2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21350E-page 1
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
Features
• Low Ground Current for Longer Battery Life
• Low Dropout Voltage
• Choice of 50 mA (TC1054), 100 mA (TC1055)
and 150 mA (TC1186) Output
• High Output Voltage Accuracy
• Standard or Custom Output Voltages:
- 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.6V, 2.7V, 2.8V, 2.85V, 3.0V,
3.3V, 3.6V, 4.0V, 5.0V
• Power-Saving Shutdown Mode
• ERROR Output Can Be Used as a Low-Battery
Detector or Microcontroller-Reset Generator
• Overcurrent and Overtemperature Protection
• 5-Pin SOT-23 Package
• Pin-Compatible Upgrades for Bipolar Regulators
Applications
• Battery Operated Systems
• Portable Computers
• Medical Instruments
• Instrumentation
• Cellular/GSM/PHS Phones
• Linear Post-Regulators for SMPS
• Pagers
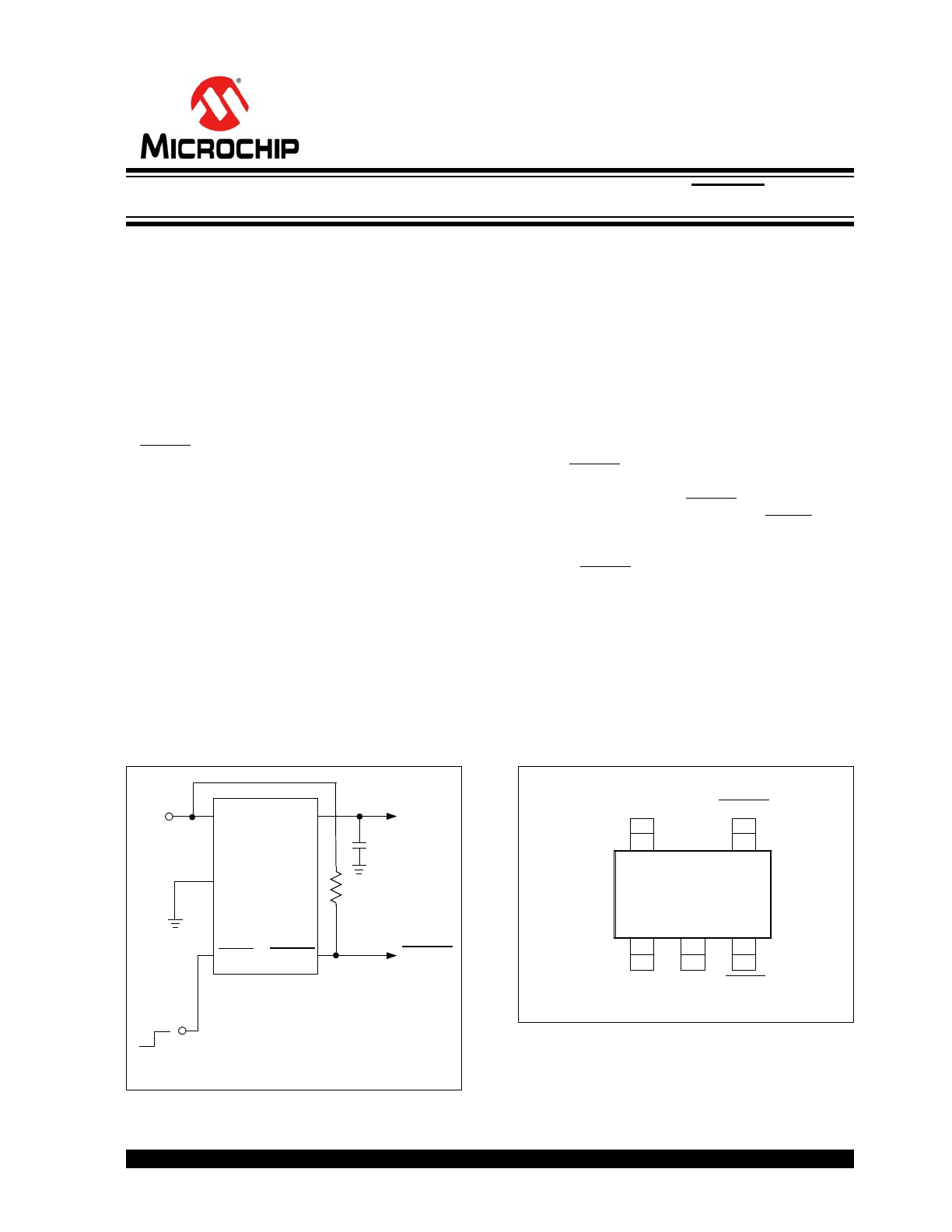
Typical Application
General Description
The TC1054, TC1055 and TC1186 are high accuracy
(typically ±0.5%) CMOS upgrades for older (bipolar)
low dropout regulators. Designed specifically for
battery-operated systems, the devices’ CMOS
construction minimizes ground current, extending
battery life. Total supply current is typically 50 µA at full
load (20 to 60 times lower than in bipolar regulators).
The devices’ key features include low noise operation,
low dropout voltage – typically 85 mV (TC1054),
180 mV (TC1055) and 270 mV (TC1186) at full load —
and fast response to step changes in load. An error
output (ERROR) is asserted when the devices are
out-of-regulation (due to a low input voltage or
excessive output current). ERROR can be used as a
low battery warning or as a processor RESET signal
(with the addition of an external RC network). Supply
current is reduced to 0.5 µA (maximum), with both
V
OUT
and ERROR disabled when the shutdown input is
low. The devices incorporate both overtemperature
and over-current protection.
The TC1054, TC1055 and TC1186 are stable with an
output capacitor of only 1 µF, and have a maximum
output current of 50 mA, 100 mA and 150 mA,
respectively. For higher output current regulators,
please refer to the TC1173 (I
OUT
= 300 mA) data sheet
(DS21632).
