
2014 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005323A-page 1
HV9910C
Features
• Switch mode controller for single switch LED drivers
• Enhanced drop-in replacement to the HV9910B
• Open loop peak current controller
• Internal 15 to 450V linear regulator
• Constant frequency or constant off-time operation
• Linear and PWM dimming capability
• Requires few external components for operation
• Over-temperature protection
Applications
• DC/DC or AC/DC LED driver applications
• RGB back-lighting LED driver
• Back lighting of flat panel displays
• General purpose constant current source
• Signage and decorative LED lighting
• Chargers
Description
HV9910C is an open-loop, current-mode control, LED
driver IC. This IC can be programmed to operate in
either a constant frequency or constant off-time mode.
It includes a 15 – 450V linear regulator which allows it
to work with a wide range of input voltages without the
need for an external low voltage supply. HV9910C
includes a TTL-compatible, PWM-dimming input that
can accept an external control signal with a duty ratio
of 0 – 100% and a frequency of up to a few kilohertz. It
also includes a 0 – 250mV linear-dimming input which
can be used for linear dimming of the LED current.
Unlike the HV9910B, the HV9910C is equipped with
built-in thermal-shutdown protection.
HV9910C is ideally suited for buck LED drivers. Since
the HV9910C operates in open-loop current mode con-
trol, the controller achieves good output current regula-
tion without the need for any loop compensation. Also,
being an open-loop controller, PWM-dimming
response is limited only by the rate of rise of the induc-
tor current, enabling a very fast rise and fall times of the
LED current. HV9910C requires only three external
components (apart from the power stage) to produce a
controlled LED current. This makes HV9910C an ideal
solution for low-cost LED drivers.
Universal High-Brightness LED Driver
