2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005659A-page 1
MIC24052
Features
• HyperLight Load
®
Efficiency: up to 80% at 10 mA
• Hyper Speed Control
®
Architecture Enables:
- High Delta V Operation (V
IN
= 19V and V
OUT
= 0.8V)
- Small Output Capacitance
• 4.5V to 19V Input Voltage Range
• 6A Output Current Capability
• Up to 95% Efficiency
• Adjustable Output from 0.8V to 5.5V
• ±1% Feedback Accuracy
• Any Capacitor Stable - Zero-to-High ESR
• 600 kHz Switching Frequency
• Power Good (PG) Output
• Foldback Current-Limit and “Hiccup Mode”
Short-Circuit Protection
• Supports Safe Start-Up into a Pre-Biased Load
• –40°C to +125°C Junction Temperature Range
• Available in a 28-pin 5 mm x 6 mm QFN Package
Applications
• Servers and Workstations
• Routers, Switches, and Telecom Equipment
• Base Stations
General Description
The MIC24052 is a constant-frequency, synchronous
DC/DC buck regulator featuring a unique adaptive
on-time control architecture. The MIC24052 operates
over an input supply range of 4.5V to 19V. It has an
internal linear regulator which provides a regulated 5V
to power the internal control circuitry. The MIC24052
operates at a constant 600 kHz switching frequency in
continuous-conduction mode and can be used to
provide up to 6A of output current. The output voltage
is adjustable down to 0.8V.
Microchip’s HyperLight Load
®
architecture provides
the same high-efficiency and ultra-fast transient
response as the Hyper Speed Control
®
architecture
under medium to heavy loads, but also maintains high
efficiency under light load conditions by transitioning to
variable-frequency, discontinuous-mode operation.
The MIC24052 offers a full suite of protection features
to ensure protection of the IC during fault conditions.
These include undervoltage lockout to ensure proper
operation under power-sag conditions, thermal
shutdown, internal soft-start to reduce the inrush
current, foldback current limit and “hiccup mode”
short-circuit protection. The MIC24052 includes a
power good (PG) output to allow simple sequencing.
The 6A Hyper Speed Control part, MIC24051, is also
available on Microchip’s web site.
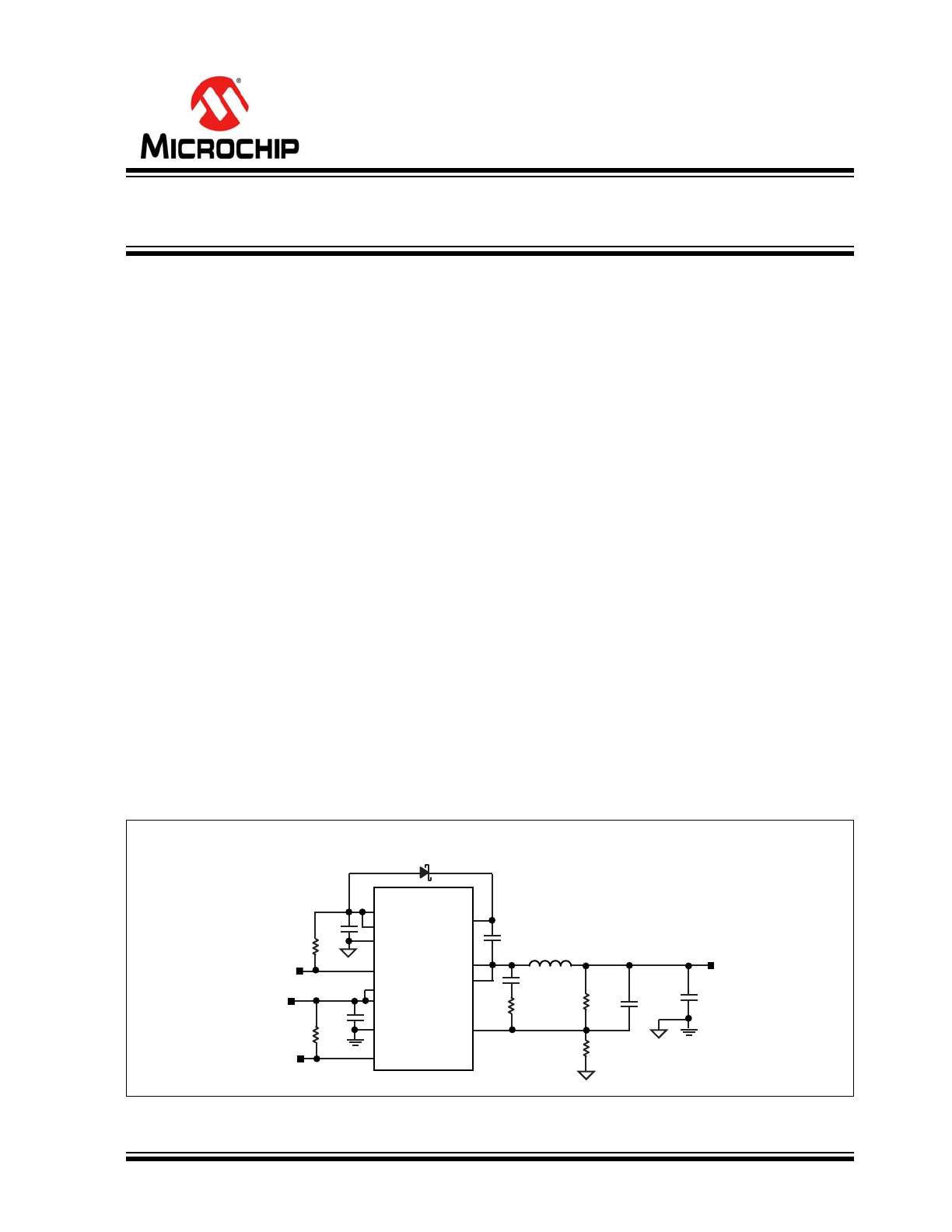