Package Type
V
OUT
GND
1 µF
+
V
IN
V
IN
V
OUT
1
5
2
4
3
SHDN
Shutdown Control
(from Power Control Logic)
ERROR
ERROR
1 M
TC1054
TC1055
TC1186
Note:
5-Pin SOT-23 is equivalent to the EIAJ (SC-74A)
5
1
4
2
3
5-Pin SOT-23
TC1054
TC1055
TC1186
V
OUT
ERROR
SHDN
GND
V
IN
50 mA, 100 mA and 150 mA CMOS LDOs with Shutdown and ERROR Output
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
DS21350E-page 2
2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
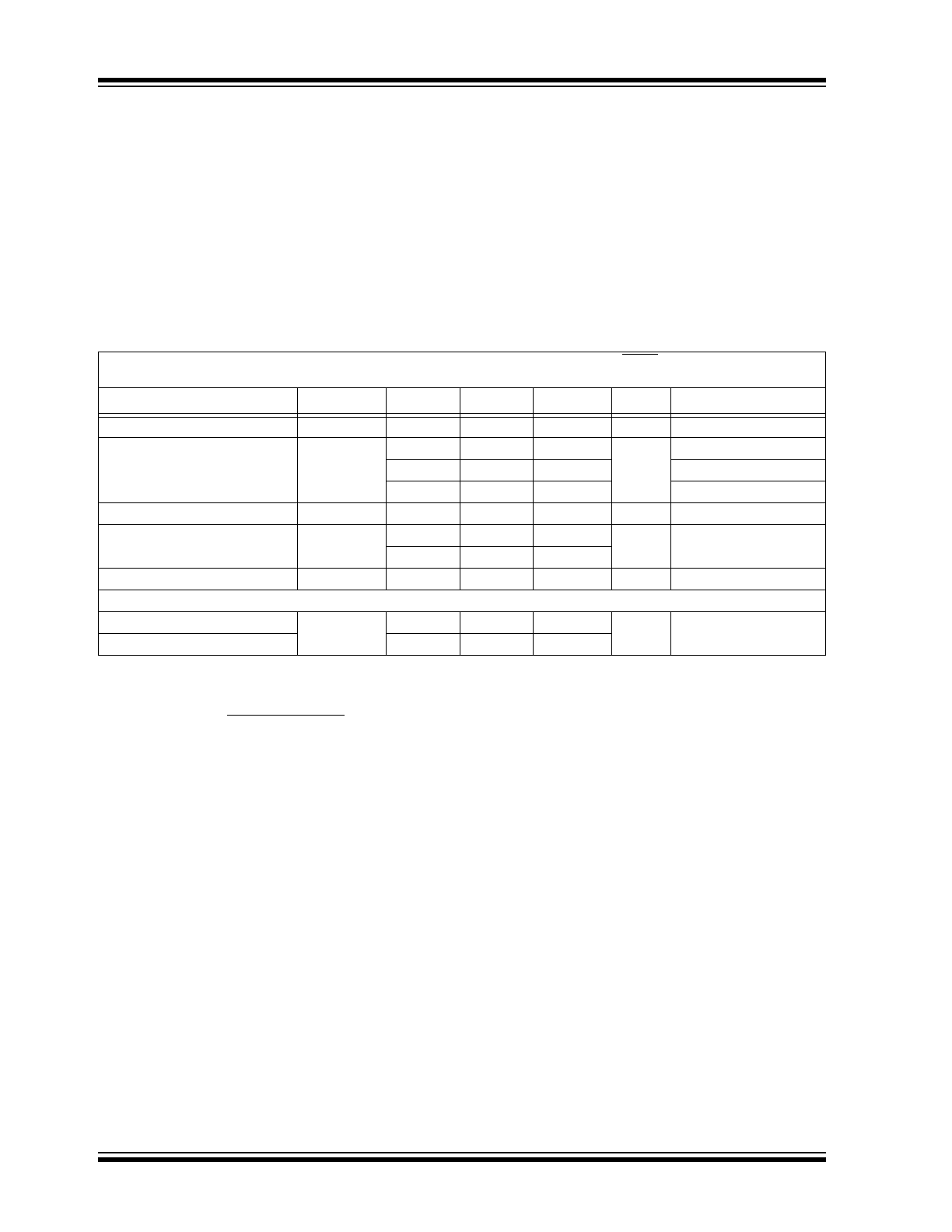
1.0
ELECTRICAL
CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings †
Input Voltage ..................................................................6.75V
Output Voltage ..................................... (-0.3V) to (V
IN
+ 0.3V)
Power Dissipation ......................... Internally Limited (
Note 6
)
Maximum Voltage on Any Pin ...................V
IN
+0.3V to -0.3V
Operating Junction Temperature Range ..-40°C <T
J
< +125°C
Storage Temperature.....................................-65°C to +150°C
† Notice:
Stresses above those listed under "Absolute
Maximum Ratings" may cause permanent damage to
the device. These are stress ratings only and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions
above those indicated in the operation sections of the
specifications is not implied. Exposure to Absolute
Maximum Rating conditions for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
DC CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Specifications:
Unless otherwise noted, V
IN
= V
OUT
+ 1V, I
L
= 100 µA, C
L
= 3.3 µF, SHDN > V
IH
, T
A
= +25°C. Boldface
type specifications apply for junction temperatures of -40°C to +125°C.
Parameters
Sym
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
Input Operating Voltage
V
IN
2.7
—
6.50
V
Note 8
Maximum Output Current
I
OUT
MAX
50
—
—
mA
TC1054
100
—
—
TC1055
150
—
—
TC1186
Output Voltage
V
OUT
V
R
– 2.5%
V
R
±0.5% V
R
+ 2.5%
V
Note 1
V
OUT
Temperature
Coefficient
TCV
OUT
—
20
—
ppm/°C
Note 2
—
40
—
Line Regulation
V
OUT
/
V
IN
—
0.05
0.35
%
(V
R
+ 1V)
V
IN
6V
Load Regulation
TC1054; TC1055
V
OUT
/V
OUT
—
0.5
2
%
(
Note 3
)
I
L
= 0.1 mA to I
OUT
MAX
TC1186
—
0.5
3
Note 1:
V
R
is the regulator output voltage setting. For example: V
R
= 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.7V, 2.85V, 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V,
4.0V, 5.0V.
2:
3:
Regulation is measured at a constant junction temperature using low-duty-cycle pulse testing. Load regu-
lation is tested over a load range from 0.1 mA to the maximum specified output current. Changes in output
voltage due to heating effects are covered by the thermal regulation specification.
4:
Dropout voltage is defined as the input to output differential at which the output voltage drops 2% below its
nominal value.
5:
Thermal Regulation is defined as the change in output voltage at a time T after a change in power dissipa-
tion is applied, excluding load or line regulation effects. Specifications are for a current pulse equal to I
L
MAX
at V
IN
= 6V for T = 10 ms.
6:
The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of ambient temperature, the maximum allowable
junction temperature and the thermal resistance from junction-to-air (i.e., T
A
, T
J
,
JA
). Exceeding the
maximum allowable power dissipation causes the device to initiate thermal shutdown. See Section 5.0
“Thermal Considerations”
for more details.
7:
Hysteresis voltage is referenced by V
R
.
8:
The minimum V
IN
has to justify the conditions: V
IN
V
R
+ V
DROPOUT
and V
IN
2.7V for I
L
= 0.1 mA to
I
OUT
MAX
.
9:
Apply for junction temperatures of -40°C to +85°C.
