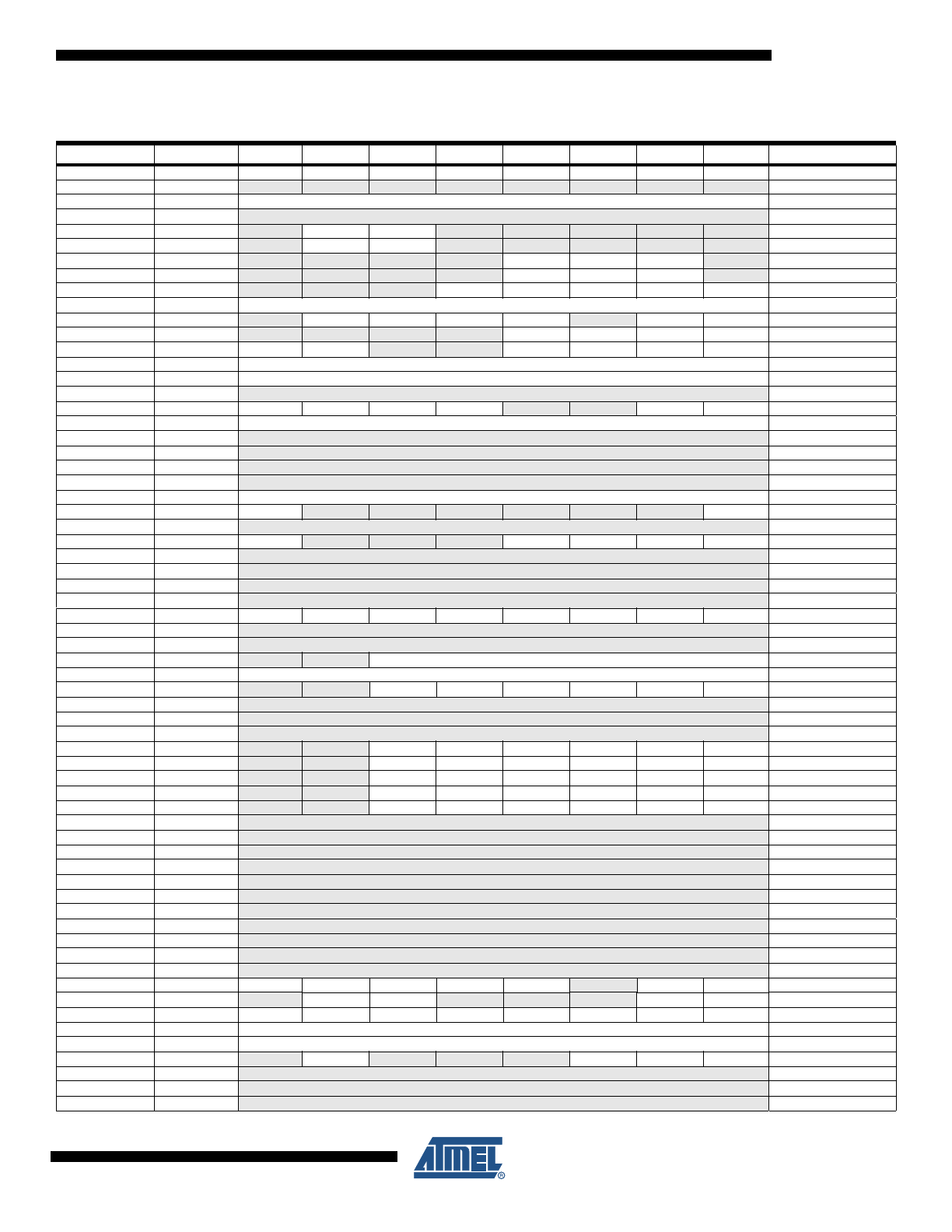
4. Register Summary
Address
Name
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Page
0x3F
SREG
I
T
H
S
V
N
Z
C
page 9
0x3E
Reserved
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
0x3D
SPL
SP[7:0]
page 11
0x3C
Reserved
–
0x3B
GIMSK
–
INT0
PCIE
–
–
–
–
–
page 46
0x3A GIFR
–
INTF0
PCIF
–
–
–
–
–
page 47
0x39 TIMSK0
–
–
–
–
OCIE0B
OCIE0A
TOIE0
–
page 74
0x38 TIFR0
–
–
–
–
OCF0B
OCF0A
TOV0
–
page 75
0x37 SPMCSR
–
–
–
CTPB
RFLB
PGWRT
PGERS
SELFPR-
page 97
0x36
OCR0A
Timer/Counter – Output Compare Register A
page 74
0x35
MCUCR
–
PUD
SE
SM1
SM0
–
ISC01
ISC00
page 32
0x34 MCUSR
–
–
–
–
WDRF
BORF
EXTRF
PORF
page 41
0x33 TCCR0B
FOC0A
FOC0B
–
–
WGM02
CS02
CS01
CS00
page 72
0x32 TCNT0
Timer/Counter
(8-bit)
page 73
0x31
OSCCAL
Oscillator Calibration Register
page 27
0x30 Reserved
–
0x2F
TCCR0A
COM0A1
COM0A0
COM0B1
COM0B0
–
–
WGM01
WGM00
page 69
0x2E
DWDR
DWDR[7:0]
page 96
0x2D
Reserved
–
0x2C
Reserved
–
0x2B
Reserved
–
0x2A Reserved
–
0x29
OCR0B
Timer/Counter – Output Compare Register B
page 74
0x28 GTCCR
TSM
–
–
–
–
–
–
PSR10
page 77
0x27 Reserved
–
0x26 CLKPR
CLKPCE
–
–
–
CLKPS3
CLKPS2
CLKPS1
CLKPS0
page 28
0x25
Reserved
–
0x24 Reserved
–
0x23 Reserved
–
0x22
Reserved
–
0x21 WDTCR
WDTIF
WDTIE
WDP3
WDCE
WDE
