2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005783C-page 1
ATA6566
Features
• Compliant with Japanese OEM Requirements
• Certified According to Latest VeLIO (Vehicle
LAN Interoperability and Optimization) Test
Specification
• Fully ISO 11898-2, ISO 11898-5,
ISO 11898-2: 2016 and SAE J2962-2 Compliant
• Communication Speed up to 2 Mbit/s
• Low Electromagnetic Emission (EME) and High
Electromagnetic Immunity (EMI)
• Differential Receiver with Wide Common-Mode
Range
• Remote Wake-up Capability via CAN Bus –
Wake-up on Pattern (WUP) as Specified in
ISO 11898-2: 2016, 3.8 µs Activity Filter Time
• Functional Behavior Predictable under All Supply
Conditions
• Transceiver Disengages from the Bus when
Not Powered Up
• RXD Recessive Clamping Detection
• High Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Handling
Capability on the Bus Pins
• Bus Pins Protected Against Transients in
Automotive Environments
• Transmit Data (TXD) Dominant Time-out Function
• Undervoltage Detection on VCC and VIO Pins
• CANH/CANL Short-Circuit and Overtemperature
Protected
• Fulfills the OEM “Hardware Requirements for LIN,
CAN and FlexRay™ Interfaces in Automotive
Applications”,
Rev. 1.3
• Qualified According to AEC-Q100
• Two Ambient Temperature Grades:
- ATA6566-GAQW1 and ATA6566-GBQW1 up
to T
amb
= +125°C
- ATA6566-GAQW0 and ATA6566-GBQW0 up
to T
amb
= +150°C
• Packages: 8-Pin SOIC, 8-Pin VDFN with Wettable
Flanks (Moisture Sensitivity Level 1)
Applications
Classical CAN and CAN FD networks in Automotive,
Industrial, Aerospace, Medical and Consumer
applications.
General Description
The ATA6566 is a high-speed CAN transceiver that
provides an interface between a Controller Area Net-
work (CAN) protocol controller and the physical
two-wire CAN bus. The transceiver is designed for
high-speed (up to 2 Mbit/s) CAN applications in the
automotive industry, providing differential transmit and
receive capability to (a microcontroller with) a CAN
protocol controller.
It offers improved Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
and Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) performance, as
well as features such as:
• Ideal passive behavior to the CAN bus when the
supply voltage is off
• Direct interfacing to microcontrollers with supply
voltages from 3V to 5V
Two operating modes, together with the dedicated
fail-safe features, make the ATA6566 an excellent
choice for all types of high-speed CAN networks,
especially in nodes requiring Low-Power mode with
wake-up capability via the CAN bus.
Package Types
ATA6566
8-Pin SOIC
ATA6566
8-Pin VDFN
STBY
CANL
CANH
VIO
TXD
VCC
GND
RXD
ATA6566
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
ATA6566
TXD
GND
VCC
RXD
STBY
CANH
CANL
VIO
TXD
GND
VCC
RXD
STBY
CANH
CANL
VIO
High-Speed CAN Transceiver with Standby Mode
for the Japanese Market – CAN FD Ready
ATA6566
DS20005783C-page 2
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
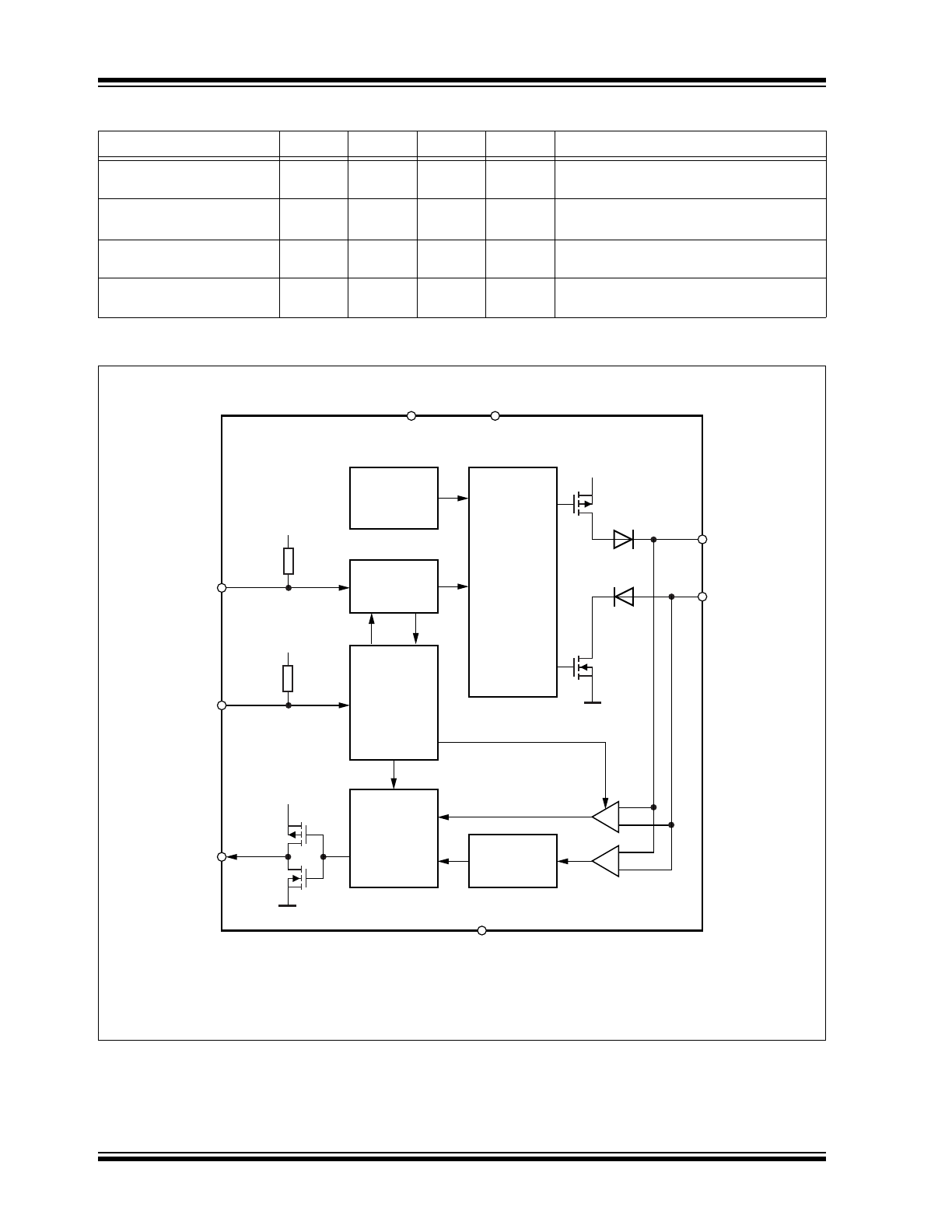
ATA6566 Family Members
Functional Block Diagram
Device
Grade 0
Grade 1
VDFN8
SOIC8
Description
ATA6566-GAQW0
X
X
Standby mode, VIO – pin for compatibility
with 3.3V and 5V microcontroller
ATA6566-GBQW0
X
X
Standby mode, VIO – pin for compatibility
with 3.3V and 5V microcontroller
ATA6566-GAQW1
X
X
Standby mode, VIO – pin for compatibility
with 3.3V and 5V microcontroller
ATA6566-GBQW1
X
X
Standby mode, VIO – pin for compatibility
with 3.3V and 5V microcontroller
Note 1: HSC: High-Speed Comparator.