TC V
OUT
= (V
OUT
MAX
– V
OUT
MIN
)x 10
6
V
OUT
x
T
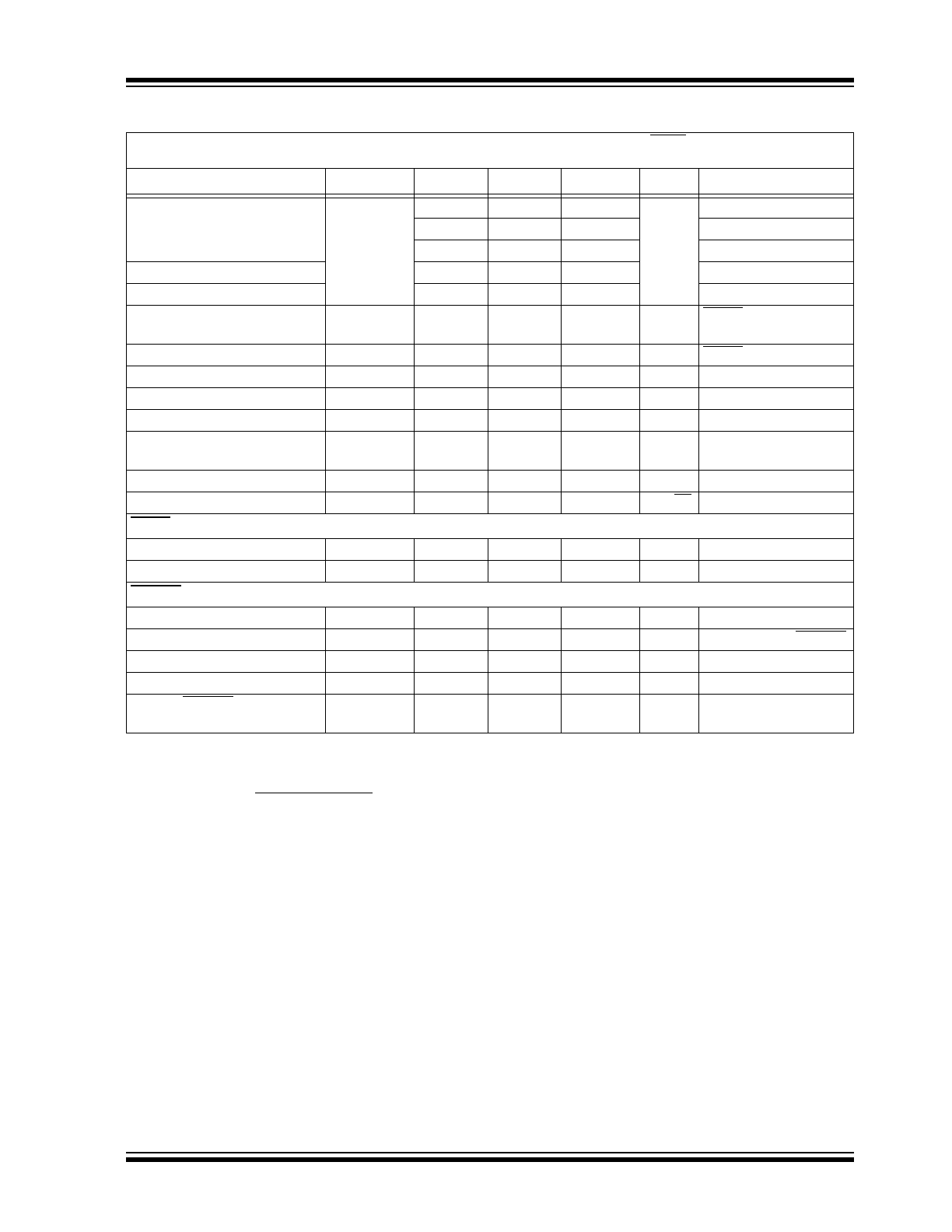
2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21350E-page 3
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
Dropout Voltage
V
IN
– V
OUT
—
2
—
mV
I
L
= 100 µA
—
65
—
I
L
= 20 mA
—
85
120
I
L
= 50 m
TC1055; TC1186
—
180
250
I
L
= 100 mA
TC1186
—
270
400
I
L
= 150 mA (
Note 4
)
Supply Current
I
IN
—
50
80
µA
SHDN = V
IH
,
I
L
= 0 µA (
Note 9
)
Shutdown Supply Current
I
INSD
—
0.05
0.5
µA
SHDN = 0V
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
PSRR
—
64
—
dB
f
1 kHz
Output Short Circuit Current
I
OUT
SC
—
300
450
mA
V
OUT
= 0V
Thermal Regulation
V
OUT
/
P
D
—
0.04
—
V/W
Notes 5
,
6
Thermal Shutdown
Die Temperature
T
SD
—
160
—
°C
Thermal Shutdown Hysteresis
T
SD
—
10
—
°C
Output Noise
eN
—
260
—
nV/
Hz I
L
= I
OUT
MAX
SHDN Input
SHDN Input High Threshold
V
IH
45
—
—
%V
IN
V
IN
= 2.5V to 6.5V
SHDN Input Low Threshold
V
IL
—
—
15
%V
IN
V
IN
= 2.5V to 6.5V
ERROR Output
Minimum V
IN
Operating Voltage
V
IN
MIN
1.0
—
—
V
Output Logic Low Voltage
V
OL
—
—
400
mV
1 mA Flows to ERROR
ERROR Threshold Voltage
V
TH
—
0.95 x V
R
—
V
See
Figure 4-2
ERROR Positive Hysteresis
V
HYS
—
50
—
mV
Note 7
V
OUT
to ERROR Delay
t
DELAY
—
2.5
—
ms
V
OUT
falling from
V
R
to V
R
– 10%
DC CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED)
Electrical Specifications:
Unless otherwise noted, V
IN
= V
OUT
+ 1V, I
L
= 100 µA, C
L
= 3.3 µF, SHDN > V
IH
, T
A
= +25°C. Boldface
type specifications apply for junction temperatures of -40°C to +125°C.
Parameters
Sym
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
Note 1:
V
R
is the regulator output voltage setting. For example: V
R
= 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.7V, 2.85V, 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V,
4.0V, 5.0V.
2:
3:
Regulation is measured at a constant junction temperature using low-duty-cycle pulse testing. Load regu-
lation is tested over a load range from 0.1 mA to the maximum specified output current. Changes in output
voltage due to heating effects are covered by the thermal regulation specification.
4:
Dropout voltage is defined as the input to output differential at which the output voltage drops 2% below its
nominal value.
5:
Thermal Regulation is defined as the change in output voltage at a time T after a change in power dissipa-
tion is applied, excluding load or line regulation effects. Specifications are for a current pulse equal to I
L
MAX
at V
IN
= 6V for T = 10 ms.
6:
The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of ambient temperature, the maximum allowable
junction temperature and the thermal resistance from junction-to-air (i.e., T
A
, T
J
,
JA
). Exceeding the
maximum allowable power dissipation causes the device to initiate thermal shutdown. See Section 5.0
“Thermal Considerations”
for more details.
7:
Hysteresis voltage is referenced by V
R
.