WDP2
WDP1
WDP0
page 41
0x20 Reserved
–
0x1F Reserved
–
0x1E
EEARL
–
–
EEPROM Address Register
page 20
0x1D
EEDR
EEPROM Data Register
page 20
0x1C
EECR
–
–
EEPM1
EEPM0
EERIE
EEMPE
EEPE
EERE
page 21
0x1B Reserved
–
0x1A
Reserved
–
0x19 Reserved
–
0x18 PORTB
–
–
PORTB5
PORTB4
PORTB3
PORTB2
PORTB1
PORTB0
page 56
0x17
DDRB
–
–
DDB5
DDB4
DDB3
DDB2
DDB1
DDB0
page 56
0x16 PINB
–
–
PINB5
PINB4
PINB3
PINB2
PINB1
PINB0
page 57
0x15
PCMSK
–
–
PCINT5
PCINT4
PCINT3
PCINT2
PCINT1
PCINT0
page 47
0x14 DIDR0
–
–
ADC0D
ADC2D
ADC3D
ADC1D
AIN1D
AIN0D
page 80
,
page 94
0x13 Reserved
–
0x12
Reserved
–
0x11 Reserved
–
0x10
Reserved
–
0x0F Reserved
–
0x0E Reserved
–
0x0D
Reserved
–
0x0C
Reserved
–
0x0B
Reserved
–
0x0A
Reserved
–
0x09
Reserved
–
0x08
ACSR
ACD
ACBG
ACO
ACI
ACIE
–
ACIS1
ACIS0
page 79
0x07
ADMUX
–
REFS0
ADLAR
–
–
–
MUX1
MUX0
page 91
0x06
ADCSRA
ADEN
ADSC
ADATE
ADIF
ADIE
ADPS2
ADPS1
ADPS0
page 92
0x05
ADCH
ADC Data Register High Byte
page 93
0x04
ADCL
ADC Data Register Low Byte
page 93
0x03
ADCSRB
–
ACME
–
–
–
ADTS2
ADTS1
ADTS0
page 94
0x02
Reserved
–
0x01
Reserved
–
0x00
Reserved
–

8
2535JS–AVR–08/10
ATtiny13
Notes: 1. For compatibility with future devices, reserved bits should be written to zero if accessed. Reserved I/O memory addresses
should never be written.
