© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21227F-page 1
25AA320/25LC320/25C320
Device Selection Table
Features:
• Low-Power CMOS Technology:
- Write current: 3 mA maximum
- Read current: 500
μA, typical
- Standby current: 500 nA, typical
• 4096 x 8 Bit Organization
• 32 Byte Page
• Write Cycle Time: 5 ms Maximum
• Self-Timed Erase and Write Cycles
• Block Write Protection:
- Protect none, 1/4, 1/2 or all of array
• Built-in Write Protection:
- Power on/off data protection circuitry
- Write enable latch
- Write-protect pin
• Sequential Read
• High Reliability:
- Endurance: 1M E/W cycles
- Data retention: > 200 years
- ESD protection: > 4000V
• 8-Pin PDIP, SOIC and TSSOP Packages
• 14-Lead TSSOP Package
• Temperature Ranges Supported:
Description:
The Microchip Technology Inc. 25AA320/25LC320/
25C320 (25XX320
*
) are 32 Kbit serial Electrically
Erasable PROMs. The memory is accessed via a
simple Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible
serial bus. The bus signals required are a clock input
(SCK) plus separate data in (SI) and data out (SO)
lines. Access to the device is controlled through a Chip
Select (CS) input.
Communication to the device can be paused via the
hold pin (HOLD). While the device is paused,
transitions on its inputs will be ignored, with the
exception of Chip Select, allowing the host to service
higher priority interrupts.
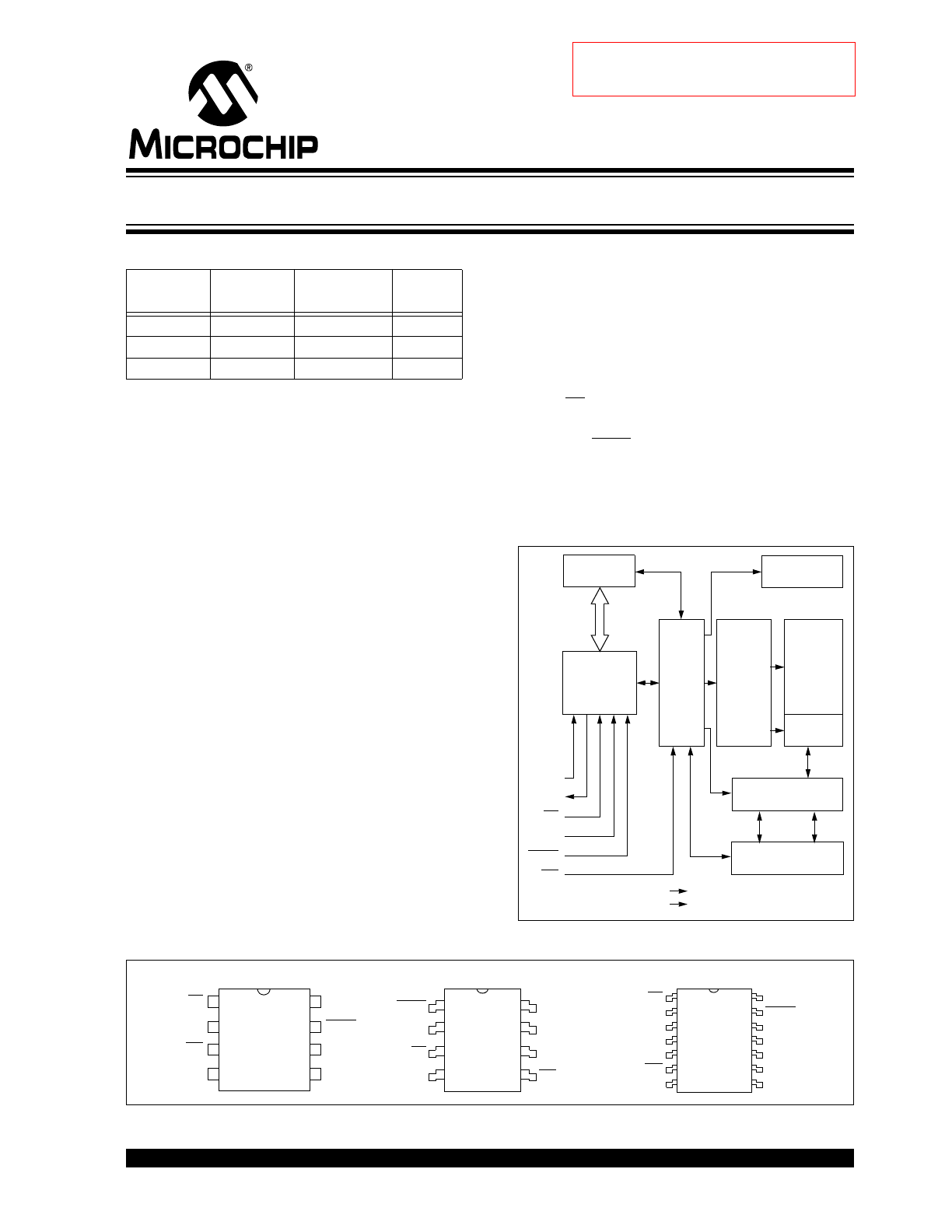
Block Diagram
Package Types
Part
Number
V
CC
Range
Max. Clock
Frequency
Temp.