8:
The minimum V
IN
has to justify the conditions: V
IN
V
R
+ V
DROPOUT
and V
IN
2.7V for I
L
= 0.1 mA to
I
OUT
MAX
.
9:
Apply for junction temperatures of -40°C to +85°C.
TC V
OUT
= (V
OUT
MAX
– V
OUT
MIN
)x 10
6
V
OUT
x
T
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
DS21350E-page 4
2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
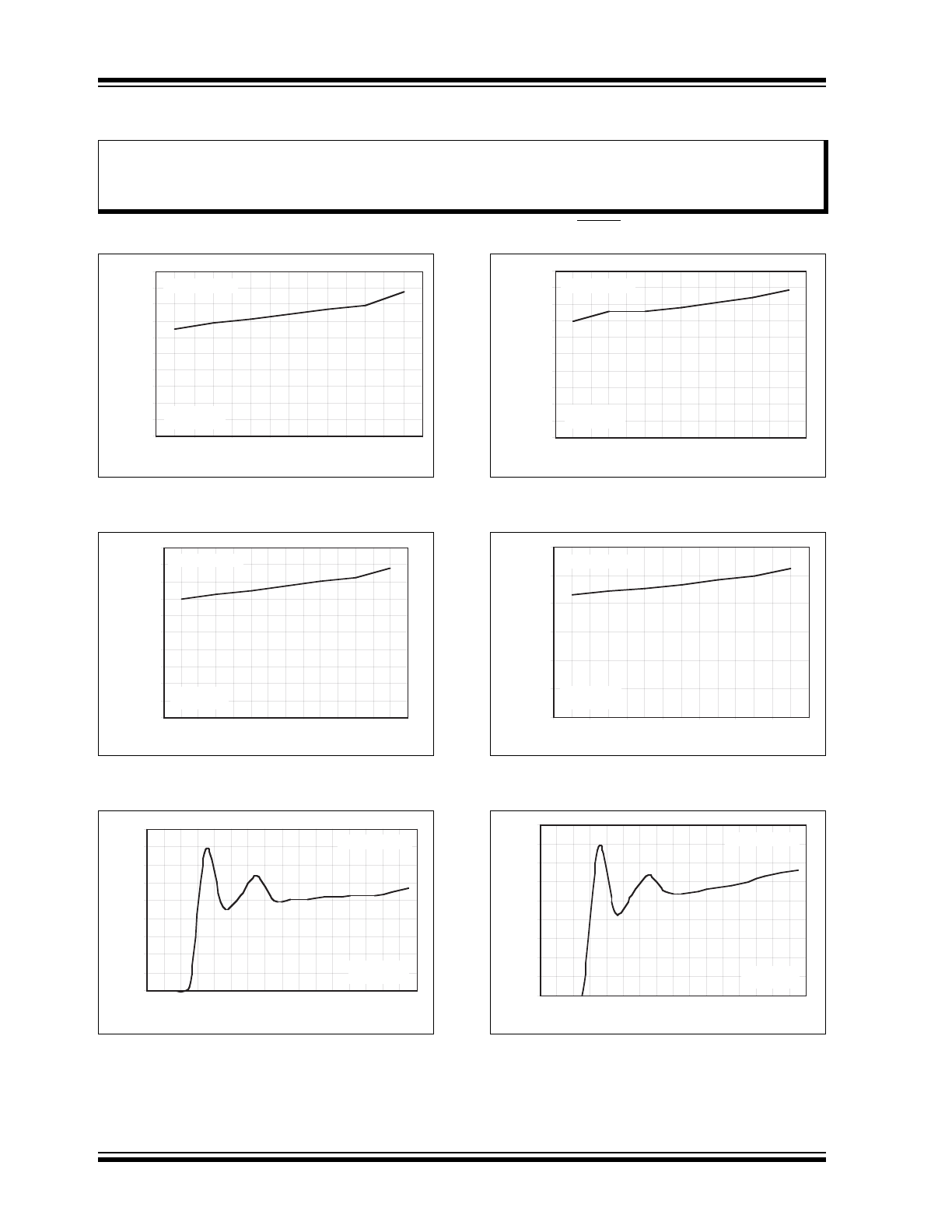
2.0
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
Note:
Unless otherwise indicated, V
IN
= V
OUT
+ 1V, I
L
= 100 µA, C
L
= 3.3 µF, SHDN > V
IH
, T
A
= +25°C.
FIGURE 2-1:
Dropout Voltage vs.
Temperature (I
LOAD
= 10 mA).
FIGURE 2-2:
Dropout Voltage vs.
Temperature (I
LOAD
= 100 mA).
FIGURE 2-3:
Ground Current vs. V
IN
(I
LOAD
= 10 mA).
FIGURE 2-4:
Dropout Voltage vs.
Temperature (I
LOAD
= 50 mA).
FIGURE 2-5:
Dropout Voltage vs.
Temperature (I
LOAD
= 150 mA).
FIGURE 2-6:
Ground Current vs. V
IN
(I
LOAD
= 100 mA).
Note:
The graphs and tables provided following this note are a statistical summary based on a limited number of
samples and are provided for informational purposes only. The performance characteristics listed herein
are not tested or guaranteed. In some graphs or tables, the data presented may be outside the specified
operating range (e.g., outside specified power supply range) and therefore outside the warranted range.