2. I/O Registers within the address range 0x00 - 0x1F are directly bit-accessible using the SBI and CBI instructions. In these
registers, the value of single bits can be checked by using the SBIS and SBIC instructions.ome of the Status Flags are
cleared by writing a logical one to them. Note that, unlike most other AVRs, the CBI and SBI instructions will only operation
the specified bit, and can therefore be used on registers containing such Status Flags. The CBI and SBI instructions work
with registers 0x00 to 0x1F only.
9
2535JS–AVR–08/10
ATtiny13
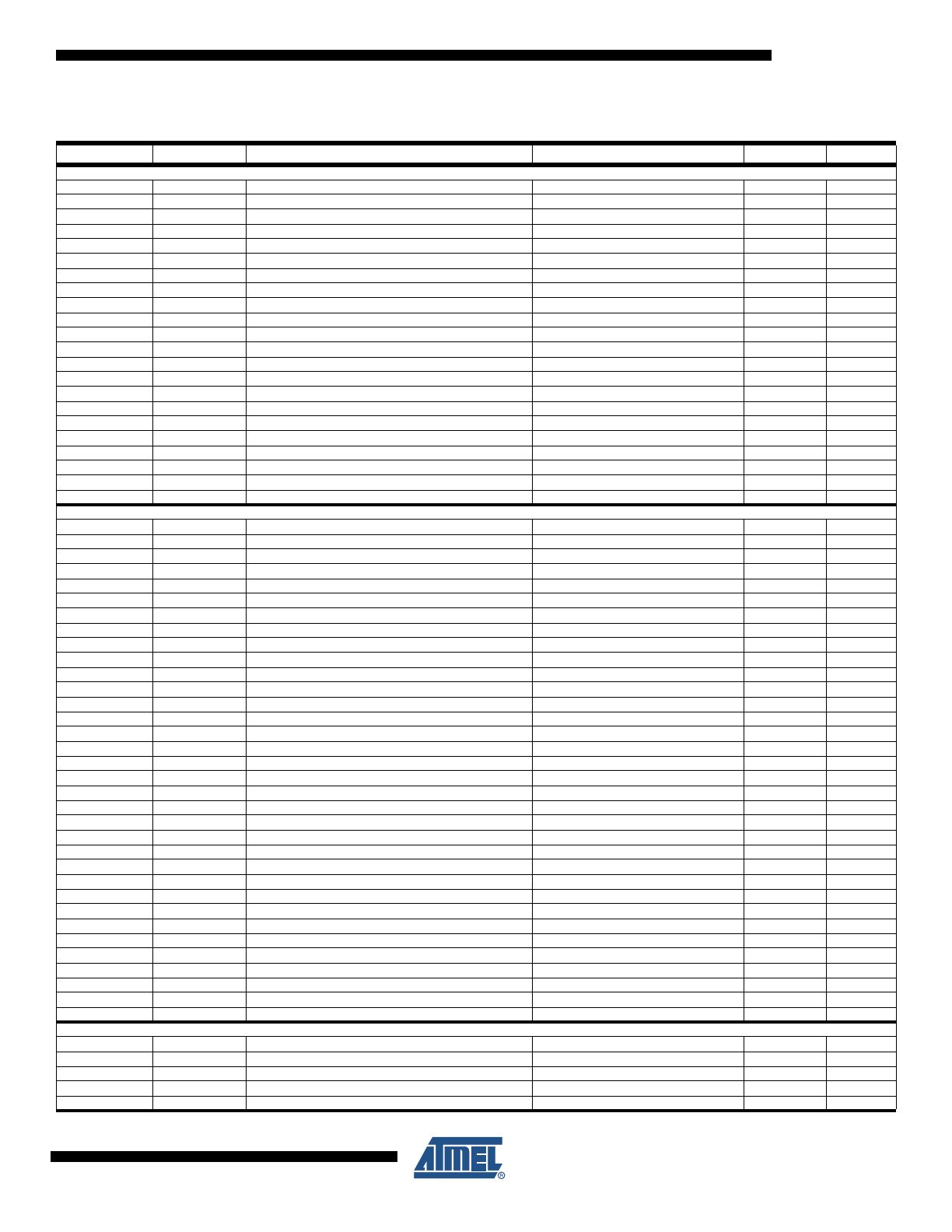
5. Instruction Set Summary
Mnemonics
Operands
Description
Operation
Flags
#Clocks
ARITHMETIC AND LOGIC INSTRUCTIONS
ADD
Rd, Rr
Add two Registers
Rd
← Rd + Rr
Z,C,N,V,H
1
ADC
Rd, Rr
Add with Carry two Registers
Rd
← Rd + Rr + C
Z,C,N,V,H
1
ADIW
Rdl,K
Add Immediate to Word
Rdh:Rdl
← Rdh:Rdl + K
Z,C,N,V,S
2
SUB
Rd, Rr
Subtract two Registers
Rd
← Rd - Rr
Z,C,N,V,H
1
SUBI
Rd, K
Subtract Constant from Register
Rd
← Rd - K
Z,C,N,V,H
1
SBC
Rd, Rr
Subtract with Carry two Registers
Rd
← Rd - Rr - C
Z,C,N,V,H
1
SBCI
Rd, K
Subtract with Carry Constant from Reg.
Rd
← Rd - K - C
Z,C,N,V,H
1
SBIW
Rdl,K
Subtract Immediate from Word
Rdh:Rdl
← Rdh:Rdl - K
Z,C,N,V,S
2
AND
Rd, Rr
Logical AND Registers
Rd
← Rd • Rr
Z,N,V
1
ANDI
Rd, K
Logical AND Register and Constant
Rd
← Rd • K
Z,N,V
1
OR
Rd, Rr
Logical OR Registers
Rd
← Rd v Rr
Z,N,V
1
ORI
Rd, K
Logical OR Register and Constant
Rd
← Rd v K
Z,N,V
1
EOR
Rd, Rr
Exclusive OR Registers
Rd
← Rd ⊕ Rr
Z,N,V
1
COM
Rd
One’s Complement
Rd
← 0xFF − Rd
Z,C,N,V
1
NEG
Rd
Two’s Complement
Rd
← 0x00 − Rd
Z,C,N,V,H
1
SBR
Rd,K
Set Bit(s) in Register
Rd
← Rd v K
Z,N,V
1
CBR
Rd,K
Clear Bit(s) in Register
Rd
← Rd • (0xFF - K)
Z,N,V
1
INC
Rd
Increment
Rd
← Rd + 1
Z,N,V
1
DEC
Rd
Decrement
Rd
← Rd − 1
Z,N,V
1
TST
Rd
Test for Zero or Minus
Rd
← Rd • Rd
Z,N,V
1
CLR
Rd
Clear Register
Rd
← Rd ⊕ Rd
Z,N,V
1
SER
