August, 27th 2009
Automotive grade
AUIPS7141R
www.irf.com
Subject to change without notice 1
CURRENT SENSE HIGH SIDE SWITCH
Features
•
Suitable for 24V systems
•
Over current shutdown
Over temperature shutdo
•
•
Current sensing
wn
/Off for EMI
amp
for trucks
is a fully protected four terminal high
•
Active clamp
•
Low current
•
ESD protection
•
Optimized Turn On
Applications
•
21W Filament l
•
Solenoid
•
24V loads
Description
The AUIPS7141R
side switch specifically designed for driving lamp. It
features current sensing, over-current, over-temperature,
ESD protection and drain to source active clamp. When
the input voltage Vcc - Vin is higher than the specified
threshold, the output power Mosfet is turned on. When the
Vcc - Vin is lower than the specified Vil threshold, the
output Mosfet is turned off. The Ifb pin is used for current
sensing. The over-current shutdown is higher than inrush
current of the lamp.
Product Summary
Rds(on) 100m
Ω
max.
Vclamp 65V
Current shutdown 20A min.
Packages
DPak
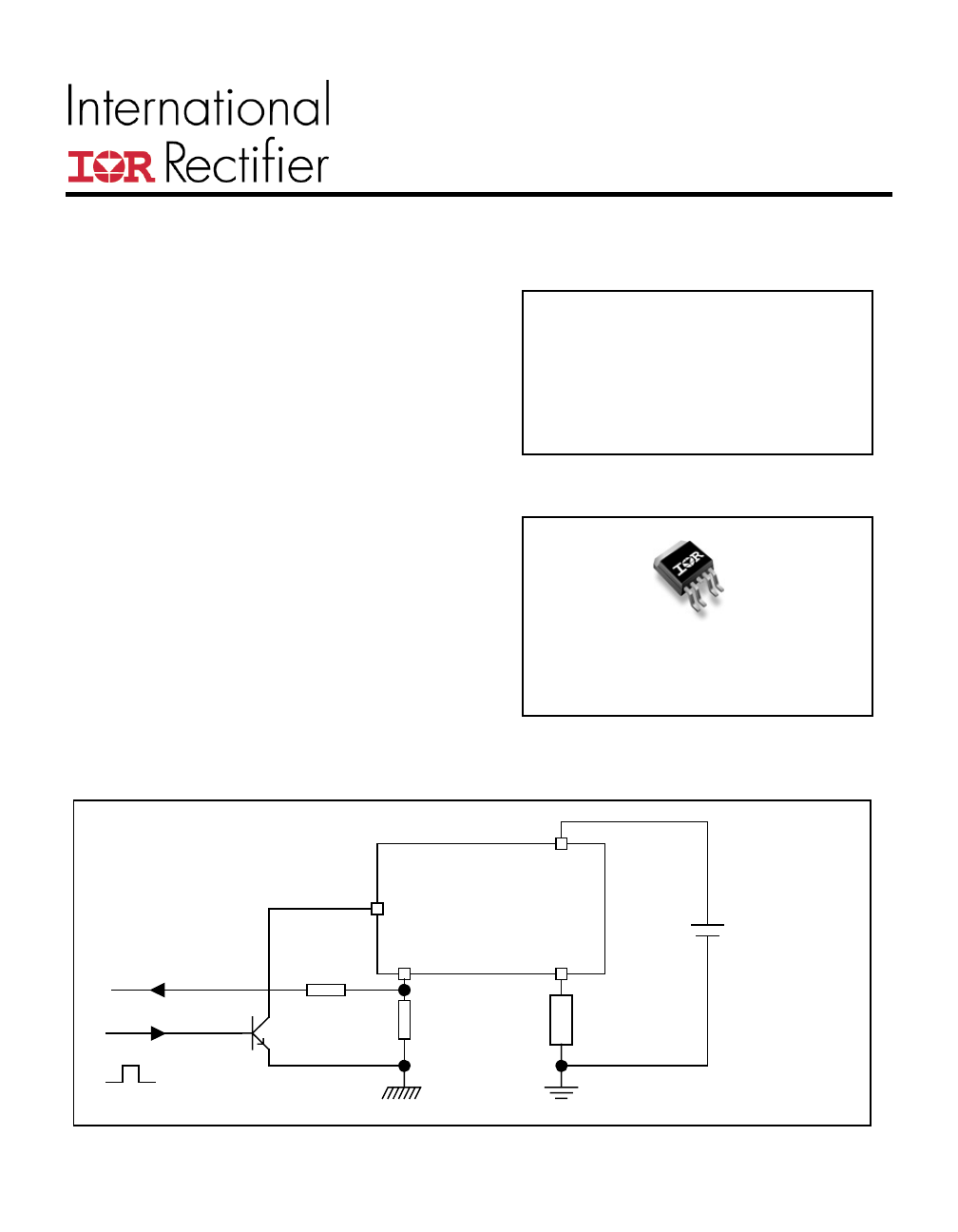
Typical Connection
Out
IPS
IN
2.5k
Vcc
Load
Battery
Input
Power
Ground
Ifb
Logic
Ground
Current feeback
10k
On
Off
AUIPS7141R
Qualification Information
†
Automotive
(per AEC-Q100
††
)
Qualification Level
Comments: This family of ICs has passed an Automotive qualification. IR’s
Industrial and Consumer qualification level is granted by extension of the
higher Automotive level.