0.000
0.002
0.004
0.006
0.008
0.010
0.012
0.014
0.016
0.018
0.020
-40
-20
0
20
50
70
125
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (V)
I
LOAD
= 10 mA
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
TEMPERATURE (
°C)
0.000
0.020
0.040
0.060
0.080
0.100
0.120
0.140
0.160
0.180
0.200
-40
-20
0
20
50
70
125
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (V)
I
LOAD
= 100 mA
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
TEMPERATURE (
°C)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
GND CURRENT (
μ
A)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7 7.5
I
LOAD
= 10 mA
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
V
IN
(V)
0.000
0.010
0.020
0.030
0.040
0.050
0.060
0.070
0.080
0.090
0.100
-40
-20
0
20
50
70
125
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (V)
I
LOAD
= 50 mA
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
TEMPERATURE (
°C)
0.000
0.050
0.100
0.150
0.200
0.250
0.300
-40
-20
0
20
50
70
125
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (V)
I
LOAD
= 150 mA
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
TEMPERATURE (
°C)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
GND CURRENT (
μ
A)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7 7.5
I
LOAD
= 100 mA
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
V
IN
(V)
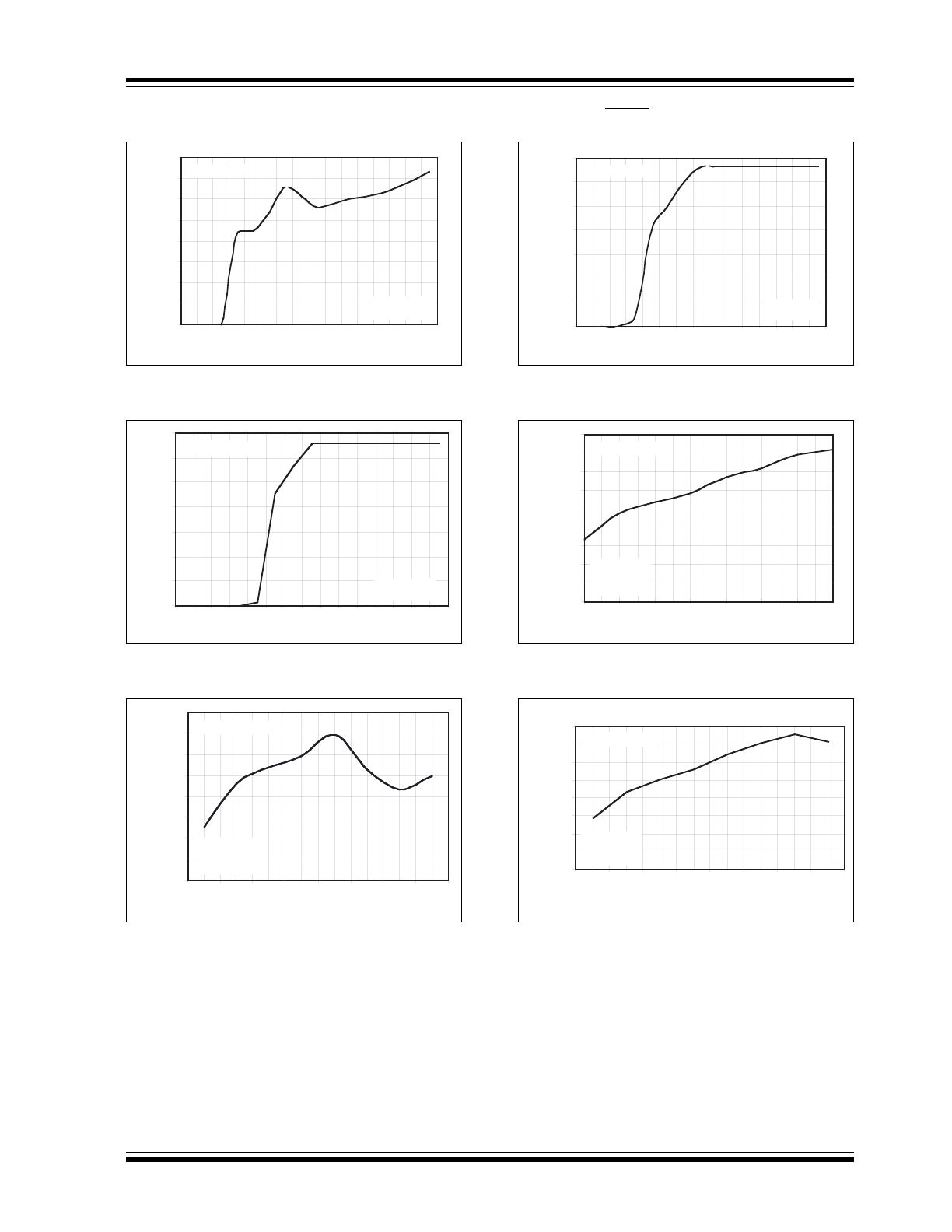
2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21350E-page 5
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
Note:
Unless otherwise indicated, V
IN
= V
OUT
+ 1V, I
L
= 100 µA, C
L
= 3.3 µF, SHDN > V
IH
, T
A
= +25°C.
FIGURE 2-7:
Ground Current vs. V
IN
(I
LOAD
= 150 mA).
FIGURE 2-8:
V
OUT
vs. V
IN
(I
LOAD
= 100 mA).
FIGURE 2-9:
V
OUT
vs. V
IN
(I
LOAD
= 150 mA).
FIGURE 2-10:
V
OUT
vs. V
IN
(I
LOAD
= 0 mA).
FIGURE 2-11:
Output Voltage (3.3V) vs.
Temperature (I
LOAD
= 10 mA).
FIGURE 2-12:
Output Voltage (5V) vs.
Temperature (I
LOAD
= 10 mA).
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
GND CURRENT (
μ
A)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7 7.5
I
LOAD
= 150 mA
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
V
IN
(V)
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
I
LOAD
= 100 mA
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7
V
IN
(V)
V
OUT
(V)
3.274
3.276
3.278
3.280
3.282
3.284
3.286
3.288
3.290
-40
-20
-10
0
20
40
85
125
I
LOAD
= 150 mA