Typical Application Schematic
MIC24052
28-P
IN
QFN
10k
2.2μF
PG
V
IN
4.5V TO 19V
4.7μF
x2
EN
0.1μF
2.2μH
0.1μF
19.6k
2.49k
4.7nF
2.00k
V
OUT
1.8V/6A
100μF
MIC24052
VDD
SGND
PG
VIN
PVIN
PGND
EN
BST
SW
CS
FB
10k
PVDD
12V, 6A High-Efficiency Buck Regulator
with HyperLight Load
®
MIC24052
DS20005659A-page 2
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
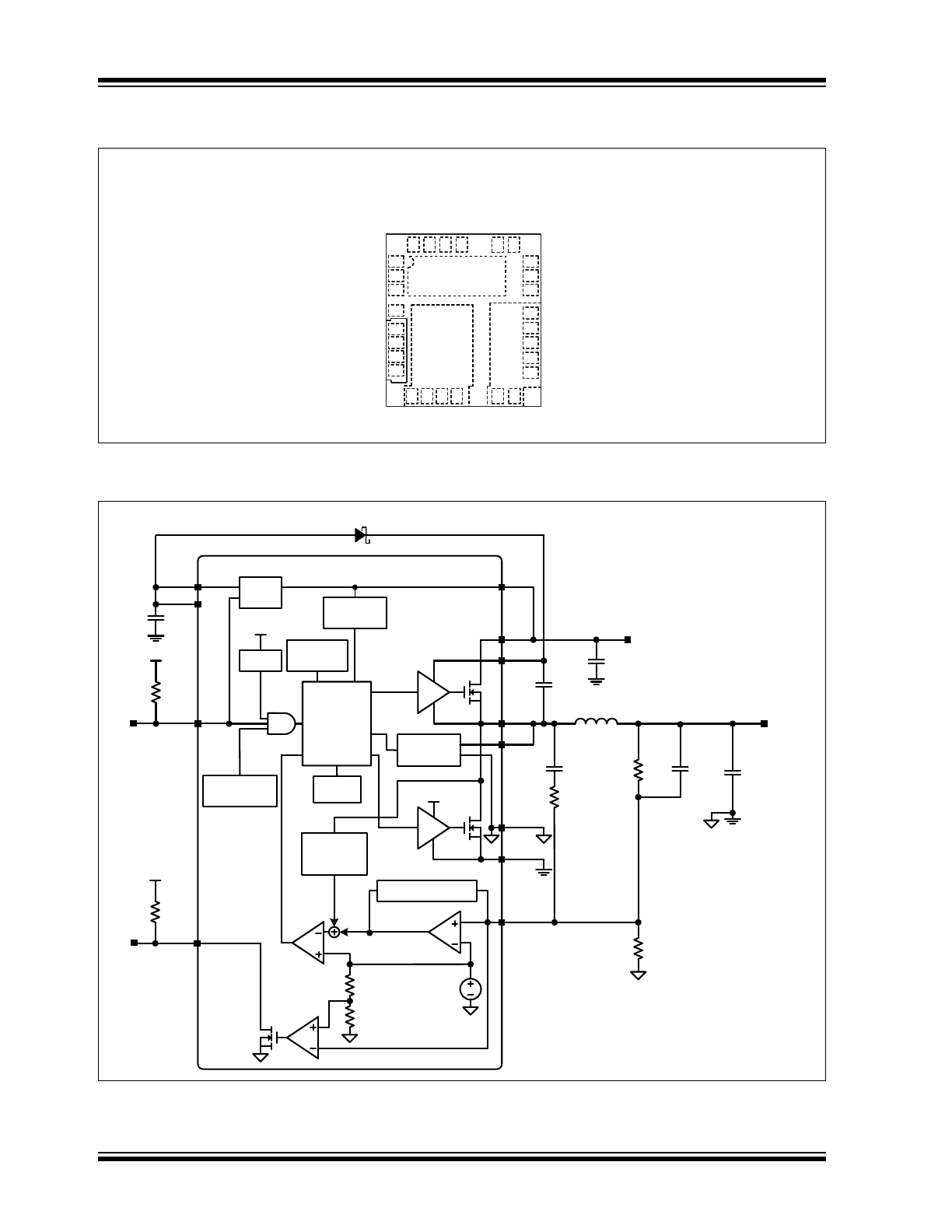
Package Type
Block Diagram
PVIN
SW
SW
SW
SW
PVIN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 10 11 12
13 14
15
16
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
28 27 26 25
CS
PGND
BST
PVIN
PVIN
PVIN
PVIN
PVIN
PVDD
PGND
NC
SW
PGND
PGND
PGND
PGND
FB
PG
EN
VIN
VDD
SGND
PGND
SW
PVIN
MIC24052
28-P
IN
QFN (JL)
(T
OP
V
IEW
)
R1
2.49k
R2
2.00k
0.1μF
19.6k
2.2μF
V
OUT
1.8V/6A
2.2μH
100μF
MIC24052
4.7nF
0.1μF
C
BST
BST
SW
FB
VDD
EN
PGND
VIN
PVIN
V
IN
4.5V to 19V
4.7μF
x2
g
m
EA
COMP
CS
CL and ZC
DETECTION
CONTROL
LOGIC
TIMER
SOFT-START
FIXED T
ON
ESTIMATE
UVLO
LDO
THERMAL
SHUTDOWN
SOFT
START
PVDD
V
REF
0.8V
COMPENSATION
SGND
D1
MODIFIED
T
OFF
PG
10k
VDD
VDD
8%
92%
10k
V
IN
HSD
LSD
INTERNAL
RIPPLE
INJECTION
PVDD

2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005659A-page 3
MIC24052
1.0
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings †
PV
IN
to PGND ............................................................................................................................................ –0.3V to +29V
V
IN
to PGND ............................................................................................................................................... –0.3V to PV
IN
PV
DD
, V
DD
to PGND .................................................................................................................................... –0.3V to +6V
V
SW
, V
CS
to PGND ....................................................................................................................... –0.3V to (PV
IN
+ 0.3V)
V
BST
to V
SW
................................................................................................................................................. –0.3V to +6V
V
BST
