
Features
•
High Performance, Low Power Atmel
®
AVR
®
8-Bit Microcontroller
•
Advanced RISC Architecture
– 130 Powerful Instructions – Most Single Clock Cycle Execution
– 32 x 8 General Purpose Working Registers
– Fully Static Operation
– Up to 16MIPS Throughput at 16MHz
– On-Chip 2-cycle Multiplier
•
High Endurance Non-volatile Memory Segments
– In-System Self-programmable Flash Program Memory
• 32KBytes (ATmega325/ATmega3250)
• 64KBytes (ATmega645/ATmega6450)
– EEPROM
• 1Kbytes (ATmega325/ATmega3250)
• 2Kbytes (ATmega645/ATmega6450)
– Internal SRAM
• 2Kbytes (ATmega325/ATmega3250)
• 4Kbytes (ATmega645/ATmega6450)
– Write/Erase Cycles: 10,000 Flash/ 100,000 EEPROM
– Data retention: 20 years at 85°C/100 years at 25°C
(1)
– Optional Boot Code Section with Independent Lock Bits
• In-System Programming by On-chip Boot Program
• True Read-While-Write Operation
– Programming Lock for Software Security
•
Atmel
®
QTouch
®
library support
– Capacitive touch buttons, sliders and wheels
– QTouch and QMatrix
®
acquisition
– Up to 64 sense channels
•
JTAG (IEEE std. 1149.1 compliant) Interface
– Boundary-scan Capabilities According to the JTAG Standard
– Extensive On-chip Debug Support
– Programming of Flash, EEPROM, Fuses, and Lock Bits through the JTAG Interface
•
Peripheral Features
– Two 8-bit Timer/Counters with Separate Prescaler and Compare Mode
– One 16-bit Timer/Counter with Separate Prescaler, Compare Mode, and Capture
Mode
– Real Time Counter with Separate Oscillator
– Four PWM Channels
– 8-channel, 10-bit ADC
– Programmable Serial USART
– Master/Slave SPI Serial Interface
– Universal Serial Interface with Start Condition Detector
– Programmable Watchdog Timer with Separate On-chip Oscillator
– On-chip Analog Comparator
– Interrupt and Wake-up on Pin Change
•
Special Microcontroller Features
– Power-on Reset and Programmable Brown-out Detection
– Internal Calibrated Oscillator
– External and Internal Interrupt Sources
– Five Sleep Modes: Idle, ADC Noise Reduction, Power-save, Power-down, and
Standby
•
I/O and Packages
– 53/68 Programmable I/O Lines
– 64-lead TQFP, 64-pad QFN/MLF, and 100-lead TQFP
•
Speed Grade:
– ATmega325V/ATmega3250V/ATmega645V/ATmega6450V:
• 0 - 4MHz @ 1.8 - 5.5V; 0 - 8MHz @ 2.7 - 5.5V
– Atmel ATmega325/3250/645/6450:
• 0 - 8MHz @ 2.7 - 5.5V; 0 - 16MHz @ 4.5 - 5.5V
•
Temperature range:
– -40
°C to 85°C IndustrSial
•
Ultra-Low Power Consumption
– Active Mode:
1MHz, 1.8V: 350µA
32kHz, 1.8V: 20µA (including Oscillator)
– Power-down Mode:
100 nA at 1.8V
8-bit Atmel
Microcontroller
with In-System
Programmable
Flash
ATmega325/V
ATmega3250/V
ATmega645/V
ATmega6450/V
Summary
2570NS–AVR–05/11
2
2570NS–AVR–05/11
ATmega325/3250/645/6450
1.