HV9910C
DS20005323A-page 2
2014 Microchip Technology Inc.
TO OUR VALUED CUSTOMERS
It is our intention to provide our valued customers with the best documentation possible to ensure successful use of your Microchip
products. To this end, we will continue to improve our publications to better suit your needs. Our publications will be refined and
enhanced as new volumes and updates are introduced.
If you have any questions or comments regarding this publication, please contact the Marketing Communications Department via
E-mail at
docerrors@microchip.com
. We welcome your feedback.
Most Current Data Sheet
To obtain the most up-to-date version of this data sheet, please register at our Worldwide Web site at:
http://www.microchip.com
You can determine the version of a data sheet by examining its literature number found on the bottom outside corner of any page.
The last character of the literature number is the version number, (e.g., DS30000000A is version A of document DS30000000).
Errata
An errata sheet, describing minor operational differences from the data sheet and recommended workarounds, may exist for current
devices. As device/documentation issues become known to us, we will publish an errata sheet. The errata will specify the revision
of silicon and revision of document to which it applies.
To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please check with one of the following:
• Microchip’s Worldwide Web site;
http://www.microchip.com
• Your local Microchip sales office (see last page)
When contacting a sales office, please specify which device, revision of silicon and data sheet (include literature number) you are
using.
Customer Notification System
Register on our web site at
www.microchip.com
to receive the most current information on all of our products.
2014 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005323A-page 3
HV9910C
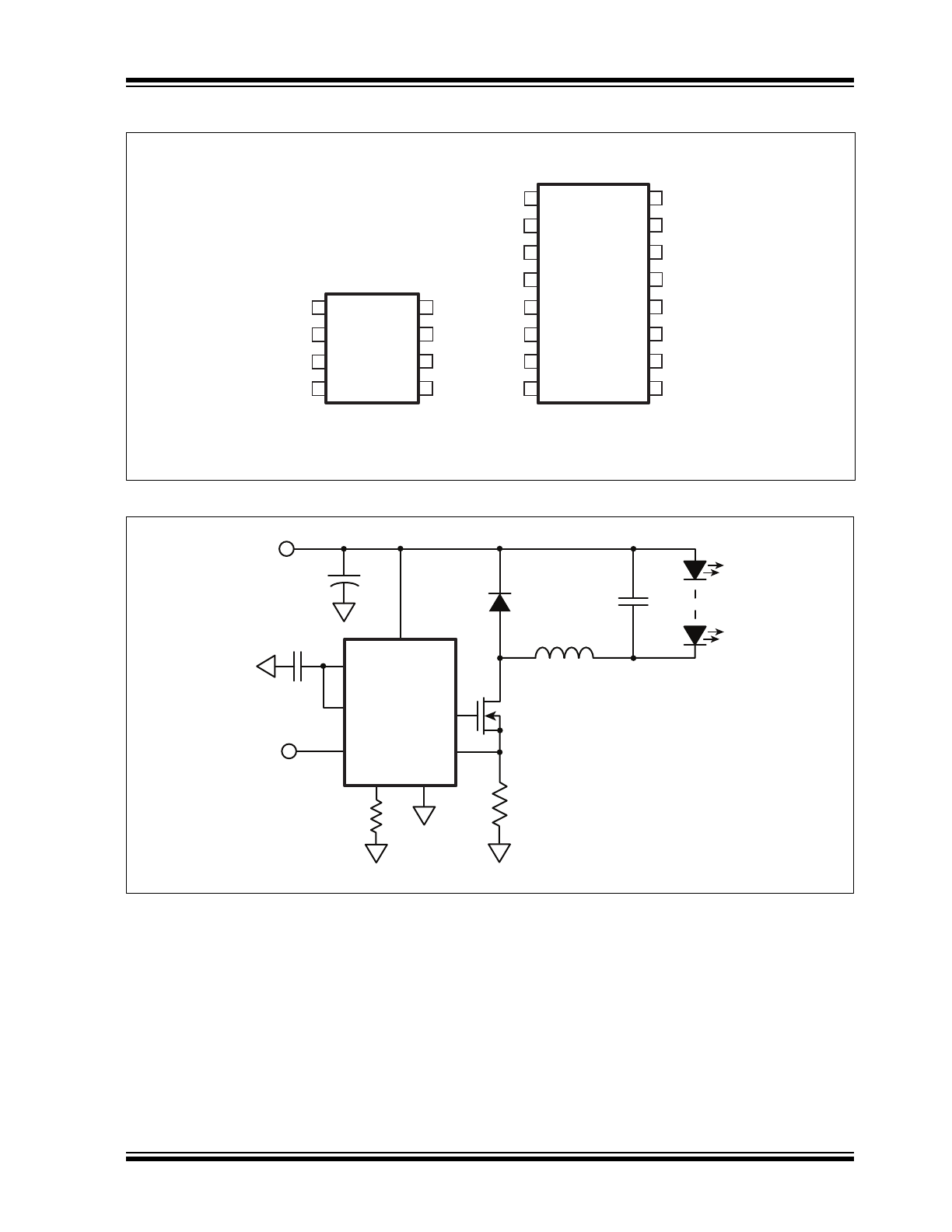
