2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005519A-page 1
Features
• 10 to 450V input voltage range
• <1.3 mA supply current
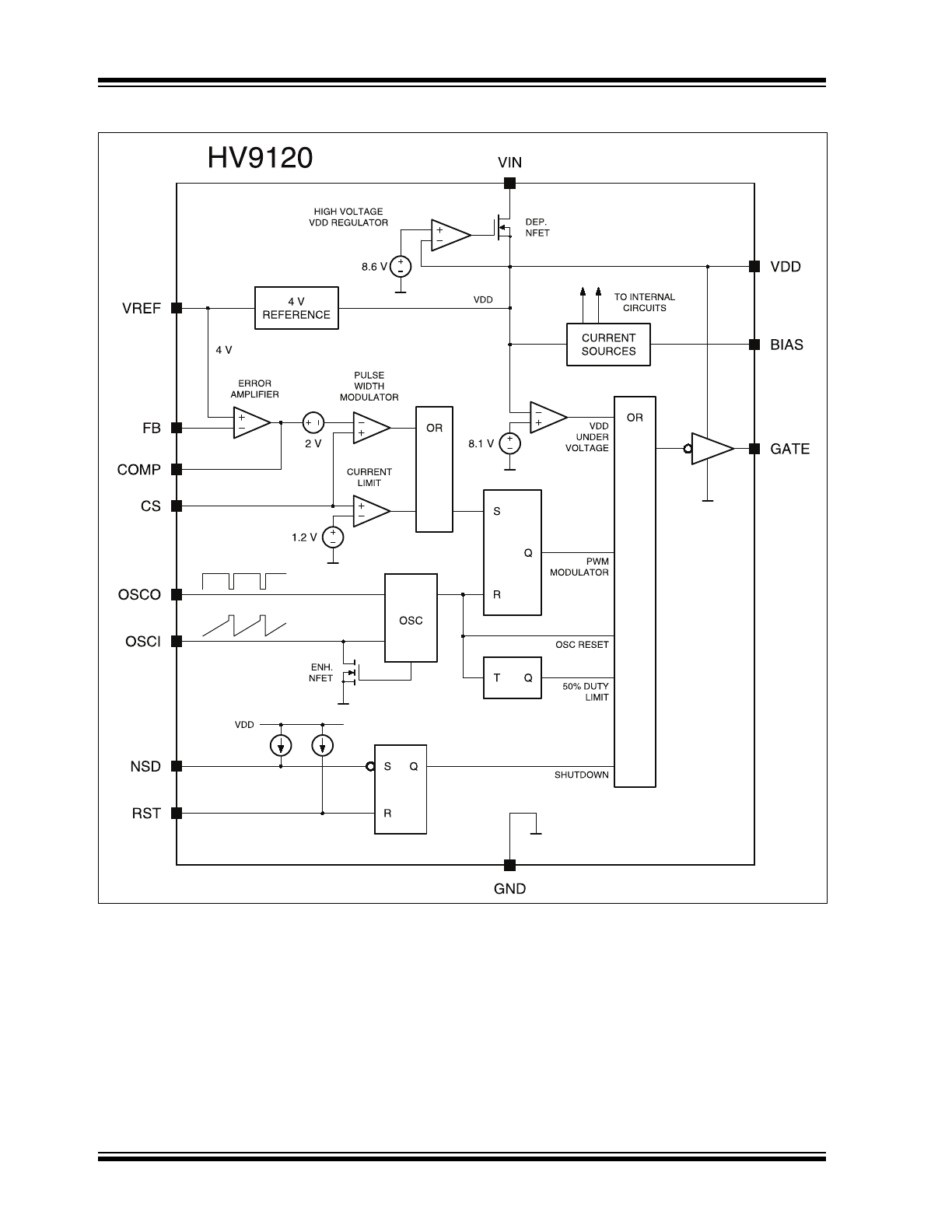
• >1 MHz clock
• 49% maximum duty version
Applications
• Off-line high frequency power supplies
• Universal input power supplies
• High density power supplies
• Very high efficiency power supplies
• Extra wide load range power supplies
Description
HV9120 and HV9123 are Switch-Mode Power Supply
(SMPS) controllers suitable for the control of a variety
of converter topologies, including flyback and forward
converter.
Using an internal, high-voltage regulator, HV9120 and
HV9123 can derive a bias supply for starting-up and
powering a converter from a variety of power sources,
such as a 12V battery or the rectified AC (230 VAC)
line.