to PGND............................................................................................................................................ –0.3V to +35V
V
FB
, V
PG
to PGND ......................................................................................................................... –0.3V to (V
DD
+ 0.3V)
V
EN
to PGND ...................................................................................................................................–0.3V to (V
IN
+ 0.3V)
PGND to SGND ........................................................................................................................................ –0.3V to +0.3V
ESD Rating (
Note 1
) .................................................................................................................................. ESD Sensitive
Operating Ratings ‡
Supply Voltage (PV
IN
, V
IN
)......................................................................................................................... +4.5V to +19V
PV
DD
, V
DD
Supply Voltage (PV
DD
, V
DD
)................................................................................................... +4.5V to +5.5V
Enable Input (V
EN
) ..............................................................................................................................................0V to V
IN
†
Notice: Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device.
This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at those or any other conditions above those indicated
in the operational sections of this specification is not intended. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended
periods may affect device reliability.
‡ Notice:
The device is not guaranteed to function outside its operating ratings.
Note 1:
Devices are ESD sensitive. Handling precautions recommended. Human body model, 1.5 kΩ in series with
100 pF.
MIC24052
DS20005659A-page 4
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
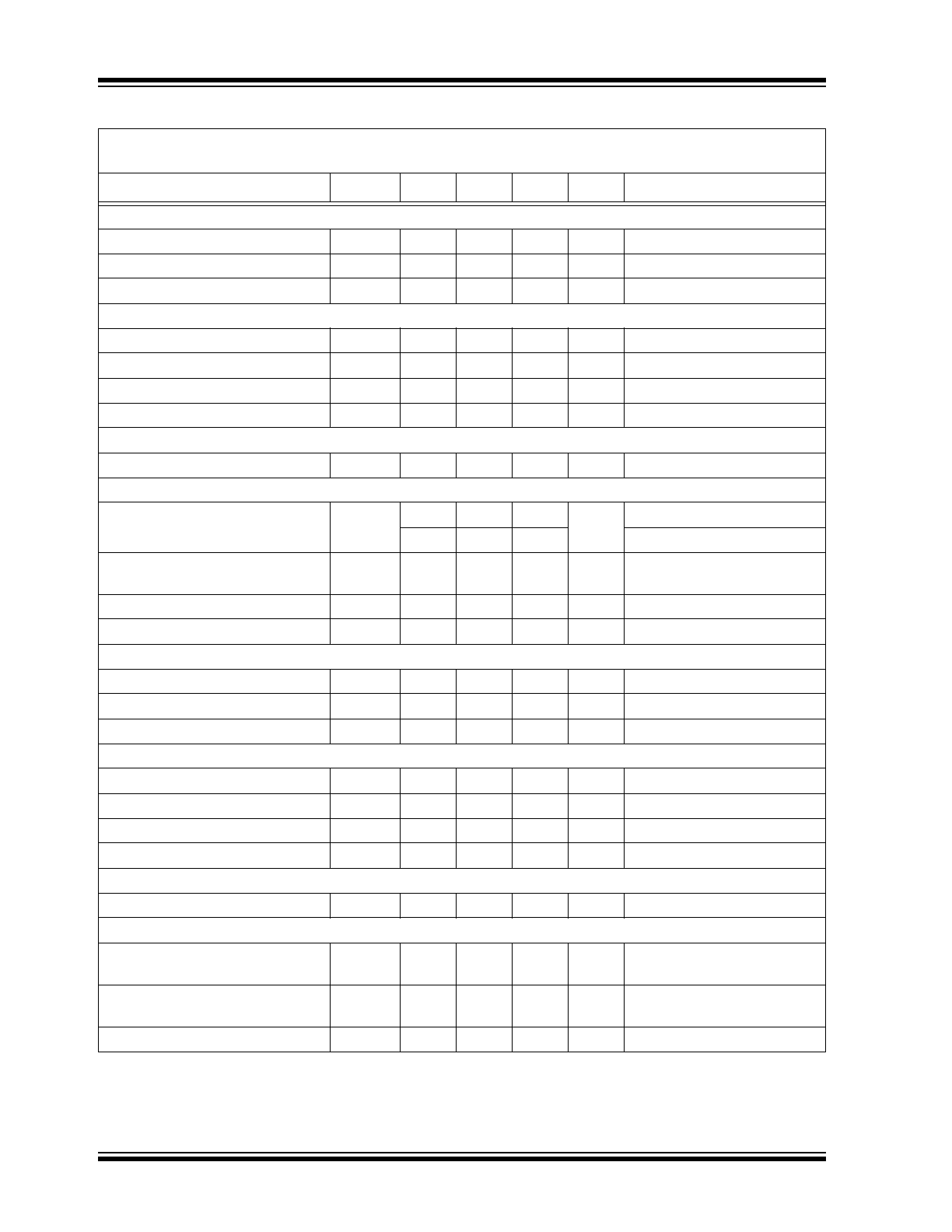
TABLE 1-1:
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Characteristics:
PV
IN
= V
IN
= V
EN
= 12V, V
BST
– V
SW
= 5V; T
A
= 25°C, unless noted. Bold values
indicate –40°C ≤ T
J
≤ +125°C. (
Note 1
)
.
