© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS22062B-page 1
MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5
Features
• High Peak Output Current: 4.0A (typical)
• Independent Enable Function for Each Driver
Output
• Low Shoot-Through/Cross-Conduction Current in
Output Stage
• Wide Input Supply Voltage Operating Range:
- 4.5V to 18V
• High Capacitive Load Drive Capability:
- 2200 pF in 15 ns (typical)
- 5600 pF in 26 ns (typical)
• Short Delay Times: 50 ns (typical)
• Latch-Up Protected: Will Withstand 1.5A Reverse
Current
• Logic Input Will Withstand Negative Swing Up To
5V
• Space-Saving Packages:
- 8-Lead 6x5 DFN, PDIP, SOIC
Applications
• Switch Mode Power Supplies
• Pulse Transformer Drive
• Line Drivers
• Motor and Solenoid Drive
General Description
The MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5 devices are a
family of 4.0A buffers/MOSFET drivers. Dual-inverting,
dual-noninvertering, and complementary outputs are
standard logic options offered.
The MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5 drivers are
capable of operating from a 4.5V to 18V single power
supply and can easily charge and discharge 2200 pF
gate capacitance in under 15 ns (typical). They provide
low impedance in both the ON and OFF states to
ensure the MOSFET’s intended state will not be
affected, even by large transients. The MCP14E3/
MCP14E4/MCP14E5 inputs may be driven directly
from either TTL or CMOS (2.4V to 18V).
Additional control of the MCP14E3/MCP14E4/
MCP14E5 outputs is allowed by the use of separate
enable functions. The ENB_A and ENB_B pins are
active high and are internally pulled up to V
DD
. The pins
maybe left floating for standard operation.
The MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5 dual-output 4.0A
driver family is offered in both surface-mount and pin-
through-hole packages with a -40°C to +125°C
temperature rating. The low thermal resistance of the
thermally enhanced DFN package allows for greater
power dissipation capability for driving heavier
capacitive or resistive loads.
These devices are highly latch-up resistant under any
conditions within their power and voltage ratings. They
are not subject to damage when up to 5V of noise
spiking (of either polarity) occurs on the ground pin.
They can accept, without damage or logic upset, up to
1.5A of reverse current being forced back into their
outputs. All terminals are fully protect against
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) up to 4 kV.
Package Types
ENB_A
IN A
GND
IN B
8-Pin
1
2
3
4
ENB_B
5
6
7
8
OUT A
OUT B
ENB_A
IN A
GND
IN B
V
DD
Note 1: Exposed pad of the DFN package is electrically isolated.
MCP14E3
MCP14E4
ENB_B
OUT A
OUT B
V
DD
MCP14E5
ENB_B
OUT A
OUT B
V
DD
ENB_B
OUT A
OUT B
V
DD
MCP14E3
MCP14E4
ENB_B
OUT A
OUT B
V
DD
MCP14E5
ENB_B
OUT A
OUT B
V
DD
PDIP/SOIC
8-Pin
6x5 DFN
(1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
4.0A Dual High-Speed Power MOSFET Drivers With Enable
MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5
DS22062B-page 2