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
V
IN
= 4.3V
TEMPERATURE (
°C)
V
OUT
(V)
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7
I
LOAD
= 0
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
V
IN
(V)
V
OUT
(V)
3.275
3.280
3.285
3.290
3.295
3.300
3.305
3.310
3.315
3.320
-40
-20
-10
0
20
40
85
125
I
LOAD
= 10 mA
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
V
IN
= 4.3V
TEMPERATURE (
°C)
V
OUT
(V)
4.985
4.990
4.995
5.000
5.005
5.010
5.015
5.020
5.025
-40
-20
-10
0
20
40
85
125
I
LOAD
= 10 mA
V
IN
= 6V
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
TEMPERATURE (
°C)
V
OUT
(V)
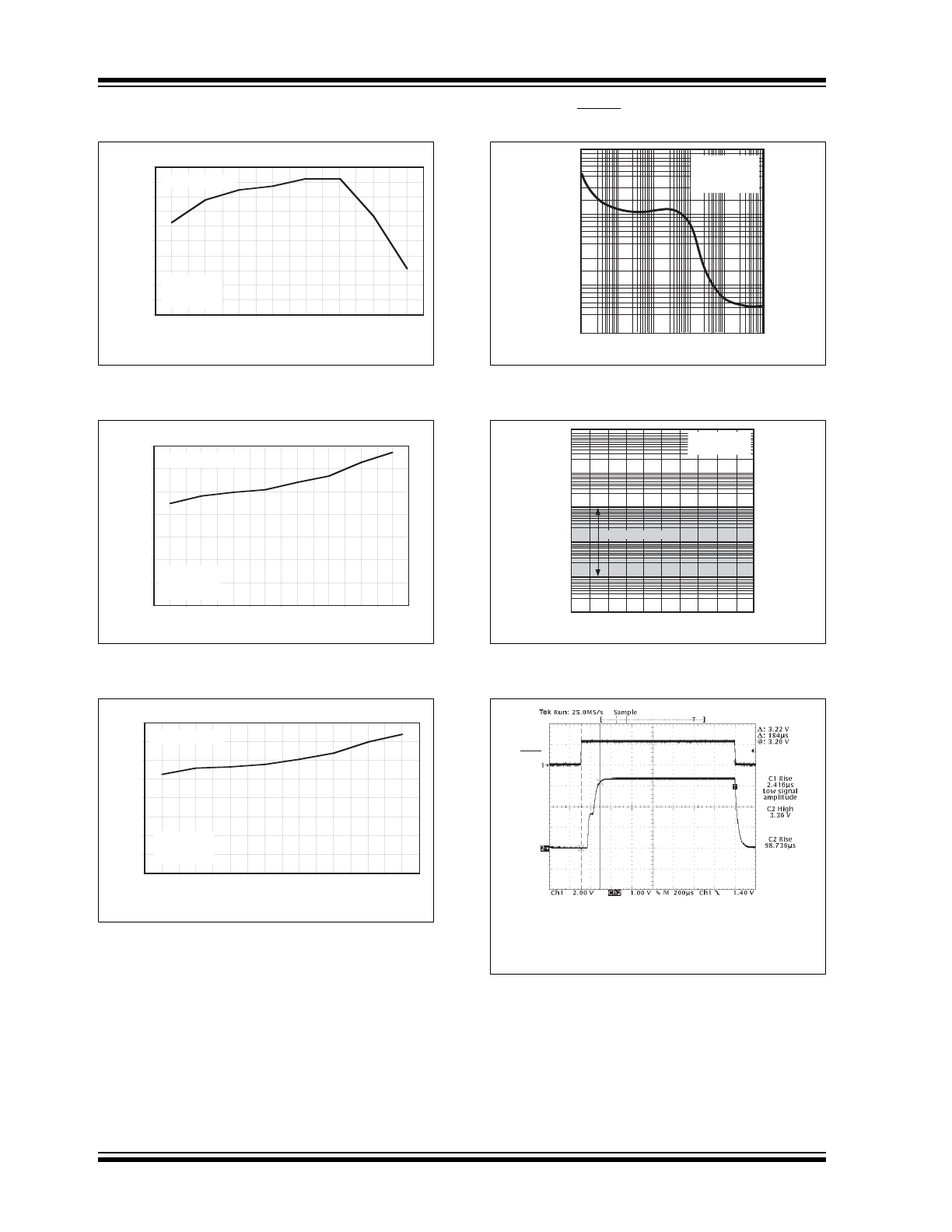
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
DS21350E-page 6
2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
Note:
Unless otherwise indicated, V
IN
= V
OUT
+ 1V, I
L
= 100 µA, C
L
= 3.3 µF, SHDN > V
IH
, T
A
= +25°C.
FIGURE 2-13:
Output Voltage (5V) vs.
Temperature (I
LOAD
= 10 mA).
FIGURE 2-14:
GND Current vs.
Temperature (I
LOAD
= 10 mA).
FIGURE 2-15:
GND Current vs.
Temperature (I
LOAD
= 150 mA).
FIGURE 2-16:
Output Noise vs. Frequency.
FIGURE 2-17:
Stability Region vs. Load
Current.
FIGURE 2-18:
Measure Rise Time of 3.3V
LDO.
4.974
4.976
4.978
4.980
4.982
4.984
4.986
4.988
4.990
4.992
4.994
-40
-20
-10
0
20
40
85
125
I
LOAD
= 150 mA
V
IN
= 6V
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
TEMPERATURE (
°C)
V
OUT
(V)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
-40
-20
-10
0
20
40
85
125
GND CURRENT (
μ
A)
I
LOAD
= 10 mA
V
IN
= 6V
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
TEMPERATURE (
°C)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
-40
-20
-10
0
20
40
85
125
GND CURRENT (
μ
A)
I
LOAD
= 150 mA
V
IN
= 6V
C
IN
= 1
μF
C
OUT
= 1
μF
TEMPERATURE (
°C)
10.0
1.0
0.1
0.0
0.01K 0.1K
1K
10K
100K
1000K
FREQUENCY (Hz)
NOISE (
μ
V/
√
Hz)
R
LOAD
= 50
Ω
C
OUT
= 1
μF
C
IN
= 1
μF
1000
100
10
1
0.1
0.01
0
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
C
OUT
ESR
(Ω
)
C
OUT
= 1
μF
to 10
μF
Stable Region
V
SHDN
V
OUT
Conditions:
C
IN
= 1 µF, C
OUT
= 1 µF,
I
LOAD
= 100 mA, V
IN
= 4.3V, Temperature = +25°C,
Fall Time = 184 µs
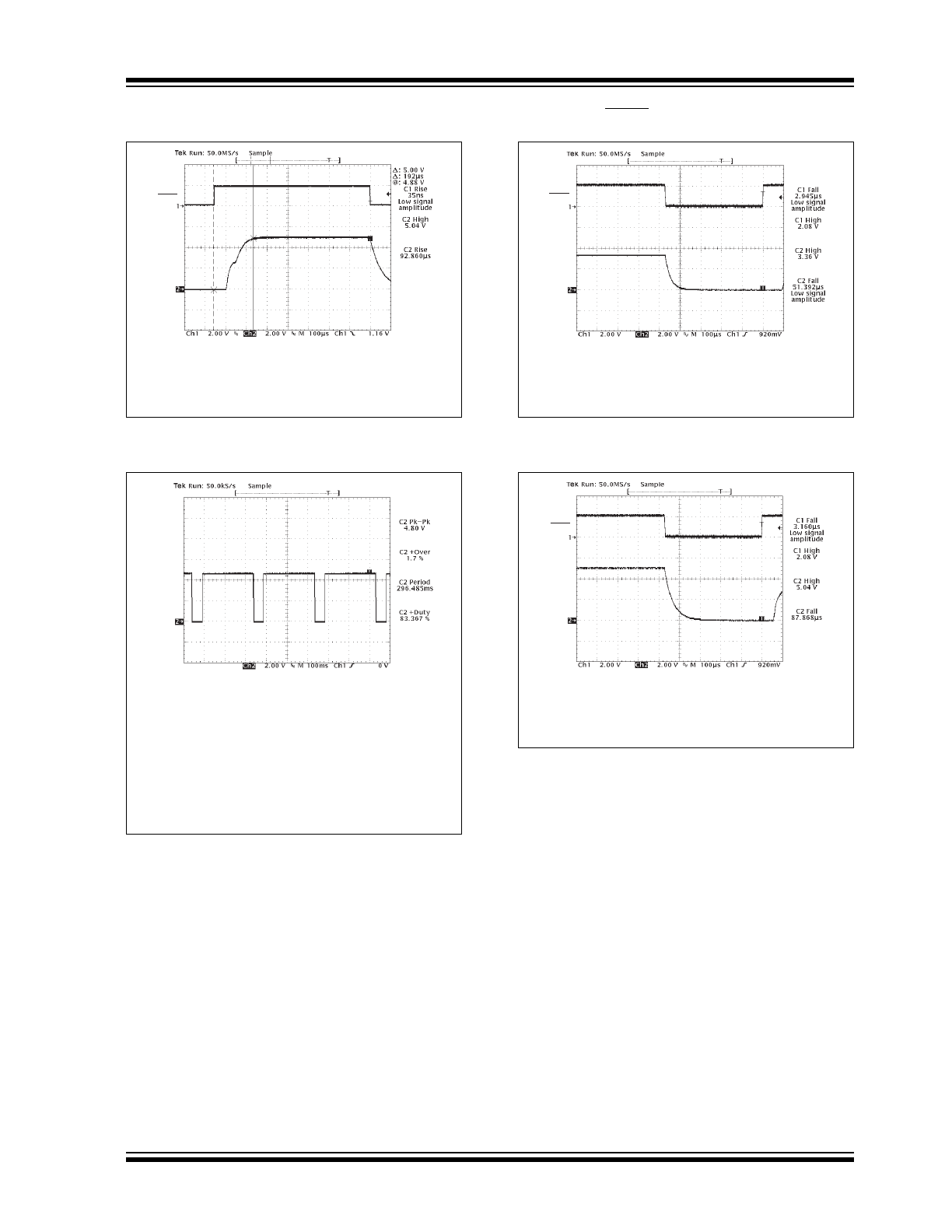
2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21350E-page 7
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
Note:
Unless otherwise indicated, V
IN
= V
OUT
+ 1V, I
L
= 100 µA, C
L
= 3.3 µF, SHDN > V
IH
, T
A
= +25°C.