Parameters
Sym.
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Conditions
Power Supply Input
Input Voltage Range
V
IN
, PV
IN
4.5
—
19
V
—
Quiescent Supply Current
—
—
450
750
µA
V
FB
= 1.5V (non-switching)
Shutdown Supply Current
—
—
5
10
µA
V
EN
= 0V
V
DD
Supply Voltage
V
DD
Output Voltage
—
4.8
5
5.4
V
V
IN
= 7V to 19V, I
DD
= 40 mA
V
DD
UVLO Threshold
—
3.7
4.2
4.5
V
V
DD
Rising
V
DD
UVLO Hysteresis
—
—
400
—
mV
—
Dropout Voltage (V
IN
– V
DD
)
—
—
380
600
mV
I
DD
= 25 mA
DC/DC Controller
Output Voltage Adjust Range
V
OUT
0.8
—
5.5
V
—
Reference
Feedback Reference Voltage
—
0.792
0.8
0.808
V
0°C ≤ T
J
≤ 85°C (±1.0%)
0.788
0.8
0.812
–40°C ≤ T
J
≤ 125°C (±1.5%)
Load Regulation
—
—
0.25
—
%
I
OUT
= 1A to 6A (Continuous
Mode)
Line Regulation
—
—
0.25
—
%
V
IN
= 4.5V to 19V
FB Bias Current
—
—
50
500
nA
V
FB
= 0.8V
Enable Control
EN Logic Level High
—
1.8
—
—
V
—
EN Logic Level Low
—
—
—
0.6
V
—
EN Bias Current
—
—
6
30
µA
V
EN
= 12V
Oscillator
Switching Frequency (
Note 2
)
—
450
600
750
kHz
V
OUT
= 2.5V
Maximum Duty Cycle (
Note 3
)
—
—
82
—
%
V
FB
= 0V
Minimum Duty Cycle
—
—
0
—
%
V
FB
= 1.0V
Minimum Off-Time
—
—
300
—
ns
—
Soft-Start
Soft-Start Time
—
—
3
—
ms
—
Short-Circuit Protection
Peak Inductor Current-Limit
Threshold
—
7.5
11
17
A
V
FB
= 0.8V, T
J
= 25°C
Peak Inductor Current-Limit
Threshold
—
6.6
11
17
A
V
FB
= 0.8V, T
J
= 125°C
Short-Circuit Current
—
—
8
—
A
V
FB
= 0V
Note 1:
Specification for packaged product only.
2:
Measured in test mode.
3:
The maximum duty-cycle is limited by the fixed mandatory off-time (t
OFF
) of typically 300 ns.
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005659A-page 5
MIC24052
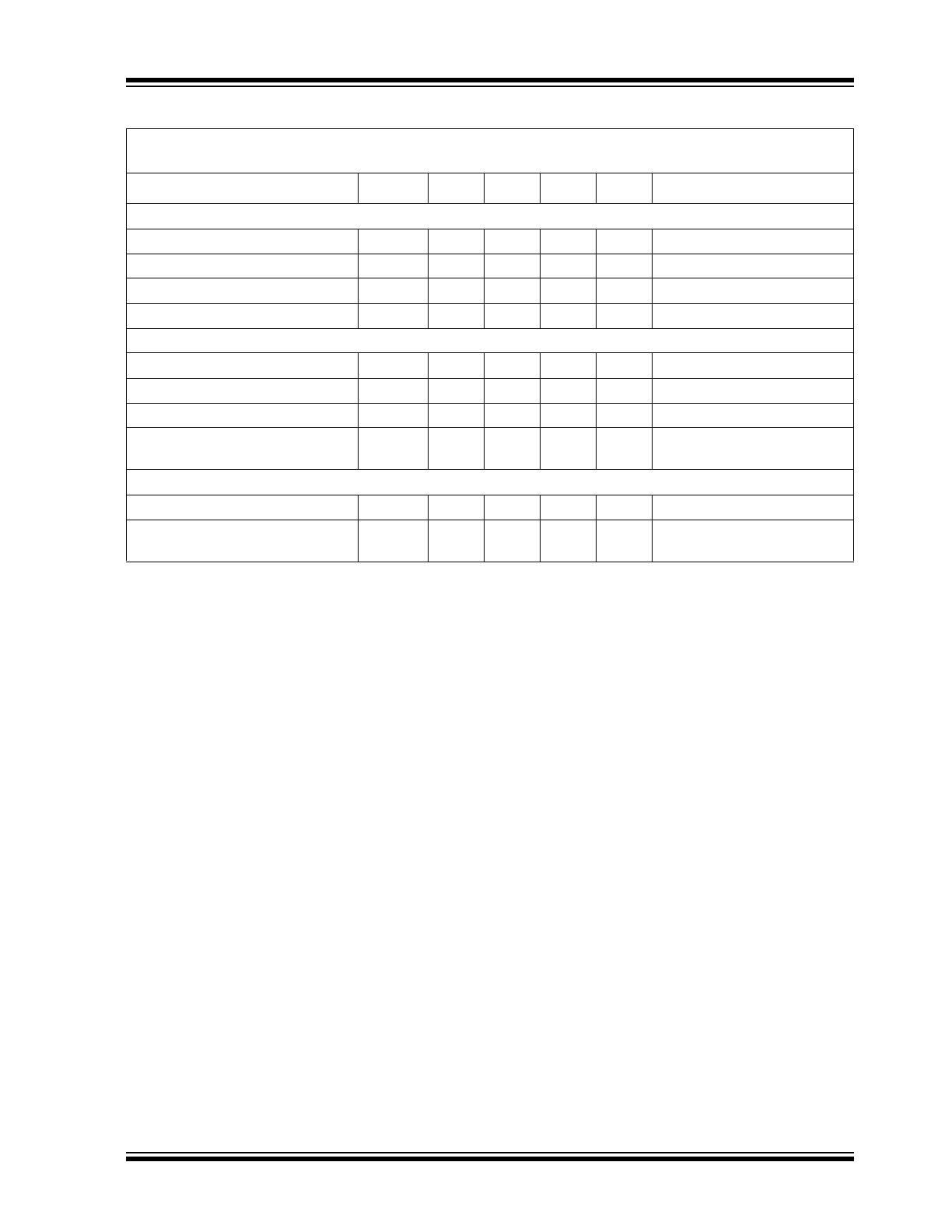
Internal FETs
Top-MOSFET R
DS(ON)
—
—
42
—
mΩ
I
SW
= 3A
Bottom-MOSFET R
DS(ON)
—
—
12.5
—
mΩ
I
SW
= 3A
SW Leakage Current
—
—
—
60
µA
V
EN
= 0V
V
IN
Leakage Current
—
—
—
25
µA
V
EN
= 0V
Power Good (PG)
Power Good Threshold Voltage
—
85
92
95
%V
OUT
Sweep V
FB