Pin Configurations
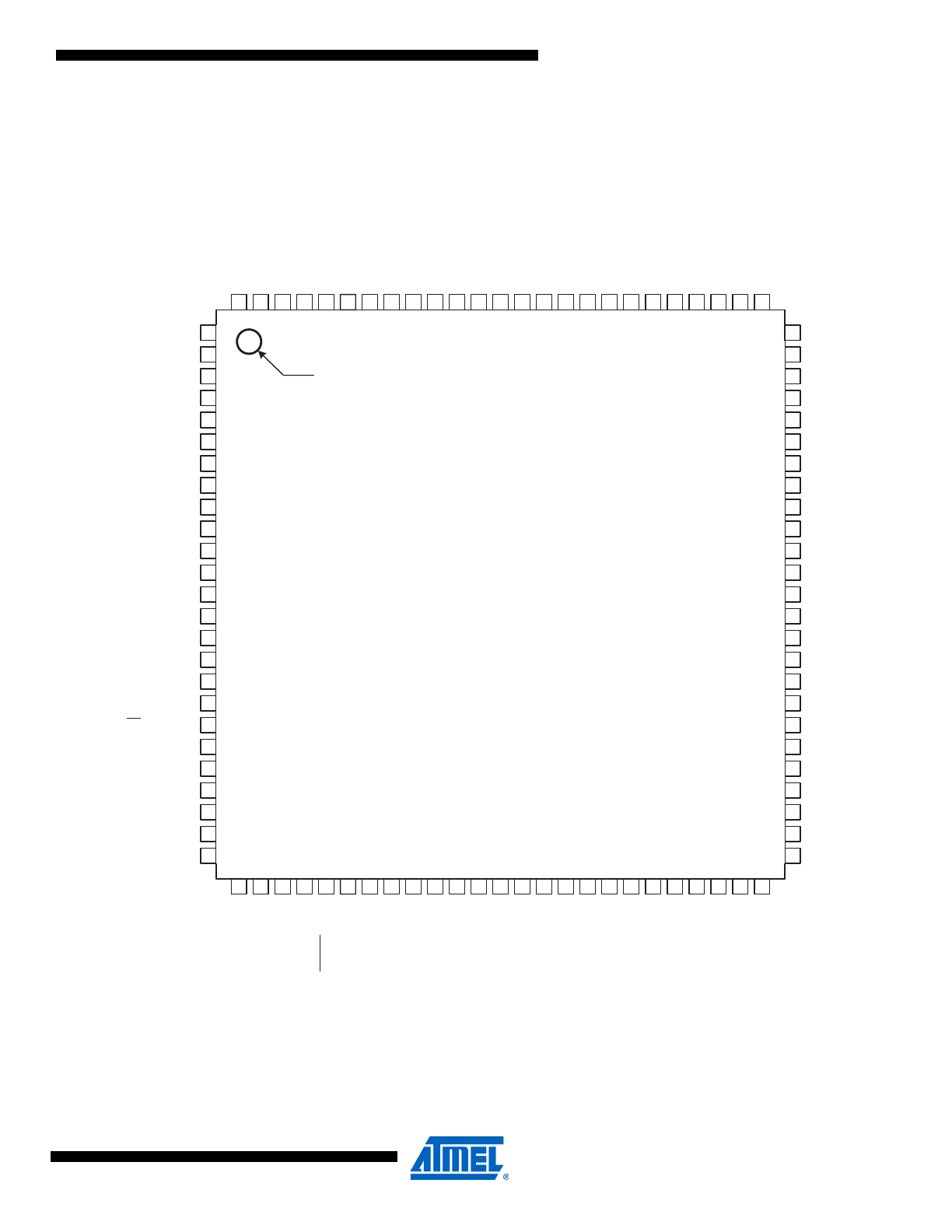
Figure 1-1.