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
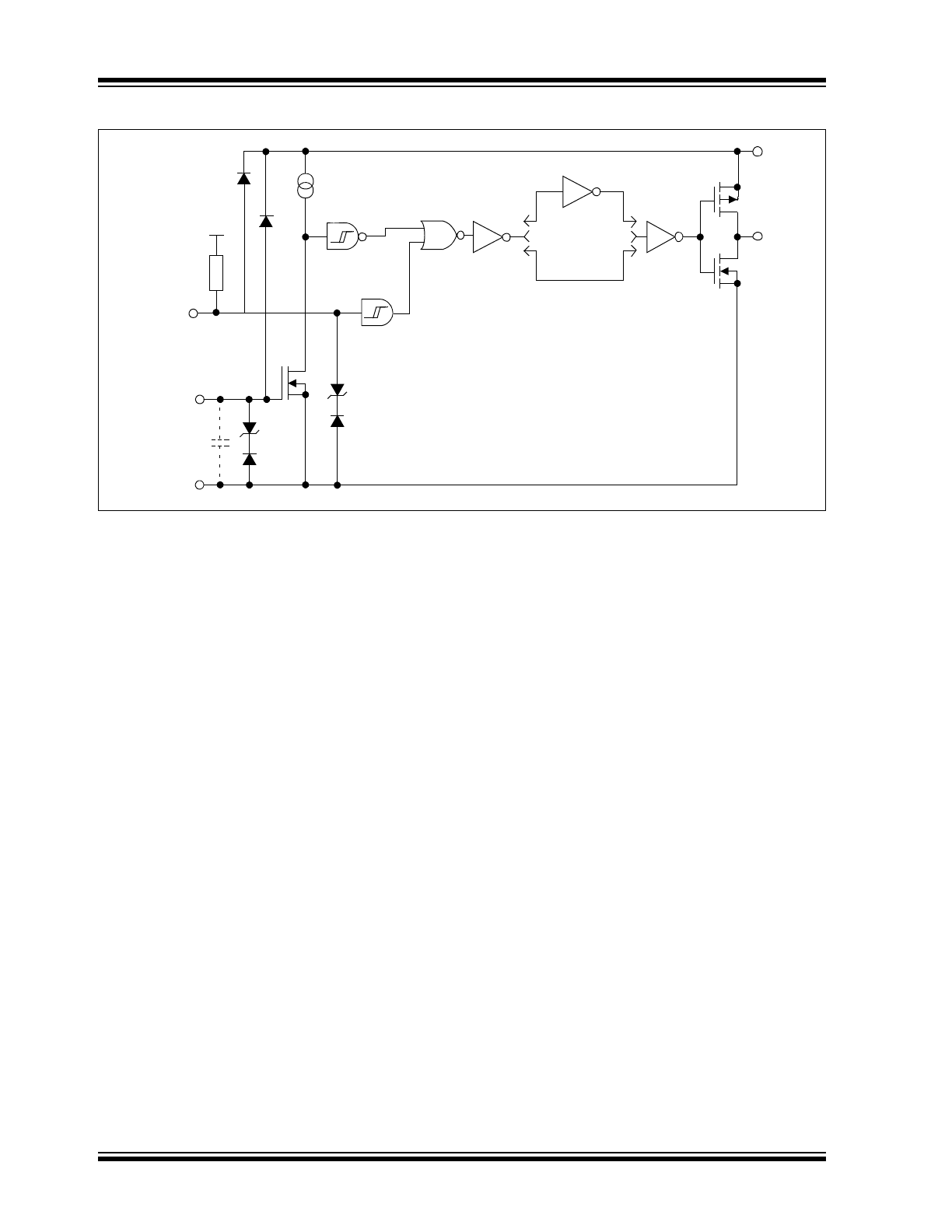
Functional Block Diagram
Effective
Input C = 20 pF
(Each Input)
MCP14E3
MCP14E4
MCP14E5
Dual Inverting
Dual Noninverting
One Inverting, One Noninverting
Output
Input
GND
V
DD
4.7 V
Inverting
Non-inverting
Enable
V
DD
Internal
Pull-up
4.7 V
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS22062B-page 3
MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5
1.0
ELECTRICAL
CHARACTERISTICS
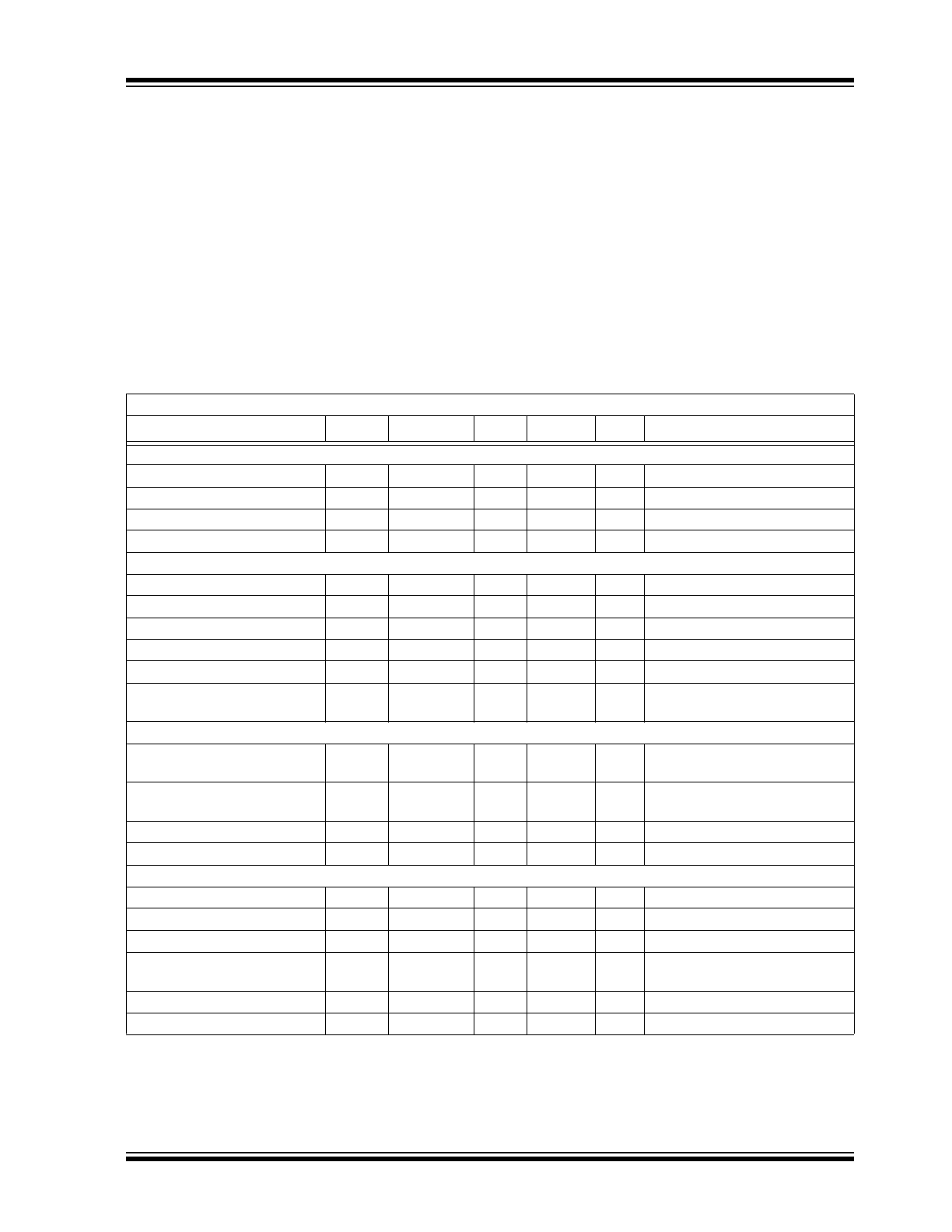
Absolute Maximum Ratings †
Supply Voltage ................................................................+20V
Input Voltage ............................... (V
DD
+ 0.3V) to (GND – 5V)
Enable Voltage .............................(V
DD
+ 0.3V) to (GND - 5V)
Input Current (V
IN
>V
DD
)................................................50 mA
Package Power Dissipation (T
A
= 50°C)
8L-DFN .......................................................................
Note 3
8L-PDIP ........................................................................1.10W
8L-SOIC .....................................................................665 mW
†
Notice: Stresses above those listed under "Maximum
Ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. This is
a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at
those or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational sections of this specification is not intended.
Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended periods
may affect device reliability.
DC CHARACTERISTICS (NOTE 2)
Electrical Specifications: Unless otherwise indicated, T
A
= +25°C, with 4.5V
≤ V
DD
≤ 18V.
Parameters
Sym
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
Input
Logic ‘1’, High Input Voltage
V
IH
2.4
1.5
—
V
Logic ‘0’, Low Input Voltage
V
IL
—
1.3
0.8
V
Input Current
I
IN
–1
—
1
µA
0V
≤ V
IN
≤ V
DD
Input Voltage
V
IN
-5
—
V
DD
+0.3
V
Output
High Output Voltage
V
OH
V
DD
– 0.025
—
—
V
DC Test
Low Output Voltage
V
OL
—
—
0.025
V
DC Test
Output Resistance, High
R
OH
—
2.5
3.5
Ω
I
OUT
= 10 mA, V
DD
= 18V
Output Resistance, Low
R
OL
—
2.5
3.0
Ω
I
OUT
= 10 mA, V
DD
= 18V
Peak Output Current
I
PK
—
4.0
—
A
V
DD
= 18V (Note 2)
Latch-Up Protection With-
stand Reverse Current
I
REV
—
>1.5
—
A
Duty cycle
≤ 2%, t ≤ 300 µs
Switching Time (Note 1)
Rise Time
t
R
—
15
30
ns
Figure 4-1
,
Figure 4-2
C
L
= 2200 pF
Fall Time
t
F
—
18
30
ns
Figure 4-1
,
Figure 4-2
C
L
= 2200 pF
Propagation Delay Time
t
D1
—
46
55
ns
Figure 4-1
,
Figure 4-2
Propagation Delay Time
t
D2
—
50
55
ns
Figure 4-1
,
Figure 4-2
Enable Function (ENB_A, ENB_B)
High-Level Input Voltage
V
EN_H
1.60
1.90
2.90
V
V
DD
= 12V, LO to HI Transition
Low-Level Input Voltage
V
EN_L
1.30
2.20
2.40
V
V
DD
= 12V, HI to LO Transition
Hysteresis
V
HYST
0.10
0.30
0.60
V
Enable Leakage Current
I
ENBL
40
85
115
µA
V
DD
= 12V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = GND
Propagation Delay Time
t
D3
—
60
—
ns
Figure 4-3
(Note 1)
Propagation Delay Time
t
D4
—
50
—
ns
Figure 4-3
(Note 1)
Note 1: Switching times ensured by design.