HV9120/HV9123 controllers include all essentials for a
power-converter design, such as a bandgap reference,
an error amplifier, a ramp generator, a high-speed
PWM comparator, and a gate driver. A shutdown latch
provides on/off control. Device power consumption is
less than 6 mW when shutdown.
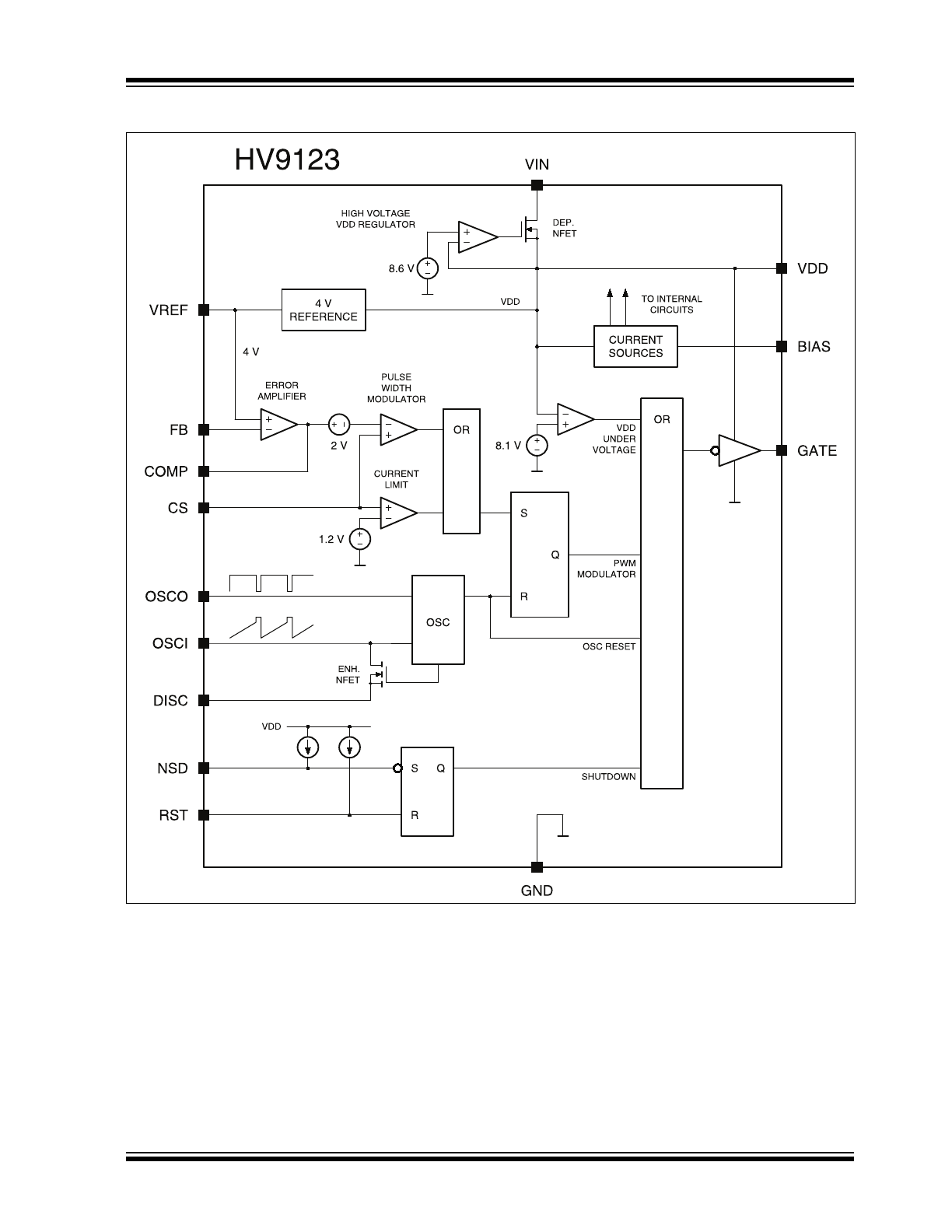
HV9120 offers 50% maximum duty and HV9123 offers
nearly 100% duty.