Ranges
25AA320
1.8-5.5V
1 MHz
I
25LC320
2.5-5.5V
2 MHz
I,E
25C320
4.5-5.5V
3 MHz
I,E
- Industrial (I):
-40
°C to +85°C
- Automotive (E):
-40°C to +125°C
SI
SO
SCK
CS
HOLD
WP
STATUS
Register
I/O Control
Memory
Control
Logic
HV Generator
EEPROM
Array
Page
Y Decoder
Sense Amp.
R/W Control
Logic
V
CC
V
SS
Latches
XDEC
TSSOP
PDIP, SOIC
TSSOP
CS
SO
WP
V
SS
V
CC
HOLD
SCK
SI
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
25X
X320
HOLD
V
CC
CS
SO
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
SCK
SI
V
SS
WP
25XX3
20
NC
CS
SO
NC
WP
V
SS
NC
NC
V
CC
HOLD
NC
SCK
SI
NC
25XX
320
1
2
3
4
14
13
12
11
5
10
9
7
8
6
32K SPI Bus Serial EEPROM
*25XX320 is used in this document as a generic part number for the 25AA320/25LC320/25C320 devices.
Not recommended for new designs –
Please use 25AA320A or 25LC320A.
25AA320/25LC320/25C320
DS21227F-page 2
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.0
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings
(†)
V
CC
.............................................................................................................................................................................7.0V
All inputs and outputs w.r.t. V
SS
........................................................................................................ -0.6V to V
CC
+ 1.0V
Storage temperature .................................................................................................................................-65°C to 150°C
Ambient temperature under bias ...............................................................................................................-40°C to 125°C
ESD protection on all pins .......................................................................................................................................... 4 kV
TABLE 1-1:
DC CHARACTERISTICS
† NOTICE: Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the
device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at those or any other conditions above those
indicated in the operational listings of this specification is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for an
extended period of time may affect device reliability.
DC CHARACTERISTICS
Industrial (I):
T
A
= -40°C to +85°C
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
Automotive (E):T
A
= -40°C to +125°C V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
Param.
No.
Sym.
Characteristics
Min.
Max.
Units
Conditions
D1
V
IH
1
High-level input
voltage
2.0
V
CC
+1
V
V
CC
≥ 2.7V (Note)
D2
V
IH
2
0.7 V
CC
V
CC
+1
V
V
CC
< 2.7V (Note)
D3
V
IL
1
Low-level input
voltage
-0.3
0.8
V
V
CC
≥ 2.7V (Note)
D4
V
IL
2
-0.3
0.3 V
CC
V
V
CC
< 2.7V (Note)
D5
V
OL
Low-level output
voltage
—
0.2
V
I
OL
= 1.0 mA, V
CC
< 2.5V
D6
V
OH
High-level output
voltage
V
CC
-0.5
—
V
I
OH
= -400
μA
D7
I
LI
Input leakage current
—
±1
μA
CS = V
CC
, V
IN
= V
SS
TO
V
CC
D8
I
LO
Output leakage
current
—
±1
μA
CS = V
CC
, V
OUT
= V
SS
TO
V
CC
D9
C
INT
Internal Capacitance
(all inputs and
outputs)
—
7
pF
T
A
= 25°C, CLK = 1.0 MHz,
V
CC
= 5.0V (Note)
D10
I
CC
Read Operating Current
—
—
1
500
mA
μA
V
CC
= 5.5V; F
CLK
= 3.0 MHz;
SO = Open
V
CC
= 2.5V; F
CLK
= 2.0 MHz;
SO = Open
D11
I
CC
Write
—
—
5
3
mA
mA
V
CC
= 5.5V
V
CC
= 2.5V
D12
I
CCS
Standby Current
—
—
5
1
μA
μA
CS = V
CC
= 5.5V, Inputs tied to V
CC
or
V
SS
CS = V
CC
= 2.5V, Inputs tied to V
CC
or
V
SS
Note:
This parameter is periodically sampled and not 100% tested.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21227F-page 3
25AA320/25LC320/25C320
TABLE 1-2:
AC CHARACTERISTICS
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Industrial (I):
T
A
= -40°C to +85°C
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
Automotive (E):
T
A
= -40°C to +125°C
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
Param.
No.
Sym.
Characteristic
Min.
Max.
Units
Conditions
1
F
CLK
Clock Frequency
—
—
—
3
2
1
MHz
MHz
MHz
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
2
T
CSS
CS Setup Time
100
250
500
—
—
—
ns
ns
ns
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
3
T
CSH
CS Hold Time
150
250
475
—
—
—
ns
ns
ns
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
4
T
CSD
CS Disable Time
500
—
ns
—
5
T
SU
Data Setup Time
30
50
50
—
—
—
ns
ns
ns
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
6
T
HD
Data Hold Time
50
100
100
—
—
—
ns
ns
ns
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
7
T
R
CLK Rise Time
—
2
μ
s
(Note 1)
8
T
F
CLK Fall Time
—
2
μ
s
(Note 1)
9
T
HI
Clock High Time
150
230
475
—
—
—
ns
ns
ns
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
10
T
LO
Clock Low Time
150
230
475
—
—
—
ns
ns
ns
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
11
T
CLD
Clock Delay Time
50
—
ns
—
12
T
CLE
Clock Enable Time
50
—
ns
—
13
T
V
Output Valid from
Clock Low
—
—
—
150
230
—
ns
ns
ns
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
14
T
HO
Output Hold Time
0
—
ns
(Note 1)
15
T
DIS
Output Disable Time
—
—
—
200
250
—
ns
ns
ns
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V (Note 1)
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V (Note 1)
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
16
T
HS
HOLD Setup Time
100
100
200
—
—
—
ns
ns
ns
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
17
T
HH
HOLD Hold Time
100
100
200
—
—
—
ns
ns
ns
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
18
T
HZ
HOLD Low to Output
High-Z
100
150
200
—
—
—
ns
ns
ns
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V (Note 1)
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V (Note 1)
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
19
T
HV
HOLD High to Output
Valid
100
150
200
—
—
—
ns
ns
ns
V
CC
= 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 2.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V
20
T
WC
Internal Write Cycle
Time
—
5
ms
—
21
—
Endurance
1M
—
E/W
Cycles
(Note 2)
Note
1: This parameter is periodically sampled and not 100% tested.