Pinout ATmega3250/6450
(OC2A/PCI
N
T15) PB7
D
N
C
(T1) PG3
(T0) PG4
RESET/PG5
V
CC
G
N
D
XT
AL2 (T
OSC2)
XT
AL1 (T
OSC1)
D
N
C
D
N
C
(PCI
N
T26) PJ2
(PCI
N
T27) PJ3
(PCI
N
T28) PJ4
(PCI
N
T29) PJ5
(PCI
N
T30) PJ6
D
N
C
(ICP1) PD0
(I
N
T0) PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
PD5
PD6
PD7
A
V
CC
AG
N
D
AREF
PF0 (ADC0)
PF1(ADC1)
PF2 (ADC2)
PF3 (ADC3)
PF4 (ADC4/TCK)
PF5 (ADC5/TMS)
PF6 (ADC6/TDO)
PF7 (ADC7/TDI)
D
N
C
D
N
C
PH7 (PCI
N
T23)
PH6 (PCI
N
T22)
PH5 (PCI
N
T21)
PH4 (PCI
N
T20)
D
N
C
D
N
C
G
N
D
V
CC
D
N
C
PA
0
PA
1
PA
2
DNC
(RXD/PCINT0) PE0
(TXD/PCINT1) PE1
(XCK/AIN0/PCINT2) PE2
(AIN1/PCINT3) PE3
(USCK/SCL/PCINT4) PE4
(DI/SDA/PCINT5) PE5
(DO/PCINT6) PE6
(CLKO/PCINT7) PE7
VCC
GND
DNC
(PCINT24) PJ0
(PCINT25) PJ1
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
(SS/PCINT8) PB0
(SCK/PCINT9) PB1
(MOSI/PCINT10) PB2
(MISO/PCINT11) PB3
(OC0A/PCINT12) PB4
(OC1A/PCINT13) PB5
(OC1B/PCINT14) PB6
PA3
PA4
PA5
PA6
PA7
PG2
PC7
PC6
DNC
PH3 (PCINT19)
PH2 (PCINT18)
PH1 (PCINT17)
PH0 (PCINT16)
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
PC5
PC4
PC3
PC2
PC1
PC0
PG1
PG0
INDEX CORNER
ATmega3250/6450
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
3
2570NS–AVR–05/11
ATmega325/3250/645/6450
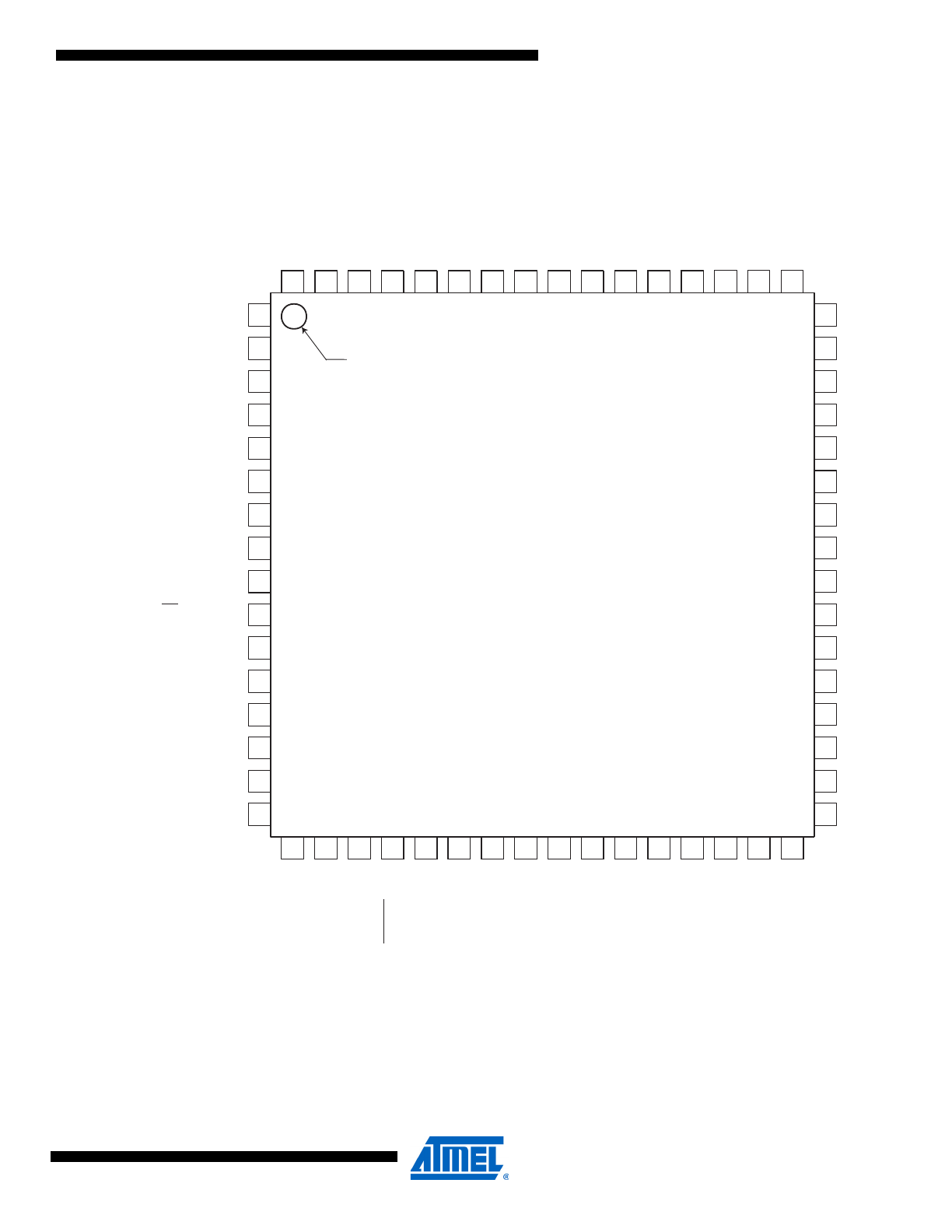
Figure 1-2.