Package Types
See
Table 3-1
for pin information
16-lead SOIC
16-lead PDIP
1
16
4
1
16
HV9120/HV9123
High-Voltage, Current-Mode, PWM Controller
HV9120/HV9123
DS20005519A-page 2
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
Block Diagram HV9120
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005519A-page 3
HV9120/HV9123
Block Diagram HV9123
HV9120/HV9123
DS20005519A-page 4
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.0
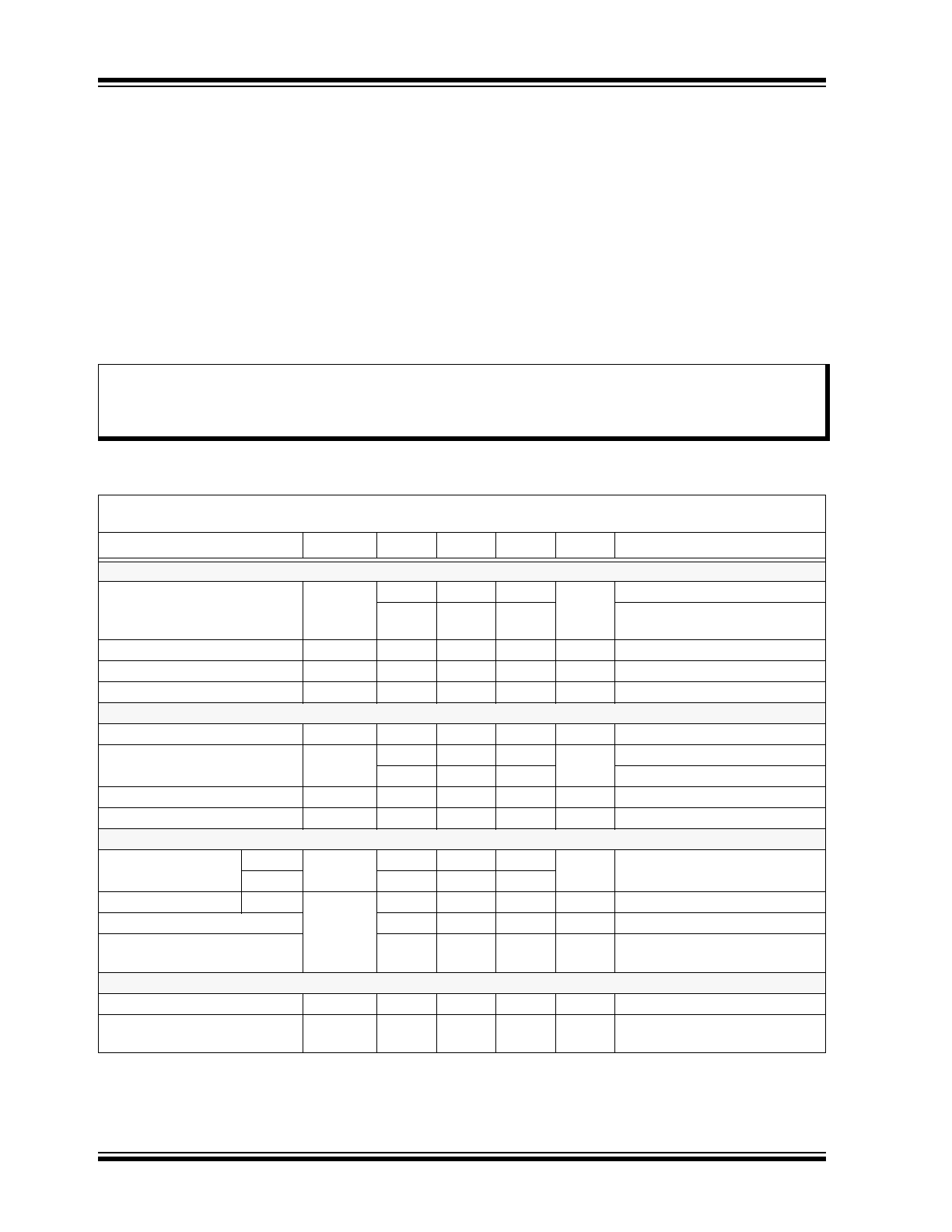
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
†
Input voltage, V
IN
.................................................................................................................................................... 450V
Device supply voltage, V
DD
.................................................................................................................................... 15.5V
Logic input voltage ........................................................................................................................... -0.3V to V
DD
+ 0.3V
Linear input voltage .......................................................................................................................... -0.3V to V
DD
+ 0.3V
High-voltage regulator input current (continuous), I
IN
.......................................................................................... 2.5 mA
Operating temperature range................................................................................................................ -40°C to +125°C
Storage temperature range ................................................................................................................... -65°C to +150°C
Power dissipation: 16-Lead SOIC ...................................................................................................................... 900 mW
16-Lead PDIP .................................................................................................................... 1000 mW
† Notice: Stresses above those listed under “Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is
a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at those or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational listings of this specification is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended periods
may affect device reliability.