2: WUC: Wake-up Comparator.
Temperature
Protection
Control
Unit
Wake-up
Filter
Slope
Control
and
Driver
TXD
Time-out
Timer
9,2
9,2
9,2
9&&
9&&
MUX
1
2
TXD
STBY
CANH
ATA6566
RXD
8
7
5
3
4
CANL
GND
6
9,2
WUC
(2)
HSC
(1)
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005783C-page 3
ATA6566
1.0
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The ATA6566 is a stand-alone, high-speed CAN
transceiver, compliant with the ISO 11898-2,
ISO 11898-2: 2016, ISO 11898-5 and SAE J2962-2
CAN standards. It provides a very low current consump-
tion in Standby mode and wake-up capability via the
CAN bus. Pin 5 is the VIO pin and should be connected
to the microcontroller supply voltage. This allows direct
interfacing to microcontrollers with supply voltages down
to 3V, and adjusts the signal levels of the TXD, RXD and
STBY pins to the I/O levels of the microcontroller. The
I/O ports are supplied by the VIO pin.
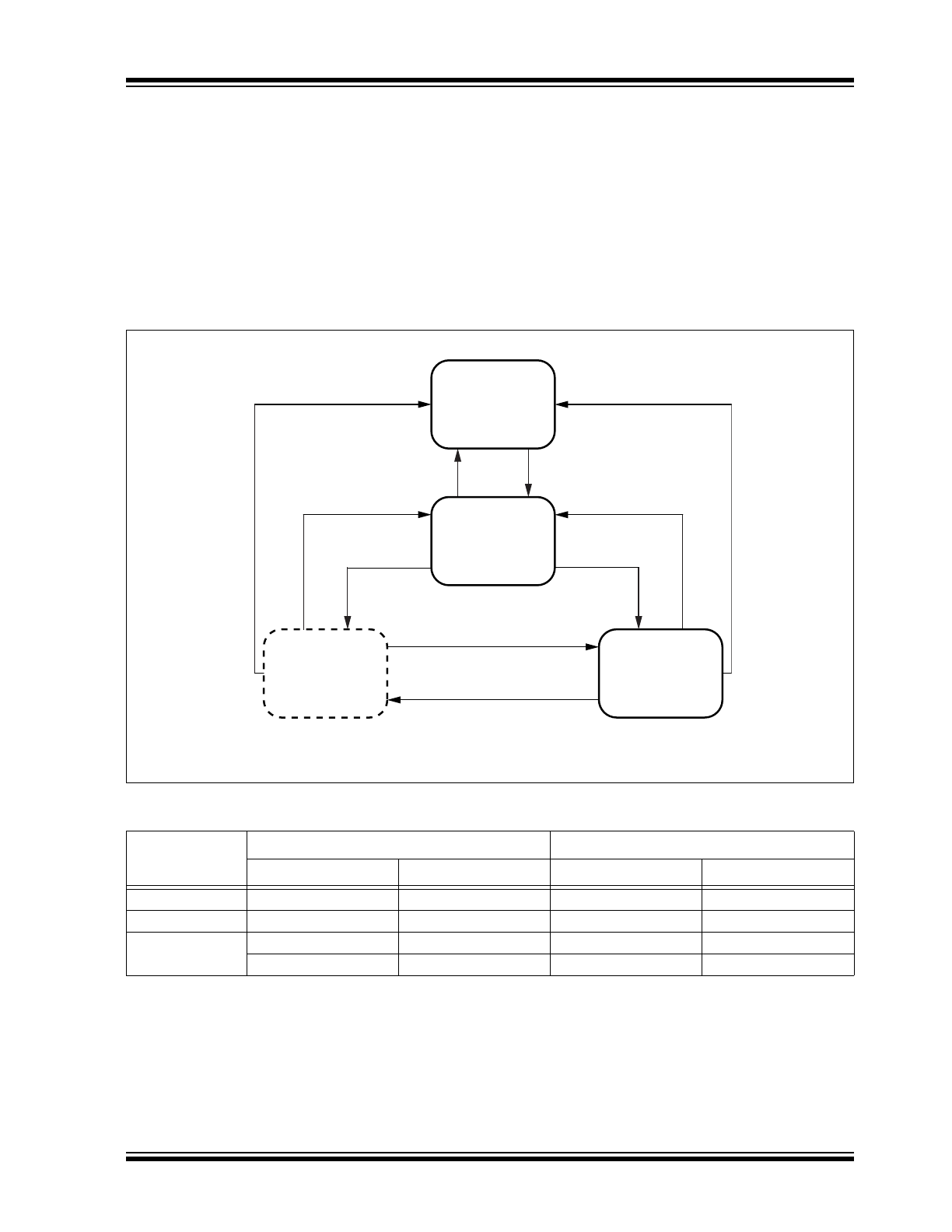
1.1
Operating Modes
The ATA6566 supports two operating modes: Silent
and Normal. These modes can be selected via the
STBY pin. See
Figure 1-1
and
Table 1-1
for a
description of the operating modes.
FIGURE 1-1:
OPERATING MODES
TABLE 1-1:
OPERATING MODES
* Silent mode is externally not accessible.
STBY = 0 and
TXD = 0
VCC < V
uvd(VCC)
or
STBY = 1
STBY = 0 and
TXD = 1 and
Error = 0 and
TXD = 1
*
Error = 1
Error = 0
VCC < V
uvd(VCC)
or
VIO < V
uvd(VIO)
VIO < V
uvd(VIO)
VCC < V
uvd(VCC)
or
VCC > V
uvd(VCC)
and
VIO < V
uvd(VIO)
VIO > V
uvd(VIO)
Unpowered
Mode
Standby
Mode
Silent Mode
(Receive only)
Normal
Mode
STBY = 1
Mode
Inputs
Outputs
STBY
Pin TXD
CAN Driver
Pin RXD
Unpowered
X
(
1
)
X
(
1
)
Recessive
Recessive
Standby
High
X
(
1
)
Recessive
Active
(
2
)
Normal
Low
Low
Dominant
Low
Low
High
Recessive
High
Note 1: Irrelevant.