2: Tested during characterization, not production tested.
3: Package power dissipation is dependent on the copper pad area on the PCB.
MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5
DS22062B-page 4
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
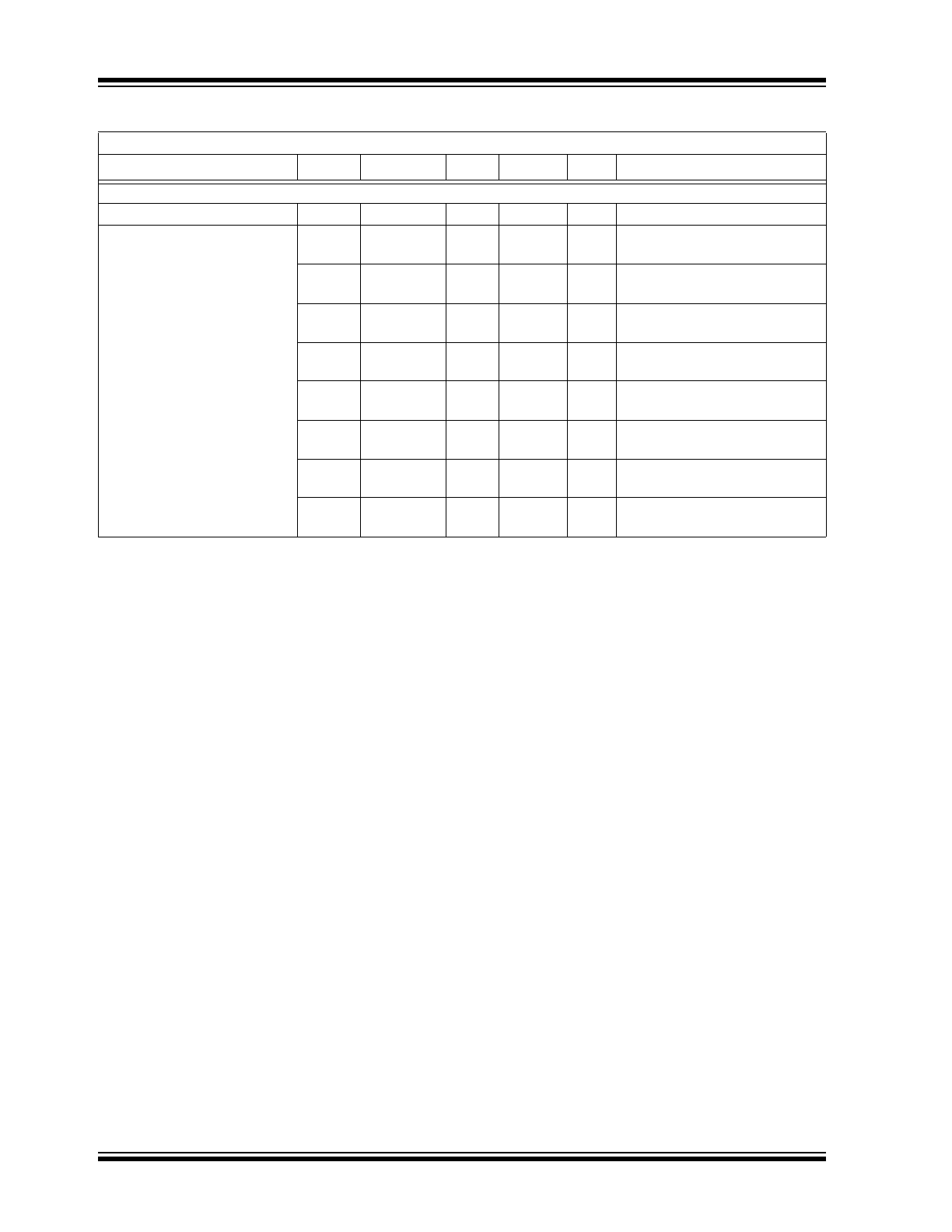
Power Supply
Supply Voltage
V
DD
4.5
—
18.0
V
Supply Current
I
DD
—
1.60
2.00
mA
V
IN_A
= 3V, V
IN_B
= 3V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = High
I
DD
—
0.60
0.90
mA
V
IN_A
= 0V, V
IN_B
= 0V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = High
I
DD
—
1.20
1.40
mA
V
IN_A
= 3V, V
IN_B
= 0V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = High
I
DD
—
1.20
1.40
mA
V
IN_A
= 0V, V
IN_B
= 3V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = High
I
DD
—
1.40
1.80
mA
V
IN_A
= 3V, V
IN_B
= 3V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = Low
I
DD
—
0.55
0.75
mA
V
IN_A
= 0V, V
IN_B
= 0V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = Low
I
DD
—
1.00
1.20
mA
V
IN_A
= 3V, V
IN_B
= 0V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = Low
I
DD
—
1.00
1.20
mA
V
IN_A
= 0V, V
IN_B
= 3V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = Low
DC CHARACTERISTICS (NOTE 2) (CONTINUED)
Electrical Specifications: Unless otherwise indicated, T
A
= +25°C, with 4.5V
≤ V
DD
≤ 18V.
Parameters
Sym
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
Note 1: Switching times ensured by design.
2: Tested during characterization, not production tested.
3: Package power dissipation is dependent on the copper pad area on the PCB.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS22062B-page 5
MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5
DC CHARACTERISTICS (OVER OPERATING TEMPERATURE RANGE)
Electrical Specifications: Unless otherwise indicated, operating temperature range with 4.5V
≤ V
DD
≤ 18V.