Pin Diagram
Typical Application Circuit
8-Lead SOIC
16-Lead SOIC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
VIN
CS
GND
GATE
RT
LD
VDD
PWMD
VIN
NC
NC
CS
GND
NC
NC
GATE
NC
NC
RT
LD
VDD
NC
NC
PWMD
C
DD
R
OSC
R
CS
L1
Q1
D1
C
O
C
IN
HV9910C
VIN
GATE
CS
VDD
LD
PWMD
RT
GND
HV9910C
DS20005323A-page 4
2014 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.0
ELECTRICAL
CHARACTERISTICS
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
V
IN
to GND ...................................................... -0.5V to +470V
V
DD
to GND.......................................................................12V
CS, LD, PWMD, GATE...........................-0.3V to (V
DD
+ 0.3V)
Junction temperature ....................................-40°C to +125°C
Storage temperature .....................................-65°C to +150°C
Continuous power dissipation (T
A
= +25°C)
8-lead SOIC ...............................................650 mW
16-lead SOIC ...........................................1300 mW
8-lead SOIC with heat slug ......................1300 mW
Note: Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum
Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is
a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at
those or any other conditions, above those indicated in the
operational listings of this specification, is not implied. Expo-
sure to maximum rating conditions for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
1.1
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
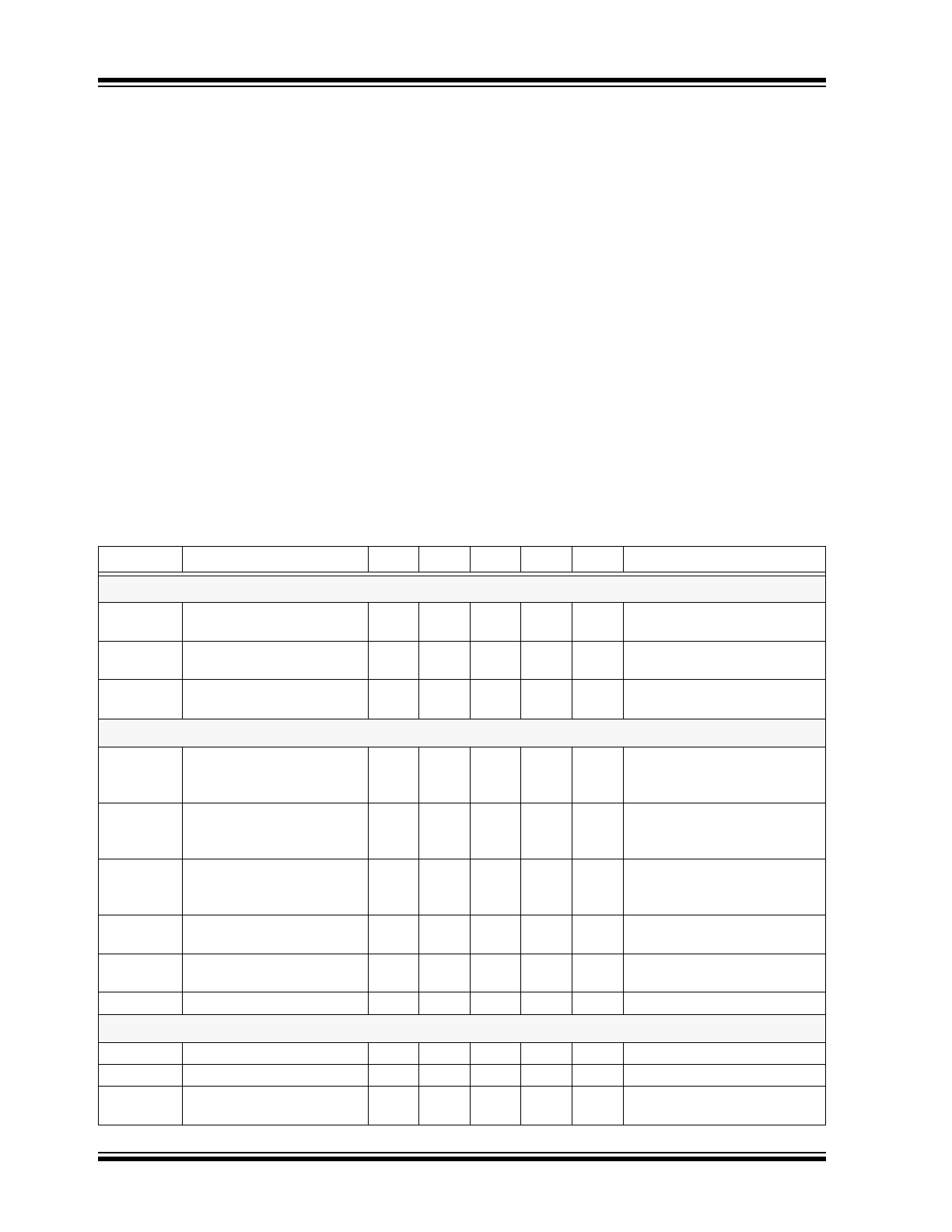
TABLE 1-1:
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (SHEET 1 OF 2)
1
Symbol
Parameter
Note
Min
Typ
Max
Units Conditions
Input
V
INDC
Input DC supply voltage
range
2
3
15
-
450
V
DC input voltage
I
IN(MAX)
Supply current
-
-
0.8
1.5
mA
Pin PWMD to V
DD
, no capaci-
tance at GATE
I
INSD
Shut-down mode supply
current
-
-
0.5
1.0
mA
Pin PWMD to GND
Internal Regulator
V
DD