2: Reflects the bus only for wake-up.
ATA6566
DS20005783C-page 4
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.1.1
NORMAL MODE
A low level on the STBY pin, together with a high level on
the TXD pin, selects the Normal mode. In this mode, the
transceiver is able to transmit and receive data via the
CANH and CANL bus lines (see the
“Functional Block
Diagram”
). The output driver stage is active and drives
data from the TXD input to the CAN bus. The High-Speed
Comparator (HSC) converts the analog data on the bus
lines into digital data, which is output to pin RXD. The bus
biasing is set to V
VCC
/2 and the undervoltage monitoring
of VCC is active.
The slope of the output signals on the bus lines is
controlled and optimized to ensure the lowest possible
Electromagnetic Emission (EME).
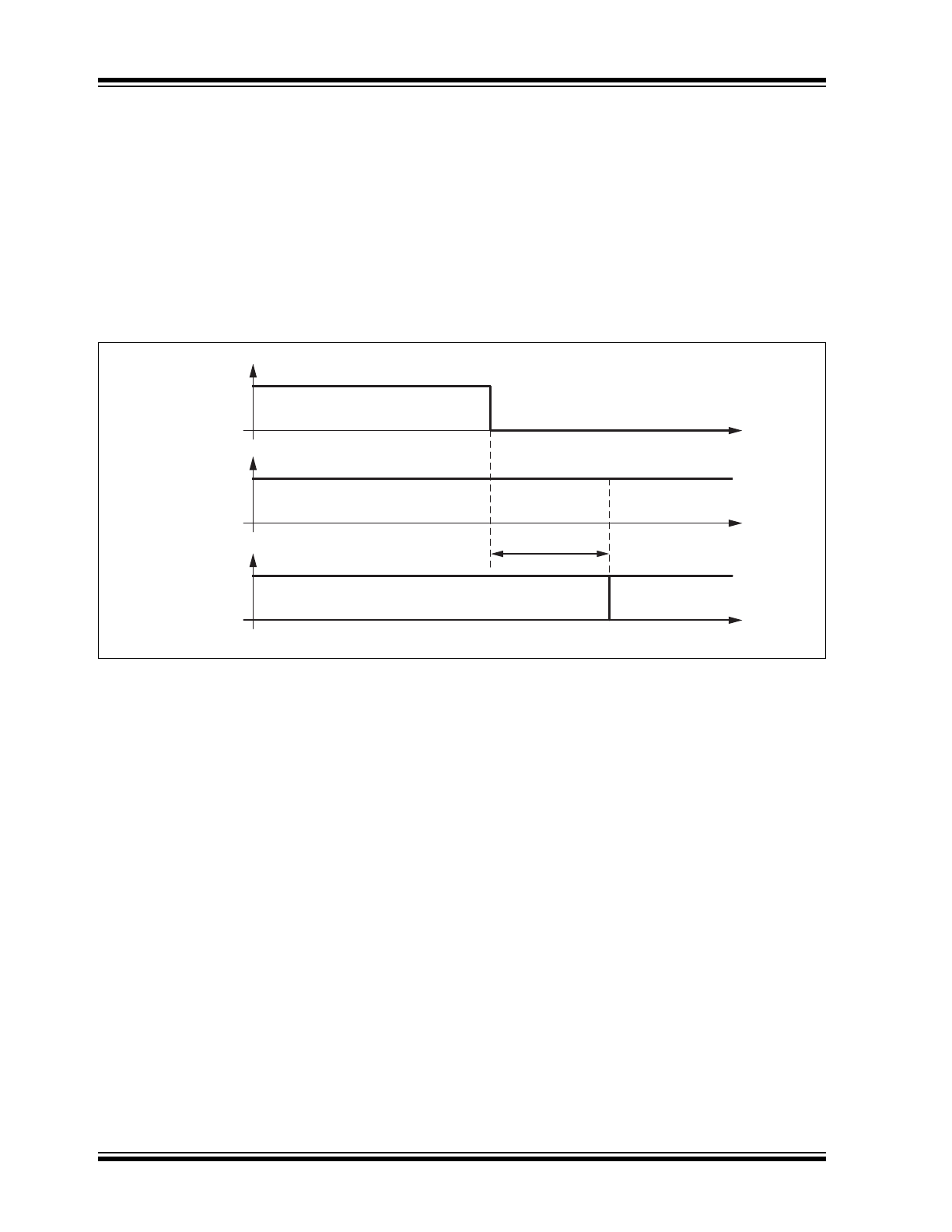
To switch the device to Normal Operating mode, set the
STBY pin to low and the TXD pin to high (see
Table 1-1
and
Figure 1-2
). The STBY and TXD pins each provide
a pull-up resistor to VIO, ensuring defined levels if the
pins are open.
Please note that the device cannot enter Normal mode
as long as TXD is at ground level.