Parameters
Sym
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
Input
Logic ‘1’, High Input Voltage
V
IH
2.4
—
—
V
Logic ‘0’, Low Input Voltage
V
IL
—
—
0.8
V
Input Current
I
IN
–10
—
+10
µA
0V
≤ V
IN
≤ V
DD
Output
High Output Voltage
V
OH
V
DD
– 0.025
—
—
V
DC TEST
Low Output Voltage
V
OL
—
—
0.025
V
DC TEST
Output Resistance, High
R
OH
—
3.0
6.0
Ω
I
OUT
= 10 mA, V
DD
= 18V
Output Resistance, Low
R
OL
—
3.0
5.0
Ω
I
OUT
= 10 mA, V
DD
= 18V
Switching Time (Note 1)
Rise Time
t
R
—
25
40
ns
Figure 4-1
,
Figure 4-2
C
L
= 2200 pF
Fall Time
t
F
—
28
40
ns
Figure 4-1
,
Figure 4-2
C
L
= 2200 pF
Delay Time
t
D1
—
50
70
ns
Figure 4-1
,
Figure 4-2
Delay Time
t
D2
—
50
70
ns
Figure 4-1
,
Figure 4-2
Enable Function (ENB_A, ENB_B)
High-Level Input Voltage
V
EN_H
1.60
2.20
2.90
V
V
DD
= 12V, LO to HI Transition
Low-Level Input Voltage
V
EN_L
1.30
1.80
2.40
V
V
DD
= 12V, HI to LO Transition
Hysteresis
V
HYST
—
0.40
—
V
Enable Leakage Current
I
ENBL
40
87
115
µA
V
DD
= 12V, ENB_A = ENB_B = GND
Propagation Delay Time
t
D3
—
50
—
ns
Figure 4-3
Propagation Delay Time
t
D4
—
60
—
ns
Figure 4-3
Power Supply
Supply Voltage
V
DD
4.5
—
18.0
V
Supply Current
I
DD
—
2.0
3.0
mA
V
IN_A
= 3V, V
IN_B
= 3V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = High
I
DD
—
0.8
1.1
mA
V
IN_A
= 0V, V
IN_B
= 0V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = High
I
DD
—
1.5
2.0
mA
V
IN_A
= 3V, V
IN_B
= 0V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = High
I
DD
—
1.5
2.0
mA
V
IN_A
= 0V, V
IN_B
= 3V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = High
I
DD
—
1.8
2.8
mA
V
IN_A
= 3V, V
IN_B
= 3V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = Low
I
DD
—
0.6
0.8
mA
V
IN_A
= 0V, V
IN_B
= 0V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = Low
I
DD
—
1.1
1.8
mA
V
IN_A
= 3V, V
IN_B
= 0V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = Low
I
DD
—
1.1
1.8
mA
V
IN_A
= 0V, V
IN_B
= 3V,
ENB_A = ENB_B = Low
Note 1: Switching times ensured by design.
MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5
DS22062B-page 6
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
TEMPERATURE CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Specifications: Unless otherwise noted, all parameters apply with 4.5V
≤ V
DD
≤ 18V.
Parameters
Sym
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
Temperature Ranges
Specified Temperature Range
T
A
–40
—
+125
°C
Maximum Junction Temperature
T
J
—
—
+150
°C
Storage Temperature Range
T
A
–65
—
+150
°C
Package Thermal Resistances
Thermal Resistance, 8L-6x5 DFN
θ
JA
—
35.7
—
°C/W
Typical four-layer board with
vias to ground plane
Thermal Resistance, 8L-PDIP
θ
JA
—
89.3
—
°C/W
Thermal Resistance, 8L-SOIC
θ
JA
—
149.5
—
°C/W
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS22062B-page 7
MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5
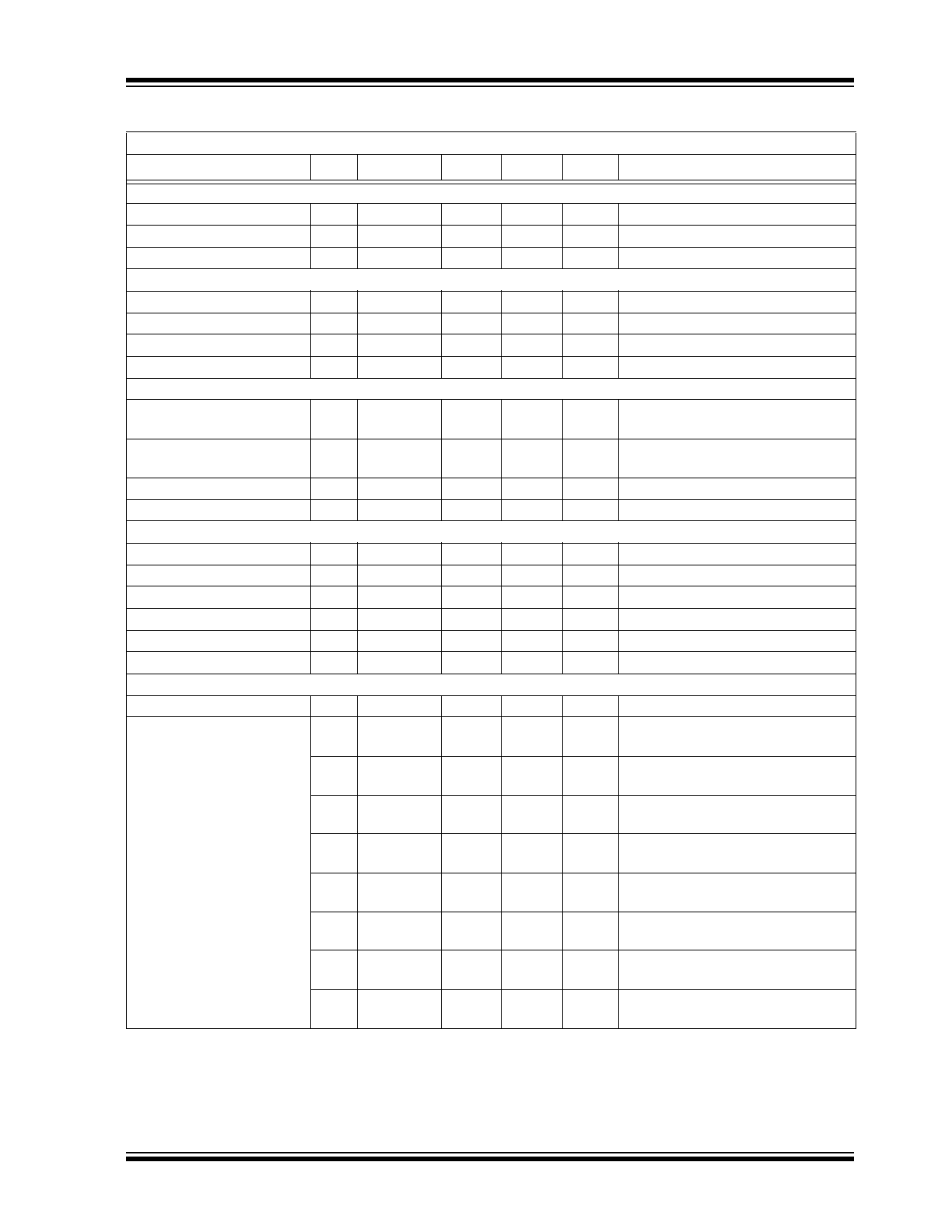
2.0
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, T
A
= +25°C with 4.5V
≤ V
DD
≤ 18V.