Moisture Sensitivity Level
DPAK-5L
MSL1,
260°C
(per IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020)
Machine Model
Class M2 (200 V)
(per AEC-Q100-003)
Human Body Model
Class H1C (1500 V)
(per AEC-Q100-002)
ESD
Charged Device Model
Class C5 (1000 V)
(per AEC-Q100-011)
IC Latch-Up Test
Class II, Level A
(per AEC-Q100-004)
RoHS Compliant
Yes
†
Qualification standards can be found at International Rectifier’s web site
http://www.irf.com/
††
Exceptions to AEC-Q100 requirements are noted in the qualification report.
††† Higher MSL ratings may be available for the specific package types listed here. Please contact your International
Rectifier sales representative for further information.
www.irf.com
2
AUIPS7141R
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute maximum ratings indicate sustained limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. (Tambient=25°C unless
otherwise specified).
meter
Symbol Para
Min.
Max.
Units
Vout
Maximum output voltage
Vcc-60 Vcc+0.3
V
Vcc-Vin max. Maximum Vcc voltage
-16
60
V
Iifb, max.
Maximum feedback current
-50
10
mA
Vcc sc.
Maximum Vcc voltage with short circuit protection see page 7
V
⎯
50
Maximum power dissipation (internally lim
rmal protection)
ited by the
Pd
Rth=50°C/W DPack 6cm² footprint
⎯
2.5
W
Tj max.
Max. storage & operating junction temperature
-40
150
°C
Thermal Characteristics
bol
p.
Max.
Units
Sym
Parameter
Ty
Rth1
Thermal resistance junction to ambient DPak Std footpri
70
⎯
nt
Rth2
junction to ambient Dpak 6cm² footp
50
⎯
Thermal resistance
rint
Rth3
Thermal resistance junction to case Dpak
4
⎯
°C/W
Recommended Operating Conditions
These values are given for a quick design.
Sym
in.
Max.
Units
bol Parameter
M
Continuous output current, Tambient=85°C, Tj=125°C
Iout
A
Rth=50°C/W, Dpak 6cm² footprint
⎯
2.1
RIfb Ifb
resistor
1.5
⎯
k
Ω
www.irf.com
3
AUIPS7141R
Static Electrical Characteristics
meter
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Test
Conditions
Tj=25°C, Vcc=28V (unless otherwise specified)
Symbol Para
Vcc op.
Operating voltage
6
⎯
60 V
ON state resistance Tj=25°C
⎯
75 100
Rds(on)
150°C(2)
⎯
135 180
m
Ω
ON state resistance Tj=
Id
A
s=2
Icc off
Supply leakage current
⎯
1 3
Iout off
Output leakage current
⎯
1 3
µA
V
cc /
=Vg
V
Vgn
in=V
Vifb
nd
out=
d
I in on
mA
Vcc-Vin=28V
Input current while on
0.6
1.6
3
V clamp1
cc to Vout clamp voltage 1
Id=10mA
V
60
64
⎯
V clamp2
65
72
Id=6A see fig. 2
Vcc to Vout clamp voltage 2
60
Vih(1)
High level Input threshold voltage
⎯
3 4.5
Id=10mA
Vil(1)
Low level Input threshold voltage
1.5
2.3
⎯
F
iode vol
orward body d
tage Tj=25°C
⎯
0.8 0.9
Vf
F
V
orward body diode voltage Tj=125°C
⎯
0.65 0.75
If=1A
(
t threshold
S
hing E
cc=28V, Resistive load=27 , Tj=25°C
in.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Test
Conditions
1) Inpu
s are measured directly between the input pin and the tab.
witc
lectrical Characteristics
Ω
V
Symbol Parameter
M
tdon
Turn on delay time to 20%
4
10
20
tr
Rise time from 20% to 80% of Vcc
2
5
10
µs
tdoff
T
80
urn off delay time
20
40
tf
F
µs
.