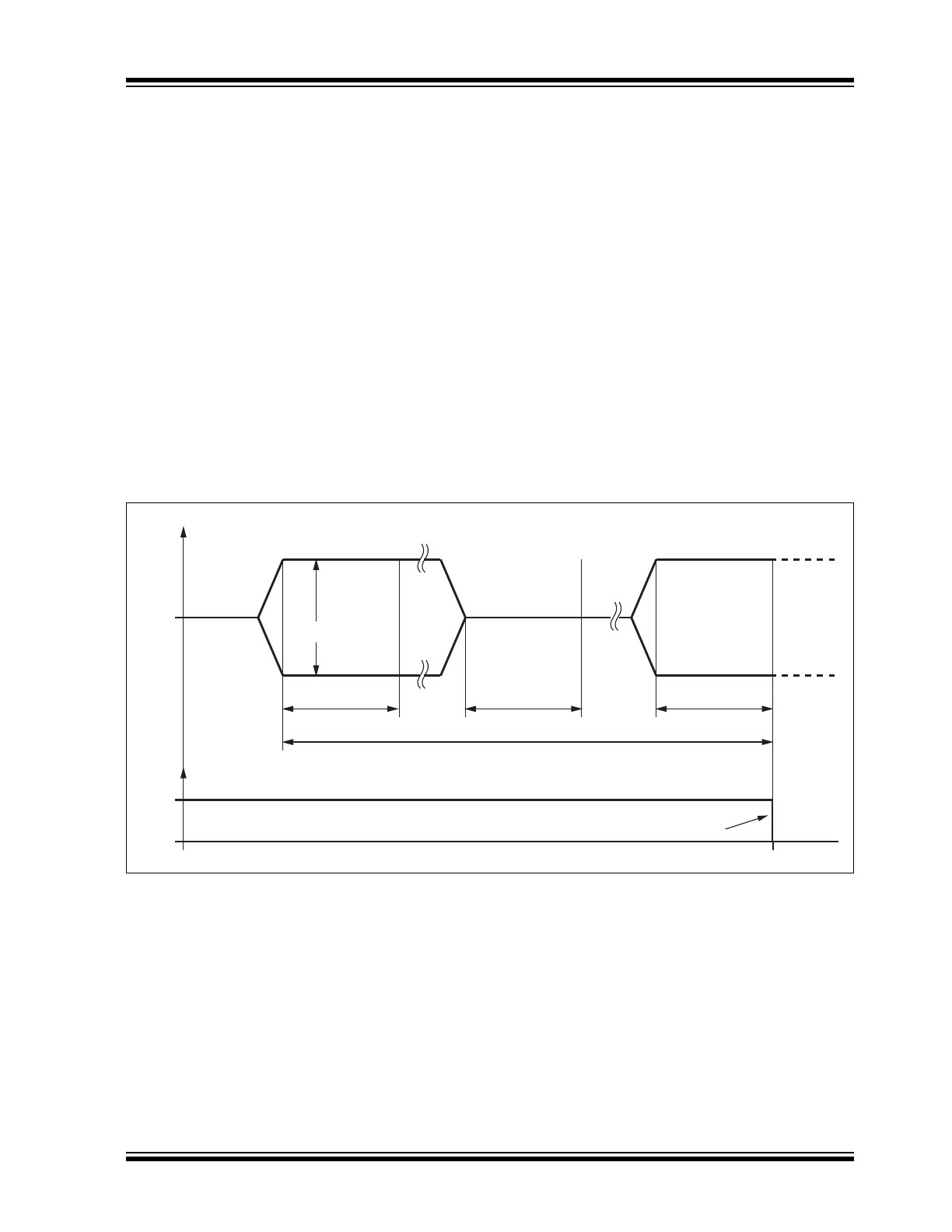
FIGURE 1-2:
SWITCHING FROM STANDBY MODE TO NORMAL MODE
STBY
TXD
Standby Mode
t
del(stby-norm)
=
47 μs max
Normal Mode
t
t
t
Operation
Mode
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005783C-page 5
ATA6566
1.1.2
STANDBY MODE
A high level on the STBY pin selects Standby mode. In
this mode, the transceiver is not able to transmit or
correctly receive data via the bus lines. The transmitter
and the High-Speed Comparator (HSC) are switched
off to reduce current consumption.
1.1.3
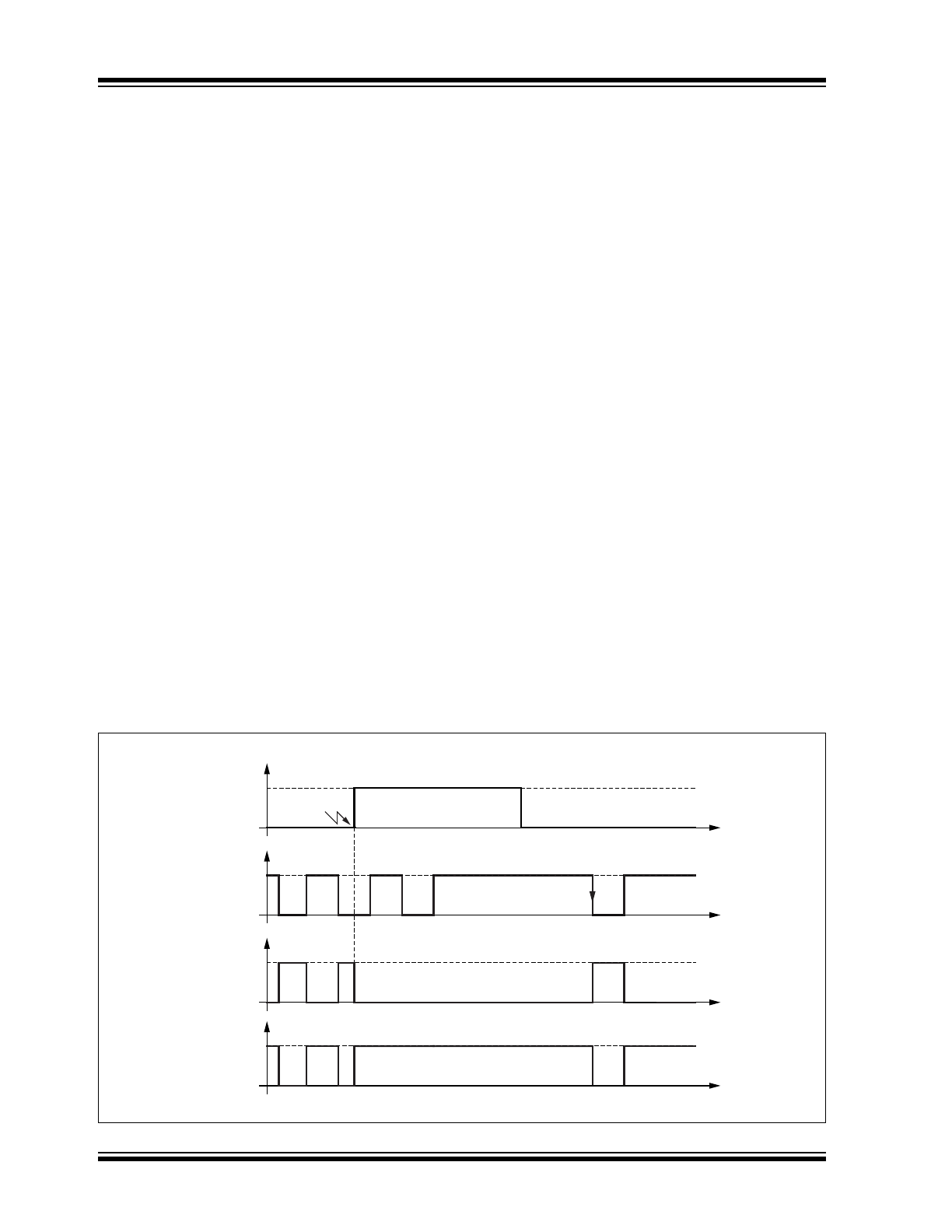
REMOTE WAKE-UP VIA THE CAN
BUS
In Standby mode, the bus lines are biased to ground to
reduce current consumption to a minimum. The
ATA6566 monitors the bus lines for a valid wake-up
pattern, as specified in the ISO 11898-2: 2016. This fil-
tering helps to avoid spurious wake-up events that
would be triggered by scenarios, such as a dominant
clamped bus or by a dominant phase due to noise,
spikes on the bus, automotive transients or EMI. The
wake-up pattern consists of at least two consecutive
dominant bus levels for a duration of at least t
Filter
, each
separated by a recessive bus level with a duration of at
least t
Filter
. Dominant or recessive bus levels shorter
than t
Filter
are always ignored. The complete domi-
nant-recessive-dominant pattern, as shown in
Figure 1-3
, must be received within the bus wake-up
time-out time, t
Wake
, to be recognized as a valid
wake-up pattern. Otherwise, the internal wake-up logic
is reset and then the complete wake-up pattern must
be retransmitted to trigger a wake-up event. The RXD
pin remains at a high level until a valid wake-up event
has been detected.