Internally regulated voltage
-
7.25
7.50
7.75
V
V
IN
= 15V, I
DD(ext)
= 0,
PWMD = V
DD
, 500pF at GATE;
R
OSC
= 249kΩ
∆V
DD
, line Line regulation of V
DD
-
0
-
1.0
V
V
IN
= 15 - 450V, I
DD(ext)
= 0,
PWMD = V
DD
, 500pF at GATE;
R
OSC
= 249kΩ
∆V
DD
, load Load regulation of V
DD
-
0
-
0.1
V
I
DD(ext)
= 0 - 1.0mA,
PWMD = V
DD
, 500pF at GATE;
ROSC = 249kΩ
UVLO
V
DD
under voltage lockout
threshold
3
6.45
6.70
6.95
V
V
DD
rising
∆UVLO
V
DD
under voltage lockout
hysteresis
-
-
500
-
mV
V
DD
falling
I
IN(MAX)
Maximum regulator current
4
5.0
-
-
mA
V
DD
= UVLO - ∆UVLO
PWM Dimming
V
EN(lo)
PWMD input low voltage
3
-
-
1.0
V
V
IN
= 15 - 450V
V
EN(hi)
PWMD input high voltage
3
2.4
-
-
V
V
IN
= 15 - 450V
R
EN
Internal pull-down resis-
tance at PWMD
-
50
100
150
kΩ
V
PWMD
= 5.0V
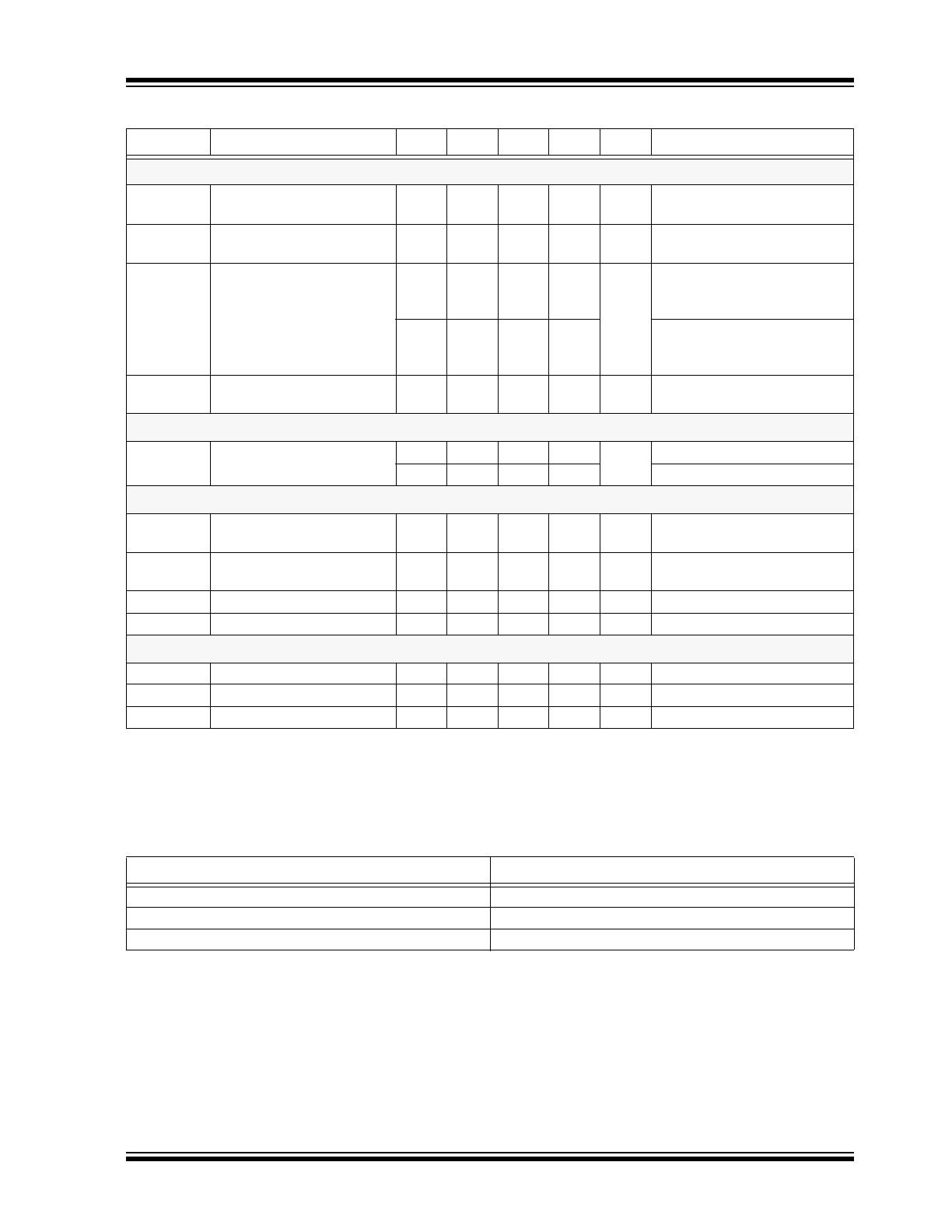
2014 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005323A-page 5
HV9910C
Current Sense Comparator
V
CS
Current sense pull-in thresh-
old voltage
-
225
250
275
mV
-40°C < T
A
< +125°C
V
OFFSET
Offset voltage for LD com-
parator
3
-12
-
+12
mV
T
BLANK
Current sense blanking
interval
-
150
215
280
ns
0 < T
A
< +85°C, V
LD
= V
DD
,
V
CS
= V
CS,TH
+ 50mV after
T
BLANK
-
145
215
315
-40 < T
A
< +125°C, V
LD
= V
DD
,
V
CS
= V
CS,TH
+ 50mV after
T
BLANK
t
DELAY
Delay to output
-
-
80
150
ns
V
IN
= 15V, VLD = 0.15,
V
CS
= 0 to 0.22V after t
BLANK
Oscillator
f
OSC
Oscillator frequency
-
20
25
30
kHz
R
OSC
= 1.00MΩ
-
80
100
120
R
OSC
= 249kΩ
Gate Driver
I
SOURCE
Maximum GATE sourcing
current
-
0.165
-
-
A
V
GATE
= 0V
I
SINK
Maximum GATE sinking cur-
rent
-
0.165
-
-
A
V
GATE
= V
DD
t
RISE
GATE output rise time
4
-
30
50
ns
C
GATE
= 500pF
t
FALL
GATE output fall time
4
-
30
50
ns
C
GATE
= 500pF
Over-Temperature Protection
T
SD
Shut-down temperature
-
128
-
150
°C
∆T
SD
Hysteresis
-
10
-
30
°C
I
SD
T
SD
-mode V
IN
current
-
-
-
350
μA
1
Specifications are T
A
= 25°C, V
IN
= 15V unless otherwise noted.