all time from 80% to 20% of Vcc
2.5
5
10
See fig 1
Protection Characteristics
Symbol Parameter
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Test
Conditions
Tsd
Over temperature threshold
150(2)
165
⎯
°C
See fig. 3 and fig.11
Isd
Over-current shutdown
20
25
35
A
See fig. 3 and page 6
I fault
Ifb after an over-current or an over-
temperature (latched)
2.7 3.3 4
mA
See fig. 3
Current Sensing Characteristics
Symbol Parameter
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Test
Conditions
Ratio
I load / Ifb current ratio
2000
2400
2800
Iload=2A
Ratio_TC
I load / Ifb variation over temperature(2)
-5%
0
+5
%
Tj=-40°C to +150°C
I offset
Load current offset
-0.2
0
0.2
A
Iout<2A
Ifb leakage
Ifb leakage current On in open load
0
8
100
µA
Iout=0A
(2) Guaranteed by design
www.irf.com
4
AUIPS7141R
Lead Assignments
1- NC
2- In
3- Vcc
4- Ifb
t
5- Ou
1 2 4 5
ak
cc
DP
3- V
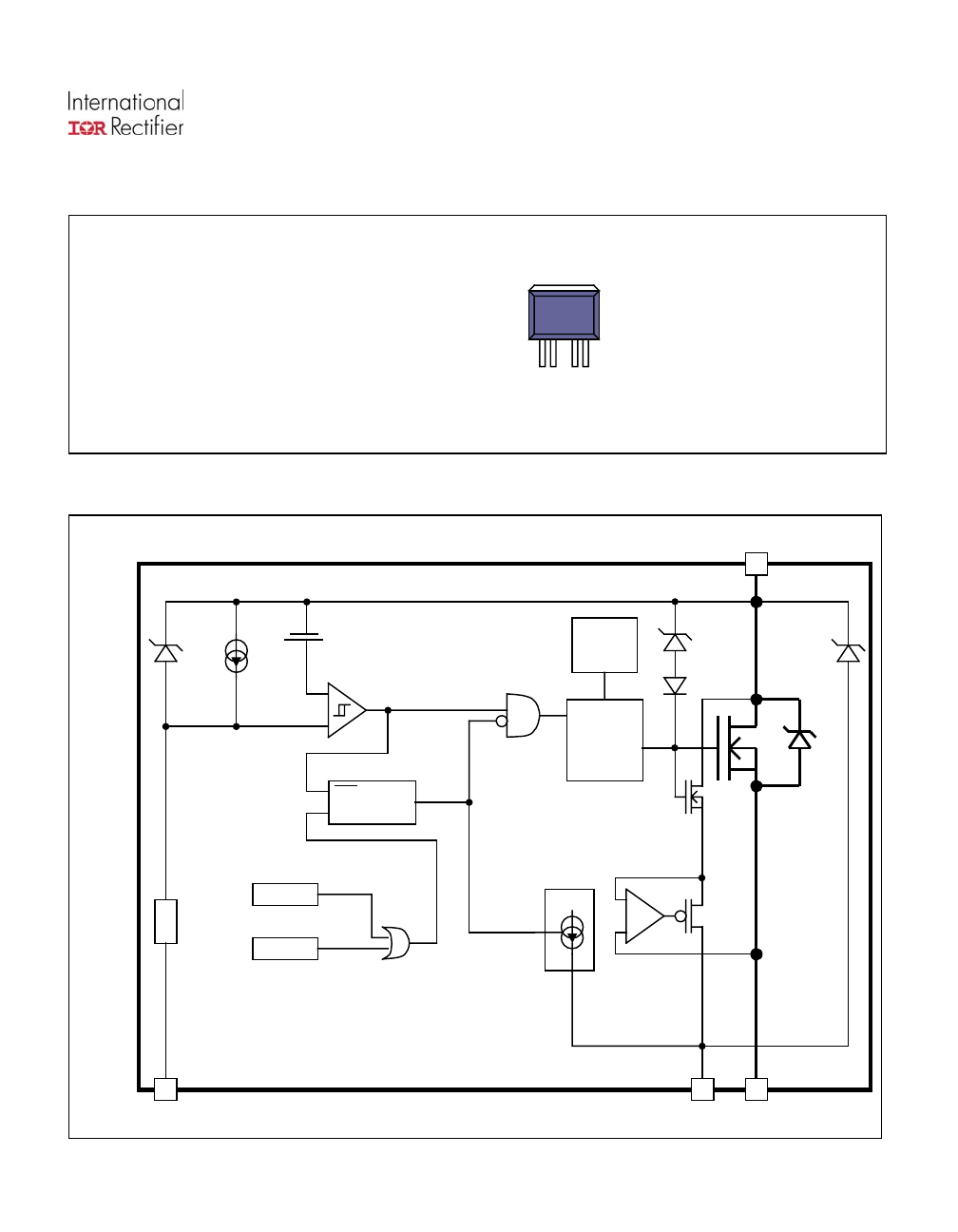
Functional Block Diagram
All values are typical
Diag
Charge
Pump
D
VCC
ri
r
ve
IFB OUT
75V
100
Ω
Tj > 165°C
Iout > 25A
60V
75V
-
+
75V
IN
Set
Reset
Latch
Q
1.5mA
3V
+
-
www.irf.com
5
AUIPS7141R
Truth Table
Op. Conditions
Input
Output
Ifb pin voltage
Normal mode
H
L
0V
Normal mode
L
H
I load x Rfb / Ratio
Open load
H
L
0V
Open load
L
H
0V
Short circuit to GND
H
L
0V
Short circuit to GND
L
L
V fault (latched)
Over temperature
H
L
0V
Over temperature
L
L
V fault (latched)
Operating voltage
Maximum Vcc voltage : this is the maximum voltage before the breakdown of the IC process.