from Low to High
Power Good Hysteresis
—
—
5.5
—
%V
OUT
Sweep V
FB
from High to Low
Power Good Delay Time
—
—
100
—
µs
Sweep V
FB
from Low to High
Power Good Low Voltage
—
—
70
200
mV
Sweep V
FB
< 0.9 x V
NOM
,
I
PG
= 1 mA
Thermal Protection
Overtemperature Shutdown
—
—
160
—
°C
T
J
Rising
Overtemperature Shutdown
Hysteresis
—
—
15
—
°C
—
TABLE 1-1:
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED)
Electrical Characteristics:
PV
IN
= V
IN
= V
EN
= 12V, V
BST
– V
SW
= 5V; T
A
= 25°C, unless noted. Bold values
indicate –40°C ≤ T
J
≤ +125°C. (
Note 1
)
.
Parameters
Sym.
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Conditions
Note 1:
Specification for packaged product only.
2:
Measured in test mode.
3:
The maximum duty-cycle is limited by the fixed mandatory off-time (t
OFF
) of typically 300 ns.
MIC24052
DS20005659A-page 6
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
TEMPERATURE SPECIFICATIONS
Parameters
Sym.
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Conditions
Temperature Ranges
Junction Operating Temperature
Range
T
J
–40
—
+125
°C
Note 1
Maximum Junction Temperature
—
—
—
+150
°C
—
Storage Temperature
T
S
–65
—
+150
°C
—
Lead Temperature
—
—
—
+260
°C
Soldering, 10s
Package Thermal Resistances
Thermal Resistance, 5x6 QFN-28
JA
—
28
—
°C/W
Note 2
Thermal Resistance, 5x6 QFN-28
JC
—
2.5
—
°C/W
—
Note 1:
The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of ambient temperature, the maximum allowable
junction temperature and the thermal resistance from junction to air (i.e., T
A
, T
J
,
JA
). Exceeding the
maximum allowable power dissipation will cause the device operating junction temperature to exceed the
maximum +125°C rating. Sustained junction temperatures above +125°C can impact the device reliability.
2:
P
D(MAX)
= (T
J(MAX)
– T
A
)/
JA
, where
JA
depends upon the printed circuit layout. A 5 square inch 4 layer,
0.62”, FR-4 PCB with 2 oz. finish copper weight per layer is used for the
JA
.