2: This parameter is not tested but established by characterization. For endurance estimates in a specific application,
please consult the Total Endurance™ Model which can be obtained from Microchip’s web site at: www.microchip.com.
25AA320/25LC320/25C320
DS21227F-page 4
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
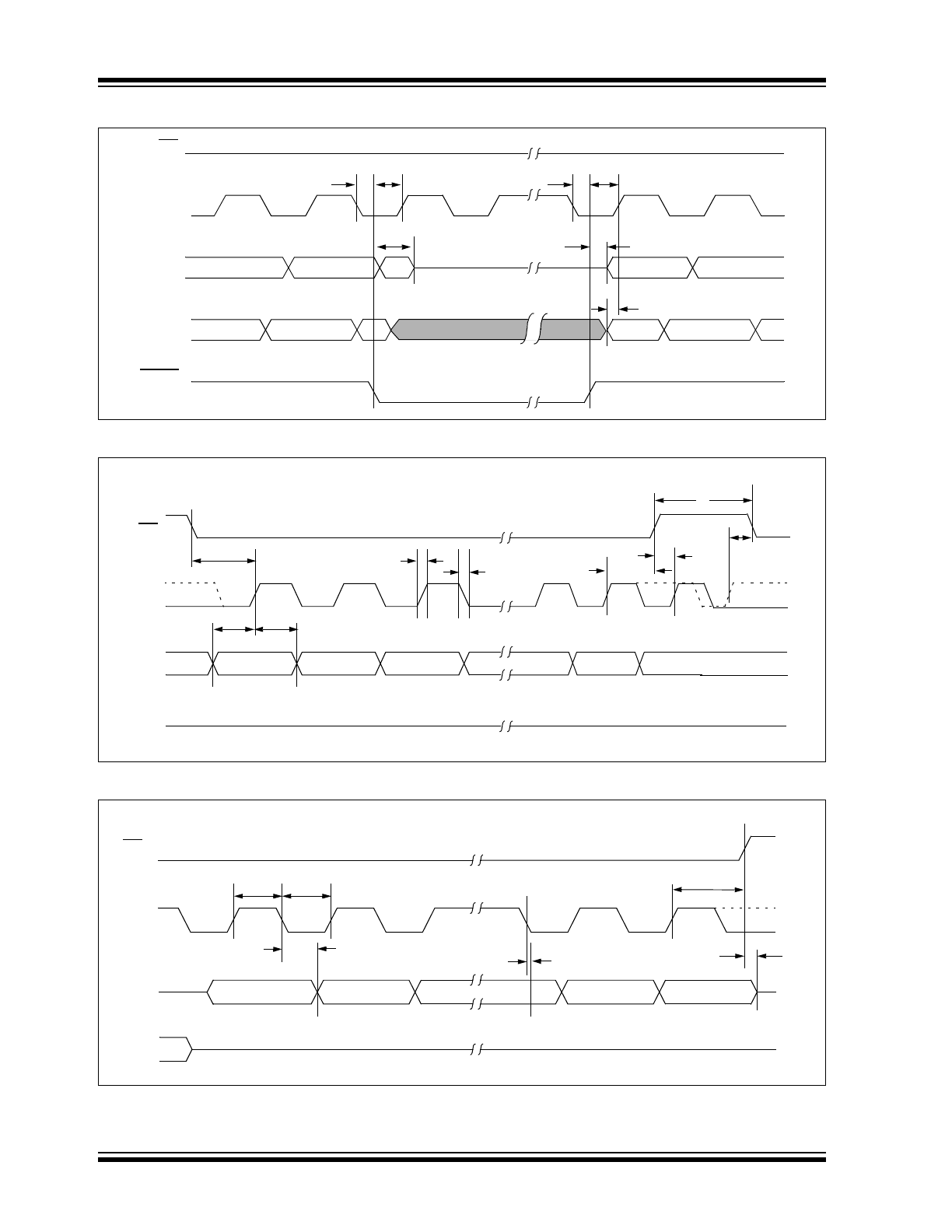
FIGURE 1-1:
HOLD TIMING
FIGURE 1-2:
SERIAL INPUT TIMING
FIGURE 1-3:
SERIAL OUTPUT TIMING
CS
SCK
SO
SI
HOLD
17
16
16
17
19
18
Don’t Care
5
High-Impedance
n + 2
n + 1
n
n - 1
n
n + 2
n + 1
n
n
n - 1
CS
SCK
SI
SO
6
5
8
7
11
3
LSB in
MSB in
High-Impedance
12
Mode 1,1
Mode 0,0
4
2
CS
SCK
SO
10
9
13
MSB out
ISB out
3
15
Don’t Care
SI
Mode 1,1
Mode 0,0
14
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21227F-page 5
25AA320/25LC320/25C320
TABLE 1-3:
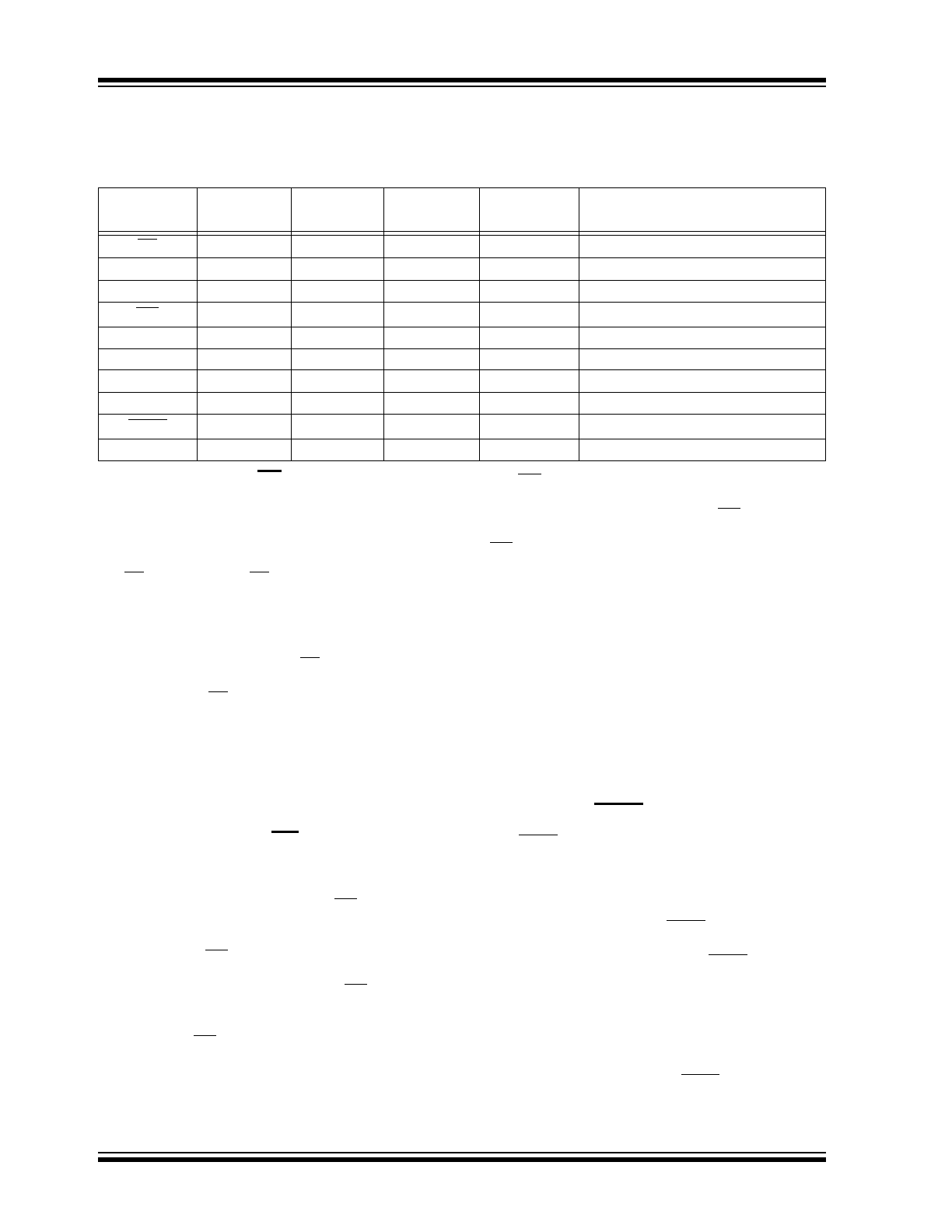
AC TEST CONDITIONS
FIGURE 1-4:
AC TEST CIRCUIT
AC Waveform:
V
LO
= 0.2V
—
V
H I
= V
CC
- 0.2V
(Note 1)
V
H I
= 4.0V
(Note 2)
Timing Measurement Reference Level
Input
0.5 V
CC
Output
0.5 V
CC
Note 1: For V
CC
≤ 4.0V
2: For V
CC
> 4.0V
V
CC
SO
100 pF
1.8 K
Ω
2.25 K
Ω
25AA320/25LC320/25C320
DS21227F-page 6
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
2.0
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
The descriptions of the pins are listed in Table 2-1.
TABLE 2-1:
PIN FUNCTION TABLE
2.1
Chip Select (CS)
A low level on this pin selects the device. A high level
deselects the device and forces it into Standby mode.
However, a programming cycle which is already
initiated or in progress will be completed, regardless of
the CS input signal. If CS is brought high during a
program cycle, the device will go into Standby mode as
soon as the programming cycle is complete. When the
device is deselected, SO goes to the high-impedance
state, allowing multiple parts to share the same SPI
bus. A low-to-high transition on CS after a valid write
sequence initiates an internal write cycle. After power-
up, a low level on CS is required prior to any sequence
being initiated.