Operating voltage : This is the Vcc range in which the functionality of the part is guaranteed. The AEC-Q100 qualification
is run at the maximum operating voltage spe
cified in the datasheet.
Reverse battery
During the reverse battery the Mosfet is kept off and the load current is flowing into the body diode of the power Mosfet.
Power dissipation in the IPS : P = I load * Vf
If the power dissipation is too high in Rifb, a diode in serial can be added to block the current.
The transistor used to pull-down the input should be a bipolar in order to block the reverse current. The 100ohm input
resistor can not sustain continuously 16V (see Vcc-Vin max. in the Absolute Maximum Ratings section)
Active clamp
The purpose of the active clamp is to limit the voltage across the MOSFET to a value below the body diode break down
voltage to reduce the amount of stress on the device during switching.
The temperature increase during active clamp can be estimated as follows:
)
t
(
Z
P
CLAMP
TH
CL
Tj
⋅
=
∆
Where:
)
t
(
Z
CLAMP
TH
is the thermal impedance at t
CLAMP
and can be read from the thermal impedance curves given in the
data sheets.
CLavg
CL
CL
I
V
P
⋅
=
: Power dissipation during active clamp
65V
V
CL
=
: Typical V
CLAMP
value.
2
I
I
CL
CLavg
=
: Average current during active clamp
dt
di
I
t
CL
CL
=
: Active clamp duration
L
V
V
dt
di
CL
Battery
−
=
: Demagnetization current
Figure 9 gives the maximum inductance versus the load current in the worst case : the part switches off after an over
temperature detection. If the load inductance exceeds the curve, a free wheeling diode is required.
Over-current protection
The threshold of the over-current protection is set in order to guarantee that the device is able to turn on a load with an
inrush current lower than the minimum of Isd. Nevertheless for high current and high temperature the device may switch
off for a lower current due to the over-temperature protection. This behavior is shown in Figure 11.