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005659A-page 7
MIC24052
2.0
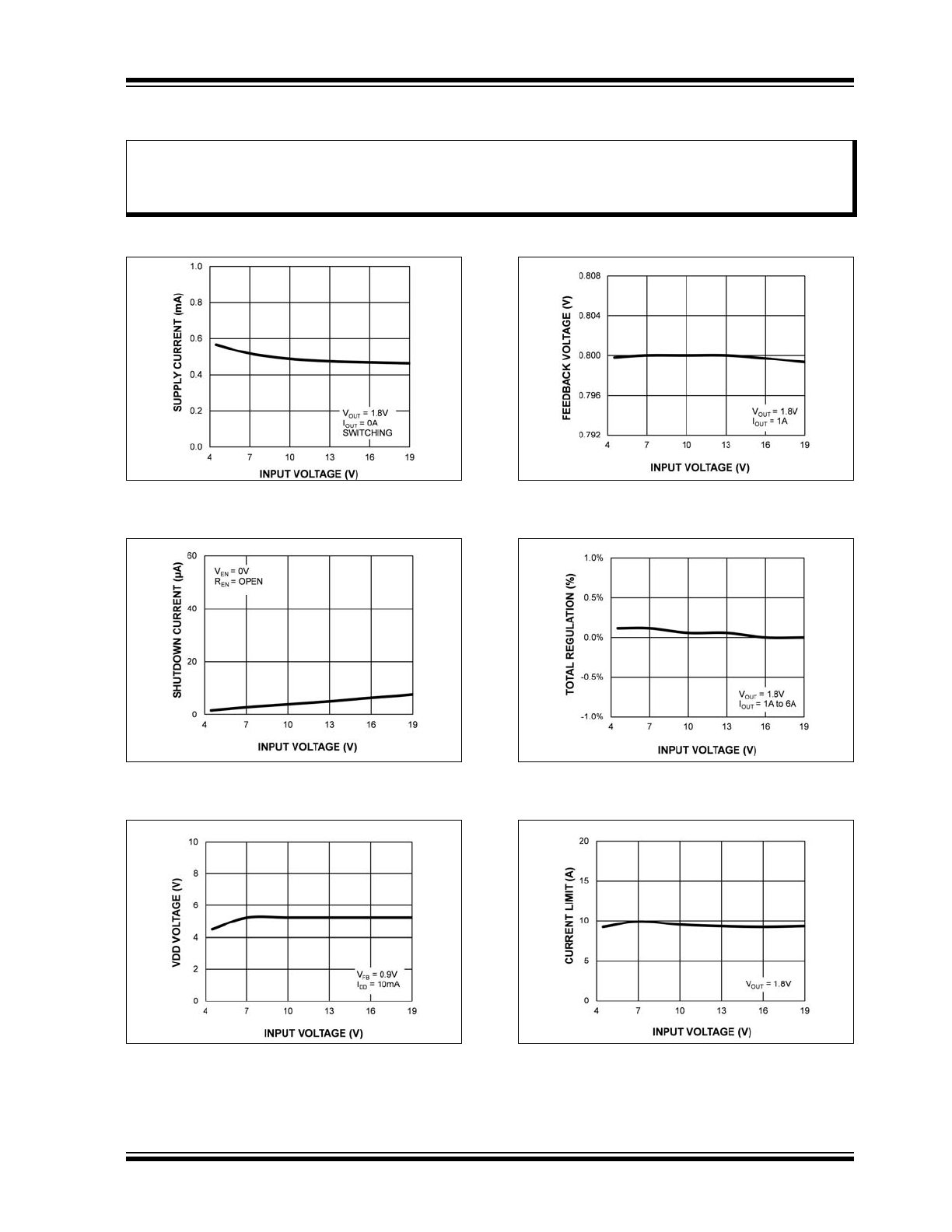
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
FIGURE 2-1:
V
IN
Operating Supply
Current vs. Input Voltage.
FIGURE 2-2:
V
IN
Shutdown Current vs.
Input Voltage.
FIGURE 2-3:
V
DD
Output Voltage vs.
Input Voltage.
FIGURE 2-4:
Feedback Voltage vs. Input
Voltage.
FIGURE 2-5:
Total Regulation vs. Input
Voltage.
FIGURE 2-6:
Output Current Limit vs.
Input Voltage.
Note:
The graphs and tables provided following this note are a statistical summary based on a limited number of
samples and are provided for informational purposes only. The performance characteristics listed herein
are not tested or guaranteed. In some graphs or tables, the data presented may be outside the specified