2
Also limited by package-power dissipation limit; Whichever is lower.
3
Applies over the full operating ambient temperature range of -40°C < T
A
< +125°C.
4
For design guidance only.
TABLE 1-1:
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED) (SHEET 2 OF 2)
1
Symbol
Parameter
Note
Min
Typ
Max
Units Conditions
TABLE 1-2:
THERMAL RESISTANCE
Package
θja
8-Lead SOIC
101°C/W
16-Lead SOIC
83°C/W
8-Lead SOIC (with heat slug)
84°C/W
HV9910C
DS20005323A-page 6
2014 Microchip Technology Inc.
2.0
PIN DESCRIPTION
The descriptions of the pins are listed in
Table 2-1
.
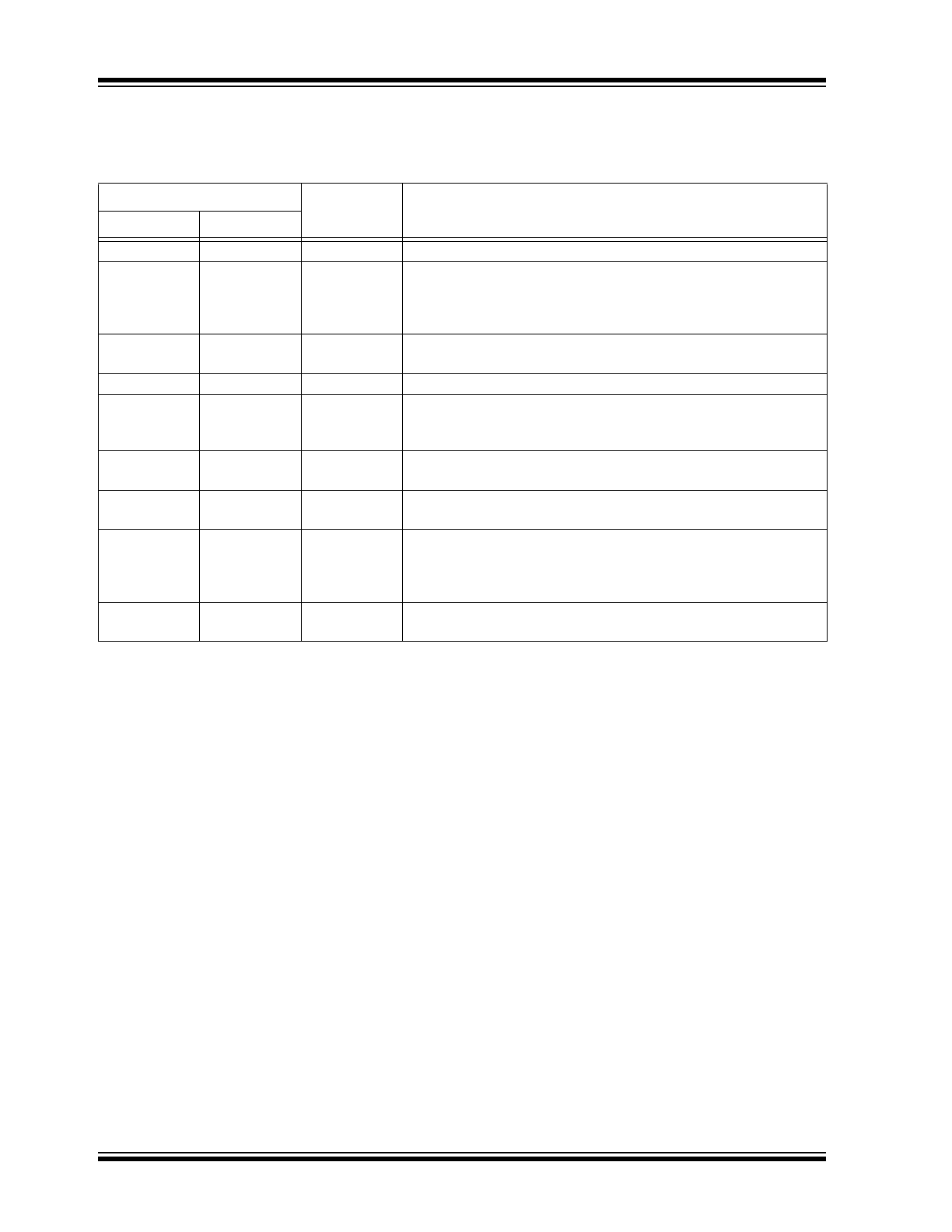
TABLE 2-1:
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin #
Function
Description
8-Lead SOIC 16-Lead SOIC
1
1
VIN
Input of an 15 - 450V linear regulator.