Rd
Set Register
Rd
← 0xFF
None
1
BRANCH INSTRUCTIONS
RJMP
k
Relative Jump
PC
← PC + k + 1
None
2
IJMP
Indirect Jump to (Z)
PC
← Z
None
2
RCALL
k
Relative Subroutine Call
PC
← PC + k + 1
None
3
ICALL
Indirect Call to (Z)
PC
← Z
None
3
RET
Subroutine Return
PC
← STACK
None
4
RETI
Interrupt Return
PC
← STACK
I
4
CPSE
Rd,Rr
Compare, Skip if Equal
if (Rd = Rr) PC
← PC + 2 or 3
None
1/2/3
CP
Rd,Rr
Compare
Rd
− Rr
Z, N,V,C,H
1
CPC
Rd,Rr
Compare with Carry
Rd
− Rr − C
Z, N,V,C,H
1
CPI
Rd,K
Compare Register with Immediate
Rd
− K
Z, N,V,C,H
1
SBRC
Rr, b
Skip if Bit in Register Cleared
if (Rr(b)=0) PC
← PC + 2 or 3
None
1/2/3
SBRS
Rr, b
Skip if Bit in Register is Set
if (Rr(b)=1) PC
← PC + 2 or 3
None
1/2/3
SBIC
P, b
Skip if Bit in I/O Register Cleared
if (P(b)=0) PC
← PC + 2 or 3
None
1/2/3
SBIS
P, b
Skip if Bit in I/O Register is Set
if (P(b)=1) PC
← PC + 2 or 3
None
1/2/3
BRBS
s, k
Branch if Status Flag Set
if (SREG(s) = 1) then PC
←PC+k + 1
None
1/2
BRBC
s, k
Branch if Status Flag Cleared
if (SREG(s) = 0) then PC
←PC+k + 1
None
1/2
BREQ
k
Branch if Equal
if (Z = 1) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRNE
k
Branch if Not Equal
if (Z = 0) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRCS
k
Branch if Carry Set
if (C = 1) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRCC
k
Branch if Carry Cleared
if (C = 0) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRSH
k
Branch if Same or Higher
if (C = 0) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRLO
k
Branch if Lower
if (C = 1) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRMI
k
Branch if Minus
if (N = 1) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRPL
k
Branch if Plus
if (N = 0) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRGE
k
Branch if Greater or Equal, Signed
if (N
⊕ V= 0) then PC ← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRLT
k
Branch if Less Than Zero, Signed
if (N