During normal mode, at a VCC or VIO undervoltage
condition or when the complete wake-up pattern is not
received within t
Wake
, no wake-up is signaled at the
RXD pin.
When a valid CAN wake-up pattern is detected on the
bus, the RXD pin switches to low to signal a wake-up
request. A transition to Normal mode is not triggered
until the STBY pin is forced back to low by the
microcontroller.
FIGURE 1-3:
TIMING OF THE BUS WAKE-UP PATTERN (WUP) IN STANDBY MODE
t
dom
= t
Filter
V
Diff
t
dom
= t
Filter
t
rec
= t
Filter
Wt
Wake
dominant
recessive
Bus Wake-up
is Signaled
CANH
CANL
RXD
dominant
ATA6566
DS20005783C-page 6
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.2
Fail-Safe Features
1.2.1
TXD DOMINANT TIME-OUT
FUNCTION
A TXD dominant time-out timer is started when the
TXD pin is set to low. If the low state on the TXD pin
persists for longer than t
to(dom)TXD
, the transmitter is
disabled, releasing the bus lines to a recessive state.
This function prevents a hardware and/or software
application failure from driving the bus lines to a
permanent dominant state (blocking all network
communications). The TXD dominant time-out timer is
reset when the TXD pin is set to high. If the low state
on the TXD pin is longer than t
to(dom)TXD
, then the TXD
pin has to be set to high ≥ 4 µs in order to reset the TXD
dominant time-out timer.
1.2.2
INTERNAL PULL-UP STRUCTURE
AT THE TXD AND STBY INPUT PINS
The TXD and STBY pins have an internal pull-up to
VIO. This ensures a safe, defined state in case one or
all of these pins are left floating. Pull-up currents flow in
these pins in all states, meaning all pins should be in a
high state during Standby mode to minimize the current
consumption.
1.2.3
UNDERVOLTAGE DETECTION ON
PINS VCC AND VIO
If V
VCC
or V
VIO
drops below its respective undervoltage
detection levels (V
uvd(VCC)
and V
uvd(VIO)
, see
Section 2.0
“Electrical Characteristics”
), the transceiver switches
off and disengages from the bus until V
VCC
and V
VIO
have
recovered. The low-power Wake-up Comparator is only
switched off during a VCC or VIO undervoltage. The logic
state of the STBY pin is ignored until the VCC voltage or
the VIO voltage has recovered.
1.2.4
BUS WAKE-UP ONLY AT
DEDICATED WAKE-UP PATTERN
Due to the implementation of the wake-up filtering, the
ATA6566 does not wake-up when the bus is in a long
dominant phase; it only wakes up at a dedicated wake-up
pattern as specified in the ISO 11898-2: 2016. This
means for a valid wake-up, at least two consecutive
dominant bus levels for a duration of at least t
Filter
, each
separated by a recessive bus level with a duration of at
least t
Filter
, must be received via the bus. Dominant or
recessive bus levels shorter than t
Filter
are always
ignored. The complete dominant-recessive-dominant
pattern, as shown in
Figure 1-3
, must be received within
the bus wake-up time-out time, t
Wake
, to be recognized as
a valid wake-up pattern. This filtering leads to a higher
robustness against EMI and transients, and therefore,
significantly reduces the risk of an unwanted bus
wake-up.
1.2.5
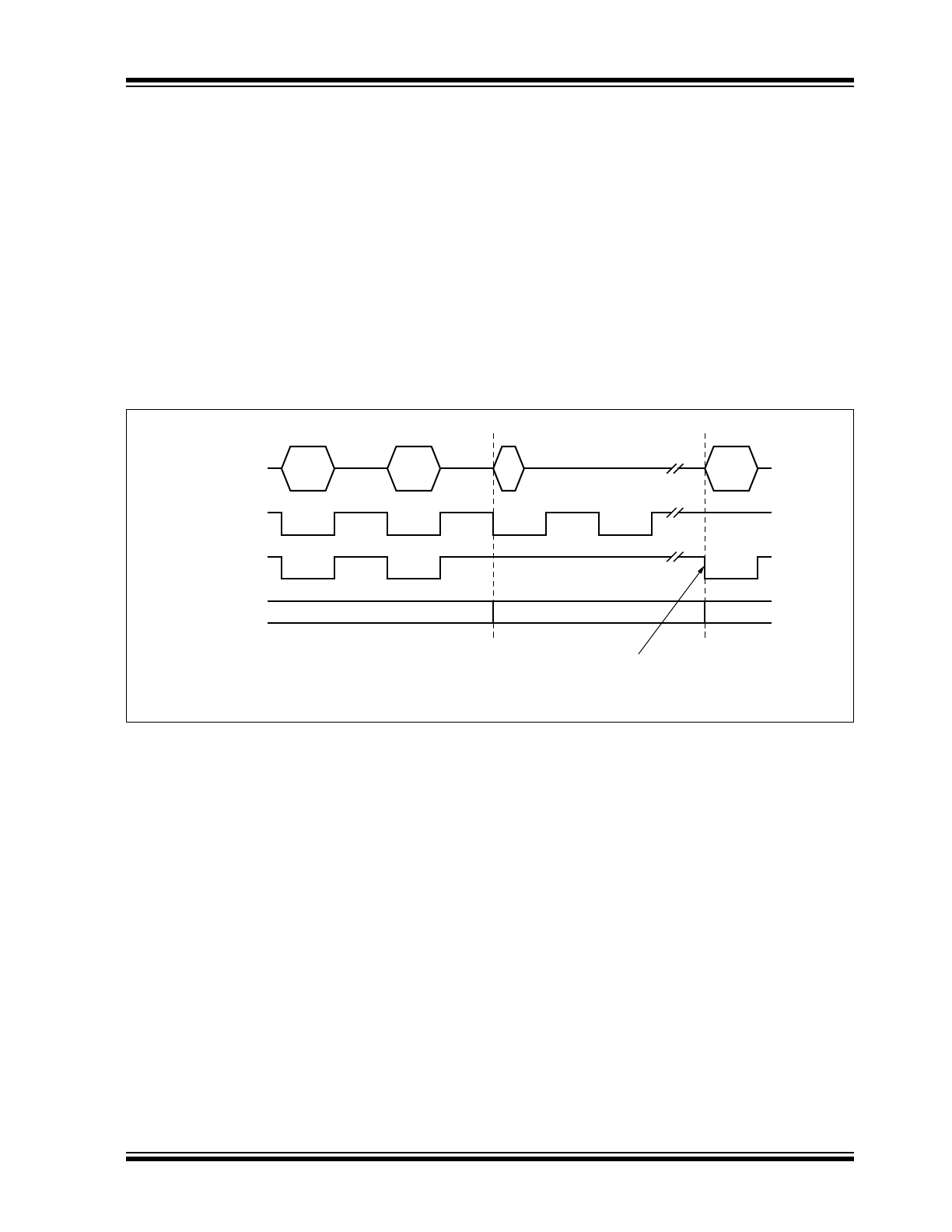
OVERTEMPERATURE PROTECTION
The output drivers are protected against overtemperature
conditions. If the junction temperature exceeds the shut-
down junction temperature, T
Jsd
, the output drivers are
disabled until the junction temperature drops below T
Jsd
and pin TXD is at a high level again. The TXD condition
ensures that output driver oscillations due to temperature
drift are avoided.