www.irf.com
6
AUIPS7141R
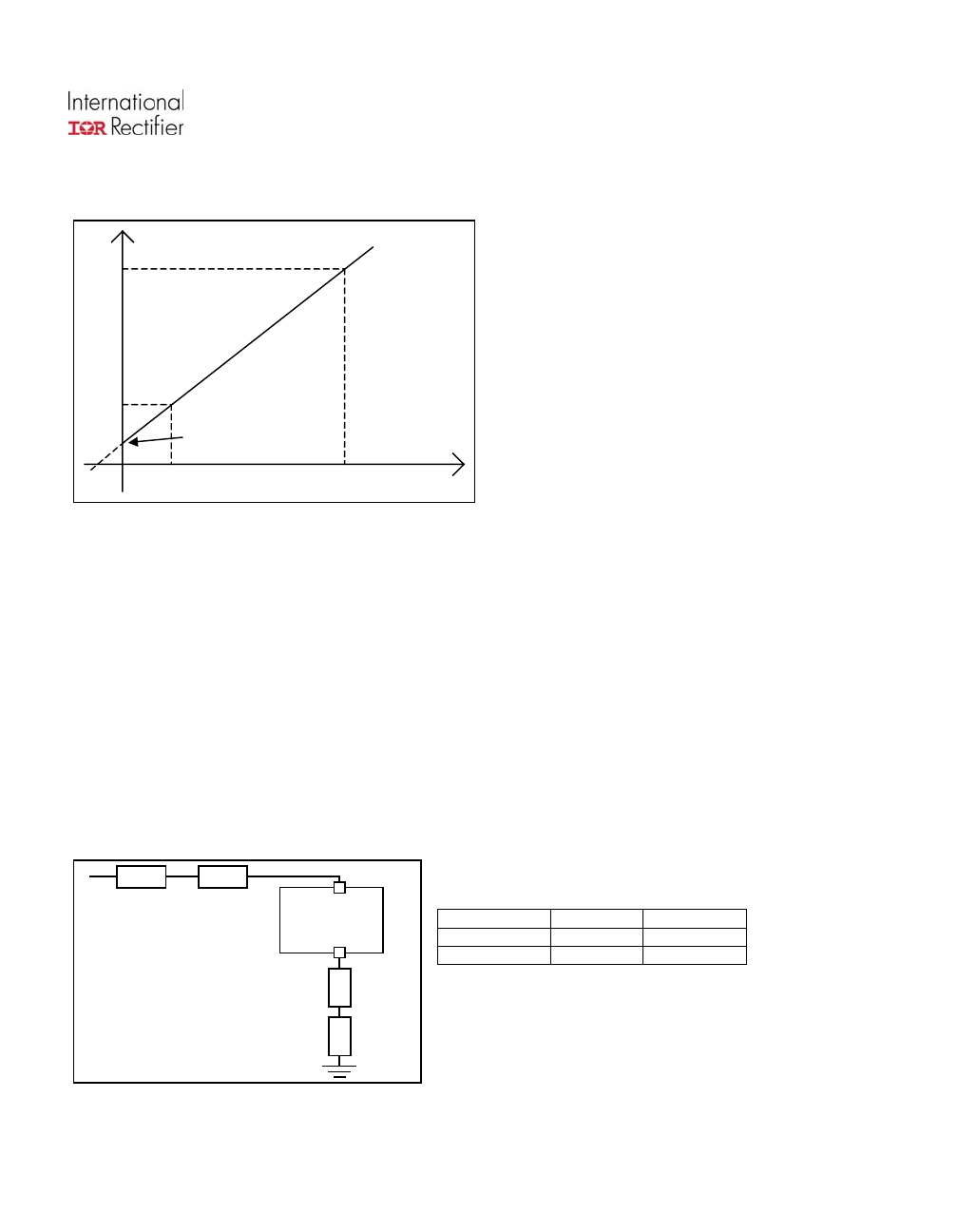
Current sensing accuracy
Ifb
Iout
Ifb leakage
Ifb2
Ifb1
Iout2
Iout1
I offset
)/( Ifb2 – Ifb1)
Iout1
the system will depends on the variation of
the I offset and the ratio over the temperature range. The
Ratio_TC specified in page 4.
on the Rdson :
set@25°C / 1.9
Maximum Vcc voltage with short circuit protection
rt circuit is the maximum voltage for which the part is able to protect itself under test
of short circuits are considered : terminal and load short circuit.
L SC
R SC
The current sensing is specified by measuring 3 points :
- Ifb1 for Iout1
- Ifb2 for Iout2
- Ifb leakage for Iout=0
The parameters in the datasheet are computed with the following formula :
Ratio = ( Iout2 – Iout1
I offset = Ifb1 x Ratio –