2
4
CS
Current sense pin used to sense the FET current by means of an
external sense resistor. When this pin exceeds the lower of either
the internal 250mV or the voltage at the LD pin, the GATE output
goes low.
3
5
GND
Ground return for all internal circuitry. Must be electrically con-
nected to the power ground.
4
8
GATE
Output GATE driver for an external N-channel power MOSFET.
5
9
PWMD
TTL-compatible, PWM-dimming input of the IC. When this pin is
pulled to GND or left open, the GATE driver is turned off. When the
pin is pulled high, the GATE driver operates normally.
6
12
VDD
Power supply pin for all internal circuits. It must be bypassed with a
low ESR capacitor to GND (≥0.1μF).
7
13
LD
Linear-dimming input and sets the current sense threshold as long
as the voltage at the pin is less than 250mV (typ).
8
14
RT
Sets the oscillator frequency. When a resistor is connected
between RT and GND, the HV9910C operates in constant fre-
quency mode. When the resistor is connected between RT and
GATE, the IC operates in constant off-time mode.
-
2, 3, 6, 7, 10,
11, 15, 16
NC
No connection

2014 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005323A-page 7
HV9910C
3.0
APPLICATION INFORMATION
HV9910C is optimized to drive buck LED drivers using
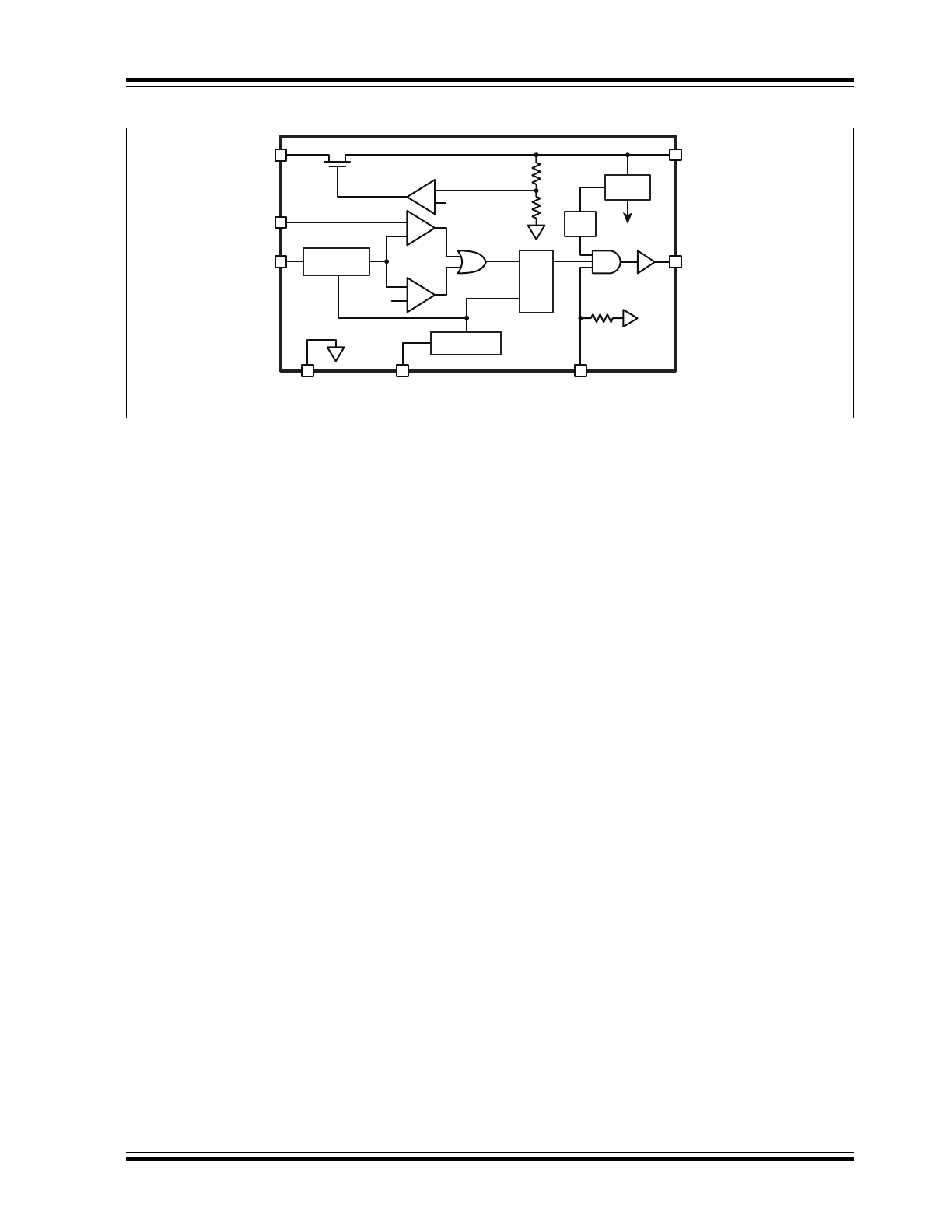
open-loop, peak-current mode control. This method of
control enables fairly accurate LED current control
without the need for high side current sensing or the
design of any closed loop controllers. The IC uses very
few external components and enables both Linear and
PWM-dimming of the LED current.