operating range (e.g., outside specified power supply range) and therefore outside the warranted range.
MIC24052
DS20005659A-page 8
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
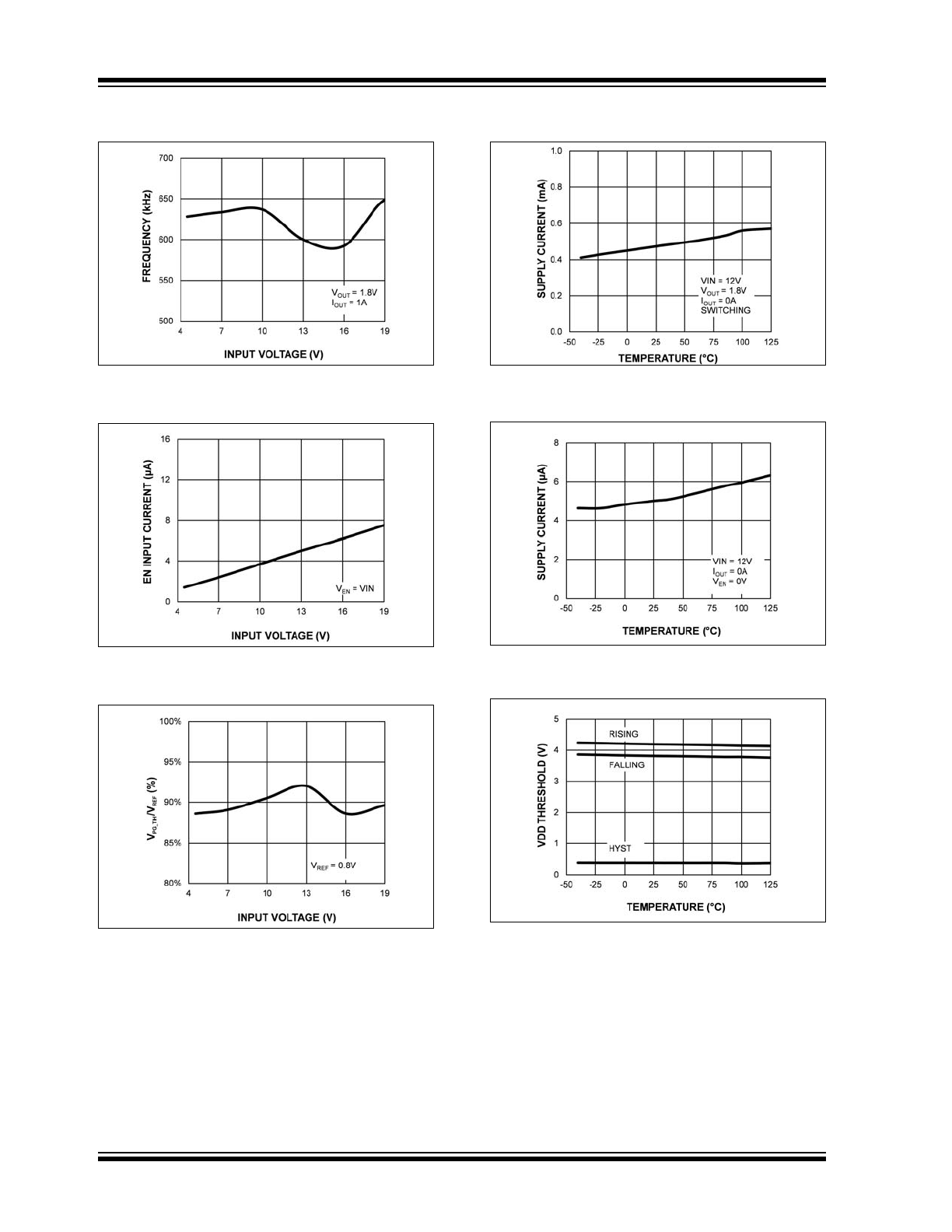
FIGURE 2-7:
Switching Frequency vs.
Input Voltage.
FIGURE 2-8:
Enable Input Current vs.
Input Voltage.
FIGURE 2-9:
PG Threshold/V
REF
Ratio
vs. Input Voltage.
FIGURE 2-10:
V
IN
Operating Supply
Current vs. Temperature.
FIGURE 2-11:
V
IN
Shutdown Current vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-12:
V
DD
UVLO Threshold vs.
Temperature.
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005659A-page 9
MIC24052
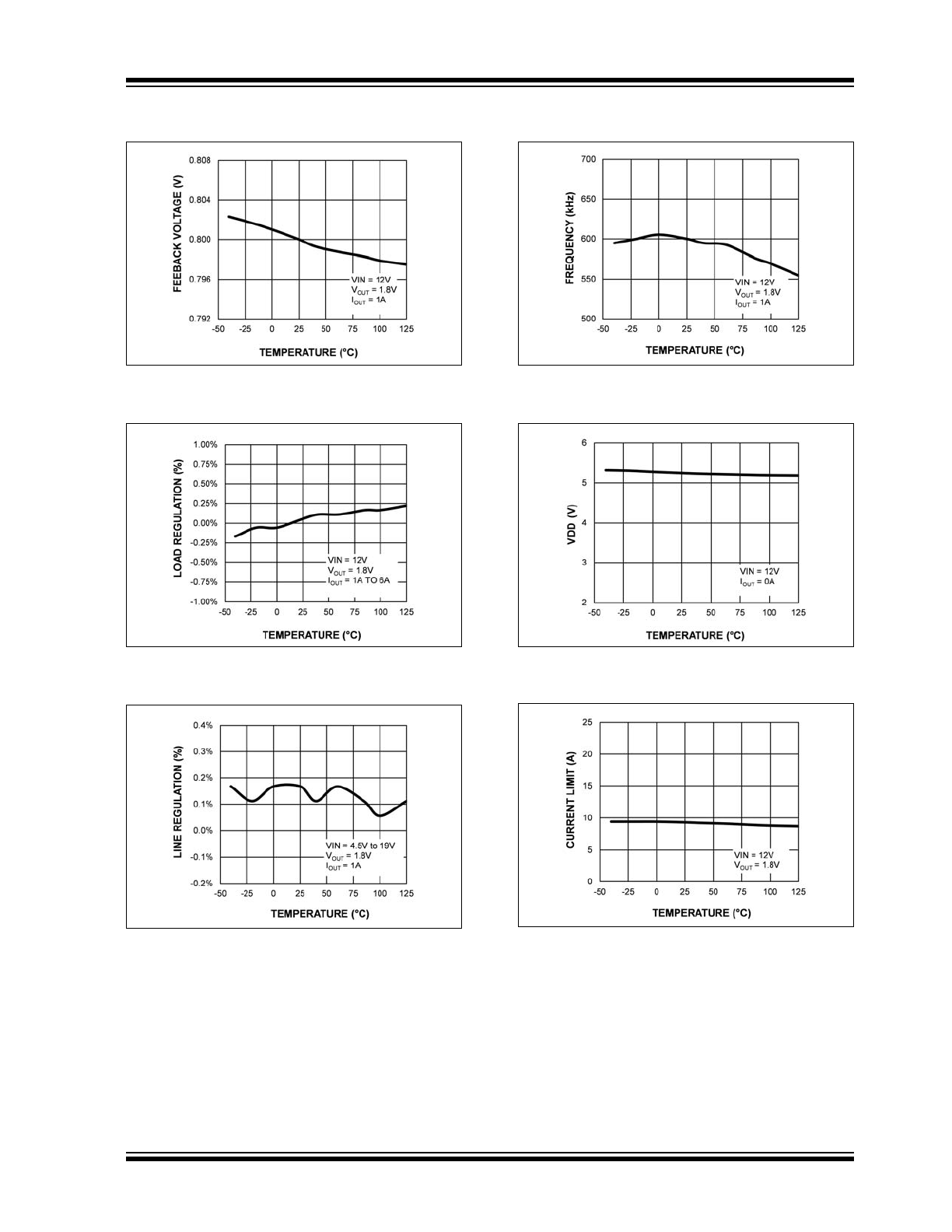
FIGURE 2-13:
Feedback Voltage vs.