2.2
Serial Output (SO)
The SO pin is used to transfer data out of the 25XX320.
During a read cycle, data is shifted out on this pin after
the falling edge of the serial clock.
2.3
Write-Protect (WP)
This pin is used in conjunction with the WPEN bit in the
STATUS register to prohibit writes to the nonvolatile
bits in the STATUS register. When WP is low and
WPEN is high, writing to the nonvolatile bits in the STA-
TUS register is disabled. All other operations function
normally. When WP is high, all functions, including
writes to the nonvolatile bits in the STATUS register
operate normally. If the WPEN bit is set, WP low during
a STATUS register write sequence will disable writing
to the STATUS register. If an internal write cycle has
already begun, WP going low will have no effect on the
write.
The WP pin function is blocked when the WPEN bit in
the STATUS register is low. This allows the user to
install the 25XX320 in a system with WP pin grounded
and still be able to write to the STATUS register. The
WP pin functions will be enabled when the WPEN bit is
set high.
2.4
Serial Input (SI)
The SI pin is used to transfer data into the device. It
receives instructions, addresses, and data. Data is
latched on the rising edge of the serial clock.
2.5
Serial Clock (SCK)
The SCK is used to synchronize the communication
between a master and the 25XX320. Instructions,
addresses, or data present on the SI pin are latched on
the rising edge of the clock input, while data on the SO
pin is updated after the falling edge of the clock input.
2.6
Hold (HOLD)
The HOLD pin is used to suspend transmission to the
25XX320 while in the middle of a serial sequence with-
out having to re-transmit the entire sequence again. It
must be held high any time this function is not being
used. Once the device is selected and a serial
sequence is underway, the HOLD pin may be pulled
low to pause further serial communication without
resetting the serial sequence. The HOLD pin must be
brought low while SCK is low, otherwise the HOLD
function will not be invoked until the next SCK high-to-
low transition. The 25XX320 must remain selected dur-
ing this sequence. The SI, SCK, and SO pins are in a
high-impedance state during the time the device is
paused and transitions on these pins will be ignored. To
resume serial communication, HOLD must be brought
high while the SCK pin is low, otherwise serial
communication will not resume. Lowering the HOLD
line at any time will tri-state the SO line.
Name
PDIP
SOIC
8-pin
TSSOP
14-lead
TSSOP
Description
CS
1
1
3
1
Chip Select Input
SO
2
2
4
2
Serial Data Output
NC
—
—
—
3,4,5
Not Connected
WP
3
3
5
6
Write-Protect Pin
Vss
4
4
6
7
Ground
SI
5
5
7
8
Serial Data Input
SCK
6
6
8
9
Serial Clock Input
NC
—
—
—
10,11,12
Not Connected
HOLD
7
7
1
13
Hold Input
Vcc
8
8
2
14
Supply Voltage

© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21227F-page 7
25AA320/25LC320/25C320
3.0
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
3.1
Principles Of Operation
The 25XX320 are 4096 byte Serial EEPROMs
designed to interface directly with the Serial Peripheral
Interface (SPI) port of many of today’s popular
microcontroller families, including Microchip’s
PIC16C6X/7X microcontrollers. It may also interface
with microcontrollers that do not have a built-in SPI port
by using discrete I/O lines programmed properly with
the software.
The 25XX320 contains an 8-bit instruction register. The
device is accessed via the SI pin, with data being
clocked in on the rising edge of SCK. The CS pin must
be low and the HOLD pin must be high for the entire
operation.
Table 3-1 contains a list of the possible instruction
bytes and format for device operation. All instructions,
addresses and data are transferred MSB first, LSB last.
Data is sampled on the first rising edge of SCK after CS
goes low. If the clock line is shared with other
peripheral devices on the SPI bus, the user can assert
the HOLD input and place the 25XX320 in ‘HOLD’
mode. After releasing the HOLD pin, operation will
resume from the point when the HOLD was asserted.