A resistor connected to the RT pin programs the fre-
quency of operation (or the off-time). The oscillator pro-
duces pulses at regular intervals. These pulses set the
SR flip-flop in the HV9910C which causes the GATE
driver to turn on. The same pulses also start the blank-
ing timer, which inhibits the reset input of the SR flip flop
and prevents false turn-offs due to the turn-on spike.
When the FET turns on, the current through the induc-
tor starts ramping up. This current flows through the
external sense resistor, R
CS
, and produces a ramp volt-
age at the CS pin. The comparators are constantly
comparing the CS pin voltage to both the voltage at the
LD pin and the internal 250mV. Once the blanking timer
is complete, the output of these comparators is allowed
to reset the flip-flop. When the output of either one of
the two comparators goes high, the flip-flop is reset and
the GATE output goes low. The GATE goes low until
the SR flip-flop is set by the oscillator. Assuming a 30%
ripple in the inductor, the current sense resistor R
CS
can be set using:
Constant frequency peak current mode control has an
inherent disadvantage – at duty cycles greater than
0.5, the control scheme goes into subharmonic oscilla-
tions. To prevent this, an artificial slope is typically
added to the current sense waveform. This slope com-
pensation scheme will affect the accuracy of the LED
current in the present form. However, a constant off-
time peak current control scheme does not have this
problem and can easily operate at duty cycles greater
than 0.5. This control scheme also gives inherent input
voltage rejection, making the LED current almost
insensitive to input voltage variations. However, this
scheme leads to variable frequency operation and the
frequency range depends greatly on the input and out-
put voltage variation. Using HV9910C, it is easy to
switch between the two modes of operation by chang-
ing one connection (see
Section 3.3 “Oscillator”
).
3.1
Input Voltage Regulator
HV9910C can be powered directly from its V
IN
pin and
can work from 15 - 450VDC at its V
IN
pin. When a volt-
age is applied at the V
IN
pin, HV9910C maintains a
constant 7.5V at the V
DD
pin. This voltage is used to
power the IC and any external-resistor dividers needed
to control the IC. The V
DD
pin must be bypassed by a
low-ESR capacitor to provide a low impedance path for
the high frequency current of the output GATE driver.
HV9910C can also be operated by supplying a voltage
at the V
DD
pin greater than the internally regulated volt-
age. This will turn off the internal linear regulator of the
IC and the HV9910C will operate directly off the voltage
supplied at the V
DD
pin. This external voltage at the
V
DD
pin should not exceed 12V.
Although the V
IN
pin of the HV9910C is rated up to
450V, the actual maximum voltage that can be applied
is limited by the power dissipation in the IC. For exam-
ple, if an 8-lead SOIC HV9910C (junction to ambient
thermal resistance R
θj-a
= 101°C/W) draws about I
IN
=
2.0mA from the V
IN
pin, and has a maximum allowable
temperature rise of the junction temperature limited to
∆T = 75°C, the maximum voltage at the V
IN
pin would
be:
In these cases, to operate HV9910C from higher input
voltages, a Zener diode can be added in series with the
V
IN
pin to divert some of the power loss from HV9910C
to the Zener diode. In the above example, using a 100V
Zener diode will allow the circuit to easily work up to
450V.
The input current drawn from the V
IN
pin is a sum of the
1.5mA (maximum) current drawn by the internal circuit
and the current drawn by the GATE driver. The GATE
driver depends on the switching frequency and the
GATE charge of the external FET.
In the above equation, f
s
is the switching frequency and
Q
g
is the GATE charge of the external FET, which can
be obtained from the data sheet of the FET.
3.2
Current Sense
The current sense input of HV9910C goes to the non-
inverting inputs of two comparators. The inverting ter-
minal of one comparator is tied to an internal 250mV
reference, whereas the inverting terminal of the other
comparator is connected to the LD pin. The outputs of
both these comparators are fed into an OR GATE and
R
CS
0.25V orV
LD
1.15 I
LED
------------------------------------
=
Note:
The Zener diode will increase the mini-
mum input voltage required to turn on the
HV9910C to 115V.