FIGURE 2-19:
Measure Rise Time of 5.0V
LDO.
FIGURE 2-20:
Thermal Shutdown
Response of 5.0V LDO.
FIGURE 2-21:
Measure Fall Time of 3.3V
LDO.
FIGURE 2-22:
Measure Fall Time of 5.0V
LDO.
V
SHDN
V
OUT
Conditions:
C
IN
= 1 µF, C
OUT
= 1 µF,
I
LOAD
= 100 mA, V
IN
= 6V, Temperature = +25°C,
Fall Time = 192 µs
V
OUT
Conditions:
V
IN
= 6V, C
IN
= 0 µF, C
OUT
= 1 µF
I
LOAD
was increased until temperature of die
reached about +160°C, at which time integrated ther-
mal protection circuitry shuts the regulator off when
die temperature exceeds approximately +160°C.
The regulator remains off until die temperature drops
to approximately +150°C.
V
SHDN
V
OUT
Conditions:
C
IN
= 1 µF, C
OUT
= 1 µF,
I
LOAD
= 100 mA, V
IN
= 4.3V, Temperature = +25°C,
Fall Time = 52 µs
V
SHDN
V
OUT
Conditions:
C
IN
= 1 µF, C
OUT
= 1 µF,
I
LOAD
= 100 mA, V
IN
= 6V, Temperature = +25°C,
Fall Time = 88 µs

TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
DS21350E-page 8
2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
3.0
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
The descriptions of the pins are listed in
Table 3-1
.
3.1
Unregulated Supply Input (V
IN
)
Connect unregulated input supply to the V
IN
pin. If
there is a large distance between the input supply and
the LDO regulator, some input capacitance is
necessary for proper operation. A 1 µF capacitor
connected from V
IN
to ground is recommended for
most applications.
3.2
Ground Terminal (GND)
Connect the unregulated input supply ground return to
GND. Also connect the negative side of the 1 µF typical
input decoupling capacitor close to GND and the
negative side of the output capacitor C
OUT
to GND.
3.3
Shutdown Control Input (SHDN)
The regulator is fully enabled when a logic-high is
applied to SHDN. The regulator enters shutdown when
a logic-low is applied to SHDN. During shutdown,
output voltage falls to zero, ERROR is open-circuited
and supply current is reduced to 0.5 µA (maximum).
3.4
Out Of Regulation Flag (ERROR)
ERROR goes low when V
OUT
is out-of-tolerance by
approximately -5%.
3.5
Regulated Voltage Output (V
OUT
)
Connect the output load to V
OUT
of the LDO. Also
connect the positive side of the LDO output capacitor
as close as possible to the V
OUT
pin.
TABLE 3-1:
PIN FUNCTION TABLE
Pin No.
SOT-23
Symbol
Description
1
V
IN
Unregulated supply input
2
GND
Ground terminal
3
SHDN
Shutdown control input
4
ERROR
Out-of-Regulation Flag (Open-drain output)
5
V
OUT
Regulated voltage output
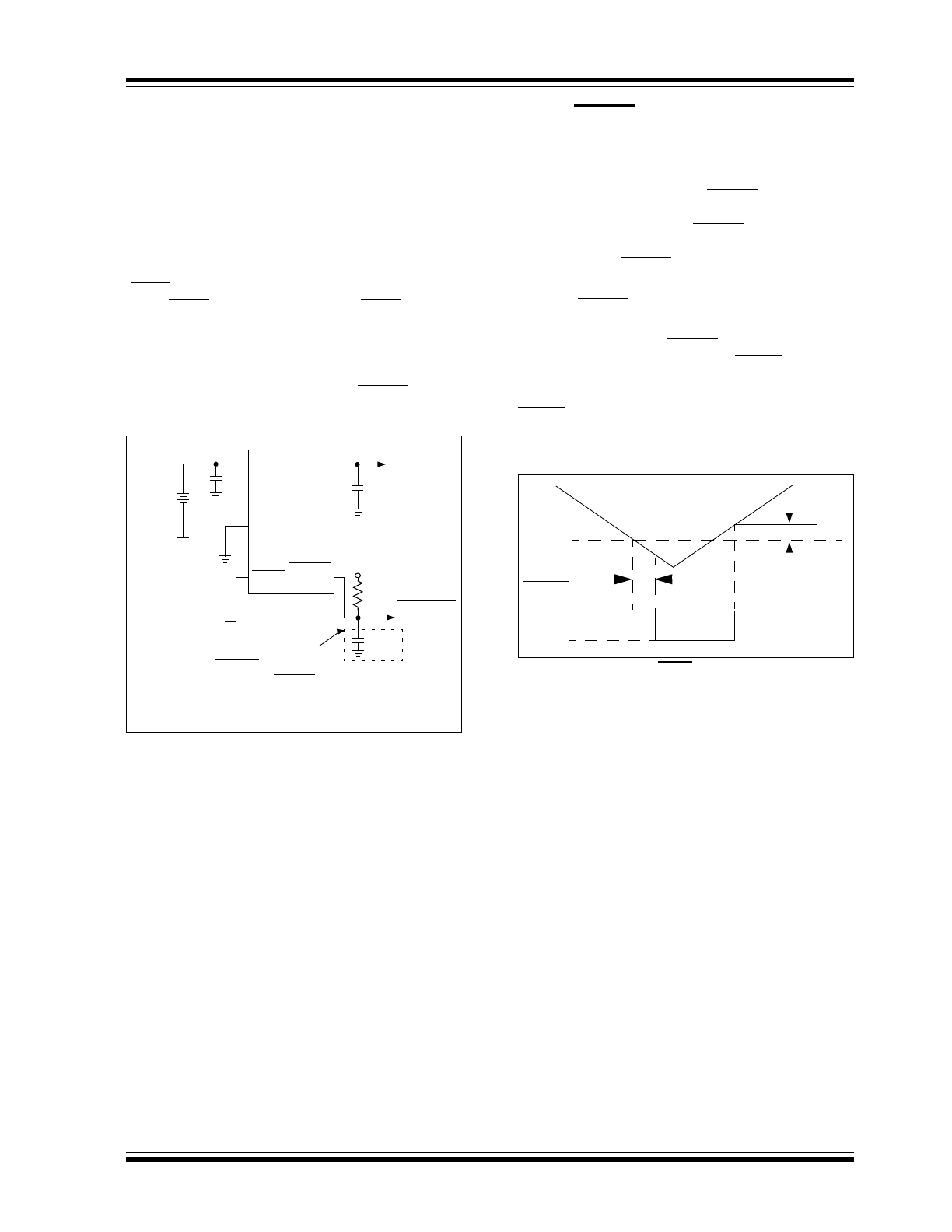
2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21350E-page 9
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
4.0
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The TC1054, TC1055 and TC1186 are precision fixed
output voltage regulators (If an adjustable version is
desired, please see the TC1070/TC1071/TC1187 data
sheet (DS21353)). Unlike bipolar regulators, the
TC1054, TC1055 and TC1186 supply current does not
increase with load current.