⊕ V= 1) then PC ← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRHS
k
Branch if Half Carry Flag Set
if (H = 1) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRHC
k
Branch if Half Carry Flag Cleared
if (H = 0) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRTS
k
Branch if T Flag Set
if (T = 1) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRTC
k
Branch if T Flag Cleared
if (T = 0) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRVS
k
Branch if Overflow Flag is Set
if (V = 1) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRVC
k
Branch if Overflow Flag is Cleared
if (V = 0) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRIE
k
Branch if Interrupt Enabled
if ( I = 1) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BRID
k
Branch if Interrupt Disabled
if ( I = 0) then PC
← PC + k + 1
None
1/2
BIT AND BIT-TEST INSTRUCTIONS
SBI
P,b
Set Bit in I/O Register
I/O(P,b)
← 1
None
2
CBI
P,b
Clear Bit in I/O Register
I/O(P,b)
← 0
None
2
LSL
Rd
Logical Shift Left
Rd(n+1)
← Rd(n), Rd(0) ← 0
Z,C,N,V
1
LSR
Rd
Logical Shift Right
Rd(n)
← Rd(n+1), Rd(7) ← 0
Z,C,N,V
1
ROL
Rd
Rotate Left Through Carry
Rd(0)
←C,Rd(n+1)← Rd(n),C←Rd(7)
Z,C,N,V
1

10
2535JS–AVR–08/10
ATtiny13
ROR
Rd
Rotate Right Through Carry
Rd(7)
←C,Rd(n)← Rd(n+1),C←Rd(0)
Z,C,N,V
1
ASR
Rd
Arithmetic Shift Right
Rd(n)
← Rd(n+1), n=0..6
Z,C,N,V
1
SWAP
Rd
Swap Nibbles
Rd(3..0)
←Rd(7..4),Rd(7..4)←Rd(3..0)
None
1
BSET
s
Flag Set
SREG(s)
← 1
SREG(s)
1
BCLR
s
Flag Clear
SREG(s)
← 0
SREG(s)
1
BST
Rr, b
Bit Store from Register to T
T
← Rr(b)
T
1
BLD
Rd, b
Bit load from T to Register
Rd(b)
← T
None
1
SEC
Set Carry
C
← 1
C
1
CLC
Clear Carry
C
← 0
C
1
SEN
Set Negative Flag
N
← 1
N
1
CLN
Clear Negative Flag
N
← 0
N
1
SEZ
Set Zero Flag
Z
← 1
Z
1
CLZ
Clear Zero Flag
Z
← 0
Z
1
SEI
Global Interrupt Enable
I
← 1
I
1
CLI
Global Interrupt Disable
I
← 0
I
1
SES
Set Signed Test Flag
S
← 1
S
1
CLS
Clear Signed Test Flag
S
← 0
S
1
SEV
Set Twos Complement Overflow.