FIGURE 2-1:
Rise Time vs. Supply
Voltage.
FIGURE 2-2:
Rise Time vs. Capacitive
Load.
FIGURE 2-3:
Rise and Fall Times vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-4:
Fall Time vs. Supply
Voltage.
FIGURE 2-5:
Fall Time vs. Capacitive
Load.
FIGURE 2-6:
Propagation Delay vs. Input
Amplitude.
Note:
The graphs and tables provided following this note are a statistical summary based on a limited number of
samples and are provided for informational purposes only. The performance characteristics listed herein are
not tested or guaranteed. In some graphs or tables, the data presented may be outside the specified
operating range (e.g., outside specified power supply range) and therefore outside the warranted range.
0
20
40
60
80
100
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
Supply Voltage (V)
Ri
se Ti
m
e
(ns
)
10,000 pF
6,800 pF
4,700 pF
2,200 pF
100 pF
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
100
1000
10000
Capacitive Load (pF)
Rise T
im
e
(ns)
5V
12V
18V
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
-40 -25 -10 5
20 35 50 65 80 95 110 125
Temperature (°C)
Time (
n
s)
V
DD
= 18V
t
RISE
t
FALL
0
30
60
90
120
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
Supply Voltage (V)
Fa
ll T
im
e (n
s)
10,000 pF
6,800 pF
4,700 pF
2,200 pF
100 pF
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
100
1000
10000
Capacitive Load (pF)
Fall Time (ns)
5V
12V
18V
35
40
45
50
55
60
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Input Amplitude (V)
Propagation Delay (ns)
V
DD
= 12V
t
D1
t
D2
MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5
DS22062B-page 8
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
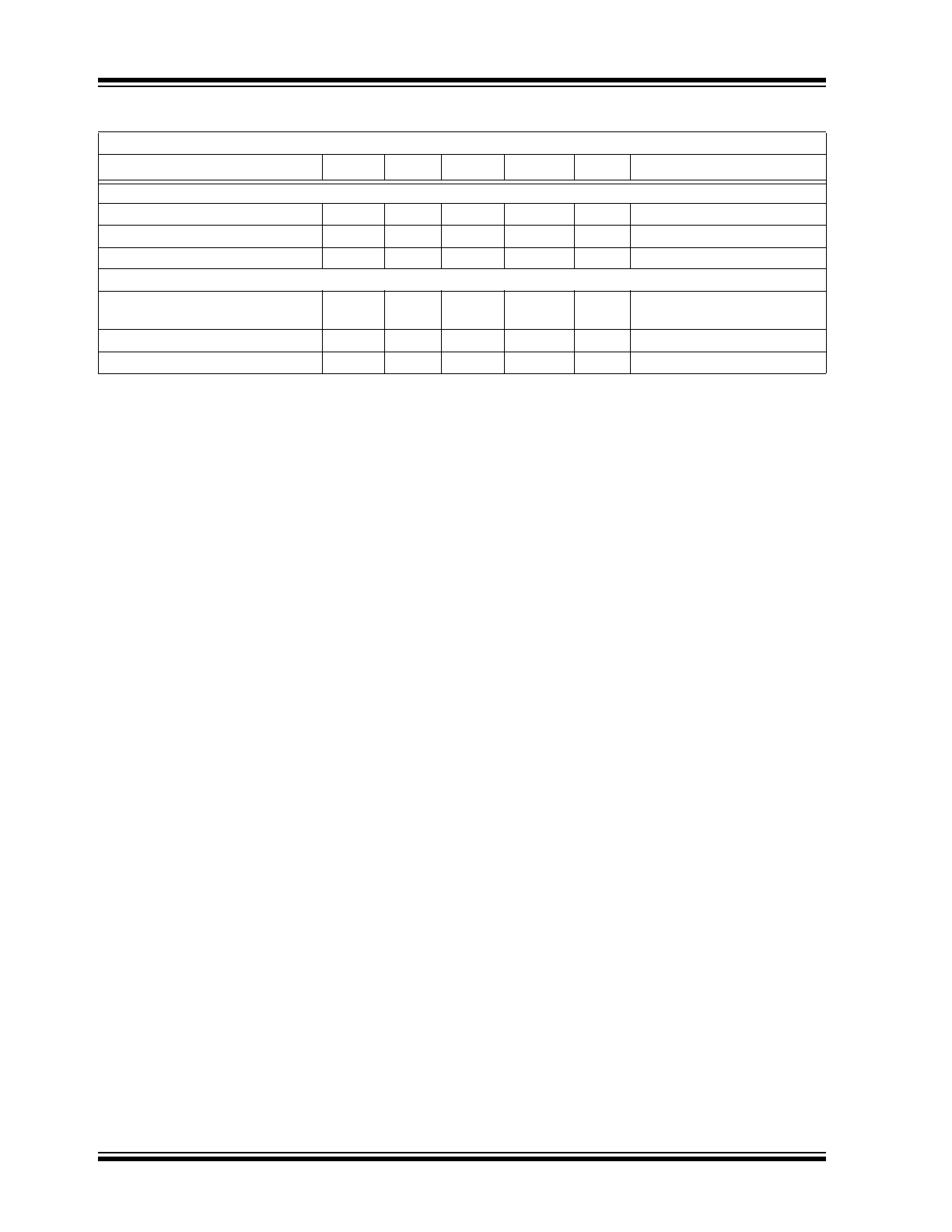
Typical Performance Curves (Continued)
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, T
A
= +25°C with 4.5V
≤ V
DD
≤ 18V.
FIGURE 2-7:
Propagation Delay Time vs.