Pinout ATmega325/645
Note:
The large center pad underneath the QFN/MLF packages is made of metal and internally con-
nected to GND. It should be soldered or glued to the board to ensure good mechanical stability. If
the center pad is left unconnected, the package might loosen from the board.
PC0
V
CC
G
N
D
PF0 (ADC0)
PF7 (ADC7/TDI)
PF1 (ADC1)
PF2 (ADC2)
PF3 (ADC3)
PF4 (ADC4/TCK)
PF5 (ADC5/TMS)
PF6 (ADC6/TDO)
AREF
G
N
D
A
V
CC
17
61
60
18
59
20
58
19
21
57
22
56
23
55
24
54
25
53
26
52
27
51
29
28
50
49
32
31
30
(RXD/PCINT0) PE0
(TXD/PCINT1) PE1
(XCK/AIN0/PCINT2) PE2
(AIN1/PCINT3) PE3
(USCK/SCL/PCINT4) PE4
(DI/SDA/PCINT5) PE5
(DO/PCINT6) PE6
(CLKO/PCINT7) PE7
(SCK/PCINT9) PB1
(MOSI/PCINT10) PB2
(MISO/PCINT11) PB3
(OC0A/PCINT12) PB4
(OC2A/PCI
N
T15) PB7
(T1) PG3
(OC1B/PCINT14) PB6
(T0) PG4
(OC1A/PCINT13) PB5
PC1
PG0
PD7
PC2
PC3
PC4
PC5
PC6
PC7
PA7
PG2
PA6
PA5
PA4
PA3
PA0
PA1
PA2
PG1
PD6
PD5
PD4
PD3
PD2
PD1 (I
N
T0)
(ICP1) PD0
XTAL1 (TOSC1)
XTAL2 (TOSC2)
RESET/PG5
G
N
D
V
CC
INDEX CORNER
(SS/PCINT8) PB0
2
3
1
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
15
64
63
62
47
46
48
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
33
34
ATmega325/645
DNC
4
2570NS–AVR–05/11
ATmega325/3250/645/6450
2.
Overview
The Atmel ATmega325/3250/645/6450 is a low-power CMOS 8-bit microcontroller based on the
AVR enhanced RISC architecture. By executing powerful instructions in a single clock cycle, the
Atmel ATmega325/3250/645/6450 achieves throughputs approaching 1 MIPS per MHz allowing
the system designer to optimize power consumption versus processing speed.