FIGURE 1-4:
RELEASE OF TRANSMISSION AFTER OVERTEMPERATURE CONDITION
Failure
Overtemp
GND
TXD
Overtemperature
R
D
R
t
t
t
OT
BUS V
DIFF
(CANH-CANL)
9,2
R
D
D
t
t
RXD
9,2
GND
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005783C-page 7
ATA6566
1.2.6
SHORT-CIRCUIT PROTECTION OF
THE BUS PINS
The CANH and CANL bus outputs are short-circuit
protected, either against GND or a positive supply
voltage. A current-limiting circuit protects the trans-
ceiver against damage. If the device is heating up
due to a continuous short on CANH or CANL, the
internal overtemperature protection switches the bus
transmitter off.
1.2.7
RXD RECESSIVE CLAMPING
This fail-safe feature prevents the controller from
sending data on the bus if its RXD line is clamped to
high (e.g., recessive). That is, if the RXD pin cannot
signalize a dominant bus condition (e.g., because it is
shorted to VCC), the transmitter within ATA6566 is
disabled to avoid possible data collisions on the bus. In
Normal mode, the device permanently compares the
state of the High-Speed Comparator (HSC) with the
state of the RXD pin. If the HSC indicates a dominant
bus state for more than t
RC_det
, without the RXD pin
doing the same, a recessive clamping situation is
detected and the device is forced into Silent mode
(receive only). This Fail-Safe mode is released by
either entering Standby or Unpowered mode, or if the
RXD pin is showing a dominant (e.g., low) level again.
FIGURE 1-5:
RXD RECESSIVE CLAMPING DETECTION
CAN
TXD
RXD
Operation
Mode
Normal
Normal
Silent
If the clamping condition is removed and a
dominant bus is detected, the transceiver
goes back to normal mode.
If the clamping condition is removed and a
dominant bus is detected, the transceiver
goes back to Normal mode.
ATA6566
DS20005783C-page 8
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.3
Pin Descriptions
The descriptions of the pins are listed in
Table 1-2
.
TABLE 1-2:
PIN FUNCTION TABLE
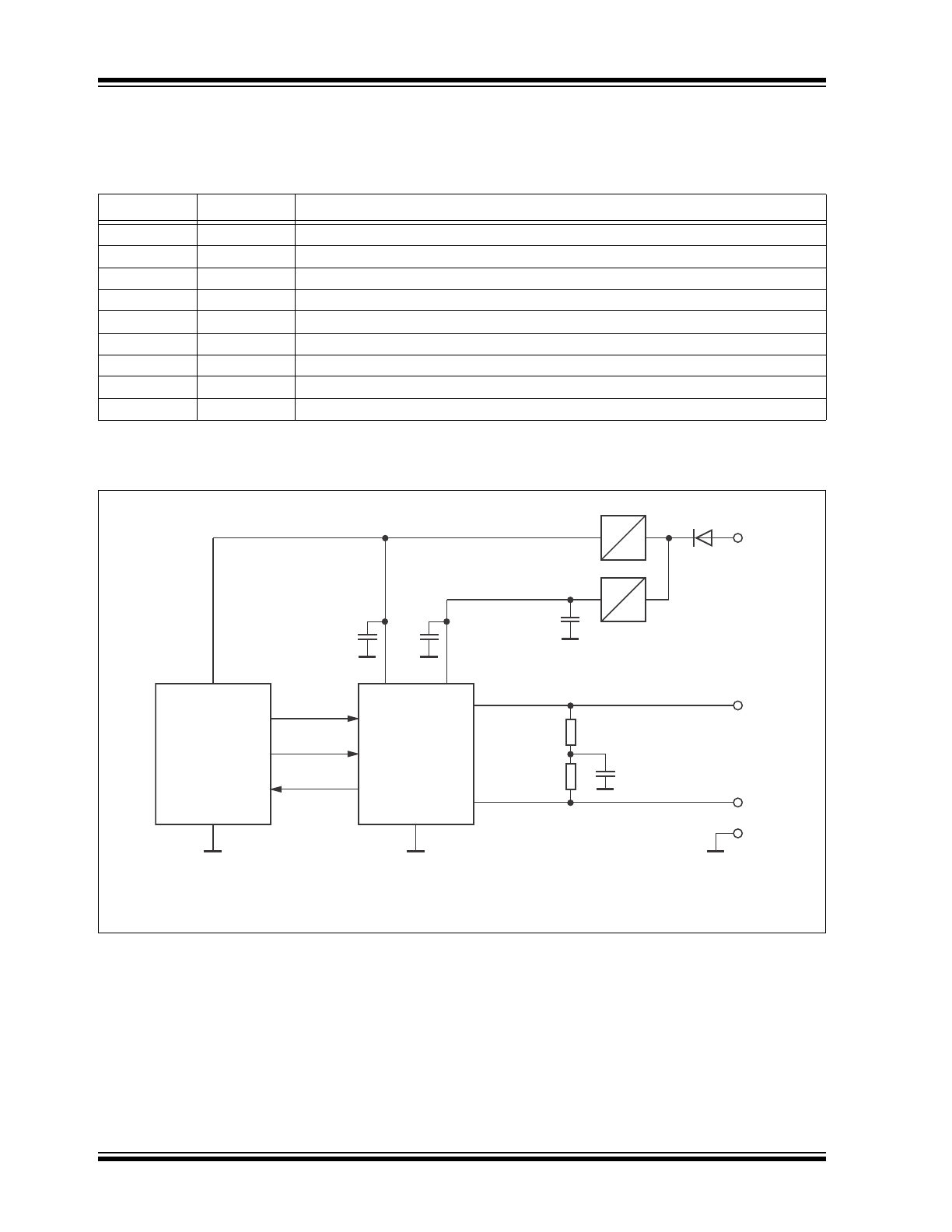
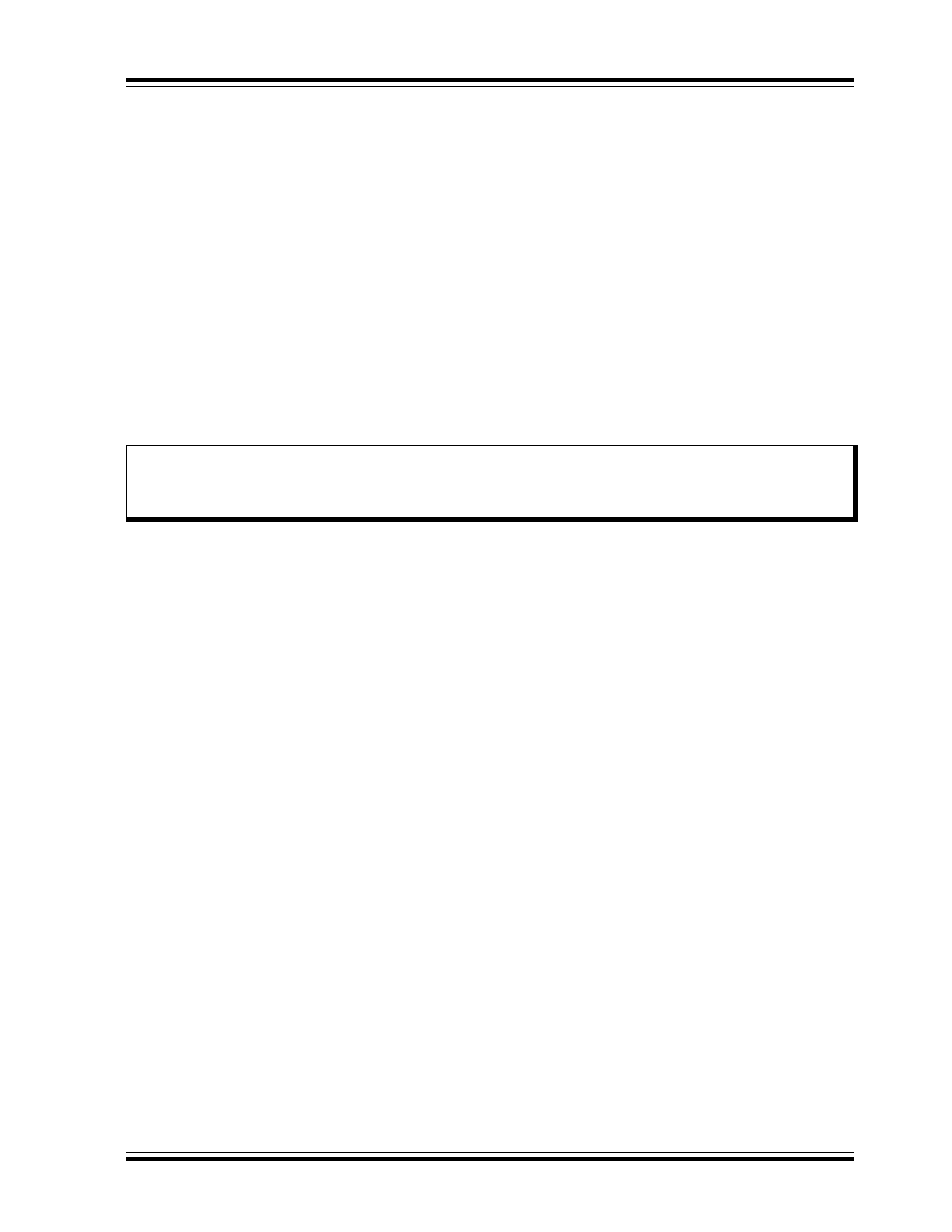
Typical Application
Pin Number
Pin Name
Description
1
TXD
Transmit Data Input
2
GND
Ground Supply
3
VCC
Supply Voltage
4
RXD
Receive Data Output; Reads Out Data from the Bus Lines
5
VIO
Supply Voltage for I/O Level Adapter
6
CANL
Low-Level CAN Bus Line
7
CANH
High-Level CAN Bus Line
8
STBY