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Specifications: V
DD
= 10V, V
IN
= 48V, V
DISC
= 0V, R
BIAS
= 390 kΩ, R
OSC
= 330 kΩ, T
A
= 25°C, unless oth-
erwise noted.
Parameter
Symbol
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
Reference
Output voltage
V
REF
3.92
4.00
4.08
V
R
L
= 10 MΩ
3.84
4.00
4.16
R
L
= 10 MΩ,
T
A
= -40°C to +125°C
Output impedance
Z
OUT
15
30
45
kΩ
(
Note 1
)
Short circuit current
I
SHORT
-
125
250
μA
V
REF
= GND
Change in V
REF
with temperature
∆V
REF
-
0.25
-
mV/°C T
A
= -40°C to +125°C (
Note 1
)
Oscillator
Oscillator frequency
f
MAX
1.0
3.0
-
MHz
R
OSC
= 0Ω
Initial accuracy
f
OSC
80
100
120
kHz
R
OSC
= 330 kΩ (
Note 2
)
160
200
240
R
OSC
= 150 kΩ (
Note 2
)
VDD regulation
-
-
-
15
%
9.5V< V
DD
<13.5V
Temperature coefficient
-
-
170
-
ppm/°C T
A
= -40°C to +125°C (
Note 1
)
PWM
Maximum duty cycle
HV9120
D
MAX
49.0
49.4
49.6
%
(
Note 1
)
HV9123
95
97
99
Dead time
HV9123
D
MIN
-
225
-
ns
HV9123 only (
Note 1
)
Minimum duty cycle
-
-
0
%
–
Pulse width where pulse drops
out
-
80
125
ns
(
Note 1
)
Current Limit
Maximum input signal
V
LIM
1.0
1.2
1.4
V
V
FB
= 0V
Delay to output
t
D
-
80
120
ns
V
CS
= 1.5V, V
COMP
≤ 2.0V
(
Note 1
)
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005519A-page 5
HV9120/HV9123
Note 1: Design guidance only; Not 100% tested in production.
2: Stray capacitance on OSC in pin must be ≤ 5 pF.
Error Amplifier
Feedback voltage
V
FB
3.92
4.00
4.08
V
FB shorted to COMP
Input bias current
I
IN
-
25
500
nA
V
FB
= 4.0V
Input offset voltage
V
OS
nulled during trim
-
–
Open loop voltage gain
A
VOL
60
80
-
dB
(
Note 1
)
Unity gain bandwidth
GB
1.0
1.3
-
MHz
(
Note 1
)
Output source current
I
SOURCE
-1.4
-2.0
-
mA
V
FB
= 3.4V
Output sink current
I
SINK
0.12
0.15
-
mA
V
FB
= 4.5V
High-voltage Regulator and Start-up
Input voltage
V
IN
10
-
450
V
I
IN
< 10 µA; V
CC
> 9.4V
Input leakage current