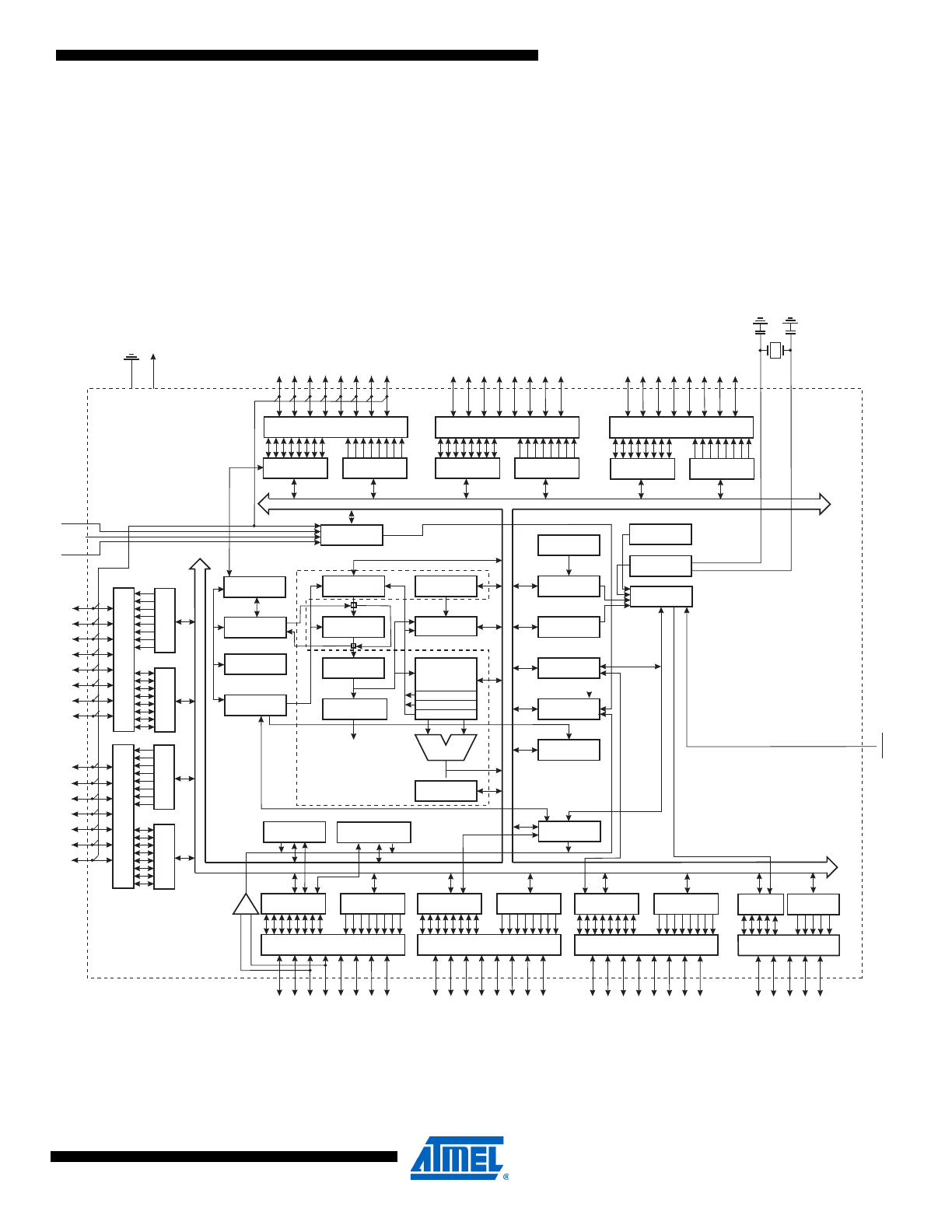
2.1
Block Diagram
Figure 2-1.
Block Diagram
The Atmel
®
AVR
®
core combines a rich instruction set with 32 general purpose working registers.
All the 32 registers are directly connected to the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), allowing two inde-
pendent registers to be accessed in one single instruction executed in one clock cycle. The
PROGRAM
COUNTER
INTERNAL
OSCILLATOR
WATCHDOG
TIMER
STACK
POINTER
PROGRAM
FLASH
MCU CONTROL
REGISTER
SRAM
GENERAL
PURPOSE
REGISTERS
INSTRUCTION
REGISTER
TIMER/
COUNTERS
INSTRUCTION
DECODER
DATA DIR.
REG. PORTB
DATA DIR.
REG. PORTE
DATA DIR.
REG. PORTA
DATA DIR.