Standby Mode Control Input
9
EP
(
1
)
Exposed Thermal Pad: Heat Slug, Internally Connected to the GND Pin
Note 1: Only for the VDFN package.
Note 1:The size of this capacitor depends on the used external voltage regulator.
2: For VDFN package: Heat slug must always be connected to GND.
7
8
1
4
5
2
3
CANH
100nF
22μF
(1)
VIO
VCC
+
VDD
Microcontroller
GND
ATA6566
CANH
STBY
TXD
RXD
CANL
BAT
5V
12V
6
CANL
GND
GND
3.3V
12V
100nF
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS20005783C-page 9
ATA6566
2.0
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
2.1
Absolute Maximum Ratings
(†)
DC Voltage at CANH and CANL ................................................................................................................ –27V to +42V
Transient Voltage on CANH and CANL (ISO 7637, Part 2) ................................................................... –150V to +100V
Maximum Differential Bus Voltage ............................................................................................................... –5V to +18V
DC Voltage on All Other Pins ................................................................................................................... –0.3V to +5.5V
ESD Protection on CANH and CANL Pins (IEC 61000-4-2) .................................................................................... ±8 kV
ESD (HBM following STM 5.1 with 1.5 k
/100 pF) – Pins CANH, CANL to GND.................................................. ±6 kV
Component Level ESD (HBM according to ANSI/ESD STM 5.1), JESD22-A114, AEC-Q 100 (002)..................... ±4 kV
CDM ESD STM 5.3.1............................................................................................................................................. ±750V
ESD Machine Model AEC-Q100-RevF(003).......................................................................................................... ±200V
Virtual Junction Temperature (T
vJ
) ........................................................................................................ –40°C to +175°C
Storage Temperature (T
stg
) .................................................................................................................... –55°C to +150°C
† Notice: Stresses beyond those listed below may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only