3.2
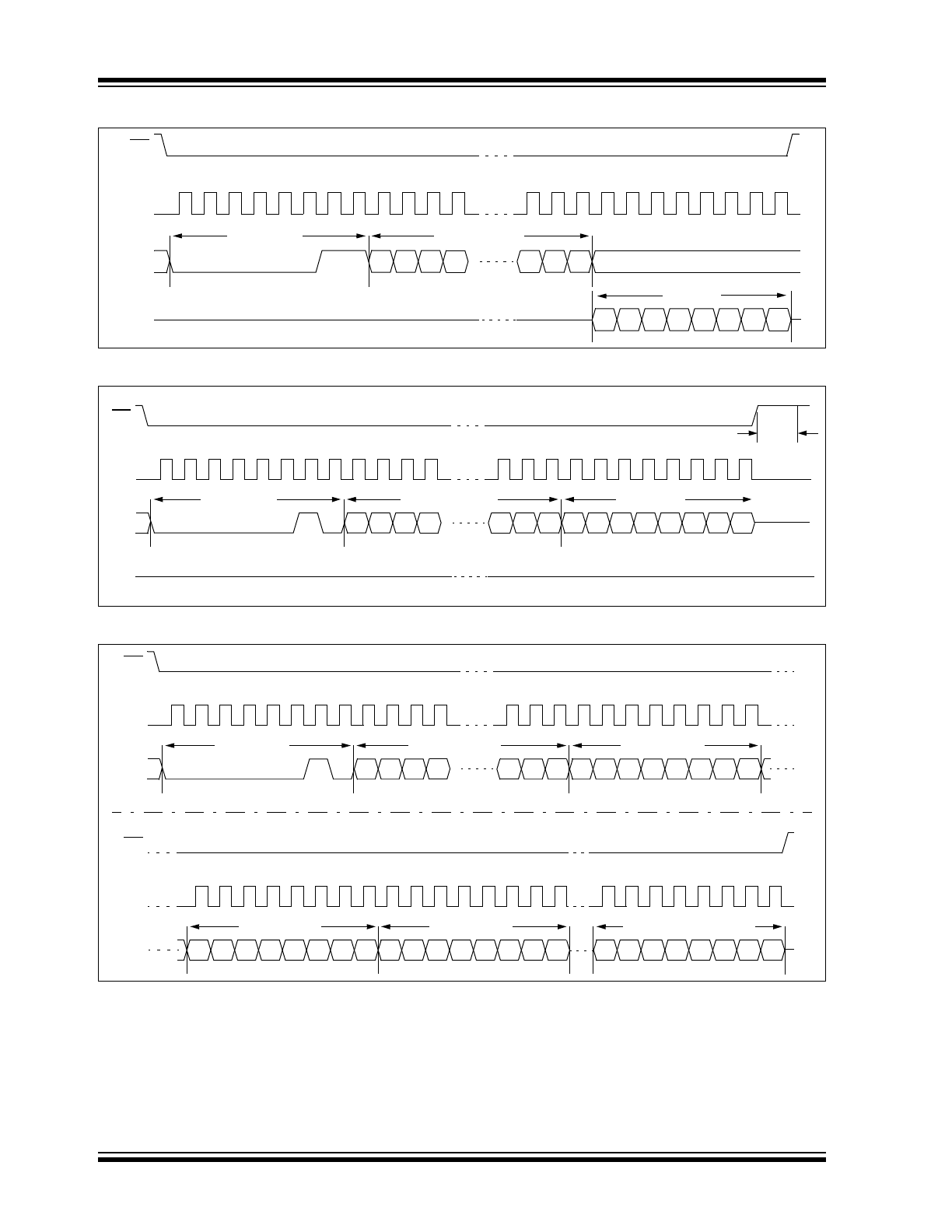
Read Sequence
The device is selected by pulling CS low. The 8-bit
READ
instruction is transmitted to the 25XX320 fol-
lowed by the 16-bit address, with the four MSBs of the
address being “don’t care” bits. After the correct READ
instruction and address are sent, the data stored in the
memory at the selected address is shifted out on the
SO pin. The data stored in the memory at the next
address can be read sequentially by continuing to pro-
vide clock pulses. The internal Address Pointer is auto-
matically incremented to the next higher address after
each byte of data is shifted out. When the highest
address is reached (0FFFh), the address counter rolls
over to address 0000h allowing the read cycle to be
continued indefinitely. The read operation is terminated
by raising the CS pin (Figure 3-1).
3.3
Write Sequence
Prior to any attempt to write data to the 25XX320, the
write enable latch must be set by issuing the WREN
instruction (Figure 3-4). This is done by setting CS low
and then clocking out the proper instruction into the
25XX320. After all eight bits of the instruction are
transmitted, the CS must be brought high to set the
write enable latch. If the write operation is initiated
immediately after the WREN instruction without CS
being brought high, the data will not be written to the
array because the write enable latch will not have been
properly set.
Once the write enable latch is set, the user may
proceed by setting the CS low, issuing a WRITE
instruction, followed by the 16-bit address, with the four
MSBs of the address being “don’t care” bits, and then
the data to be written. Up to 32 bytes of data can be
sent to the 25XX320 before a write cycle is necessary.
The only restriction is that all of the bytes must reside
in the same page. A page address begins with xxxx
xxxx xxx0 0000
and ends with xxxx xxxx xxx1
1111
. If the internal address counter reaches
xxxx
xxxx xxx1 1111
and the clock continues, the counter
will roll back to the first address of the page and over-
write any data in the page that may have been written.
For the data to be actually written to the array, the CS
must be brought high after the Least Significant bit (D0)
of the n
th
data byte has been clocked in. If CS is
brought high at any other time, the write operation will
not be completed. Refer to Figure 3-2 and Figure 3-3
for more detailed illustrations on the byte write
sequence and the page write sequence, respectively.
While the write is in progress, the STATUS register may
be read to check the status of the WPEN, WIP, WEL,
BP1 and BP0 bits (Figure 3-6). A read attempt of a
memory array location will not be possible during a
write cycle. When the write cycle is completed, the
write enable latch is reset.