I
IN
-
-
10
μA
V
DD
> 9.4V
Regulator turn-off threshold
voltage
V
TH
8.0
8.7
9.4
V
I
IN
= 10 µA
Undervoltage lockout
V
LOCK
7.0
8.1
8.9
V
–
Supply
Supply current
I
DD
-
0.75
1.3
mA
C
L
< 75 pF
Quiescent supply current
I
Q
-
0.55
-
mA
V
NSD
= 0V
Nominal bias current
I
BIAS
-
20
-
μA
–
Operating range
V
DD
9.0
-
13.5
V
–
Shutdown Logic
Shutdown delay
t
SD
-
50
100
ns
C
L
= 500 pF, V
CS
= 0V (
Note 1
)
NSD pulse width
t
SW
50
-
-
ns
(
Note 1
)
RST pulse width
t
RW
50
-
-
ns
(
Note 1
)
Latching pulse width
t
LW
25
-
-
ns
V
NSD
, V
RST
=0V(
Note 1
)
Input low voltage
V
IL
-
-
2.0
V
–
Input high voltage
V
IH
7.0
-
-
V
–
Input current, input high voltage
I
IH
-
1.0
5.0
μA
V
IN
= V
DD
Input current, input low voltage
I
IL
-
-25
-35
μA
V
IN
= 0V
Output
Output high voltage
V
OH
V
DD
-
0.25
-
-
V
I
OUT
= 10 mA
V
DD
-
0.3
-
-
I
OUT
= 10 mA,
T
A
= -40°C to 125°C
Output low voltage
V
OL
-
-
0.2
V
I
OUT
= -10 mA
-
-
0.3
I
OUT
= -10 mA,
T
A
= -40°C to 125°C
Output resistance
Pull up
R
OUT
-
15
25
Ω
I
OUT
= ±10 mA
Pull down
-
8.0
20
Pull up
-
20
30
Ω
I
OUT
= ±10 mA,
T
A
= -40°C to 125°C
Pull down
-
10
30
Rise time
t
R
-
30
75
ns
C
L
= 500 pF (
Note 1
)
Fall time
t
F
-
20
75
ns
C
L
= 500 pF(
Note 1
)
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED)
Electrical Specifications: V
DD
= 10V, V
IN
= 48V, V
DISC
= 0V, R
BIAS
= 390 kΩ, R
OSC
= 330 kΩ, T
A
= 25°C, unless oth-
erwise noted.
Parameter
Symbol
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
HV9120/HV9123
DS20005519A-page 6
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.1
Truth Table
TEMPERATURE SPECIFICATIONS
Parameter
Symbol
Min
Typ
Max
Units Conditions
Temperature Ranges
Operating Temperature
-40
125
°C
Storage Temperature
-65
–
150
°C
Package Thermal Resistances
Thermal Resistance, SOIC
θ
ja
–
83
–
°C/W
Thermal Resistance, PDIP
θ
ja
–
51
–
°C/W
TRUTH TABLE
SHUTDOWN
RESET