Temperature
.
FIGURE 2-14:
Load Regulation vs.
Temperature
.
FIGURE 2-15:
Line Regulation vs.
Temperature.
FIGURE 2-16:
Switching Frequency vs.
Temperature
.
FIGURE 2-17:
V
DD
vs. Temperature
.
FIGURE 2-18:
Output Current Limit vs.
Temperature
.
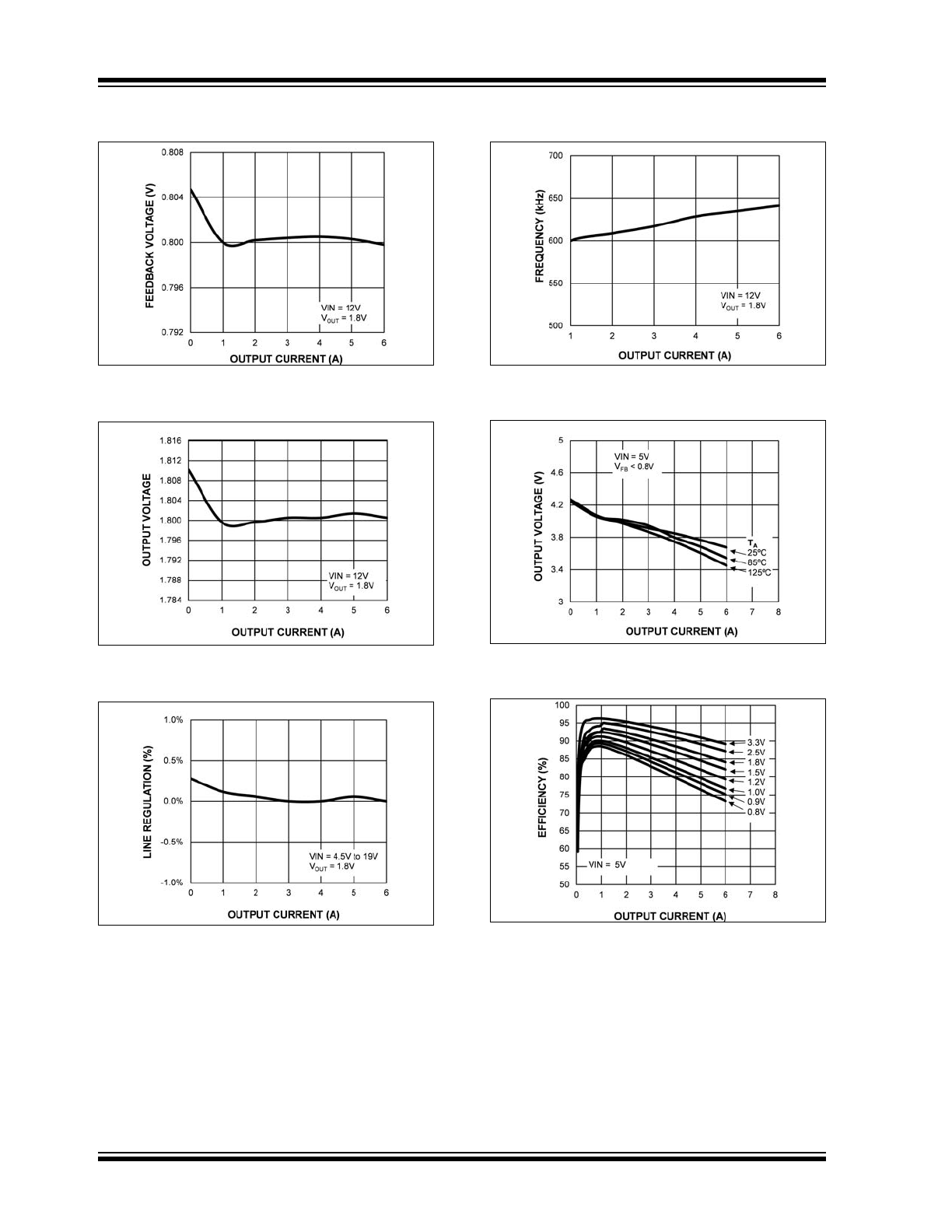
MIC24052
DS20005659A-page 10
2016 Microchip Technology Inc.
FIGURE 2-19:
Feedback Voltage vs.
Output Current.
FIGURE 2-20:
Output Voltage vs. Output
Current.
FIGURE 2-21:
Line Regulation vs. Output
Current.
FIGURE 2-22:
Switching Frequency vs.
Output Current.
FIGURE 2-23:
Output Voltage (V
IN
= 5V)
vs. Output Current.
FIGURE 2-24:
Efficiency (V
IN
= 5V) vs.
Output Current.