TABLE 3-1:
INSTRUCTION SET
Instruction Name
Instruction Format
Description
READ
0000 0011
Read data from memory array beginning at selected address
WRITE
0000 0010
Write data to memory array beginning at selected address
WRDI
0000 0100
Reset the write enable latch (disable write operations)
WREN
0000 0110
Set the write enable latch (enable write operations)
RDSR
0000 0101
Read STATUS register
WRSR
0000 0001
Write STATUS register
25AA320/25LC320/25C320
DS21227F-page 8
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
FIGURE 3-1:
READ SEQUENCE
FIGURE 3-2:
BYTE WRITE SEQUENCE
FIGURE 3-3:
PAGE WRITE SEQUENCE
SO
SI
SCK
CS
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 10 11
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
15 14 13 12
2
1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Instruction
16-bit Address
Data Out
High-Impedance
SO
SI
CS
9 10 11
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
15 14 13 12
2
1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Instruction
16-bit Address
Data Byte
High-Impedance
SCK
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
8
Twc
SI
CS
9 10 11
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
15 14 13 12
2
1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Instruction
16-bit Address
Data Byte 1
SCK
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
8
SI
CS
41 42 43
46 47
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Data Byte n (32 max)
SCK
32
34 35 36 37 38 39
33
40
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Data Byte 3
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Data Byte 2
44 45
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21227F-page 9
25AA320/25LC320/25C320
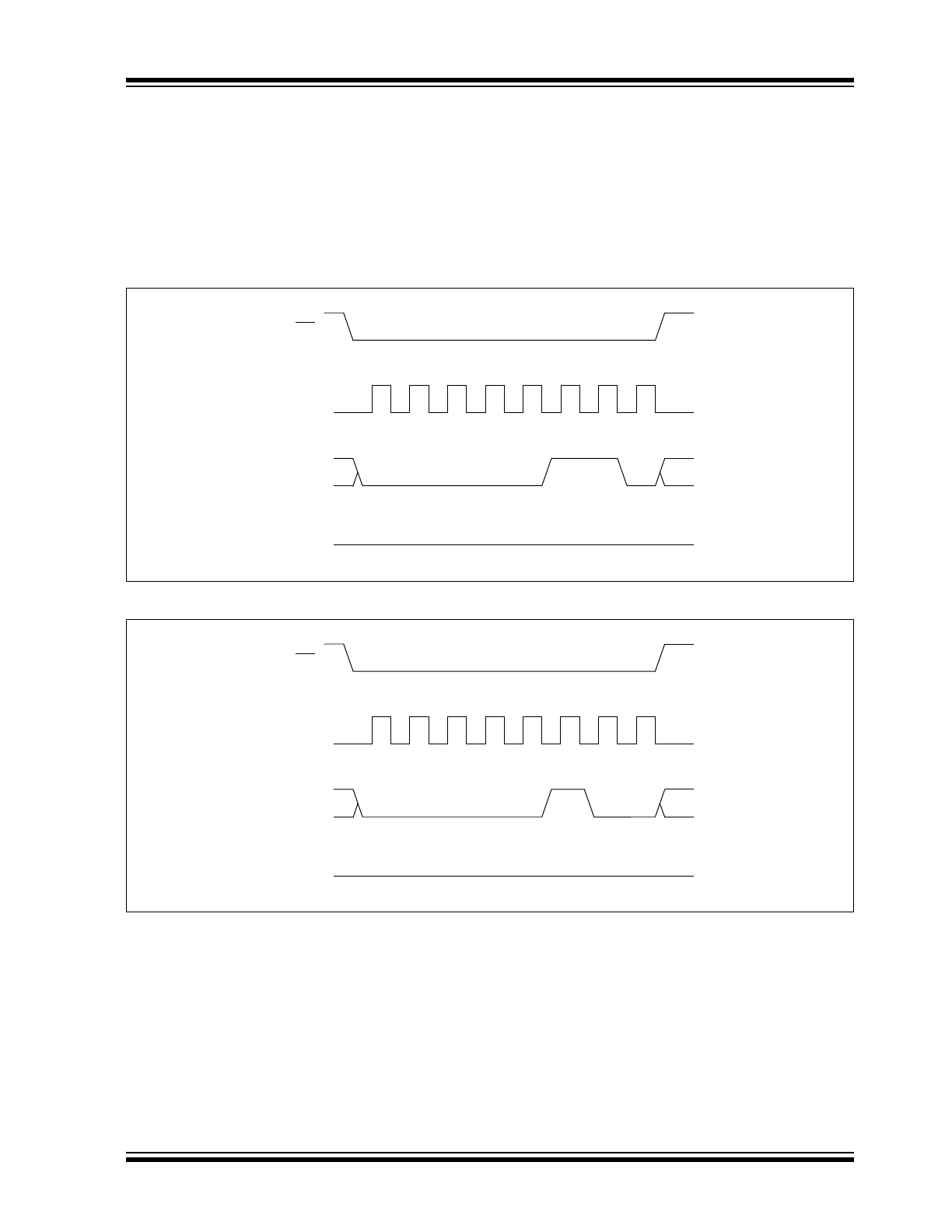
3.4
Write Enable (WREN) and Write
Disable (WRDI)
The 25XX320 contains a write enable latch. See
Table 3-3 for the Write-Protect Functionality Matrix.
This latch must be set before any write operation will be
completed internally. The WREN instruction will set the
latch, and the WRDI will reset the latch.