Figure 4-1
shows a typical application circuit, where the
regulator is enabled any time the shutdown input
(SHDN) is at or above V
IH
, and shutdown (disabled)
when SHDN is at or below V
IL
. SHDN may be
controlled by a CMOS logic gate or I/O port of a
microcontroller. If the SHDN input is not required, it
should be connected directly to the input supply. While
in Shutdown, supply current decreases to 0.05 µA
(typical), V
OUT
falls to zero volts, and ERROR is open-
circuited.
FIGURE 4-1:
Typical Application Circuit.
4.1
ERROR Open-Drain Output
ERROR is driven low whenever V
OUT
falls out of
regulation by more than -5% (typical). This condition
may be caused by low input voltage, output current
limiting or thermal limiting. The ERROR threshold is 5%
below rated V
OUT
, regardless of the programmed
output voltage value (e.g. ERROR = V
OL
at 4.75V
(typical) for a 5.0V regulator and 2.85V (typical) for a
3.0V regulator). ERROR output operation is shown in
Figure 4-2
.
Note that ERROR is active when V
OUT
falls to V
TH
and
inactive when V
OUT
rises above V
TH
by V
HYS
.
As shown in
Figure 4-1
, ERROR can be used either as
a battery low flag or as a processor RESET signal (with
the addition of timing capacitor C
2
). R
1
x C
2
should be
chosen to maintain ERROR below V
IH
of the processor
RESET input for at least 200 ms to allow time for the
system to stabilize. Pull-up resistor R
1
can be tied to
V
OUT
, V
IN
or any other voltage less than (V
IN
+ 0.3V).
FIGURE 4-2:
Error Output Operation.
4.2
Output Capacitor
A 1 µF (minimum) capacitor from V
OUT
to ground is
recommended. The output capacitor should have an
effective series resistance greater than 0.1
and less
than 10.0
, with a resonant frequency above 1 MHz. A
1 µF capacitor should be connected from V
IN
to GND if
there is more than 10 inches of wire between the
regulator and the AC filter capacitor, or if a battery is
used as the power source. Aluminum electrolytic or
tantalum capacitor types can be used (since many
aluminum electrolytic capacitors freeze at approxi-
mately -30°C, solid tantalums are recommended for
applications operating below -25°C). When operating
from sources other than batteries, supply-noise
rejection and transient response can be improved by
increasing the value of the input and output capacitors
and employing passive filtering techniques.
or RESET
V
OUT
SHDN
GND
ERROR
+
V
IN
V
OUT
1 µF
+
Battery
+
0.2 µF
C
2
R
1
1 MΩ
V+
BATTLOW
1 µF
C
1
TC1054
TC1055
TC1186
C
2
Required Only if
ERROR is used as a
Processor RESET
Signal (see Text)
Shutdown
Control (to
CMOS Logic or
Tie to V
IN
if
unused)
V
TH
V
OUT
ERROR
V
IH
V
OL
HYSTERESIS
(V
H
)
t
DELAY
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
DS21350E-page 10
2002-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
5.0
THERMAL CONSIDERATIONS
5.1
Thermal Shutdown
Integrated thermal protection circuitry shuts the
regulator off when die temperature exceeds +160°C.
The regulator remains off until the die temperature
drops to approximately +150°C.
5.2
Power Dissipation
The amount of power the regulator dissipates is
primarily a function of input voltage, output voltage and
output current. The following equation is used to
calculate worst-case actual power dissipation:
EQUATION 5-1:
The maximum allowable power dissipation
(
Equation 5-2
) is a function of the maximum ambient
temperature (T
A
MAX
), the maximum allowable die
temperature (T
J
MAX
) and the thermal resistance from
junction-to-air (
JA
). The 5-Pin SOT-23 package has a
JA
of approximately 220°C/Watt.
EQUATION 5-2:
Equation 5-1
can be used in conjunction with
Equation 5-2
to ensure regulator thermal operation is
within limits.
For example:
Actual power dissipation:
Maximum allowable power dissipation:
In this example, the TC1054 dissipates a maximum of
20.7 mW; below the allowable limit of 318 mW. In a
similar manner,
Equation 5-1
and
Equation 5-2
can be
used to calculate maximum current and/or input
voltage limits.
5.3
Layout Considerations
The primary path of heat conduction out of the package
is via the package leads. Layouts having a ground
plane, wide traces at the pads and wide power supply
bus lines, combine to lower θJA and increase the max-
imum allowable power dissipation limit.
P
D
V
INMAX
V
OUTMIN
–
I
LOADMAX
Where:
P
D
= Worst-case actual power dissipation
V
INmax
= Maximum voltage on V
IN
V
OUTmin
= Minimum regulator output voltage
I
LOADmax
= Maximum output (load) current
Where all terms are previously defined.
P
DMAX
T
J MAX
T
AMAX
–
JA
--------------------------------------------
=
Given:
V
IN
MAX
= 3.0V +5%
V
OUT
MIN
= 2.7V – 2.5%
I
LOAD
MAX
= 40 mA
T
J
MAX
= +125°C
T
A
MAX
= +55°C
Find:
1.
Actual power dissipation
2.
Maximum allowable dissipation
P
D
V
INMAX
V
OUTMIN
–
I
LOADMAX
3.0
1.05
2.7
0.975
–
40 10
-3
=
20.7mW
=
P
DMAX
T
JMAX
T
AMAX
–
J A
--------------------------------------------
=
125
55
–
220
-------------------------
=
318mW
=