OUTPUT
H
H
Normal operation
H
H → L
Normal operation, no change
L
H
Off, not latched
L
L
Off, latched
L → H
L
Off, latched, no change
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005519A-page 7
HV9120/HV9123
2.0
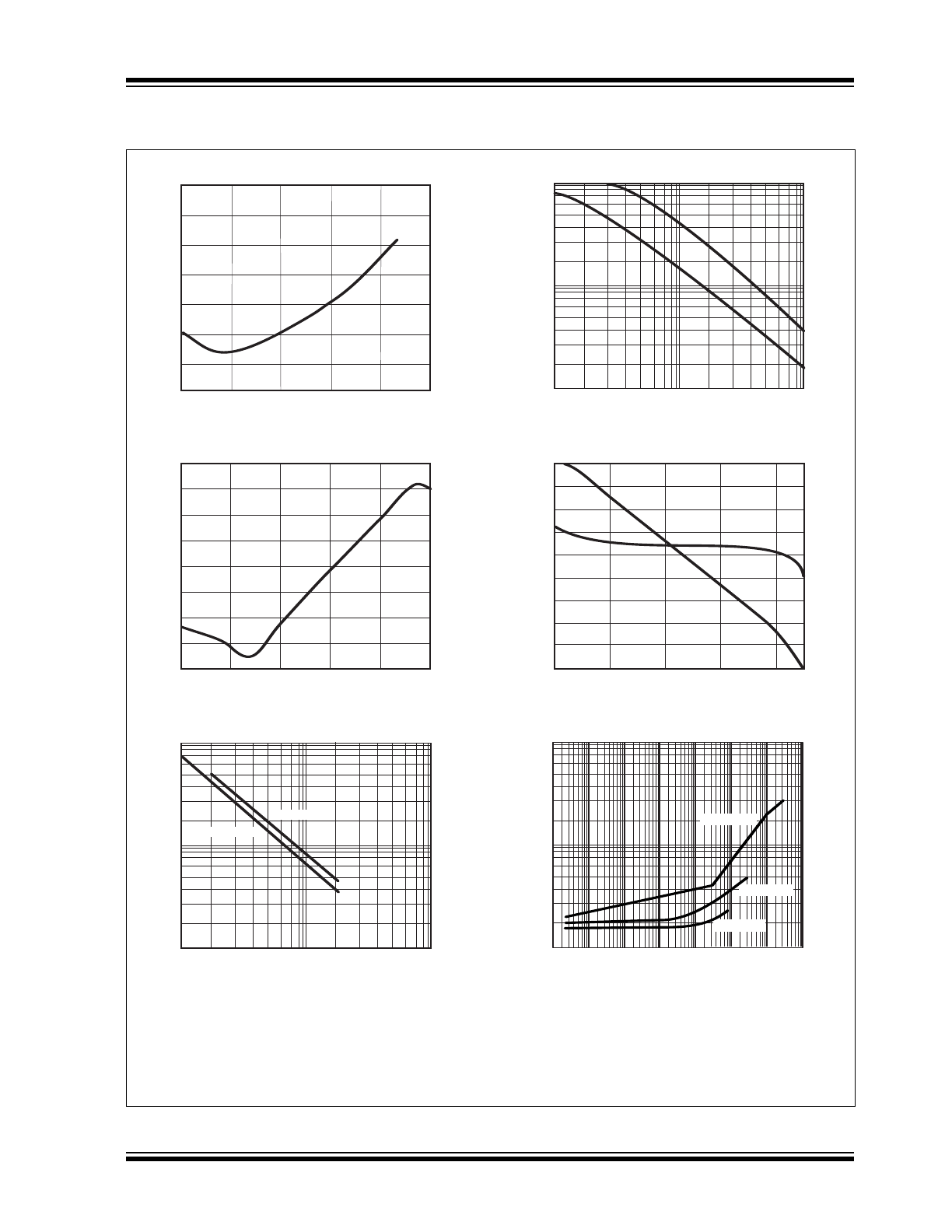
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
FIGURE 2-1:
Typical Performance Curves
Output Switching Frequency
vs. Oscillator Resistance
10k 100k 1M
R
OSC
(Ω)
f
OUT
(Hz)
1M
100k
10k
PSRR - Error Amplifier and Reference
10 100 1K 10K 100K 1M
80
70
60
50
40
20
10
0
-10
Error Amplifier Open Loop Gain/Phase
Gain (dB)
Phase (
O
C)
180
120
60
0
-60
-120
-180
Frequency (Hz)
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
1.0
0.1
Error Amplifier Output Impedance (Z
0
)
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
Bias Resistance (Ω)
10
5
10
6
10
7
Bias Current (μA)
V
DD
= 10V
PSRR (dB)
Frequency (Hz)
Z
0
(Ω)
100 1K 10K 100K 1M 10M
Frequency (Hz)
V
DD
= 10V
100 1K 10K 100K 1M
100
10
1.0
HV9120
HV9123
R
DISCHARGE
vs. t
OFF
(HV9123 only)
R
DISCHARGE
(Ω)
t
OFF
(nsec)
R
OSC
= 10k
R
OSC
= 1.0k
R
OSC
= 100k
10
-1
10 10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
10
6
10
4
10
3
10
2
HV9120/HV9123
DS20005519A-page 8
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
3.0
PIN DESCRIPTION
The locations of the pins are listed in
Features
.
TABLE 3-1:
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin #
Symbol HV9120
Symbol HV9123
Description
1
V
IN
V
IN
High-voltage, V
DD
regulator input
2
NC
NC
No connect
3
NC
NC
No connect
4
CS
CS
Current-sense input
5
GATE
GATE
Gate-drive output
6
GND
GND
Ground
7
VDD
VDD
High-voltage, V
DD
regulator output
8
OSCO
OSCO
Oscillator output
9
OSCI
OSCI
Oscillator Input
10
NC
DISC
Oscillator discharge, current set
11
VREF
VREF
4V Reference output
Reference voltage level can be over-
ridden by an externally-applied volt-
age source.