REG. PORTD
DATA REGISTER
PORTB
DATA REGISTER
PORTE
DATA REGISTER
PORTA
DATA REGISTER
PORTD
TIMING AND
CONTROL
OSCILLATOR
INTERRUPT
UNIT
EEPROM
SPI
USART
STATUS
REGISTER
Z
Y
X
ALU
PORTB DRIVERS
PORTE DRIVERS
PORTA DRIVERS
PORTF DRIVERS
PORTD DRIVERS
PORTC DRIVERS
PB0 - PB7
PE0 - PE7
PA0 - PA7
PF0 - PF7
VCC
GND
XT
AL1
XT
AL2
CONTROL
LINES
+
-
ANALOG
COMP
ARA
T
O
R
PC0 - PC7
8-BIT DATA BUS
RESET
CALIB. OSC
DATA DIR.
REG. PORTC
DATA REGISTER
PORTC
ON-CHIP DEBUG
JTAG TAP
PROGRAMMING
LOGIC
BOUNDARY-
SCAN
DATA DIR.
REG. PORTF
DATA REGISTER
PORTF
ADC
PD0 - PD7
DATA DIR.
REG. PORTG
DATA REG.
PORTG
PORTG DRIVERS
PG0 - PG4
AGND
AREF
AVCC
UNIVERSAL
SERIAL INTERFACE
AVR CPU
POR
TH DRIVERS
PH0 - PH7
D
A
T
A
DIR.
REG.
POR
T
H
D
A
T
A
REGISTER
POR
T
H
POR
TJ DRIVERS
PJ0 - PJ6
D
A
T
A
DIR.
REG.
POR
T
J
D
A
T
A
REGISTER
POR
T
J

5
2570NS–AVR–05/11
ATmega325/3250/645/6450
resulting architecture is more code efficient while achieving throughputs up to ten times faster
than conventional CISC microcontrollers.
The Atmel ATmega325/3250/645/6450 provides the following features: 32/64K bytes of In-Sys-
tem Programmable Flash with Read-While-Write capabilities, 1/2K bytes EEPROM, 2/4K byte
SRAM, 54/69 general purpose I/O lines, 32 general purpose working registers, a JTAG interface
for Boundary-scan, On-chip Debugging support and programming, three flexible Timer/Counters
with compare modes, internal and external interrupts, a serial programmable USART, Universal
Serial Interface with Start Condition Detector, an 8-channel, 10-bit ADC, a programmable
Watchdog Timer with internal Oscillator, an SPI serial port, and five software selectable power
saving modes. The Idle mode stops the CPU while allowing the SRAM, Timer/Counters, SPI
port, and interrupt system to continue functioning. The Power-down mode saves the register
contents but freezes the Oscillator, disabling all other chip functions until the next interrupt or
hardware reset. In Power-save mode, the asynchronous timer will continue to run, allowing the
user to maintain a timer base while the rest of the device is sleeping. The ADC Noise Reduction
mode stops the CPU and all I/O modules except asynchronous timer and ADC to minimize
switching noise during ADC conversions. In Standby mode, the crystal/resonator Oscillator is
running while the rest of the device is sleeping. This allows very fast start-up combined with low-
power consumption.
Atmel offers the QTouch
®
library for embedding capacitive touch buttons, sliders and wheels-
functionality into AVR microcontrollers. The patented charge-transfer signal acquisition
offersrobust sensing and includes fully debounced reporting of touch keys and includes Adjacent
KeySuppression
®
(AKS
™
) technology for unambiguous detection of key events. The easy-to-use
QTouch Suite toolchain allows you to explore, develop and debug your own touch applications.
The device is manufactured using Atmel’s high density non-volatile memory technology. The
On-chip In-System re-Programmable (ISP) Flash allows the program memory to be repro-
grammed In-System through an SPI serial interface, by a conventional non-volatile memory
programmer, or by an On-chip Boot program running on the AVR core. The Boot program can
use any interface to download the application program in the Application Flash memory. Soft-
ware in the Boot Flash section will continue to run while the Application Flash section is updated,
providing true Read-While-Write operation. By combining an 8-bit RISC CPU with In-System
Self-Programmable Flash on a monolithic chip, the Atmel Atmel ATmega325/3250/645/6450 is a
powerful microcontroller that provides a highly flexible and cost effective solution to many
embedded control applications.