V
IN MAX
T
R
ja
-----------
1
I
IN
------
75
C
101
C W
---------------------------
1
2mA
-------------
371V
=
=
=
I
IN
1.5mA Q
g
f
s
+
=

HV9910C
DS20005323A-page 8
2014 Microchip Technology Inc.
the output of the OR GATE is fed into the reset pin of
the flip-flop. Thus, the comparator which has the lowest
voltage at the inverting terminal determines when the
GATE output is turned off.
The outputs of the comparators also include a 150-
280ns blanking time which prevents spurious turn-offs
of the external FET due to the turn-on spike normally
present in peak-current mode control. In rare cases,
this internal blanking might not be enough to filter out
the turn-on spike. In these instances, an external RC fil-
ter needs to be added between the external sense
resistor (RCS) and the CS pin.
Please note that the comparators are fast (with a typi-
cal 80ns response time). A proper layout minimizing
external inductances will prevent false triggering of
these comparators.
3.3
Oscillator
The oscillator in HV9910C is controlled by a single
resistor connected at the RT pin. The equation govern-
ing the oscillator time period T
osc
is given by:
If the resistor is connected between RT and GND,
HV9910C operates in a constant frequency mode and
the above equation determines the time period. If the
resistor is connected between RT and GATE,
HV9910C operates in a constant off-time mode and the
above equation determines the off-time.
3.4
Gate Output
The gate output of the HV9910C is used to drive an
external FET. It is recommended that the GATE charge
of the external FET be less than 25nC for switching fre-
quencies ≤ 100kHz and less than 15nC for switching
frequencies > 100kHz.
3.5
Linear Dimming
The Linear Dimming pin is used to control the LED cur-
rent. There are two cases when it may be necessary to
use the Linear Dimming pin.
1.
In some cases, when using the internal 250mV,
it may not be possible to find the exact R
CS
value required to obtain the LED current. In
these cases, an external voltage divider from the
V
DD
pin can be connected to the LD pin to obtain
a voltage (less than 250mV) corresponding to
the desired voltage across RCS.
2.
Linear dimming may be desired to adjust the
current level to reduce the intensity of the LEDs.
In these cases, an external 0-250mV voltage
can be connected to the LD pin to adjust the
LED current during operation.
To use the internal 250mV, the LD pin can be con-
nected to V
DD
.
3.6
PWM Dimming
PWM Dimming can be achieved by driving the PWMD
pin with a low frequency square wave signal. When the
PWM signal is zero, the GATE driver is turned off; when
the PWMD signal if high, the GATE driver is enabled.
The PWMD signal does not turn off the other parts of
the IC, therefore, the response of HV9910C to the
PWMD signal is almost instantaneous. The rate of rise
and fall of the LED current is thus determined solely by
the rise and fall times of the inductor current.
To disable PWM Dimming and enable the HV9910C
permanently, connect the PWMD pin to V
DD
.
3.7
Over-Temperature Protection
The auto-recoverable thermal shutdown at 140°C (typ.)
junction temperature with 20°C hysteresis is featured
to avoid thermal runaway. When the junction tempera-
ture reaches T
SD
= 140°C (typ.), HV9910C enters a low
power consumption shut-down mode with I
IN
<350µA.
T
OSC
s
R
OSC
k
25
---------------------------
=
Note:
Although the LD pin can be pulled to GND,
the output current will not go to zero. This
is due to the presence of a minimum on-
time, which is equal to the sum of the
blanking time and the delay to output time,
or about 450ns. This minimum on-time
causes the FET to be on for a minimum of
450ns, and thus the LED current when LD
= GND is not zero. This current is also
dependent on the input voltage, induc-
tance value, forward voltage of the LEDs,
and circuit parasitics. To get zero LED cur-
rent, the PWMD pin has to be used.
2014 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005323A-page 9
HV9910C
FIGURE 3-1:
INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
POR
250mV
VDD
GATE
VIN
LD
CS
GND RT PWMD
S
R
Q
Blanking
+
-
+
-
+
-
1.25V
Bandgap
Reference
OTP
Oscillator

HV9910C
DS20005323A-page 10
2014 Microchip Technology Inc.
4.0
PACKAGING INFORMATION
4.1
Package Marking Information
16-Lead SOIC
8-Lead SOIC
X = Product Code
YY = Year Sealed
WW = Week Sealed
NNN = Traceability Code
e# = JEDEC Symbol
● = Pin 1 Indicator
Note: The JEDEC environmental marking symbols (e#) illustrated are
examples only, and might not reflect the actual value for the listed
package code.