The following is a list of conditions under which the
write enable latch will be reset:
• Power-up
• WRDI instruction successfully executed
• WRSR instruction successfully executed
• WRITE instruction successfully executed
FIGURE 3-4:
WRITE ENABLE SEQUENCE
FIGURE 3-5:
WRITE DISABLE SEQUENCE
SCK
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
SI
High-Impedance
SO
CS
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
SCK
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
SI
High-Impedance
SO
CS
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
10
25AA320/25LC320/25C320
DS21227F-page 10
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
3.5
Read Status Register Instruction
(RDSR)
The Read Status Register instruction (RDSR) provides
access to the STATUS register. The STATUS register
may be read at any time, even during a write cycle. The
STATUS register is formatted as follows:
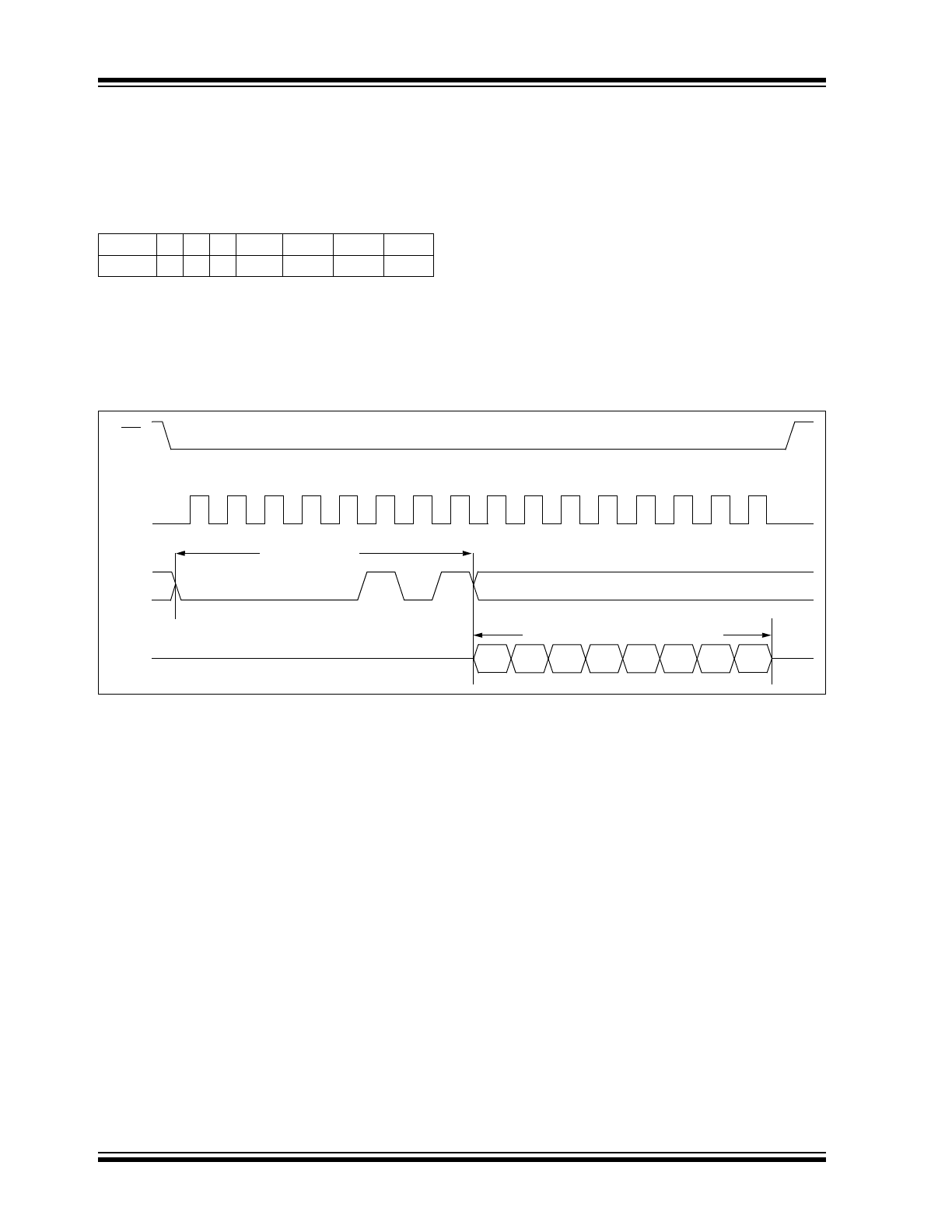
The Write-In-Process (WIP) bit indicates whether the
25XX320 is busy with a write operation. When set to a
‘
1
’, a write is in progress; when set to a ‘
0
’, no write is
in progress. This bit is read-only.
The Write Enable Latch (WEL) bit indicates the status
of the write enable latch. When set to a ‘
1
’, the latch
allows writes to the array, when set to a ‘
0
’, the latch
prohibits writes to the array. The state of this bit can
always be updated via the WREN or WRDI commands
regardless of the state of write protection on the STA-
TUS register. This bit is read-only.
The Block Protection (BP0 and BP1) bits indicate
which blocks are currently write-protected. These bits
are set by the user issuing the WRSR instruction. These
bits are nonvolatile.
See Figure 3-6 for the RDSR timing sequence.
FIGURE 3-6:
READ STATUS REGISTER TIMING SEQUENCE
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
WPEN
X
X
X
BP1
BP0
WEL
WIP
SO
SI
CS
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
7
6
5
4
2
1
0
Instruction
Data from STATUS Register
High-Impedance
SCK
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
8
3