The Atmel ATmega325/3250/645/6450 is supported with a full suite of program and system
development tools including: C Compilers, Macro Assemblers, Program Debugger/Simulators,
In-Circuit Emulators, and Evaluation kits.
6
2570NS–AVR–05/11
ATmega325/3250/645/6450
2.2
Comparison between ATmega325, ATmega3250, ATmega645 and ATmega6450
The ATmega325, ATmega3250, ATmega645, and ATmega6450 differ only in memory sizes, pin
count and pinout.
Table 2-1 on page 6
summarizes the different configurations for the four
devices.
2.3
Pin Descriptions
The following section describes the I/O-pin special functions.
2.3.1
V
CC
Digital supply voltage.
2.3.2
GND
Ground.
2.3.3
Port A (PA7..PA0)
Port A is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port A output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port A pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port A pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
2.3.4
Port B (PB7..PB0)
Port B is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port B output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port B pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port B pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port B has better driving capabilities than the other ports.
P o r t B a l s o s e r v e s t h e f u n c t i o n s o f v a r i o u s s p e c i a l f e a t u r e s o f t h e A t m e l
ATmega325/3250/645/6450 as listed on
page 68
.
2.3.5
Port C (PC7..PC0)
Port C is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port C output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port C pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port C pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Table 2-1.
Configuration Summary
Device
Flash
EEPROM
RAM
General Purpose
I/O Pins
ATmega325
32Kbytes
1Kbytes
2Kbytes
54
ATmega3250
32Kbytes
1Kbytes
2Kbytes
69
ATmega645
64Kbytes
2Kbytes
4Kbytes
54
ATmega6450
64Kbytes
2Kbytes
4Kbytes
69

7
2570NS–AVR–05/11
ATmega325/3250/645/6450
2.3.6
Port D (PD7..PD0)
Port D is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port D output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port D pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port D pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
P o r t D a l s o s e r v e s t h e f u n c t i o n s o f v a r i o u s s p e c i a l f e a t u r e s o f t h e A t m e l
ATmega325/3250/645/6450 as listed on
page 71
.
2.3.7
Port E (PE7..PE0)
Port E is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port E output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port E pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port E pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
P o r t E a l s o s e r v e s t h e f u n c t i o n s o f v a r i o u s s p e c i a l f e a t u r e s o f t h e A t m e l
ATmega325/3250/645/6450 as listed on
page 72
.
2.3.8
Port F (PF7..PF0)
Port F serves as the analog inputs to the A/D Converter.
Port F also serves as an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port, if the A/D Converter is not used. Port pins
can provide internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The Port F output buffers have sym-
metrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability. As inputs, Port F pins
that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated. The Port F
pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running. If the
JTAG interface is enabled, the pull-up resistors on pins PF7(TDI), PF5(TMS), and PF4(TCK) will
be activated even if a reset occurs.
Port F also serves the functions of the JTAG interface.
2.3.9
Port G (PG5..PG0)
Port G is a 6-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port G output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port G pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port G pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
P o r t G a l s o s e r v e s t h e f u n c t i o n s o f v a r i o u s s p e c i a l f e a t u r e s o f t h e A t m e l
ATmega325/3250/645/6450 as listed on
page 72
.
2.3.10
Port H (PH7..PH0)
Port H is a 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port H output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port H pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port H pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port H also serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega3250/6450 as listed
on
page 72
.

8
2570NS–AVR–05/11
ATmega325/3250/645/6450
2.3.11
Port J (PJ6..PJ0)
Port J is a 7-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port J output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capa-
bility. As inputs, Port J pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port J pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port J also serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega3250/6450 as listed on
page 72
.
2.3.12
RESET
Reset input. A low level on this pin for longer than the minimum pulse length will generate a
reset, even if the clock is not running. The minimum pulse length is given in
Table 28-4 on page
301
. Shorter pulses are not guaranteed to generate a reset.
2.3.13
XTAL1
Input to the inverting Oscillator amplifier and input to the internal clock operating circuit.