12
NSD
NSD
Active low input to set shutdown latch
13
RST
RST
Active high input to reset shutdown
latch
14
COMP
COMP
Error-amplified output
15
FB
FB
Feedback-voltage input
16
BIAS
BIAS
Internal bias, current set
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005519A-page 9
HV9120/HV9123
4.0
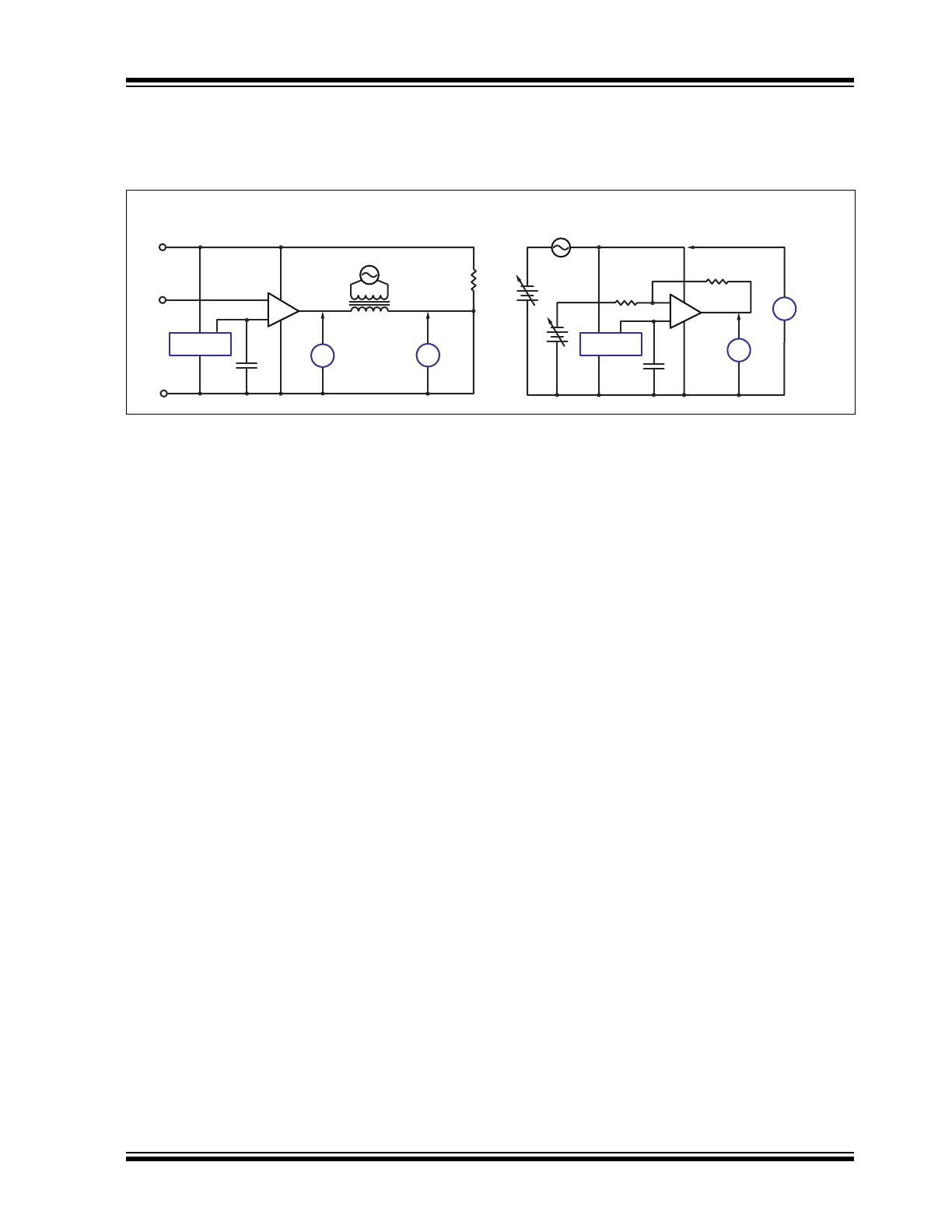
TEST CIRCUITS
The test circuits for characterizing error-amplifier output impedance, Z
OUT
, and error-amplifier, power-supply rejection
ration, PSRR, are shown in
Figure 4-1
.
FIGURE 4-1:
Test Circuits
+
–
60.4k
40.2k
1.0V swept 100Hz - 2.2MHz
Tektronix
P6021
(1 turn
secondary)
0.1μF
+10V
(V
DD
)
GND
(-V
IN
)
(FB)
Error Amp Z
OUT
+
–
Reference
V
2
10.0V
4.0V
100k 1%
100k 1%
PSRR
0.1μF
0.1V swept 10Hz - 1.0MHz
V
1
V
2
V
1
Reference

HV9120/HV9123
DS20005519A-page 10
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
5.0
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
5.1
High-Voltage Regulator
The high-voltage regulator included in HV9120 and
HV9123 consists of a high-voltage, n-channel, deple-
tion-mode DMOS transistor, driven by an error ampli-
fier, providing a current path between the V
IN
terminal
and the V
DD
terminal. The maximum current, about 20
mA, occurs when V
DD
= 0, with current reducing as V
DD
rises. This path shuts off when V
DD
rises to somewhere
between 7.8 and 9.4V. So, if V
DD
is held at 10 or 12V
by an external source, no current other than leakage is
drawn through the high voltage transistor. This mini-
mizes dissipation.