This allows the designer to evaluate the Ifb for any Iout value using :
Ifb = ( Iout + I offset ) / Ratio if Ifb > Ifb leakage
For some applications, a calibration is required. In that case, the accuracy of
ratio variation is given by
The Ioffset variation depends directly
I offset@-40°C= I offset@25°C / 0.8
I offset@150°C= I off
The maximum Vcc voltage with sho
conditions representative of the application. 2 kind
Terminal SC
0.1 µH
10 mohm
Load SC
10 µH
100 mohm
Out
IPS
Vcc
L SC
L s
5µ
upply
H
R supply
10mohm
R SC
www.irf.com
7
AUIPS7141R
Tj
Tsd
165°C
Ids
Vin
I shutdown
Tshutdown
Vifb
V fault
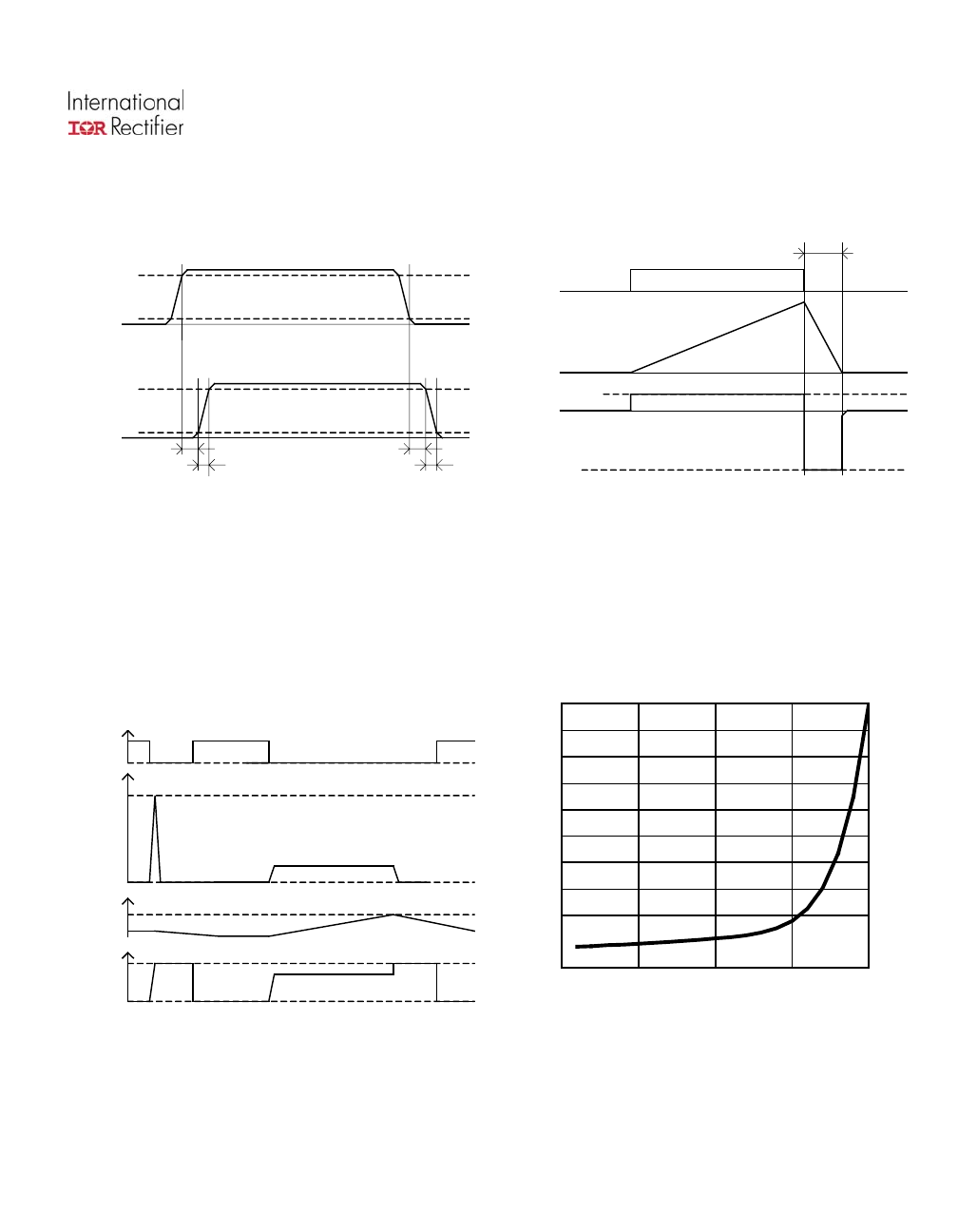
Figure 3 – Protection timing diagram
itching definitions
Vds
Ids
Vcc-Vin
Figure 1 – IN rise time & sw
Vcc
Vds clamp
T clamp
See Application Notes to evaluate power dissipation