and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections
of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ATA6566
DS20005783C-page 10
2017 Microchip Technology Inc.
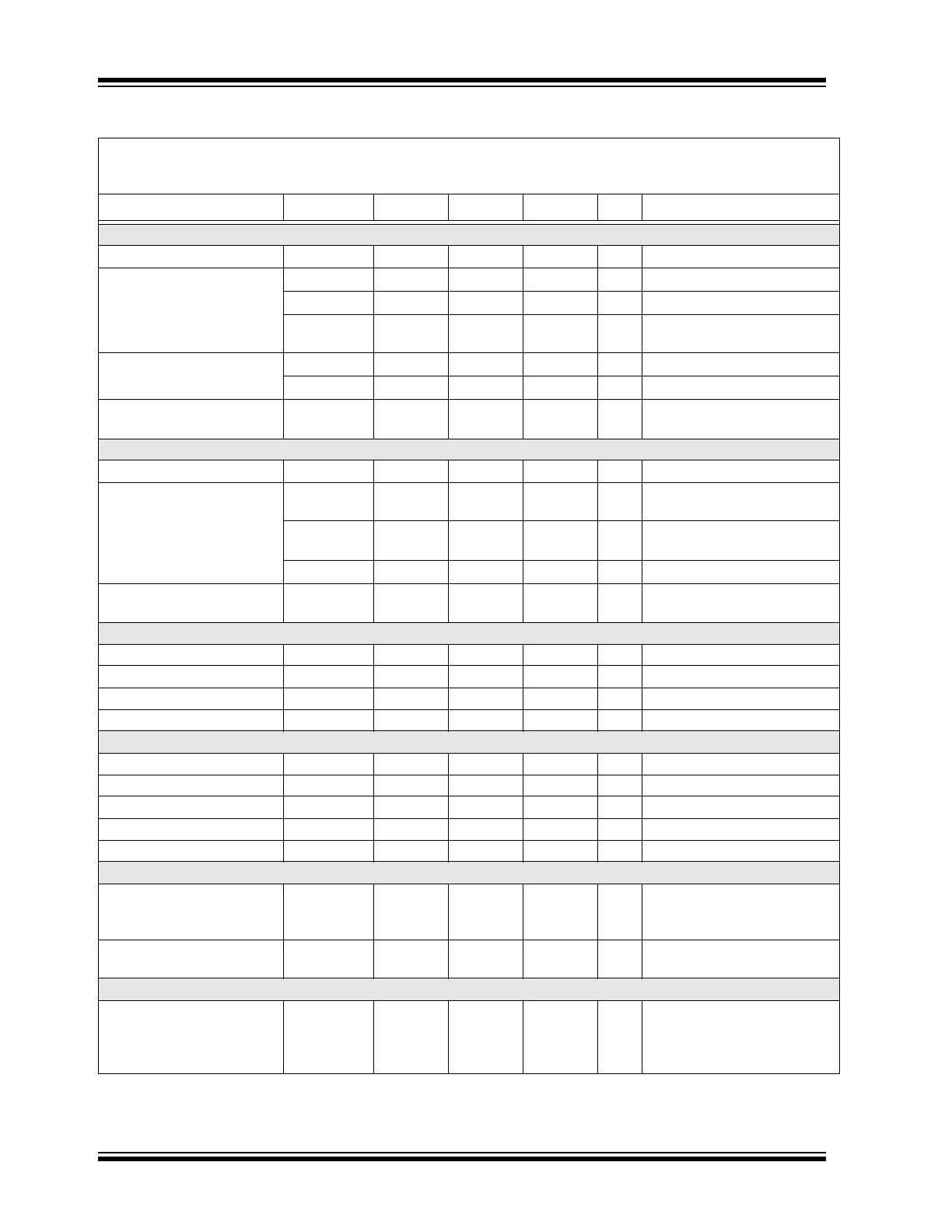
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Electrical Specifications: Grade 1: T
amb
= –40°C to +125°C; Grade 0: T
amb
= –40°C to +150°C;
V
VCC
= 4.75V to 5.25V; V
VIO
= 2.8V to 5.5V; R
L
= 60
, C
L
= 100 pF unless otherwise specified. All voltages are
defined in relation to ground; positive currents flow into the IC.
Parameters
Sym.
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Conditions
Supply, Pin VCC
Supply Voltage
V
VCC
4.75
—
5.25
V
Supply Current in Normal
Mode
I
VCC_rec
2
—
5
mA
Recessive, V
TXD
= V
VIO
I
VCC_dom
30
50
70
mA
Dominant, V
TXD
= 0V
I
VCC_short
—
—
85
mA
Short between CANH and
CANL (
Note 1
)
Supply Current in Standby
Mode
I
VCC_STBY
—
—
12
µA
V
VCC
= V
VIO
, V
TXD
= V
VIO
I
VCC_STBY
—
7
—
µA
T
amb
= +25°C (
Note 3
)
Undervoltage Detection
Threshold on Pin VCC
V
uvd(VCC)
2.75
—
4.5
V
I/O Level Adapter Supply, Pin VIO
Supply Voltage on Pin VIO
V
VIO
2.8
—
5.5
V
Supply Current on Pin VIO
I
VIO_rec
10
80
250
µA
Normal mode
recessive, V
TXD
= V
VIO
I
VIO_dom
50
350
500
µA
Normal mode
dominant, V
TXD
= 0V
I
VIO_STBY
—
—
1
µA
Standby mode
Undervoltage Detection
Threshold on Pin VIO
V
uvd(VIO)
1.3
—
2.7
V
Mode Control Input, Pin STBY
High-Level Input Voltage
V
IH
0.7
V
VIO
—
V
VIO
+ 0.3
V
Low-Level Input Voltage
V
IL
–0.3
—
0.3
V
VIO
V
Pull-up Resistor to VIO
R
pu
75
125
175
kΩ
V
STBY
= 0V
Low-Level Leakage Current
I
L
–2
—
+2
µA
V
STBY
= V
VIO
CAN Transmit Data Input, Pin TXD
High-Level Input Voltage
V
IH
0.7
V
VIO
—
V
VIO
+ 0.3
V
Low-Level Input Voltage
V
IL
–0.3
—
0.3
V
VIO
V
Pull-up Resistor to VIO
R
TXD
20
35
50
kΩ
V
TXD
= 0V
High-Level Leakage Current
I
TDX
–2
—
+2
µA
Normal mode, V
TXD
= V
VIO
Input Capacitance
C
TXD
—
5
10
pF
(
Note 3
)
CAN Receive Data Output, Pin RXD
High-Level Output Current
I
OH
–8
—
–1
mA
Normal mode,
V
RXD
= V
VIO
– 0.4V,
V
VIO
= V
VCC
Low-Level Output Current
I
OL
2
—
12
mA
Normal mode,
V
RXD
= 0.4V, bus dominant
Bus Lines, Pins CANH and CANL
Single-Ended Dominant
Output Voltage
V
O(dom)
2.75
0.5
3.5
1.5
4.5
2.25
V
V
V
TXD
= 0V, t < t
to(dom)TXD
,
R
L
= 50
to 65,
CANH pin
CANL pin (
Note 1
)
Note 1: Type B: 100% correlation tested.
2: Type C: Characterized on samples.
3: Type D: Design parameter.