Supply Voltage.
FIGURE 2-8:
Quiescent Current vs.
Supply Voltage.
FIGURE 2-9:
Output Resistance (Output
High) vs. Supply Voltage.
FIGURE 2-10:
Propagation Delay Time vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-11:
Quiescent Current vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-12:
Output Resistance (Output
Low) vs. Supply Voltage.
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
Supply Voltage (V)
Propagation Delay (ns)
t
D1
t
D2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
Supply Voltage (V)
Quie
sc
ent
Current
(mA)
Input = 1
Input = 0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
Supply Voltage (V)
R
OU
T
-HI
(
Ω
)
T
A
= 125°C
T
A
= 25°C
V
IN
= 0V (MCP14E3)
V
IN
= 5V (MCP14E4)
40
50
60
70
80
-40 -25 -10 5
20 35 50 65 80 95 110 125
Temperature (°C)
P
ropagat
in Delay (
n
s)
t
D1
t
D2
V
DD
= 12V
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
-40 -25 -10 5
20 35 50 65 80 95 110 125
Temperature (°C)
Quie
sc
ent
Current
(mA)
Input = 1
Input = 0
V
DD
= 18V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
Supply Voltage (V)
R
OUT
-LO
(
Ω
)
T
A
= 125°C
T
A
= 25°C
V
IN
= 5V (MCP14E3)
V
IN
= 0V (MCP14E4)
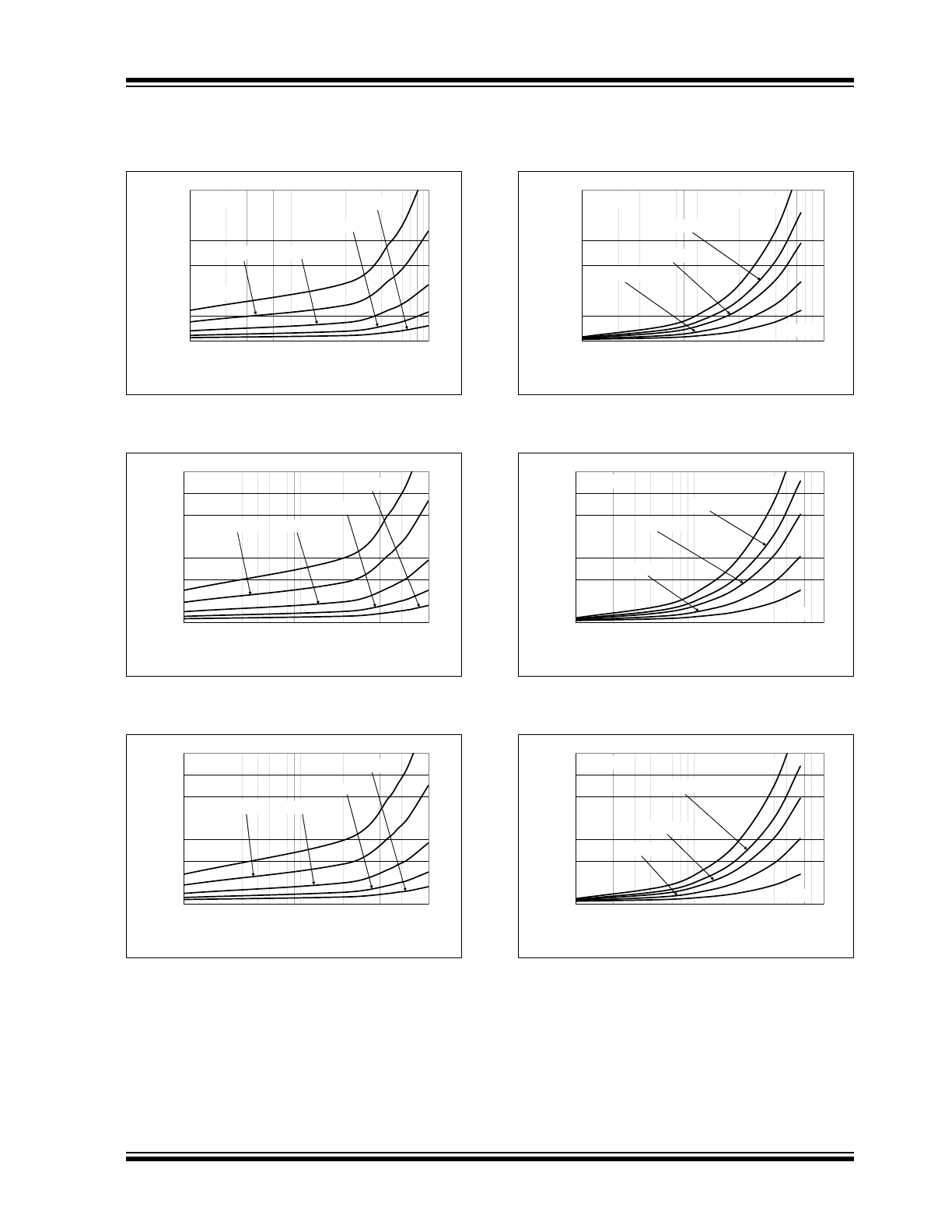
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS22062B-page 9
MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5
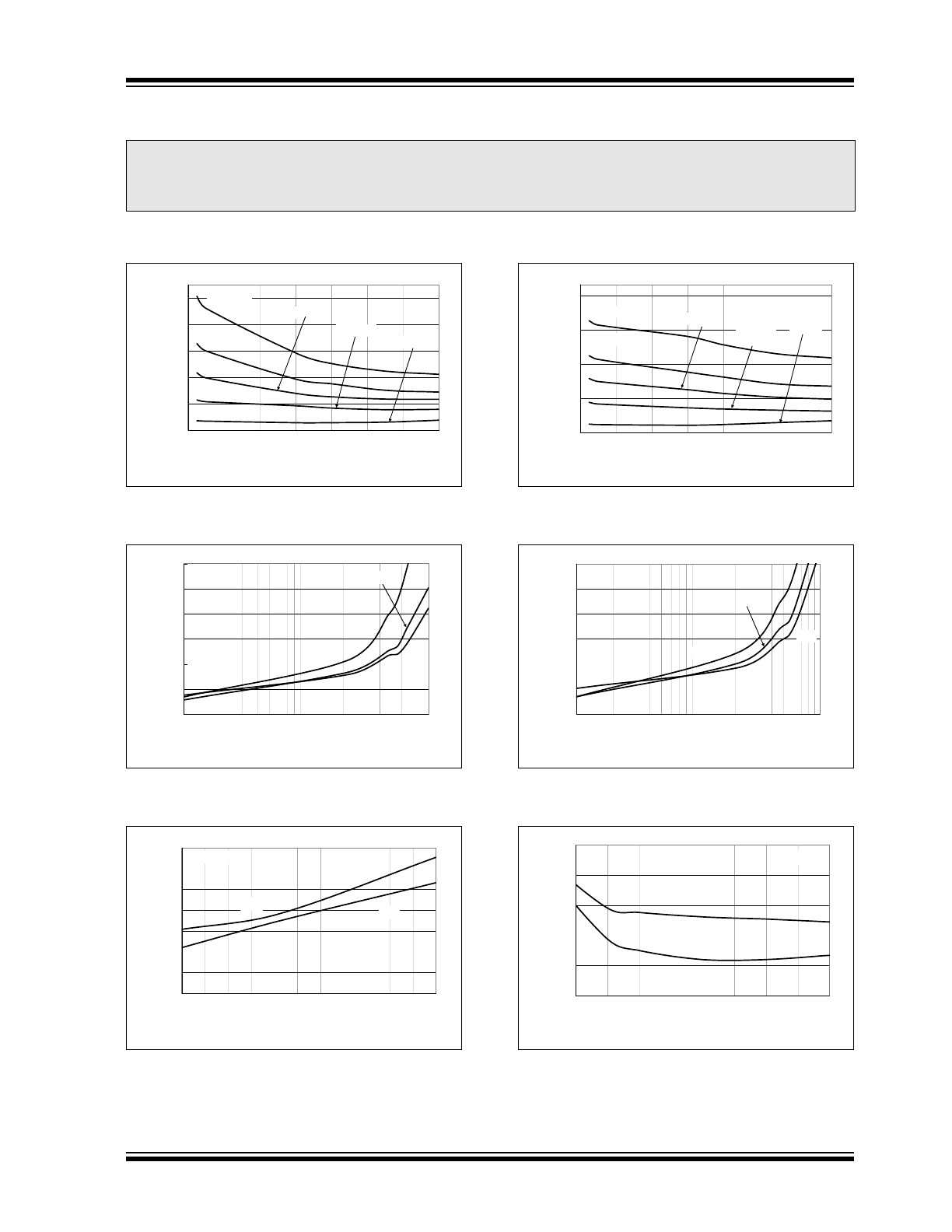
Typical Performance Curves (Continued)