2.3.14
XTAL2
Output from the inverting Oscillator amplifier.
2.3.15
AVCC
AVCC is the supply voltage pin for Port F and the A/D Converter. It should be externally con-
nected to V
CC
, even if the ADC is not used. If the ADC is used, it should be connected to V
CC
through a low-pass filter.
2.3.16
AREF
This is the analog reference pin for the A/D Converter.

9
2570NS–AVR–05/11
ATmega325/3250/645/6450
3.
Resources
A comprehensive set of development tools, application notes and datasheets are available for
download on http://www.atmel.com/avr.
Note:
1.
4.
Data Retention
Reliability Qualification results show that the projected data retention failure rate is much less
than 1 PPM over 20 years at 85°C or 100 years at 25°C.
5.
About Code Examples
This documentation contains simple code examples that briefly show how to use various parts of
the device. These code examples assume that the part specific header file is included before
compilation. Be aware that not all C compiler vendors include bit definitions in the header files
and interrupt handling in C is compiler dependent. Please confirm with the C compiler documen-
tation for more details.
For I/O Registers located in extended I/O map, “IN”, “OUT”, “SBIS”, “SBIC”, “CBI”, and “SBI”
instructions must be replaced with instructions that allow access to extended I/O. Typically
“LDS” and “STS” combined with “SBRS”, “SBRC”, “SBR”, and “CBR”.
6.
Capacitive touch sensing
The Atmel
®
QTouch
®
Library provides a simple to use solution to realize touch sensitive inter-
faces on most Atmel AVR
®
microcontrollers. The QTouch Library includes support for the
QTouch and QMatrix
®
acquisition methods.
Touch sensing can be added to any application by linking the appropriate Atmel QTouch Library
for the AVR Microcontroller. This is done by using a simple set of APIs to define the touch chan-
nels and sensors, and then calling the touch sensing API’s to retrieve the channel information
and determine the touch sensor states.
The QTouch Library is FREE and downloadable from the Atmel website at the following location:
www.atmel.com/qtouchlibrary
. For implementation details and other information, refer to the
Atmel QTouch Library User Guide
- also available for download from the Atmel website.
10
2570NS–AVR–05/11
ATmega325/3250/645/6450
7.
Register Summary
Note:
Registers with bold type only available in ATmega3250/6450.
Address
Name
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Page
(0xFF)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xFE)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xFD)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xFC)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xFB)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xFA)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xF9)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xF8)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xF7)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xF6)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xF5)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xF4)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xF3)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xF2)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xF1)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xF0)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xEF)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xEE)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xED)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xEC)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xEB)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xEA)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xE9)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xE8)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xE7)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xE6)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xE5)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xE4)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xE3)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xE2)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xE1)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xE0)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xDF)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xDE)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xDD)
PORTJ
-
PORTJ6
PORTJ5
PORTJ4
PORTJ3
PORTJ2
PORTJ1
PORTJ0
84
(0xDC)
DDRJ
-
DDJ6
DDJ5
DDJ4
DDJ3
DDJ2
DDJ1
DDJ0
84
(0xDB)
PINJ
-
PINJ6
PINJ5
PINJ4
PINJ3
PINJ2
PINJ1
PINJ0
84
(0xDA)
PORTH
PORTH7
PORTH6
PORTH5
PORTH4
PORTH3
PORTH2
PORTH1
PORTH0
84
(0xD9)
DDRH
DDH7
DDH6
DDH5
DDH4
DDH3
DDH2
DDH1
DDH0
84
(0xD8)
PINH
PINH7
PINH6
PINH5
PINH4
PINH3
PINH2
PINH1
PINH0
84
(0xD7)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xD6)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xD5)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xD4)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xD3)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xD2)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xD1)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xD0)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xCF)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xCE)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xCD)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xCC)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xCB)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xCA)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xC9)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xC8)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xC7)
Reserved
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(0xC6)
UDR0
USART0 Data Register
179
(0xC5)
UBRR0H
USART0 Baud Rate Register High
184
(0xC4)
UBRR0L
USART0 Baud Rate Register Low
184