Figure 2 – Active clamp waveforms
0
2
4
8
-50
0
50
100
150
Tj, junction temperature (°C)
Figure 4 – Icc off (µA) Vs Tj (°C)
Vout
Vcc-Vin
80%
20%
80%
20%
Td on
Tr
Td off
Tf
10
6
Icc off, supply leakage current (µA)
www.irf.com
8
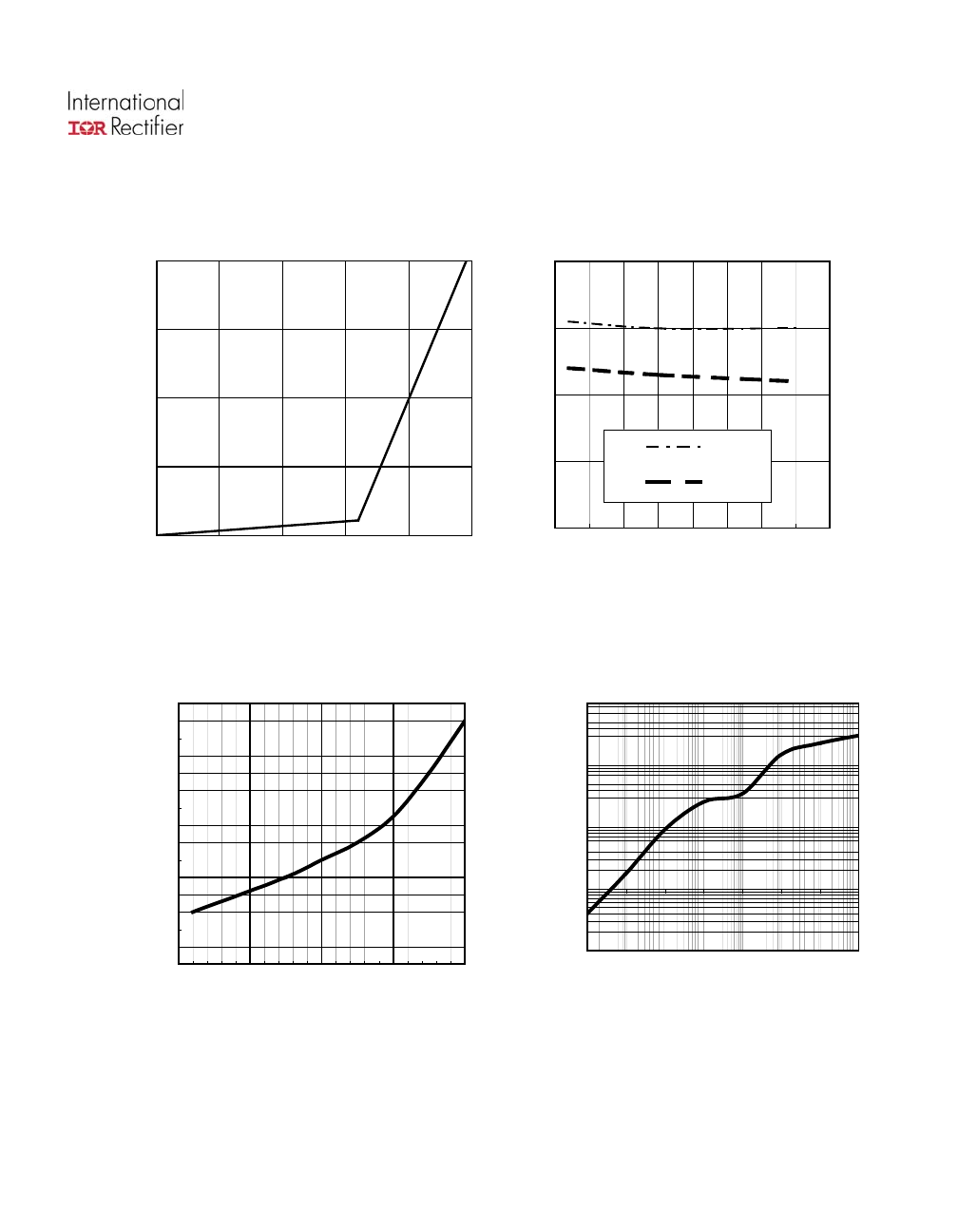
AUIPS7141R
www.irf.com
9
Figure 8 – Transient thermal impedance (°C/W)
Vs time (s)
)
h
,
tr
a
n
s
ie
n
t
th
e
rm
a
l
im
p
e
d
a
n
c
e
(
°C
/W
Z
t
Time (s)
50%
100%
150%
200%
-50
0
50
100
150
Rds(on), Drain-to-Source On Resistance
(Normalized)
Fig
C)
Tj, junction temperature (°C)
ure 7 - Normalized Rds(on) (%) Vs Tj (°
0
-50
-25
0
25
50
75
100 125 150
1
2
3
4
VIH
VIL
Tj, junction temperature (°C)
Vih and Vil (V)
Vcc-Vout, supply voltage (V)
Figure 6 – Vih and Vil (V) Vs Tj (°C)
Figure 5 – Icc off (µA) Vs Vcc-Vout (V)