Use an external capacitor between V
DD
and GND to
store energy used by the chip in the time between shut-
off of the high voltage path and the V
DD
supply’s output
rising enough to take over powering the chip. This
capacitor should have a value of 100X or more the
effective gate capacitance of the MOSFET being
driven, as well as very good high-frequency character-
istics. See the equation below. Ceramic caps work well.
Electrolytic capacitors are generally not suitable.
The device uses a resistor divider string to monitor V
DD
for both the under voltage lockout circuit and the shutoff
circuit of the high voltage FET. Setting the under volt-
age sense point about 0.6V lower on the string than the
FET shutoff point guarantees that the under voltage
lockout releases before the FET shuts off.
5.2
Bias Circuit
HV9120 and HV9123 require an external bias resistor,
connected between the BIAS pin and GND
,
to set cur-
rents in a series of current mirrors used by the analog
sections of the chip. The nominal external bias current
requirement is 15 to 20 µA, which can be set by a 390
kΩ to 510 kΩ resistor if V
DD
= 10V, or a 510 kΩ to 680
kΩ resistor if V
DD
= 12V. A precision resistor is not
required, ±5% meets the device requirements.
5.3
Clock Oscillator
The clock oscillator of the HV9120 and HV9123 con-
sists of a ring of CMOS inverters, timing capacitors, and
a capacitor-discharge FET. A single external resistor
between the OSCI and OSCO sets the oscillator fre-
quency (see
Figure 2-1
, Output Switching Frequency
vs Oscillator Resistance).
HV9120 includes a frequency-dividing flip-flop that
allows the part to operate with a 50% duty limit. Accord-
ingly, the effective switching frequency of the power
converter is half the oscillator frequency (see
Figure 2-
1
, Output Switching Frequency vs Oscillator Resis-
tance).
An internal, discharge FET resets the oscillator ramp at
the end of the oscillator cycle. The FET is internally
connected to GND in HV9120 (50% max duty version).
Whereas, the FET is externally connected to GND, by
way of a resistor, in the HV9123 (100% duty version).
The resistor programs the oscillator dead time at the
end of the oscillator period in HV9123 applications.
The oscillator turns off during shutdown to reduce sup-
ply current by about 150 μA.
5.4
Reference
The reference of the HV9120 and HV9123 consists of
a band-gap reference, followed by a buffer amplifier,
which scales the voltage up to 4.0V. The scaling resis-
tors of the buffer amplifier are trimmed during manufac-
ture so that the output of the error amplifier, when
connected in a gain of -1 configuration, is as close to
4.0V as possible. This nulls out the input offset of the
error amplifier. As a consequence, even though the
observed reference voltage of a specific part may not
be exactly 4.0V, the feedback voltage required for
proper regulation will be 4.0V.
An approximately 50 kΩ resistor is located internally
between the output of the reference buffer amplifier
and the circuitry it feeds–reference output pin and non-
inverting input to the error amplifier. This allows overrid-
ing the internal reference with a low impedance voltage
source ≤6.0V. Using an external reference reinstates
the input offset voltage of the error amplifier. Overriding
the reference should seldom be necessary.
The reference of the HV9120 and HV9123 is a high
impedance node, and usually there will be significant
electrical noise nearby. Therefore, a bypass capacitor
between the reference pin and GND is strongly recom-
mended. The reference buffer amplifier is compen-
sated to be stable with a capacitive load of 0.01 to
0.1 µF.
5.5
Error Amplifier
The error amplifier in HV9120 and HV9123 is a low-
power, differential-input, operational amplifier. A PMOS
input stage is used, so the common mode range
includes ground and the input impedance is high.
5.6
Current Sense Comparators
HV9120 and HV9123 use a dual-comparator system
with independent comparators for modulation and cur-
rent limiting. This allows the designer greater latitude in
compensation design, as there are no clamps, except
ESD protection, on the compensation pin.
C
VDD
100
gate charge of FET at 10V