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, T
A
= +25°C with 4.5V
≤ V
DD
≤ 18V.
FIGURE 2-13:
Supply Current vs.
Capacitive Load.
FIGURE 2-14:
Supply Current vs.
Capacitive Load.
FIGURE 2-15:
Supply Current vs.
Capacitive Load.
FIGURE 2-16:
Supply Current vs.
Frequency.
FIGURE 2-17:
Supply Current vs.
Frequency.
FIGURE 2-18:
Supply Current vs.
Frequency.
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
100
1000
10000
Capacitive Load (pF)
S
upply Current
(mA)
650 kHz
400 kHz
200 kHz
100 kHz
50 kHz
V
DD
= 18V
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
100
1000
10000
Capacitive Load (pF)
Supply Current (
m
A
)
650 kHz
400 kHz
200 kHz
100 kHz
50 kHz
V
DD
= 12V
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
100
1000
10000
Capacitive Load (pF)
Supply Current (
m
A
)
650 kHz
400 kHz
200 kHz
100 kHz
50 kHz
V
DD
= 6V
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
10
100
1000
Frequency (kHz)
S
upply Current (
m
A)
10,000 pF
6,800 pF
4,700 pF
2,200 pF
100 pF
V
DD
= 18V
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
10
100
1000
Frequency (kHz)
Supply Current (
m
A
)
10,000 pF
6,800 pF
4,700 pF
2,200 pF
100 pF
V
DD
= 12V
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
10
100
1000
Frequency (kHz)
S
upply Current (
m
A)
10,000 pF
6,800 pF
4,700 pF
2,200 pF
100 pF
V
DD
= 6V
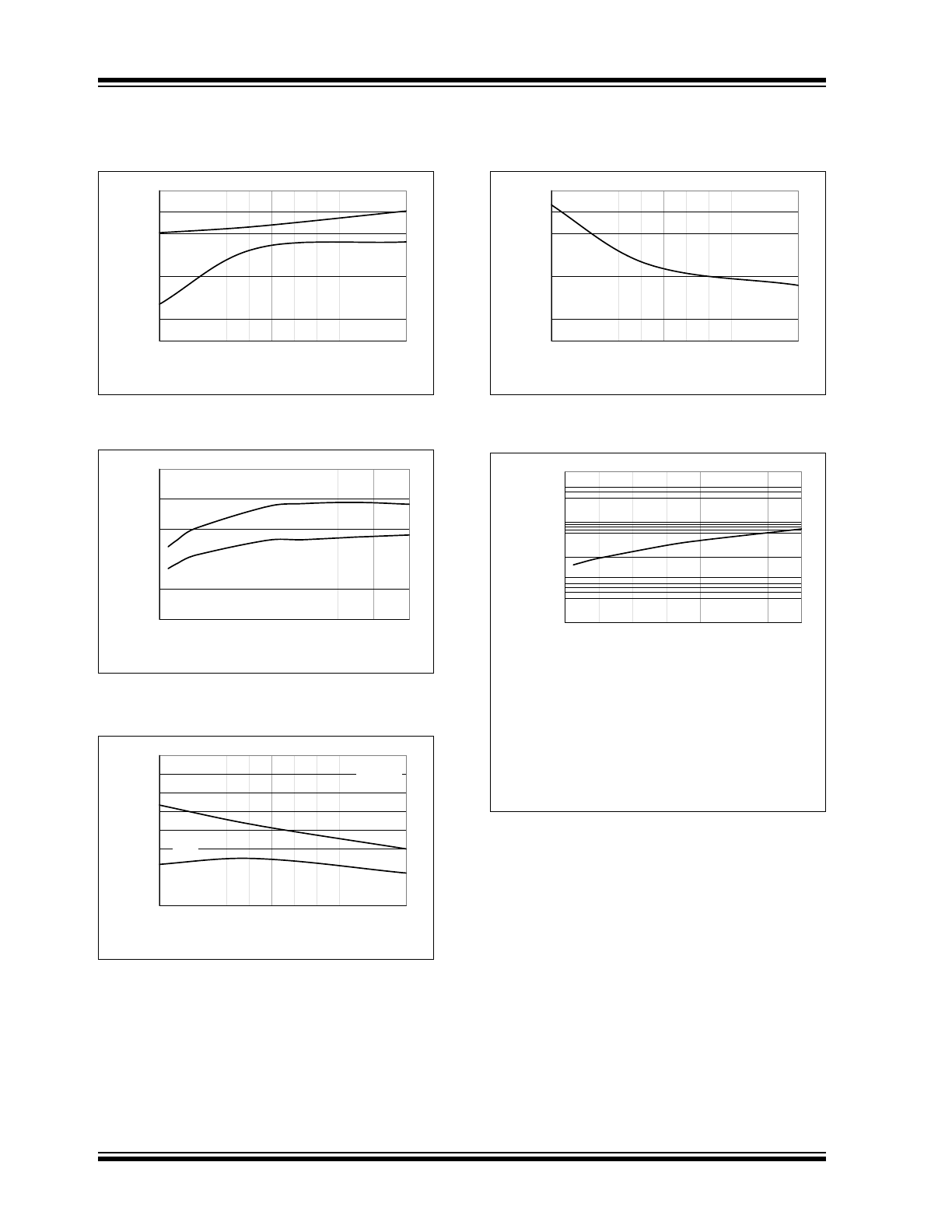
MCP14E3/MCP14E4/MCP14E5
DS22062B-page 10