V
← 1
V
1
CLV
Clear Twos Complement Overflow
V
← 0
V
1
SET
Set T in SREG
T
← 1
T
1
CLT
Clear T in SREG
T
← 0
T
1
SEH
Set Half Carry Flag in SREG
H
← 1
H
1
CLH
Clear Half Carry Flag in SREG
H
← 0
H
1
DATA TRANSFER INSTRUCTIONS
MOV
Rd, Rr
Move Between Registers
Rd
← Rr
None
1
MOVW
Rd, Rr
Copy Register Word
Rd+1:Rd
← Rr+1:Rr
None
1
LDI
Rd, K
Load Immediate
Rd
← K
None
1
LD
Rd, X
Load Indirect
Rd
← (X)
None
2
LD
Rd, X+
Load Indirect and Post-Inc.
Rd
← (X), X ← X + 1
None
2
LD
Rd, - X
Load Indirect and Pre-Dec.
X
← X - 1, Rd ← (X)
None
2
LD
Rd, Y
Load Indirect
Rd
← (Y)
None
2
LD
Rd, Y+
Load Indirect and Post-Inc.
Rd
← (Y), Y ← Y + 1
None
2
LD
Rd, - Y
Load Indirect and Pre-Dec.
Y
← Y - 1, Rd ← (Y)
None
2
LDD
Rd,Y+q
Load Indirect with Displacement
Rd
← (Y + q)
None
2
LD
Rd, Z
Load Indirect
Rd
← (Z)
None
2
LD
Rd, Z+
Load Indirect and Post-Inc.
Rd
← (Z), Z ← Z+1
None
2
LD
Rd, -Z
Load Indirect and Pre-Dec.
Z
← Z - 1, Rd ← (Z)
None
2
LDD
Rd, Z+q
Load Indirect with Displacement
Rd
← (Z + q)
None
2
LDS
Rd, k
Load Direct from SRAM
Rd
← (k)
None
2
ST
X, Rr
Store Indirect
(X)
← Rr
None
2
ST
X+, Rr
Store Indirect and Post-Inc.
(X)
← Rr, X ← X + 1
None
2
ST
- X, Rr
Store Indirect and Pre-Dec.
X
← X - 1, (X) ← Rr
None
2
ST
Y, Rr
Store Indirect
(Y)
← Rr
None
2
ST
Y+, Rr
Store Indirect and Post-Inc.
(Y)
← Rr, Y ← Y + 1
None
2
ST
- Y, Rr
Store Indirect and Pre-Dec.
Y
← Y - 1, (Y) ← Rr
None
2
STD
Y+q,Rr
Store Indirect with Displacement
(Y + q)
← Rr
None
2
ST
Z, Rr
Store Indirect
(Z)
← Rr
None
2
ST
Z+, Rr
Store Indirect and Post-Inc.
(Z)
← Rr, Z ← Z + 1
None
2
ST
-Z, Rr
Store Indirect and Pre-Dec.
Z
← Z - 1, (Z) ← Rr
None
2
STD
Z+q,Rr
Store Indirect with Displacement
(Z + q)
← Rr
None
2
STS
k, Rr
Store Direct to SRAM
(k)
← Rr
None
2
LPM
Load Program Memory
R0
← (Z)
None
3
LPM
Rd, Z
Load Program Memory
Rd
← (Z)
None
3
LPM
Rd, Z+
Load Program Memory and Post-Inc
Rd
← (Z), Z ← Z+1
None
3
SPM
Store Program Memory
(z)
← R1:R0
None
IN
Rd, P
In Port
Rd
← P
None
1
OUT
P, Rr
Out Port
P
← Rr
None
1
PUSH
Rr
Push Register on Stack
STACK
← Rr
None
2
POP
Rd
Pop Register from Stack
Rd
← STACK
None
2
MCU CONTROL INSTRUCTIONS
NOP
No Operation
None
1
SLEEP
Sleep
(see specific descr. for Sleep function)
None
1
WDR
Watchdog Reset
(see specific descr. for WDR/Timer)
None
1
BREAK
Break
For On-chip Debug Only
None
N/A
Mnemonics
Operands
Description
Operation
Flags
#Clocks