Icc, supply current (µA)
0.01
0.10
1.00
10.00
100.00
1.E-
05
1.E-
04
1.E-
03
1.E-
02
1.E-
01
1.E+0
0
1.E+0
1
1.E+0
2
20
5
10
15
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
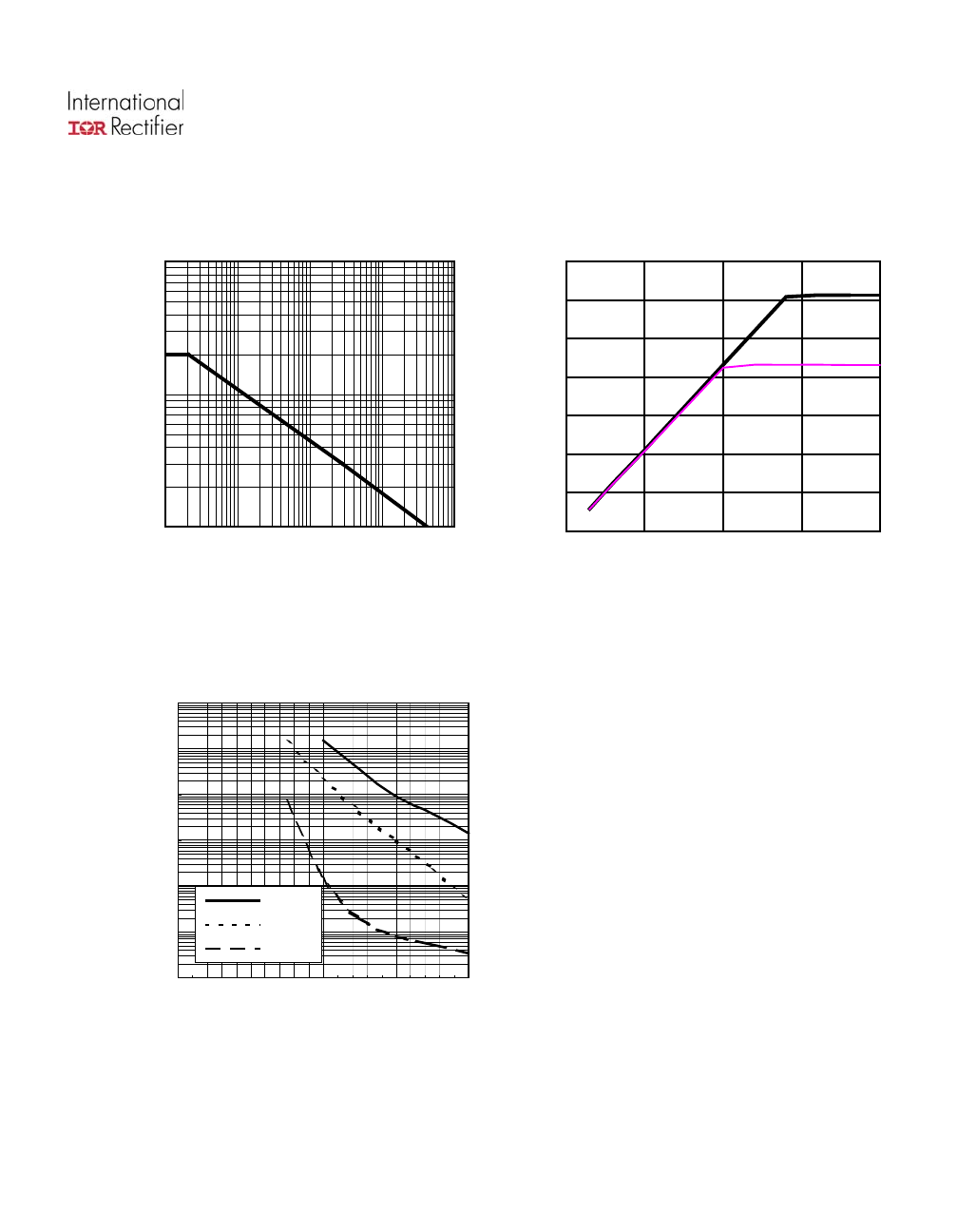
AUIPS7141R
www.irf.com
10
1
10
100
1.E+01
1.E+02
1.E+03
1.E+04
1.E+05
Fi
)
If
b
,
c
u
rr
e
e
n
t
(m
A
)
gure 9 – Max. Iout (A) Vs inductance (µH
Inductance (µH)
Max. output current (A)
Figure 10 – Ifb (mA) Vs Iout (A)
Iout, output current (A)
n
t
fe
e
d
b
a
c
k
c
u
rr
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
0
1
2
3
25°C
150°C
4
SMD with 6cm²
T
s
d
,
ti
m
e
t
o
s
h
u
td
o
w
n
(s
)
0.0001
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
0
5
10
15
20
'-40°C
'+25°C
'+125°C
Iout, output current (A)
Figure 11 – Tsd (s) Vs I out (A)