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
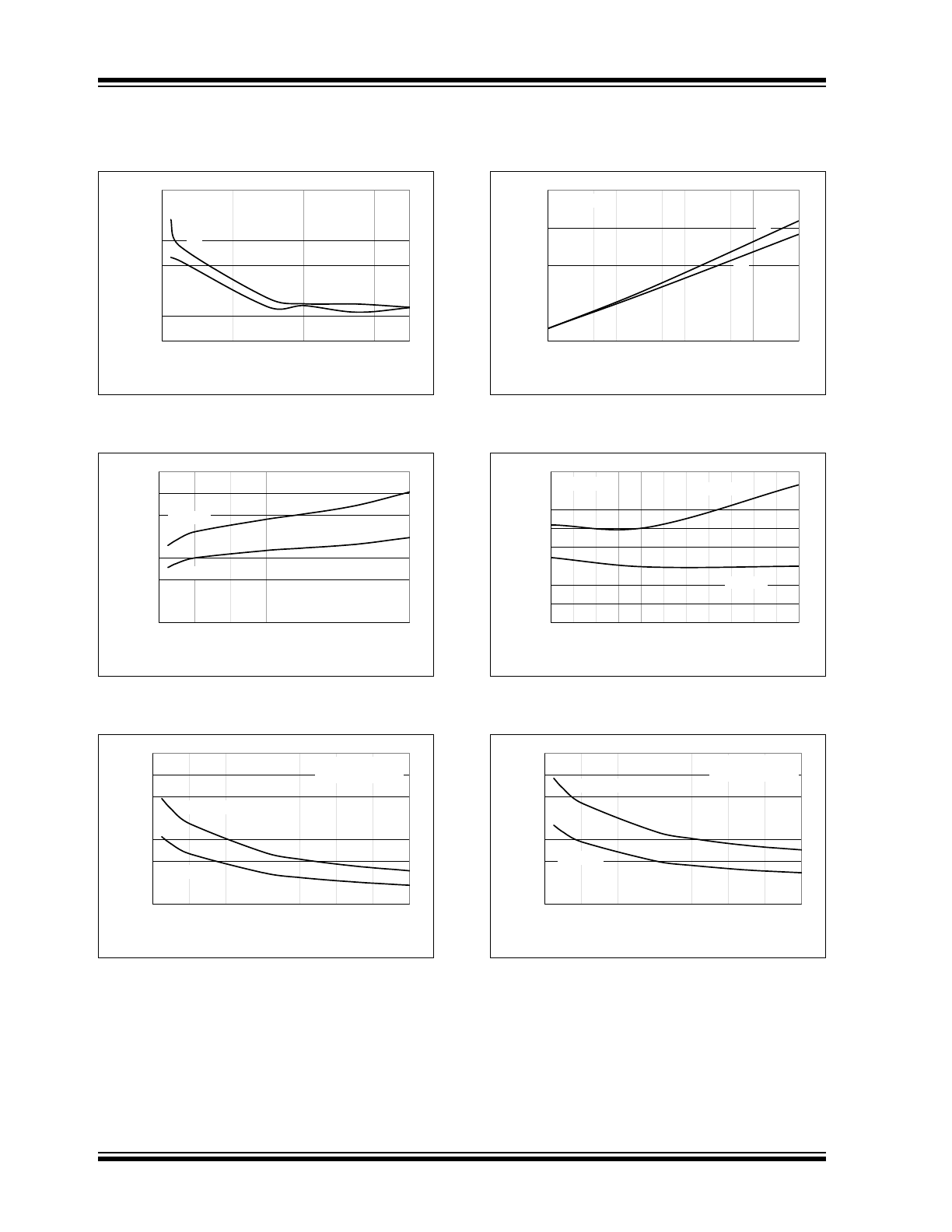
Typical Performance Curves (Continued)
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, T
A
= +25°C with 4.5V
≤ V
DD
≤ 18V.
FIGURE 2-19:
Input Threshold vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-20:
Input Threshold vs. Supply
Voltage.
FIGURE 2-21:
Enable Threshold vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-22:
Enable Hysteresis vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-23:
Crossover Energy vs.
Supply Voltage.
0.7
0.9
1.1
1.3
1.5
1.7
1.9
2.1
-40 -25 -10 5
20 35 50 65 80 95 110 125
Temperature (°C)
Input
Threshold (
V
)
V
HI
V
LO
V
DD
= 18V
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
Supply Voltage (V)
Inp
u
t Thresho
ld (
V
)
V
HI
V
LO
1.5
1.7
1.9
2.1
2.3
2.5
2.7
2.9
3.1
-40 -25 -10 5
20 35 50 65 80 95 110 125
Temperature (°C)
Enable Threshold (V)
V
EN_H
V
EN_L
V
DD
= 12V
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
-40 -25 -10 5
20 35 50 65 80 95 110 125
Temperature (°C)
Ena
b
le Hy
st
er
es
is (V)
V
DD
= 12V
1E-09
1E-08
1E-07
1E-06
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
Supply Voltage (V)
Cr
oss
o
ve
r Ener
gy
(A*
s
ec
)
Note:
The values on this graph represent the
loss seen by both drivers in a package
during one complete cycle.
For a single driver, divide the stated
value by 2.
For a signal transition of a single driver,
divide the state value by 4.
